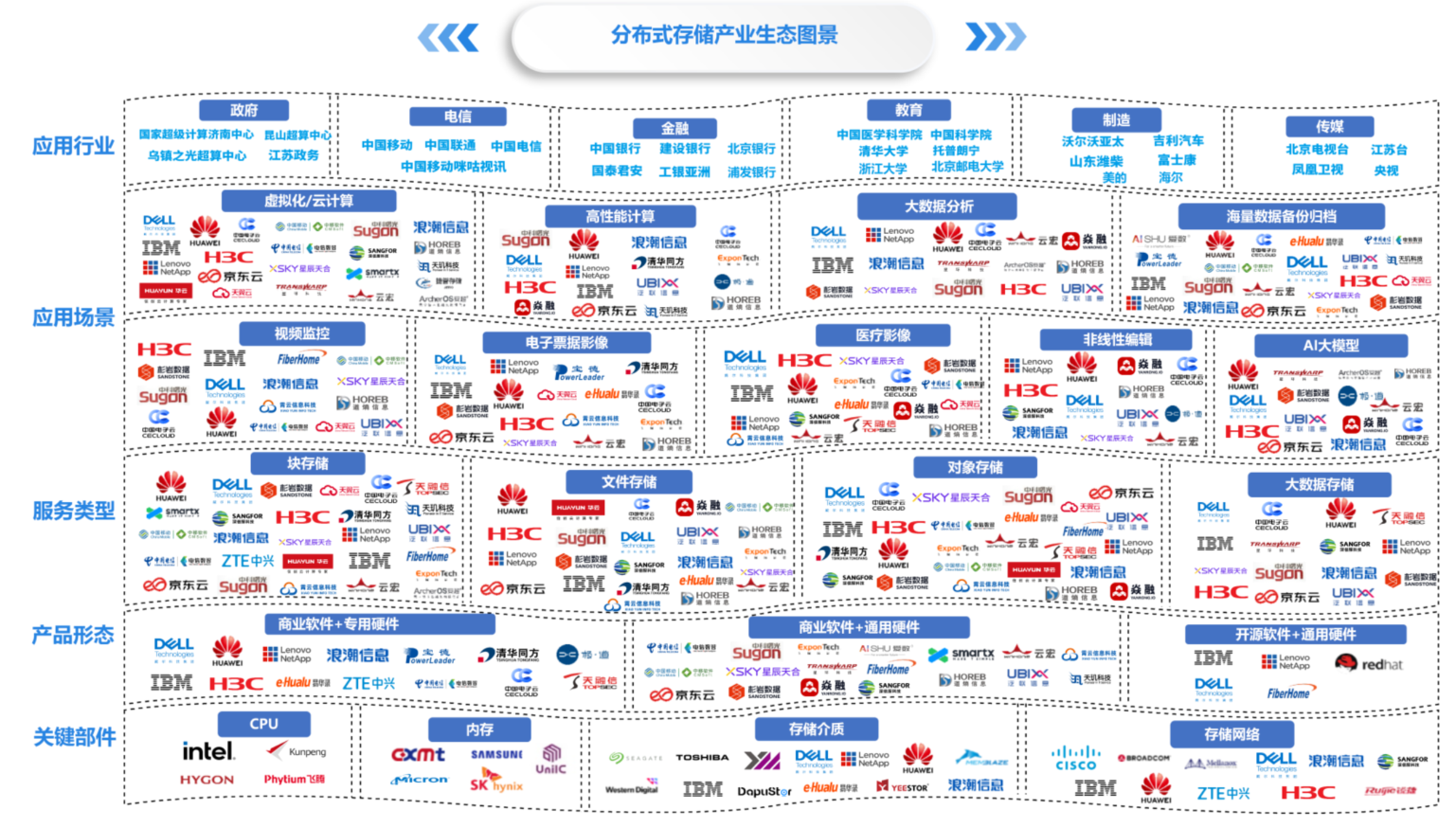
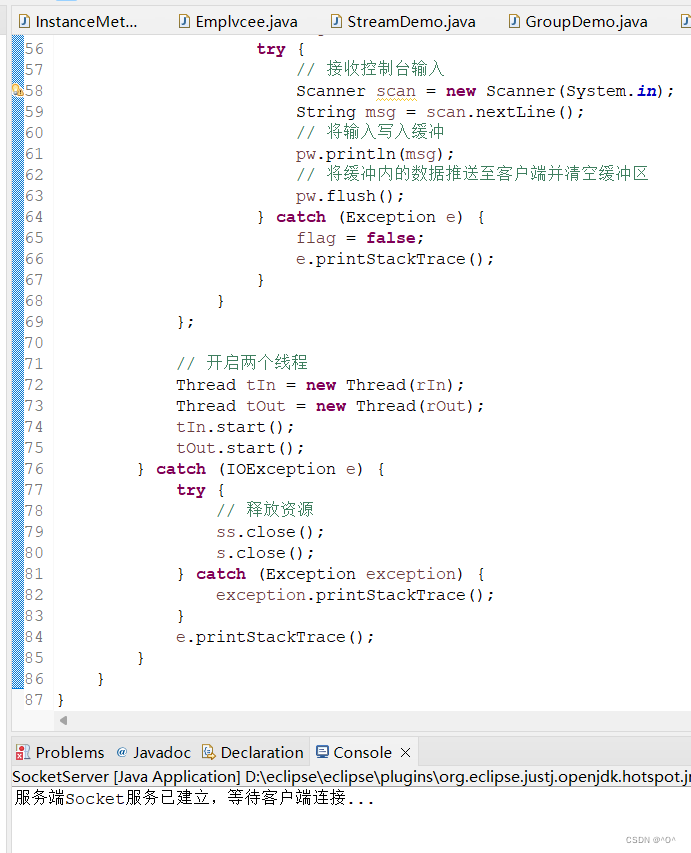
package 二十一章;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Socket服务端
**/
public class SocketServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket s = null;
try {
// 创建监听端口为12345的Socket服务端
ss = new ServerSocket(12345);
System.out.println("服务端Socket服务已建立,等待客户端连接...");
// 通过ss.accept()开始持续监听12345端口,当有连接时获取收到的包装成Socket的客户端对象
s = ss.accept();
// 获取客户端的IP地址和端口号
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = s.getPort();
System.out.println("服务端与 " + ip + ":" + port + " 已建立连接");
// 创建输入流接收客户端发送的消息(字节流)
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
// 将客户端发送的字节流转化为字符流
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
// 创建字符流读取缓冲区,方便每行读取
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
// 创建输出流返回消息
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
// 创建输出流缓冲
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(os);
// 创建接受信息的线程
Runnable rIn = () -> {
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
try {
// 逐行读取客户端发送的消息并打印
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("客户端的消息:" + str);
} catch (IOException e) {
flag = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 创建发送消息的线程
Runnable rOut = () -> {
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
try {
// 接收控制台输入
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String msg = scan.nextLine();
// 将输入写入缓冲
pw.println(msg);
// 将缓冲内的数据推送至客户端并清空缓冲区
pw.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
flag = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 开启两个线程
Thread tIn = new Thread(rIn);
Thread tOut = new Thread(rOut);
tIn.start();
tOut.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
// 释放资源
ss.close();
s.close();
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}} 
package 二十一章;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Socket客户端
**/
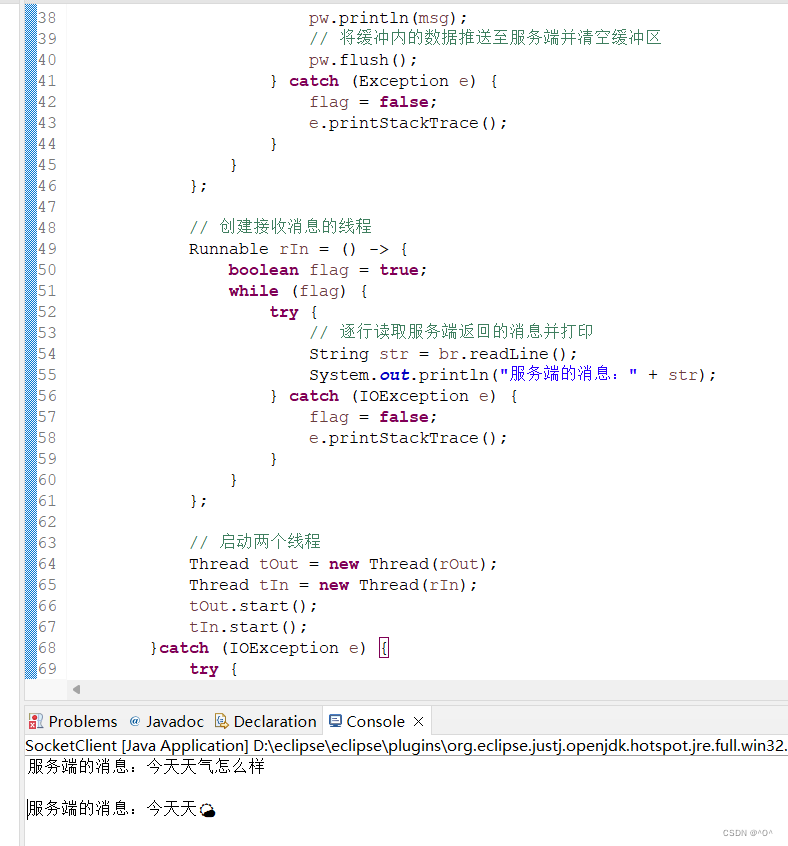
public class SocketClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket s = null;
try {
// 与ip为127.0.0.1、端口为12345的服务端建立连接
s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 12345);
// 创建输入流接收服务端发送的消息(字节流)
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
// 将服务端返回的字节流转化为字符流
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
// 创建字符流读取缓冲区,方便每行读取
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
// 创建输出流返回消息
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
// 创建输出流缓冲
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(os);
// 创建发送消息的线程
Runnable rOut = () -> {
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
try {
// 接收控制台输入
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String msg = scan.nextLine();
// 将输入写入缓冲
pw.println(msg);
// 将缓冲内的数据推送至服务端并清空缓冲区
pw.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
flag = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 创建接收消息的线程
Runnable rIn = () -> {
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
try {
// 逐行读取服务端返回的消息并打印
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("服务端的消息:" + str);
} catch (IOException e) {
flag = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 启动两个线程
Thread tOut = new Thread(rOut);
Thread tIn = new Thread(rIn);
tOut.start();
tIn.start();
}catch (IOException e) {
try {
// 释放资源
s.close();
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}