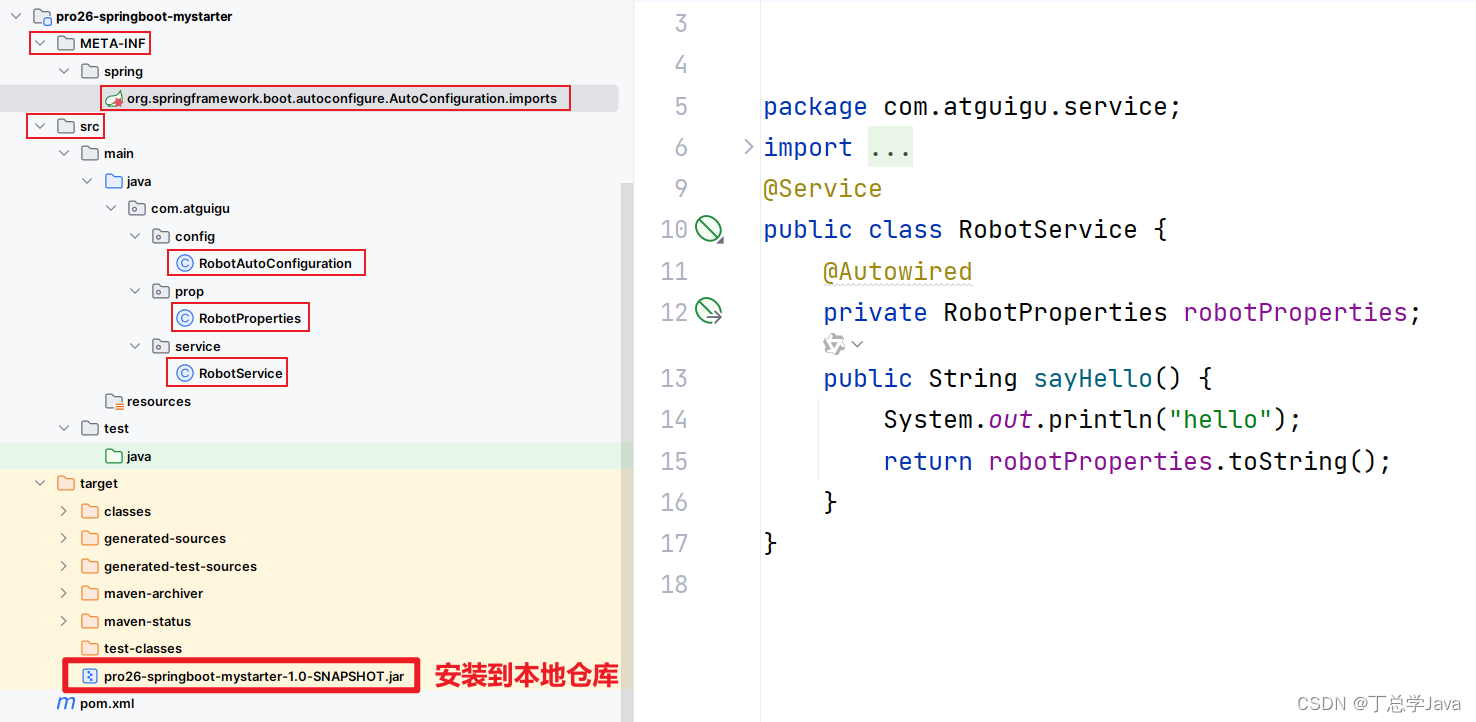
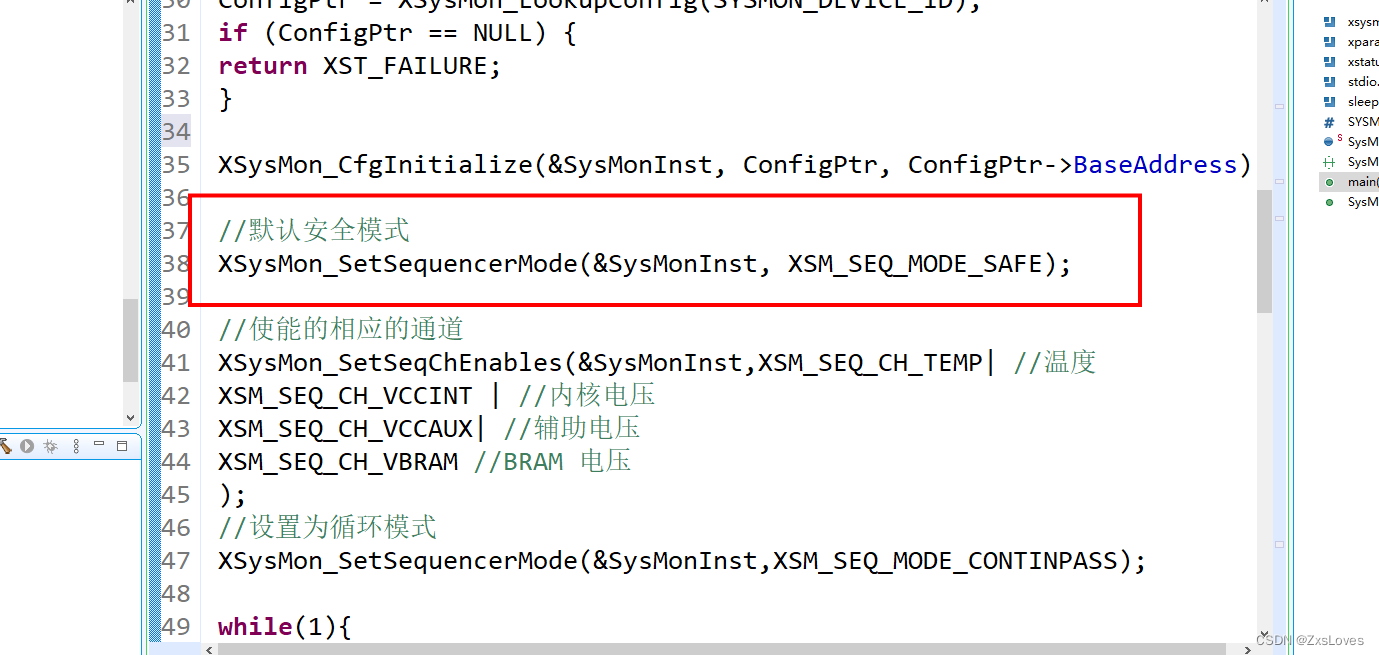
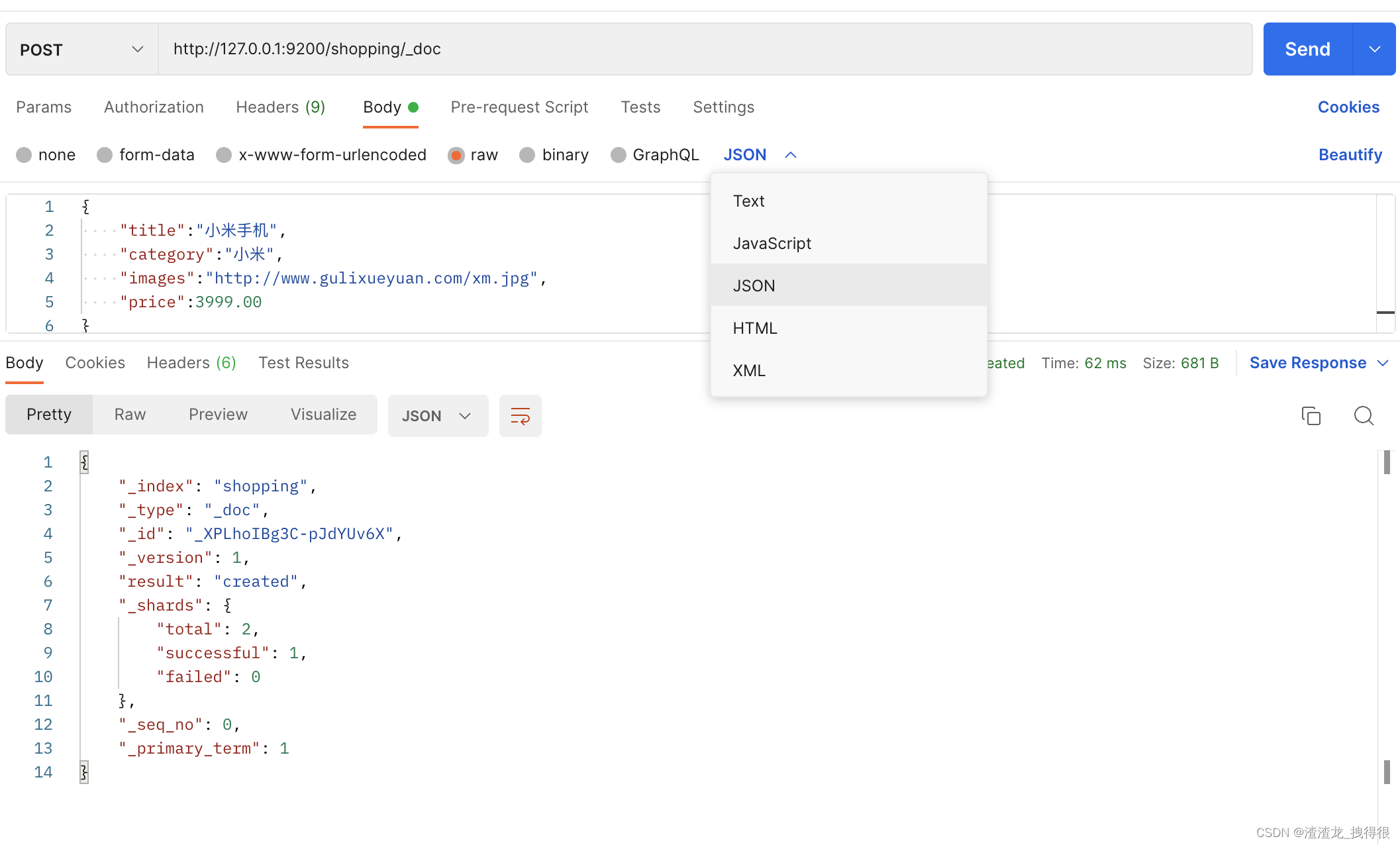
1、创建自定义启动工程pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.atguigu</groupId> <artifactId>pro26-springboot-mystarter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <!--所有springboot项目都必须继承自 spring-boot-starter-parent --> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>3.0.5</version> <relativePath /> <!-- 根据情况添加 --> </parent> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <!--web开发的场景启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--导入配置处理器,配置文件自定义的properties配置都会有提示--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>2、RobotProperties.java
package com.atguigu.prop; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Data @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "atguigu.robot") public class RobotProperties { private String name,age, email; }3、RobotService.java
package com.atguigu.service; import com.atguigu.prop.RobotProperties; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class RobotService { @Autowired private RobotProperties robotProperties; public String sayHello() { System.out.println("hello"); return robotProperties.toString(); } }4、RobotAutoConfiguration.java
package com.atguigu.config; import com.atguigu.prop.RobotProperties; import com.atguigu.service.RobotService; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; @Configuration @Import({RobotProperties.class, RobotService.class}) public class RobotAutoConfiguration { }5、org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
com.atguigu.config.RobotAutoConfiguration
6、使用自定义启动器pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.atguigu</groupId> <artifactId>pro27-springboot-use-mystarter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <!--所有springboot项目都必须继承自 spring-boot-starter-parent --> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>3.0.5</version> <relativePath /> <!-- 根据情况添加 --> </parent> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> </properties> <dependencies> <!--web开发的场景启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--导入配置处理器,配置文件自定义的properties配置都会有提示--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.atguigu</groupId> <artifactId>pro26-springboot-mystarter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>7、HelloController.java
package com.atguigu.controller; import com.atguigu.service.RobotService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/hello") public class HelloController { @Autowired private RobotService robotService; @GetMapping public String h01() { return robotService.sayHello(); } }8、application.yml
atguigu: robot: name: jim age: 20 email: jim@sina.com.cn9、MyApplication.java
package com.atguigu; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class MyApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class); } }
10、.yml
在Spring Boot中,
.yml和.yaml文件是用于配置应用的。它们是YAML(Yet Another Markup Language)格式的文件,这种格式是基于Unicode的,容易阅读和与脚本语言交互的编程语言。它以数据为中心,比JSON和XML更适合做配置文件。Spring Boot的配置文件主要分为两种类型:
application.properties和application.yml。这些文件通常放在src/main/resources路径下,可以对默认属性进行修改。具体来说,YAML配置文件的作用主要表现在以下几个方面:
- 修改Spring Boot自动配置的默认值。在底层,Spring Boot已经自动配置好了一些默认属性,通过YAML文件,我们可以修改这些默认配置。
- 添加额外的自定义配置。除了修改默认配置,我们还可以在YAML文件中添加额外的自定义配置。
总的来说,YAML配置文件使得我们能够更灵活地定制Spring Boot应用的行为和属性。
在英语中,“yet”通常表示“仍然”、“但是”或“还”的意思,强调某事尚未完成或仍然存在。在YAML(Yet Another Markup Language)中,“yet”并没有特定的含义,它只是作为一个标识符(或名称)用于区分其他类似的标记语言。YAML的设计者选择这个名称可能是为了强调它是一种新的、与众不同的标记语言,或者仅仅是因为他们喜欢这个单词的发音和拼写。无论原因是什么,这个名称已经成为了YAML的代名词,被广泛使用和接受。