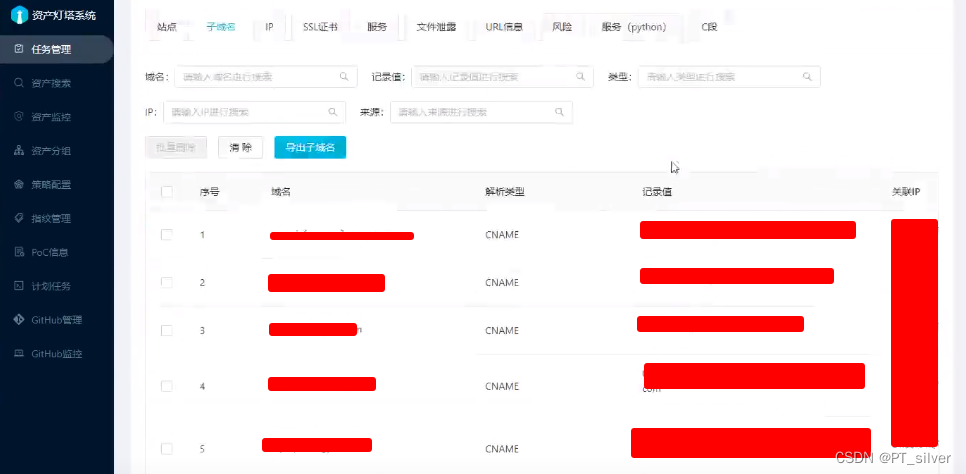
文章目录
- 反三角函数
- 反三角函数图形
- 利用反函数的性质绘制反三角图形
- 反三角函数的定义域&值域
- 反三角函数的恒等式
- 推导
反三角函数
- 反三角函数 (wikipedia.org)

反三角函数图形
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
| sin ( x ) , arcsin ( x ) \sin(x),\arcsin(x) sin(x),arcsin(x) | cos ( x ) , arccos ( x ) \cos(x),\arccos(x) cos(x),arccos(x) | tan ( x ) , arctan ( x ) \tan{(x)},\arctan{(x)} tan(x),arctan(x) |
 |  |  |
| arcsin x , arccos x \arcsin{x},\arccos{x} arcsinx,arccosx | arctan x , arccot x \arctan{x},\operatorname{arccot}{x} arctanx,arccotx | a r c s e c x , a r c c s c x \mathrm{arcsec}{x},\mathrm{arccsc}{x} arcsecx,arccscx |
利用反函数的性质绘制反三角图形
- 由于反函数与其原本的直接函数关于 y = x y=x y=x这一直线对称,因此我们可以根据反三角函数 b ( x ) b(x) b(x)的值域,在直接三角函数上 b ( x ) b(x) b(x)截取一段相应的区间,这部分函数记为 c ( x ) c(x) c(x)
- 再将 c ( x ) c(x) c(x)关于 y = x y=x y=x作对称图形
- 另一方面结合相关不等式,来提高草图准确度,例如:
- 由 sin x < x < arcsin x \sin{x}<x<\arcsin{x} sinx<x<arcsinx, ( x ∈ ( 0 , 1 ) ) (x\in(0,1)) (x∈(0,1)),三条曲线 sin x , x , arctan x \sin{x},x,\arctan{x} sinx,x,arctanx在 ( 0 , 1 ) (0,1) (0,1)区间内没有交点,而在 x = 0 x=0 x=0处三个函数交于原点
- 又因为三个函数都是奇函数,从而在第三象限三个函数的大小关系相反,且仍然没有交点
- 也可以结合函数的凹凸性,提高函数图形草图的走势准确度
- 因此绘制反三角函数草图时,先绘制 y = x y=x y=x,(虚线)然后以其对称轴,绘制直接函数的对称部分
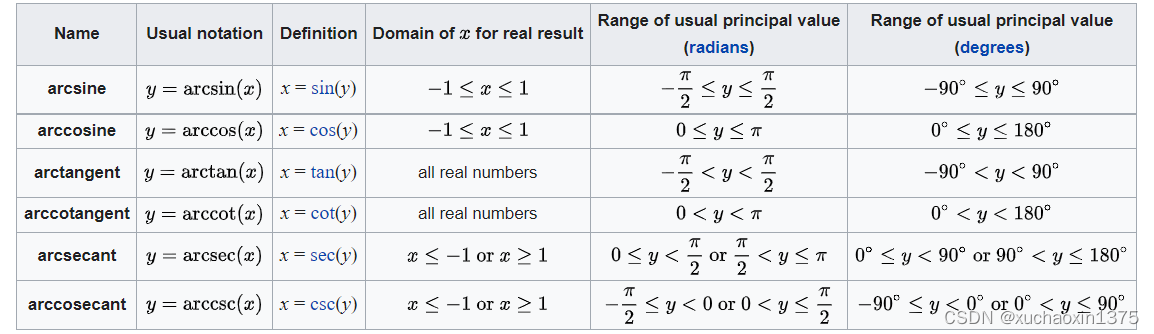
反三角函数的定义域&值域
反三角函数的恒等式
-
arcsin x + arccos x = π 2 \arcsin x+\arccos x={\frac {\pi }{2}} arcsinx+arccosx=2π
-
arctan x + arccot x = π 2 . \arctan x+\operatorname{arccot} x={\frac {\pi }{2}}. arctanx+arccotx=2π.
-
arctan x + arctan 1 x = { π 2 , i f x > 0 − π 2 , i f x < 0 \arctan x+\arctan {\frac {1}{x}} =\left\{{\begin{matrix}{\frac {\pi }{2}},&{\mathrm {if }}x>0\\ -{\frac {\pi }{2}},&{\mathrm {if }}x<0\end{matrix}}\right. arctanx+arctanx1={2π,−2π,ifx>0ifx<0
-
arctan x + arctan y = arctan x + y 1 − x y + { π , i f x , y > 0 − π , i f x , y < 0 0 , o t h e r w i s e \arctan x+\arctan y=\arctan {\frac {x+y}{1-xy}}+\left\{{\begin{matrix}\pi ,&{\mathrm {if }}x,y>0\\ -\pi ,&{\mathrm {if }}x,y<0\\ 0,&{\mathrm{otherwise }}\end{matrix}}\right. arctanx+arctany=arctan1−xyx+y+⎩ ⎨ ⎧π,−π,0,ifx,y>0ifx,y<0otherwise
-
sin ( arccos x ) = 1 − x 2 \sin(\arccos x)={\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}\, sin(arccosx)=1−x2
-
sin ( arctan x ) = x 1 + x 2 \sin(\arctan x)={\frac {x}{{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}} sin(arctanx)=1+x2x
-
cos ( arctan x ) = 1 1 + x 2 \cos(\arctan x)={\frac {1}{{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}} cos(arctanx)=1+x21
-
cos ( arcsin x ) = 1 − x 2 \cos(\arcsin x)={\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}\, cos(arcsinx)=1−x2
-
tan ( arcsin x ) = x 1 − x 2 \tan(\arcsin x)={\frac {x}{{\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}}} tan(arcsinx)=1−x2x
-
tan ( arccos x ) = 1 − x 2 x \tan(\arccos x)={\frac {{\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}}{x}} tan(arccosx)=x1−x2
推导
以第一个 arcsin x + arccos x = π 2 \arcsin x+\arccos x={\frac {\pi }{2}} arcsinx+arccosx=2π为例
- 由于
cos
θ
=
sin
(
π
2
−
θ
)
\cos\theta=\sin(\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta)
cosθ=sin(2π−θ),设它们都等于
x
x
x.则得到
cos
θ
=
x
\cos{\theta}=x
cosθ=x
(1); sin ( π 2 − θ ) = x \sin(\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta)=x sin(2π−θ)=x(2)- 对(1)两边同时取 arcsin \arcsin arcsin,得 θ = arcsin x \theta=\arcsin{x} θ=arcsinx; π 2 − θ = arccos x \frac{\pi}{2}-\theta=\arccos{x} 2π−θ=arccosx,两式相加,得 arcsin x + arccos x = π 2 \arcsin x+\arccos x={\frac {\pi }{2}} arcsinx+arccosx=2π
以第一个 arctan x + arccot x = π 2 \arctan x+\operatorname{arccot} x={\frac {\pi }{2}} arctanx+arccotx=2π也是类似的
- 由于 tan ( π 2 − θ ) \tan(\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta) tan(2π−θ)= cot θ \cot{\theta} cotθ,可令 tan ( π 2 − θ ) \tan(\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta) tan(2π−θ)= x x x; cot θ = x \cot\theta=x cotθ=x
- 所以 π 2 − θ = arctan x \frac{\pi}{2}-\theta=\arctan{x} 2π−θ=arctanx; θ = arccot θ \theta=\operatorname{arccot}{\theta} θ=arccotθ
- 两式相加,得 arctan x + arccot x = π 2 \arctan x+\operatorname{arccot} x={\frac {\pi }{2}} arctanx+arccotx=2π