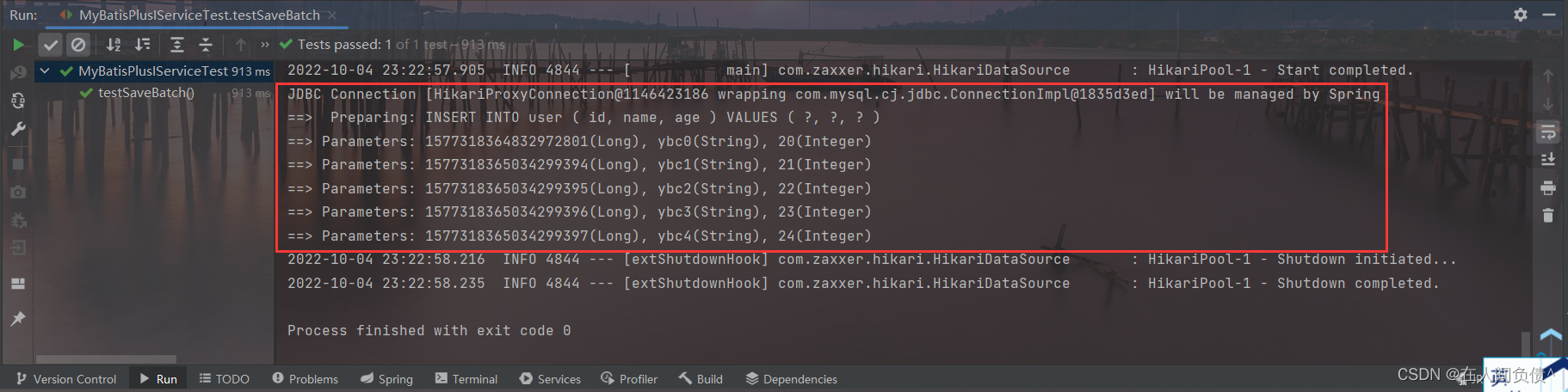
天梯赛结束后,某企业的人力资源部希望组委会能推荐一批优秀的学生,这个整理推荐名单的任务就由静静姐负责。企业接受推荐的流程是这样的:
- 只考虑得分不低于 175 分的学生;
- 一共接受 K 批次的推荐名单;
- 同一批推荐名单上的学生的成绩原则上应严格递增;
- 如果有的学生天梯赛成绩虽然与前一个人相同,但其参加过 PAT 考试,且成绩达到了该企业的面试分数线,则也可以接受。
给定全体参赛学生的成绩和他们的 PAT 考试成绩,请你帮静静姐算一算,她最多能向企业推荐多少学生?
输出格式:
在一行中输出静静姐最多能向企业推荐的学生人数。
输入样例:
10 2 90
203 0
169 91
175 88
175 0
175 90
189 0
189 0
189 95
189 89
256 100
输出样例:
8
样例解释:
第一批可以选择 175、189、203、256 这四个分数的学生各一名,此外 175 分 PAT 分数达到 90 分的学生和 189 分 PAT 分数达到 95 分的学生可以额外进入名单。第二批就只剩下 175、189 两个分数的学生各一名可以进入名单了。最终一共 8 人进入推荐名单。
我对样例的解释:
先对数据排一下序,按照天梯赛分数递增
//pat分数线90
169 91
175 88
175 0
175 90
189 0
189 0
189 95
189 89203 0
256 100
我的思路是给已经选走的人做标记。
首先得分低于175的直接就不考虑了,所以在输入的时候可以直接标记,相当于被选走了;
然后我们要最多能向企业推荐的学生人数;
在一个批次中,当我们选了某一个分数的学生后,比如175分;但是还有学生得了175分,只有当这个学生的pat分数超过分数线,才能一起被选走。
我们在第一个批次中将这种有一样分数的学生全部选走,这样在剩下的批次中选择的都是分数不一样的学生,而且不用再考虑pat分数。
输入时的选择:
169 91 被选走,加标记
175 88
175 0
175 90
189 0
189 0
189 95
189 89203 0
256 100
第一批:
169 91
175 88
175 0 * *表示第一批选走的人
175 90 *
189 0 *
189 0
189 95 *
189 89203 0 *
256 100 *
第二批:
169 91
175 88 ** **表示第二批选走的人
175 0 *
175 90 *
189 0 *
189 0 * 在这里其实选189 0和189 89没区别,在现实中肯定是选189 89
189 95 *
189 89203 0 *
256 100 *
但是部分正确QAQ
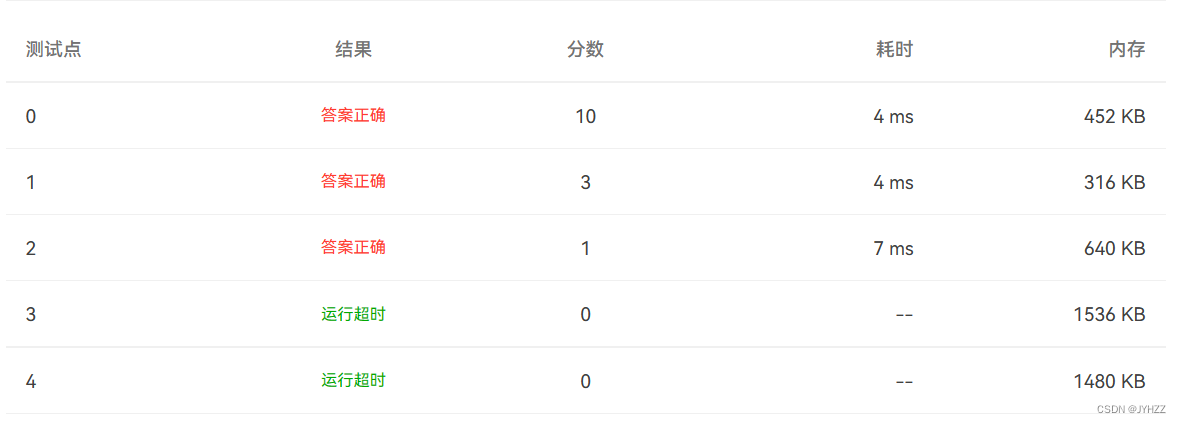
代码:(部分正确)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct List {
int score;
int PATscore;
int flag;
};
List list[100000];
bool cmp(List l1, List l2) {
return l1.score < l2.score;
}
int main() {
int count = 0, percount = 0;
int n, k, s;
cin >> n >> k >> s;
int one, two;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> one >> two;
list[i].score = one;
list[i].PATscore = two;
if (one < 175) {
list[i].flag = 1;
}
else {
list[i].flag = 0;
}
}
int array[300];
sort(list,list+n,cmp);
while (k--) {
percount = 0;
fill(array, array + 300, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (list[i].flag == 0) {
if (array[list[i].score] == 0) {
array[list[i].score] = 1;
list[i].flag = 1;
percount++;
}
else {
if (list[i].PATscore >= 90) {
list[i].flag = 1;
percount++;
}
}
}
}
if (percount == 0) {
break;
}
else {
count += percount;
}
}
cout << count;
return 0;
}别人的代码:
PTA L1-088 静静的推荐
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// - - - - - - - - -
int main()
{
int ans = 0;
int n, k, ss;
cin >> n >> k >> ss;
priority_queue<int> qu[300];
set<int>s;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
int s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
if(s1 < 175) continue;
if(s2 >= ss)
{
ans ++;
continue;
}
qu[s1].push(s2);
s.insert(s1);
}
while(k --)
{
for(auto it:s)
{
if(qu[it].empty())
continue;
ans ++;
qu[it].pop();
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
堆排序,建初始堆以及优先队列(priority_queue)
C++-STL-set的使用