文章目录
- 题目列表
- 316. 去除重复字母⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐(类型题模板:单调栈,字典序最小)
- 221021天池-03. 整理书架(保留数量为 limit 的字典序最小)
- 402. 移掉 K 位数字(最多删除 k 次 + 前导零的处理)
- 321. 拼接最大数🚹🚹🚹🚹🚹(繁琐)(分成两组+合并)💩
- 相关链接
题目列表
从第一题模板题入手。
316. 去除重复字母⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐(类型题模板:单调栈,字典序最小)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicate-letters/description/
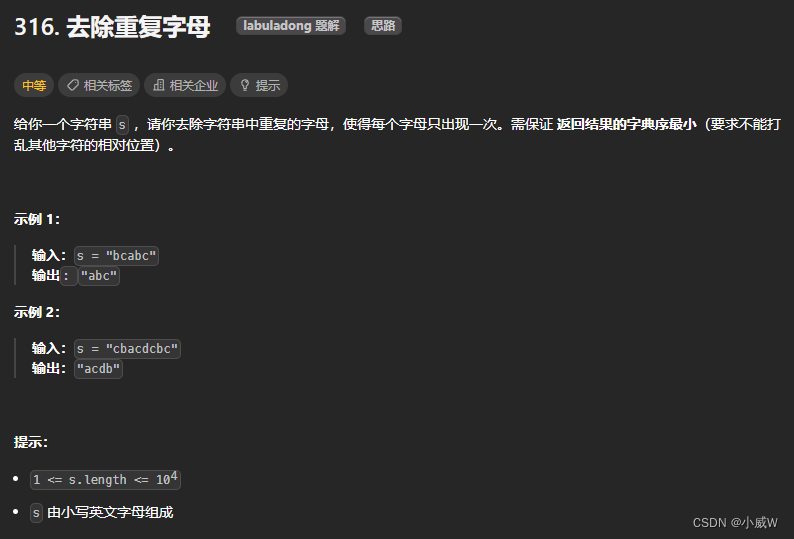
注意:该题与 316 https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicate-letters/ 相同
冷静分析,先去掉一个字符,该去掉哪一个? 为了字典序越小,肯定要越往前的字符越小越好,那么就应该将最靠前的,且满足s[i]>s[i+1]的那个s[i]删掉即可。
怎么模拟多次这个过程呢?由于最先被删掉的一定更靠前,所以可以使用单调栈从前到后维护保留下来的字符。
除此之外,
- 要求每种原来就有的字符至少会保留下来一次,因此如果之后没有这种字符了,那么就不应该将其pop出栈。
- 如果一个字符已经在栈中了,那么后续的字符就不需要再加入栈了。
可以直接使用StringBuilder作为栈。
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
int[] cnt = new int[128];
for (char ch: s.toCharArray()) cnt[ch]++; // 记录各个字符剩余的数量
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(); // StringBuilder可以当栈使用
for (char ch: s.toCharArray()) {
cnt[ch]--; // 将剩余数量-1
if (ans.indexOf(String.valueOf(ch)) != -1) continue; // 如果前面已经有ch了,后面不需要再有了
// 将stk中比当前ch更大且后面还有剩余的字符pop出去
while (ans.length() > 0 && ch <= ans.charAt(ans.length() - 1) && cnt[ans.charAt(ans.length() - 1)] > 0) {
ans.deleteCharAt(ans.length() - 1);
}
ans.append(ch);
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
也可以使用栈,再转换成字符串。
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
int[] cnt = new int[128];
for (char ch: s.toCharArray()) cnt[ch]++; // 记录各个字符剩余的数量
Deque<Character> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (char ch: s.toCharArray()) {
cnt[ch]--; // 将剩余数量-1
if (stk.contains(ch)) continue; // 如果前面已经有ch了,后面不需要再有了
// 将stk中比当前ch更大且后面还有剩余的字符pop出去
while (!stk.isEmpty() && ch <= stk.peek() && cnt[stk.peek()] > 0) {
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(ch);
}
// 将栈中的结果转成String返回
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
while (!stk.isEmpty()) ans.append(stk.pop());
return ans.reverse().toString();
}
}
221021天池-03. 整理书架(保留数量为 limit 的字典序最小)
https://leetcode.cn/contest/tianchi2022/problems/ev2bru/

提示:
1 <= order.length <= 10^5
1 <= limit <= 10
1 <= order[i] <= 10^6
class Solution {
public int[] arrangeBookshelf(int[] order, int limit) {
Deque<Integer> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 分别记录剩余的数量,在栈中的数量
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt_residue = new HashMap<>(), cnt2 = new HashMap<>();
for (int x: order) cnt_residue.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
for (int x: order) {
cnt_residue.merge(x, -1, Integer::sum);
if (cnt2.getOrDefault(x, 0) >= limit) continue; // 如果栈中已经有足够的x了,就不再添加进去
// 要求栈中的元素+剩余的元素>limit才会被弹出
while (!stk.isEmpty() && x < stk.peek() && cnt_residue.get(stk.peek()) + cnt2.getOrDefault(stk.peek(), 0) > limit) {
cnt2.merge(stk.peek(), -1, Integer::sum);
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(x);
cnt2.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
}
int n = stk.size();
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
ans[i] = stk.pop();
}
return ans;
}
}
402. 移掉 K 位数字(最多删除 k 次 + 前导零的处理)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-k-digits/description/
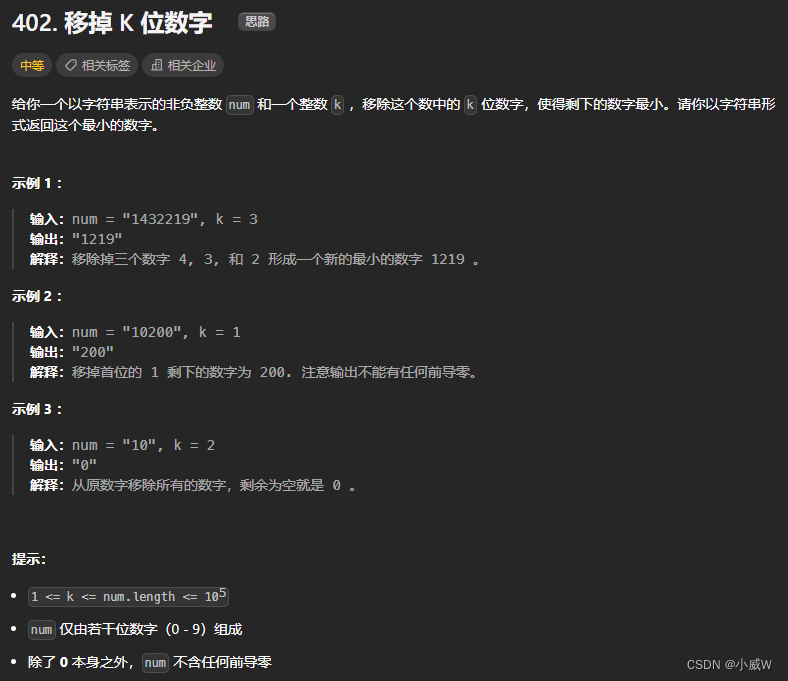
跟之前题目的区别在于,最多删除k次。
以及0可以不删,留着当前导零直接去除。
class Solution {
public String removeKdigits(String num, int k) {
Deque<Character> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (char x: num.toCharArray()) {
while (!stk.isEmpty() && x < stk.peek() && k > 0) {
stk.pop();
k--;
}
stk.push(x);
}
// 如果还有没用的k,从后往前删除
while (!stk.isEmpty() && k-- > 0) stk.pop();
if (stk.size() == 0) return "0";
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
while (!stk.isEmpty()) ans.append(stk.pop());
// 去除前导零
while (ans.length() > 1 && ans.charAt(ans.length() - 1) == '0') ans.deleteCharAt(ans.length() - 1);
return ans.reverse().toString();
}
}
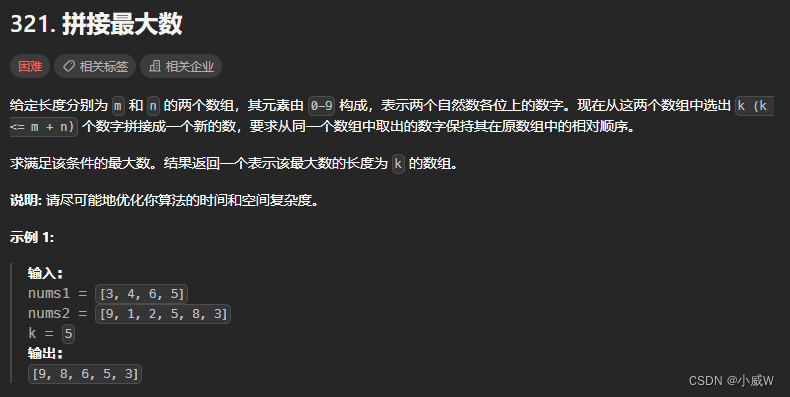
321. 拼接最大数🚹🚹🚹🚹🚹(繁琐)(分成两组+合并)💩
https://leetcode.cn/problems/create-maximum-number/description/
class Solution {
public int[] maxNumber(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
int m = nums1.length, n = nums2.length;
int[] maxSubSequence = new int[k];
int start = Math.max(0, k - n), end = Math.min(k, m);
for (int i = start; i <= end; ++i) {
int[] subSequence1 = maxSubSequence(nums1, i);
int[] subSequence2 = maxSubSequence(nums2, k - i);
int[] curMaxSubSequence = merge(subSequence1, subSequence2);
if (compare(curMaxSubSequence, 0, maxSubSequence, 0) > 0) {
System.arraycopy(curMaxSubSequence, 0, maxSubSequence, 0, k);
}
}
return maxSubSequence;
}
// 求最大子序列
public int[] maxSubSequence(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] stk = new int[k];
int top = -1, remain = n - k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int num = nums[i];
while (top >= 0 && num > stk[top] && remain > 0) {
top--;
remain--;
}
if (top < k - 1) {
stk[++top] = num;
} else {
--remain;
}
}
return stk;
}
// 合并两个子序列
public int[] merge(int[] subSequence1, int[] subSequence2) {
int x = subSequence1.length, y = subSequence2.length;
if (x == 0) return subSequence2;
if (y == 0) return subSequence1;
int mergeLength = x + y;
int[] res = new int[mergeLength];
int index1 = 0, index2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < mergeLength; ++i) {
if (compare(subSequence1, index1, subSequence2, index2) > 0) {
res[i] = subSequence1[index1++];
} else {
res[i] = subSequence2[index2++];
}
}
return res;
}
// 比较两个子序列的大小
public int compare(int[] subSequence1, int index1, int[] subSequence2, int index2) {
int x = subSequence1.length, y = subSequence2.length;
while (index1 < x && index2 < y) {
int diff = subSequence1[index1] - subSequence2[index2];
if (diff != 0) return diff;
index1++;
index2++;
}
return (x - index1) - (y - index2);
}
}
相关链接
【算法】单调栈题单(矩阵系列、字典序最小、贡献法)


![[github全教程]github版本控制最全教学------- 大厂找工作面试必备!](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/083e22ef77cd4326a05791a0b41e9c51.png)


![[网鼎杯 2020 青龙组]singal 1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7235c021c4cf45edaccf557910d797f7.png)