1、误用shared_ptr
int* p = new int;
shared_ptr<int> sp1(p);
shared_ptr<int> sp2(p); //error
// 通过原始指针两次创建shared_ptr是错误的
shared_ptr<int> sp1(new int);
shared_ptr<int> sp2(sp1); //ok如果对C++相关闲碎记录(1)中记录的shared_ptr的使用例子修改为如下:父类添加孩子的shared_ptr时调用下面这个函数来实现,同样会出现问题:
class Person {
public:
string name;
shared_ptr<Person> mother;
shared_ptr<Person> father;
vector<weak_ptr<Person>> kids; //使用weak_ptr
Person(const string& n, shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr,
shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) :name(n), mother(m), father(f) {}
~Person() {
cout << "delete " << name << endl;
}
void setParentAndTheirKids(shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr, shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) {
mother = m;
father = f;
if (m != nullptr) {
m->kids.push_back(shared_ptr<Person>(this)); //error
// 为什么这里会报错,因为this所指的对象已经有一个shared_ptr了,再通过这种方式创建shared_ptr就会报错,因为会重新开启一个拥有者团队
}
if (f != nullptr){
f->kids.push_back(shared_ptr<Person>(this)); //error
}
}
};
shared_ptr<Person> initFamily(const string& name) {
shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name + "'s mom"));
shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name + "'s dad"));
shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name));
kid->setParentAndTheirKids(mom, dad);
return kid;
}使用enable_shared_from_this<Person>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class Person : public enable_shared_from_this<Person> {
public:
string name;
shared_ptr<Person> mother;
shared_ptr<Person> father;
vector<weak_ptr<Person>> kids; // weak pointer !!!
Person (const string& n)
: name(n) {
}
void setParentsAndTheirKids (shared_ptr<Person> m = nullptr,
shared_ptr<Person> f = nullptr) {
mother = m;
father = f;
if (m != nullptr) {
m->kids.push_back(shared_from_this());
}
if (f != nullptr) {
f->kids.push_back(shared_from_this());
}
}
~Person() {
cout << "delete " << name << endl;
}
};
shared_ptr<Person> initFamily (const string& name)
{
shared_ptr<Person> mom(new Person(name+"'s mom"));
shared_ptr<Person> dad(new Person(name+"'s dad"));
shared_ptr<Person> kid(new Person(name));
kid->setParentsAndTheirKids(mom,dad);
return kid;
}
int main()
{
shared_ptr<Person> p = initFamily("nico");
cout << "nico's family exists" << endl;
cout << "- nico is shared " << p.use_count() << " times" << endl;
cout << "- name of 1st kid of nico's mom: "
<< p->mother->kids[0].lock()->name << endl;
p = initFamily("jim");
cout << "jim's family exists" << endl;
}shared_ptr各种操作:


shared_ptr<void> sp(new int);
shared_ptr<int>(static_cast<int*>(sp.get())) //error
static_pointer_cast<int*>(sp)
std::unique_ptr<int> up = new int; //error
std::unique_ptr<int> up(new int); // okunique_ptr不必一定拥有对象,也可以是empty。
std::unique_ptr<std::string> up;
可以赋值为nullptr或者调用reset
up = nullptr;
up.reset();unique_ptr可以调用release(),释放所拥有的对象,并将所有权交给调用者。
std::unique_ptr<std::string> up(new std::string("nico"));
std::string* sp = up.release();2、转移unique_ptr的拥有权
std::string* sp = new std::string("hello");
std::unique_ptr<std::string> up1(sp);
std::unique_ptr<std::string) up2(sp); //error up1 and up2 own same data
std::unique_ptr<std::string[]> up(new std::string[10]); //ok
此偏特化不再提供操作符*和->,而提供[]操作符,访问array中的一个对象时,使用[]
std::cout << *up << std::endl; //error
std::cout << up[0] << std::endl; //ok
指定自定义删除器:通过类的方式指定
class ClassADeleter {
public:
void operator() (ClassA* p) {
std::cout << "call delete for ClassA object" << std::endl;
delete p;
}
};
std::unique_ptr<ClassA, ClassADeleter> up(new ClassA());如果是个函数或者lambda,必须声明deleter的类型为void(*)(T*)或者std::function<void(T*)>,要不就使用decltype,例如要为array of int指定自己的deleter,并以lambda形式呈现:
std::unique_ptr<int, void(*)(int*)> up(new int[10],
[](int* p) {
delete []p;});
std::unique_ptr<int, std::function<void(int*)>> up(new int[10],
[](int* p) {
delete []p;});
或者
auto l = [](int*) {delete [] p;};
std::unique_ptr<int, decltype(l)>> up(new int[10], l);为了避免传递function pointer 或者lambda 时必须指明deleter的类型,你可以使用alias template
template<typename T>
using uniquePtr = std::unique_ptr<T, void(*)(T*)>;
uniquePtr<int> up(new int[10], [](int* p) {delete [] p;});unique_ptr各种操作:

3、numeric_limits<>
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// use textual representation for bool
cout << boolalpha;
// print maximum of integral types
cout << "max(short): " << numeric_limits<short>::max() << endl;
cout << "max(int): " << numeric_limits<int>::max() << endl;
cout << "max(long): " << numeric_limits<long>::max() << endl;
cout << endl;
// print maximum of floating-point types
cout << "max(float): "
<< numeric_limits<float>::max() << endl;
cout << "max(double): "
<< numeric_limits<double>::max() << endl;
cout << "max(long double): "
<< numeric_limits<long double>::max() << endl;
cout << endl;
// print whether char is signed
cout << "is_signed(char): "
<< numeric_limits<char>::is_signed << endl;
cout << endl;
// print whether numeric limits for type string exist
cout << "is_specialized(string): "
<< numeric_limits<string>::is_specialized << endl;
}4、type trait的使用
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// type trait
template <typename T>
void foo_impl(T val, true_type) {
std::cout << "Integer" << std::endl;
}
template <typename T>
void foo_impl(T val, false_type) {
std::cout << "not Integer" << std::endl;
}
template <typename T>
void foo(T val) {
foo_impl(val, std::is_integral<T>());
}
int main()
{
double d_a = 1.2;
long long int ll_b = 33333;
foo(d_a);
foo(ll_b);
}
输出:
not Integer
Integer类型判断工具

用以阐明class细节的trait
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<int>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<const volatile int>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<int* const>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<const int*>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<const int&>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<int[3]>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<const int[3]>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<int[]>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<const int[]>::value << endl; //true
return 0;
}指向const类型的非常量指针或者引用,并不是一个常量,尽管内含元素是常量,例如const int* 并不是常量,只是描述指针所指向的这个变量是常量类型,但是指针本身可以重新指向新的变量。
用以检测copy和move语义的那些个trait,只检测是否相应的表达式为可能,例如一个带有copy构造函数的(接受常量实参)但没有move构造函数的类型,仍然是move constructible.
用以检验类型关系的trait

int main()
{
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<int, int>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<int&, int>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<int&&, int>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<long&, int>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<int&, void*>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<void*, int>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<const char*, std::string>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_assignable<std::string, const char*>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<int>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<int, int>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<long, int>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<int, void*>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<void*, int>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<const char*, std::string>::value << endl; //false
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<std::string, const char*>::value << endl; //true
std::cout << boolalpha << is_constructible<std::string, const char*, int, int>::value << endl; //true
return 0;
}5、类型修饰符
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <type_traits>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <cxxabi.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
typedef int T;
typedef add_const<T>::type A; //const int
typedef add_lvalue_reference<T>::type B; //int&
typedef add_rvalue_reference<T>::type C; //int&&
typedef add_pointer<T>::type D; //int*
typedef make_signed<T>::type E; //int
typedef make_unsigned<T>::type F; //unsigned int
typedef remove_const<T>::type G; //int
typedef remove_reference<T>::type H; //int
typedef remove_pointer<T>::type I; //int
std::cout << boolalpha << is_const<A>::value << std::endl;
// 查看完整类型
std::cout << abi::__cxa_demangle(typeid(A).name(),0,0,0 ) << std::endl;
std::cout << typeid(B).name() << std::endl;
std::cout << "A is same const int ?" << boolalpha << is_same<const int, A>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "B is same int& ?" << boolalpha << is_same<int&, B>::value << std::endl;
typedef const int& T1;
typedef add_const<T1>::type A1; // const int&
typedef add_lvalue_reference<T1>::type B1; //const int&
typedef add_rvalue_reference<T1>::type C1; //const int& (yes, lvalue remains lvalue)
typedef add_pointer<T1>::type D1; //const int*
// typedef make_signed<T1>::type E1; //undefined behavior
// typedef make_unsigned<T1>::type F1; //undefined bahavior
typedef remove_const<T1>::type G1; //const int&
typedef remove_reference<T1>::type H1; //const int
typedef remove_pointer<T1>::type I1; //cosnt int&
std::cout << "A1 is same const int& ?" << boolalpha << is_same<const int&, A1>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << is_const<A1>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << "G1 is same const int& ?" << boolalpha << is_same<const int&, G1>::value << std::endl;
return 0;
}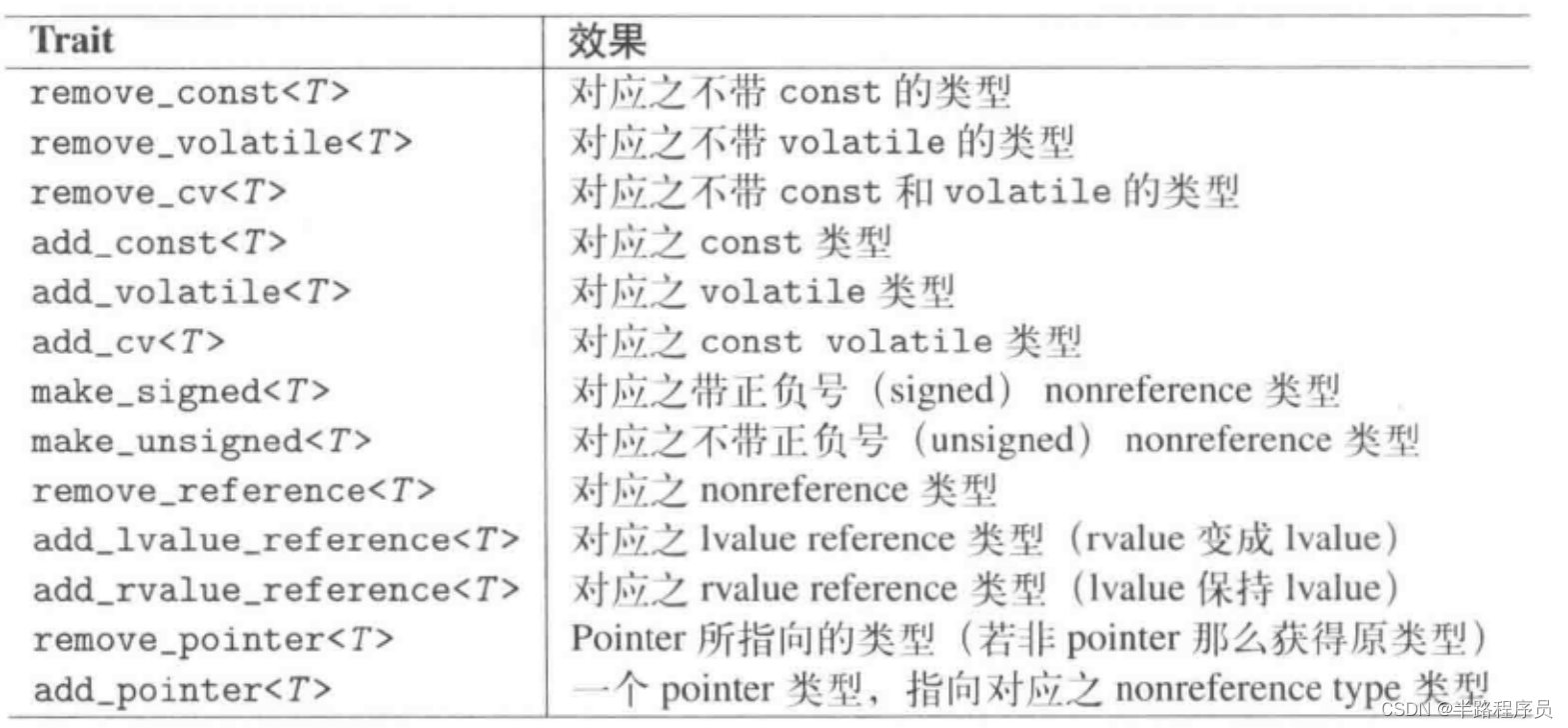
指向某常量类型的reference本身并不是常量,所以不可以移除const,add_pointer<>必然包含使用remove_reference<>,然而make_signed<>和make_unsigned<>必须是整型,枚举型,bool除外,所以传入引用会导致不明确的行为。add_lvalue_reference<>把一个rvalue reference转换为一个lvalue reference,然而add_rvalue_reference<>并不会把一个lvalue reference转换为一个rvalue reference.
6、其他type trait

#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <type_traits>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <cxxabi.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::cout << rank<int>::value << std::endl; //0
std::cout << rank<int[]>::value << std::endl; //1
std::cout << rank<int[3]>::value << std::endl; //1
std::cout << rank<int[][4]>::value << std::endl; //2
std::cout << rank<int[3][4]>::value << std::endl; //2
std::cout << extent<int>::value << std::endl; //0
std::cout << extent<int[]>::value << std::endl; //0
std::cout << extent<int[3]>::value << std::endl; //3
std::cout << extent<int[][4]>::value << std::endl; //0
std::cout << extent<int[3][3]>::value << std::endl; //3
std::cout << extent<int[][3], 1>::value << std::endl; //3
std::cout << extent<int[5][6], 1>::value << std::endl; //6
std::cout << extent<int[3][4], 2>::value << std::endl; //0
typedef remove_extent<int>::type A; //int
typedef remove_extent<int[]>::type B; //int
typedef remove_extent<int[3]>::type C; //int
typedef remove_extent<int[][8]>::type D; //int[8]
typedef remove_extent<int[5][6]>::type E; //int[7]
typedef remove_all_extents<int>::type F; //int
typedef remove_all_extents<int>::type G; //int
typedef remove_all_extents<int[]>::type H; //int
typedef remove_all_extents<int[5]>::type I; //int
typedef remove_all_extents<int[][9]>::type J; //int
typedef remove_all_extents<int[5][8]>::type K; //int
return 0;
}



![[原创][3]探究C#多线程开发细节-“用ConcurrentQueue<T>解决多线程的无顺序性的问题“](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c11e1e0a8bbe4c3e968333a96e568a90.png)