系列文章目录
目录
系列文章目录
前言
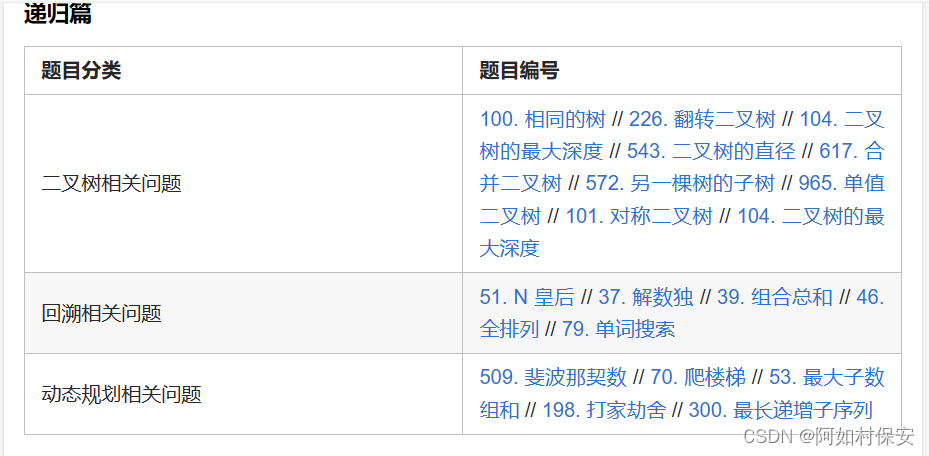
一、二叉树相关问题
二、回溯相关问题
三、动态规划相关问题
总结
前言
刷题按照:[力扣刷题攻略] Re:从零开始的力扣刷题生活 - 力扣(LeetCode),如图,因为是讲递归,所以所有题的首解都是给的递归。
递归不要看全过程,看一次递归就好,可以参考三道题套路解决递归问题 | lyl's blog (lyl0724.github.io)

一、二叉树相关问题
100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)


/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) return true;
if(p == null || q == null) return false;
if(p.val != q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}
226. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)


递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return null;
TreeNode leftTree = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode rightTree = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = rightTree;
root.right = leftTree;
return root;
}
}
非递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode current = root;
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// 将当前节点及其左子树全部入栈
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
// 出栈并交换左右子节点的位置
current = stack.pop();
TreeNode temp = current.left;
current.left = current.right;
current.right = temp;
// 继续处理右子树
current = current.left;
}
return root;
}
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)


/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
// //终止条件:当树为空时结束递归,并返回当前深度0
// if(root == null){
// return 0;
// }
// //root的左、右子树的最大深度
// int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
// int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
// //返回的是左右子树的最大深度+1
// return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
return root == null ? 0 : Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
543. 二叉树的直径 - 力扣(LeetCode)

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int max = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
dfs(root);
return max;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftSize = root.left == null? 0: dfs(root.left) + 1;
int rightSize = root.right == null? 0: dfs(root.right) + 1;
max = Math.max(max, leftSize + rightSize);
return Math.max(leftSize, rightSize);
}
}
617. 合并二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)


/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null) return root2;
if (root2 == null) return root1;
return new TreeNode(root1.val + root2.val,
mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left), // 合并左子树
mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right)); // 合并右子树
}
}
572. 另一棵树的子树 - 力扣(LeetCode)



isSubtree 函数判断 root 树是否包含 subRoot 树,而 nb 函数用于比较两个树是否相等。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 主函数,判断树 root 是否包含树 subRoot
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
return nb(root, subRoot, subRoot);
}
// 辅助函数,判断两个树是否相等
public boolean nb(TreeNode root, TreeNode curRoot, TreeNode subRoot) {
// 如果两个树都为空,返回 true
if (root == null && curRoot == null)
return true;
// 如果一个为空而另一个不为空,返回 false
if (root == null || curRoot == null)
return false;
// 如果两个节点值相等,判断左右子树是否相等,或者当前树是否是 root 的左/右子树的子树
if (root.val == curRoot.val) {
return (nb(root.left, curRoot.left, curRoot) && nb(root.right, curRoot.right, curRoot))
|| nb(root.left, subRoot, subRoot) || nb(root.right, subRoot, subRoot);
} else
// 如果节点值不相等,判断当前树是否是 root 的左/右子树的子树
return nb(root.left, subRoot, subRoot) || nb(root.right, subRoot, subRoot);
}
}

965. 单值二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)


如果根节点为null,返回true。如果根节点值和左右子树值相同并且左右子树都是单值树返回true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isUnivalTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (root.left != null && root.left.val != root.val) {
return false;
}
if (root.right != null && root.right.val != root.val) {
return false;
}
return isUnivalTree(root.right) && isUnivalTree(root.left);
}
}
101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return cmp(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean cmp(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (node1 == null || node2 == null || node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
return cmp(node1.left, node2.right) && cmp(node1.right, node2.left);
}
} 
二、回溯相关问题
回溯法:回溯算法详细总结 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)

51. N 皇后 - 力扣(LeetCode)


使用回溯法,逐行放置皇后,保证每一行、每一列、以及两条对角线都没有冲突。在放置皇后的过程中,使用位运算来记录可以放置皇后的位置。当找到一种解法时,将当前的棋盘状态添加到结果中。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
ArrayList<List<String>> arrayList;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
arrayList = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
// 初始化棋盘
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
// 开始深度优先搜索
dfs(board, 0, 0, 0, 0, (1 << n) - 1);
return arrayList;
}
// 深度优先搜索
public void dfs(char[][] board, int column, int left, int right, int row, int test) {
// 如果列已经填满,说明找到了一种解法,将棋盘添加到结果中
if (column == test) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
list.add(new String(board[i]));
}
arrayList.add(list);
return;
}
// 获取可以放置皇后的位置
int availablePos = test & (~(column | left | right));
// 遍历可以放置皇后的位置
while (availablePos != 0) {
int pos = availablePos & (-availablePos);
int count = Integer.bitCount(pos - 1);
// 在当前位置放置皇后,并继续搜索下一行
board[row][count] = 'Q';
dfs(board, column | pos, (left | pos) >>> 1, (right | pos) << 1, row + 1, test);
// 恢复当前位置
board[row][count] = '.';
// 移除当前位置,准备下一次搜索
availablePos ^= pos;
}
}
}

37. 解数独 - 力扣(LeetCode)



使用了位运算来高效地存储和查询数字的填充状态,通过递归和回溯实现对数独的解法。
/**
* 解数独问题的算法
*/
class Solution {
private int[] line = new int[9]; // 行的状态,标记每一行已经填入的数字
private int[] column = new int[9]; // 列的状态,标记每一列已经填入的数字
private int[][] block = new int[3][3]; // 3x3 小九宫格的状态,标记每个小九宫格已经填入的数字
private boolean valid = false; // 记录是否找到了解
private List<int[]> spaces = new ArrayList<int[]>(); // 记录所有空白位置的坐标
/**
* 解数独入口函数
*/
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
// 初始化已经填入的数字状态
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] != '.') {
int digit = board[i][j] - '0' - 1;
flip(i, j, digit); // 标记已经填入的数字
}
}
}
// 初步填充数独
while (true) {
boolean modified = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
int mask = ~(line[i] | column[j] | block[i / 3][j / 3]) & 0x1ff;
if ((mask & (mask - 1)) == 0) {
int digit = Integer.bitCount(mask - 1);
flip(i, j, digit); // 标记已经填入的数字
board[i][j] = (char) (digit + '0' + 1);
modified = true;
}
}
}
}
if (!modified) {
break;
}
}
// 找出所有空白位置
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
spaces.add(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
// 使用深度优先搜索解数独
dfs(board, 0);
}
/**
* 深度优先搜索解数独的递归函数
*/
public void dfs(char[][] board, int pos) {
// 已经找到解,直接返回
if (pos == spaces.size()) {
valid = true;
return;
}
int[] space = spaces.get(pos);
int i = space[0], j = space[1];
int mask = ~(line[i] | column[j] | block[i / 3][j / 3]) & 0x1ff;
for (; mask != 0 && !valid; mask &= (mask - 1)) {
int digitMask = mask & (-mask);
int digit = Integer.bitCount(digitMask - 1);
flip(i, j, digit); // 标记已经填入的数字
board[i][j] = (char) (digit + '0' + 1);
dfs(board, pos + 1);
flip(i, j, digit); // 回溯,取消标记
}
}
/**
* 翻转某个位置的二进制位,用于标记已经填入的数字
*/
public void flip(int i, int j, int digit) {
line[i] ^= (1 << digit);
column[j] ^= (1 << digit);
block[i / 3][j / 3] ^= (1 << digit);
}
}

39. 组合总和 - 力扣(LeetCode)

通过递归的方式,在候选数字中搜索所有可能的组合总和,同时使用回溯的思想。
import java.util.AbstractList;
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res;
// 主函数,返回组合总和的结果
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
// 返回一个 AbstractList,实现了 List 接口
return new AbstractList<List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public int size() {
init();
return res.size();
}
@Override
public List<Integer> get(int index) {
init();
return res.get(index);
}
// 初始化函数,在第一次调用 get 或 size 时执行
protected void init() {
if (res != null)
return;
res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
// 调用深度优先搜索函数,找到所有组合总和
dfsHelper(candidates, target, 0, new LinkedList<Integer>(), res);
}
};
}
// 深度优先搜索函数,递归查找组合总和
private void dfsHelper(int[] nums, int target, int i, LinkedList<Integer> combination, List<List<Integer>> res) {
if (target < 0) {
return;
} else if (target == 0) {
// 找到一个组合总和,将其加入结果集
res.add(new LinkedList<>(combination));
} else if (target > 0) {
// 遍历候选数字,递归查找组合总和
for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++) {
combination.add(nums[j]);
dfsHelper(nums, target - nums[j], j, combination, res);
combination.removeLast();
}
}
}
}
46. 全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
//** 待深入理解
// 结果列表
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 如果数组为空,直接返回结果
if (nums.length == 0) return res;
// 访问标记数组,用于标记数组中的元素是否已经在当前路径中
boolean[] visit = new boolean[nums.length];
// 回溯
backTrack(nums, 0, visit, new ArrayList<>(), res);
return res;
}
void backTrack(int[] nums, int index, boolean[] visit, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// 递归终止条件,如果路径长度等于数组长度,将当前路径添加到结果中
if (index == nums.length) {
// **变量 path 所指向的列表 在深度优先遍历的过程中只有一份 ,深度优先遍历完成以后,回到了根结点,成为空列表。
//在 Java 中,参数传递是 值传递,对象类型变量在传参的过程中,复制的是变量的地址。
// 这些地址被添加到 res 变量,但实际上指向的是同一块内存地址,因此我们会看到 6个
// 空的列表对象。解决的方法很简单,在 res.add(path); 这里做一次拷贝即可。
//res.add(path); //错的
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果当前元素未被访问
if (!visit[i]) {
// 将当前元素添加到路径中
path.add(nums[i]);
// 标记当前元素已被访问
visit[i] = true;
// 递归处理下一个元素
backTrack(nums, index + 1, visit, path, res);
// ** 回溯,撤销访问标记
visit[i] = false;
// 回溯,从路径中移除当前元素
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
// 递归之前 => [1]
// 递归之前 => [1, 2]
// 递归之前 => [1, 2, 3]
// 递归之后 => [1, 2]
// 递归之后 => [1]
// 递归之前 => [1, 3]
// 递归之前 => [1, 3, 2]
// 递归之后 => [1, 3]
// 递归之后 => [1]
// 递归之后 => []
// 递归之前 => [2]
// 递归之前 => [2, 1]
// 递归之前 => [2, 1, 3]
// 递归之后 => [2, 1]
// 递归之后 => [2]
// 递归之前 => [2, 3]
// 递归之前 => [2, 3, 1]
// 递归之后 => [2, 3]
// 递归之后 => [2]
// 递归之后 => []
// 递归之前 => [3]
// 递归之前 => [3, 1]
// 递归之前 => [3, 1, 2]
// 递归之后 => [3, 1]
// 递归之后 => [3]
// 递归之前 => [3, 2]
// 递归之前 => [3, 2, 1]
// 递归之后 => [3, 2]
// 递归之后 => [3]
// 递归之后 => []
// 输出 => [[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]]
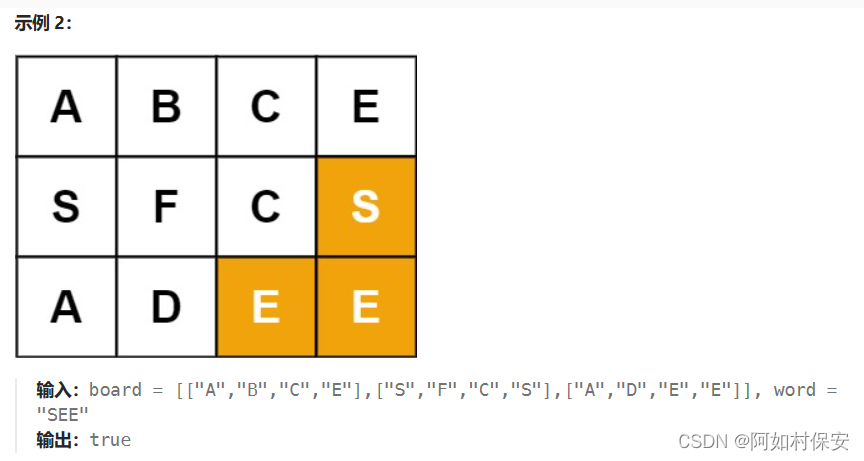
79. 单词搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
boolean ans = false;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
int m = board.length;
int n = board[0].length;
// 同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用!!!
// 标识字母是否被使用
boolean[][] used = new boolean[m][n];
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
// 开头开始匹配
if(board[i][j] == chars[0]){
backtrack(board, i, j, chars, 0, used);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public void backtrack(char[][] board, int i, int j, char[] chars, int startIdx, boolean[][] used){
if(ans){
// 已找到答案直接结束
return;
}
int m = board.length;
int n = board[0].length;
if(startIdx == chars.length){
ans = true;
return;
}
// 越界 或者不相等
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= m || j >= n || board[i][j] != chars[startIdx]){
return;
}
// 使用过的不能再用了
if(used[i][j]){
return;
}
// 没使用过的,置为已使用
used[i][j] = true;
// 递归 上下左右四个方向
backtrack(board, i - 1, j, chars, startIdx + 1, used);
backtrack(board, i + 1, j, chars, startIdx + 1, used);
backtrack(board, i, j - 1, chars, startIdx + 1, used);
backtrack(board, i, j + 1, chars, startIdx + 1, used);
// 回溯
used[i][j] = false;
}
}
三、动态规划相关问题
509. 斐波那契数 - 力扣(LeetCode)


class Solution {
// //动态规划
// public int fib(int n) {
// if(n<=1) return n;
// int[] dp=new int[n+1];
// dp[0]=0;
// dp[1]=1;
// for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
// dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
// }
// return dp[n];
// }
//循环
public int fib(int n){
if(n<=1) return n;
int result=0;
int pre=1;
int prePre=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
result=pre+prePre;
prePre=pre;
pre=result;
}
return result;
}
}
70. 爬楼梯 - 力扣(LeetCode)


class Solution {
//递归解法
private Map<Integer,Integer> storeMap=new HashMap<>();
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1) return 1;
if(n==2) return 2;
if(null!=storeMap.get(n)){
return storeMap.get(n);
}else{
int result=climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
storeMap.put(n,result);
return result;
}
}
}
53. 最大子数组和 - 力扣(LeetCode)


class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {
count = Math.max(count + nums[i], nums[i]);
ans = Math.max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
}
198. 打家劫舍 - 力扣(LeetCode)


使用两个变量 p 和 q 分别表示前前一个房子和前一个房子的最大金额。通过遍历房子,计算在当前房子偷或不偷的情况下的最大金额,并更新 p 和 q。最终返回 q,即能够偷到的最大金额。
class Solution {
// 主函数,返回能够偷到的最大金额
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int p = 0; // 表示前前一个房子的最大金额
int q = nums[0]; // 表示前一个房子的最大金额
// 从第二个房子开始遍历
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int tmp = p + nums[i]; // 计算偷当前房子的金额和前前一个房子的金额之和
p = q; // 更新前前一个房子的最大金额为前一个房子的最大金额
q = Math.max(tmp, q); // 更新前一个房子的最大金额为当前房子和前前一个房子的金额之和和前一个房子的最大金额中的较大值
}
return q; // 返回最终的最大金额
}
}

300. 最长递增子序列 - 力扣(LeetCode)


class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
/**
dp[i]: 所有长度为i+1的递增子序列中, 最小的那个序列尾数.
由定义知dp数组必然是一个递增数组, 可以用 maxL 来表示最长递增子序列的长度.
对数组进行迭代, 依次判断每个数num将其插入dp数组相应的位置:
1. num > dp[maxL], 表示num比所有已知递增序列的尾数都大, 将num添加入dp
数组尾部, 并将最长递增序列长度maxL加1
2. dp[i-1] < num <= dp[i], 只更新相应的dp[i]
**/
int maxL = 0;
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
for(int num : nums) {
// 二分法查找, 也可以调用库函数如binary_search
int lo = 0, hi = maxL;
while(lo < hi) {
int mid = lo+(hi-lo)/2;
if(dp[mid] < num)
lo = mid+1;
else
hi = mid;
}
dp[lo] = num;
if(lo == maxL)
maxL++;
}
return maxL;
}
}
总结
总结完了递归,但我总感觉还是没有信心,还需要多敲,特别是回溯部分,希望继续努力吧。



![[SpringCloud] SpringCloud配置中心的核心原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d3cb3e27a4b64d7d8f7968362288c45d.png)