1.什么是跨域
出于浏览器的同源策略限制。同源策略(Sameoriginpolicy)是一种约定,它是浏览器最核心也最基本的安全功能,如果缺少了同源策略,则浏览器的正常功能可能都会受到影响。可以说Web是构建在同源策略基础之上的,浏览器只是针对同源策略的一种实现。同源策略会阻止一个域的。javascript脚本和另外一个域的内容进行交互。所谓同源(即指在同一个域)就是两个页面具有相同的协议(protocol),主机(host)和端口号(port)。
协议,主机(ip),端口号,这三个有一个不同就属于跨域访问
跨域访问前端和后端不设置一些东西的话,不能访问
| 当前页面URL | 被请求页面URL | 是否跨域 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|---|
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.test.com/index.html | 否 | 同源(协议、域名、端口) |
| http://www.test.com/ | https://www.test.com/index.html | 跨域 | 协议不同 |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.test1.com/ | 跨域 | 域名不同 |
| http://www.test.com:8080/ | http://www.test.com:8081/ | 跨域 | 端口不同 |
2. 跨域问题的解决方案
比较常用的3种
1.Jsonp 最早的解决方案,利用script标签可以跨域的原理实现。
前端解决方案,不知道好不好用,
2. nginx反向代理
思路是:利用nginx反向代理把跨域改为不跨域,支持各种请求方式
缺点:需要在nginx进行额外配置,语义不清晰
3.CORS【重要】
-
规范化的跨域请求解决方案,安全可靠。
优势:
-
在服务端进行控制是否允许跨域,可自定义规则
- 支持各种请求方式
-
缺点:
会产生额外请求
cors是一种机制,这种机制通过在http头部添加字段,
通常情况下,web应用A告诉浏览器,自己有权限访问应用B
CORS的标准定义是:通过设置http头部字段,让客户端有资格跨域访问资源。通过服务器的验证和授权之后,浏览器有责任支持这些http头部字段并且确保能够正确的施加限制。
JSON与CORS的比较
1.JSONP 只能实现 GET 请求,而 CORS 支持所有类型的 HTTP 请求
2.使用 CORS ,开发者可以是使用普通的 XMLHttpRequest 发起请求和获取数据,比起 JSONP 有更好的错误处理
3.虽然绝大多数现代的浏览器都已经支持 CORS,但是 CORS 的兼容性比不上 JSONP,一些比较老的浏览器只支持 JSONP
3.SpringBoot通过CORS实现跨域
3.1 使用注解实现跨域
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
}
@RestController
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")//实行全局跨域
@Slf4j
public class HelloController {
@Reference
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping(value = "/hello",name = "测试")
public ResponseEntity hello(@RequestParam String name){
String hello = helloService.hello(name);
return ResponseEntity.ok(hello);
}
}
@RestController
public class HiController {
@Reference
private HiService hiService;
@GetMapping(value = "/hi")
public ResponseEntity hiName(@RequestParam String name){
String respHiName = hiService.hiName(name);
return ResponseEntity.ok(respHiName);
}
}
我们可以看到,后端有连个controller HiController中没有添加@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")
跨域访问试试看
前端:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/axios-0.18.0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="hello">hello</button>
<button id="hi">hi</button>
<script>
var hello = document.getElementById("hello");
var hi = document.getElementById("hi");
hello.onclick = function(){
axios.get("http://localhost:8082/hello?name=张三")
.then(resp=>{
alert(resp.data);
})
}
hi.onclick = function(){
axios.get("http://localhost:8082/hi?name=张三")
.then(resp=>{
alert(resp.data);
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html> 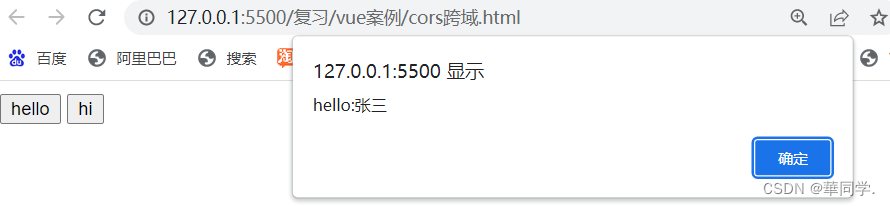
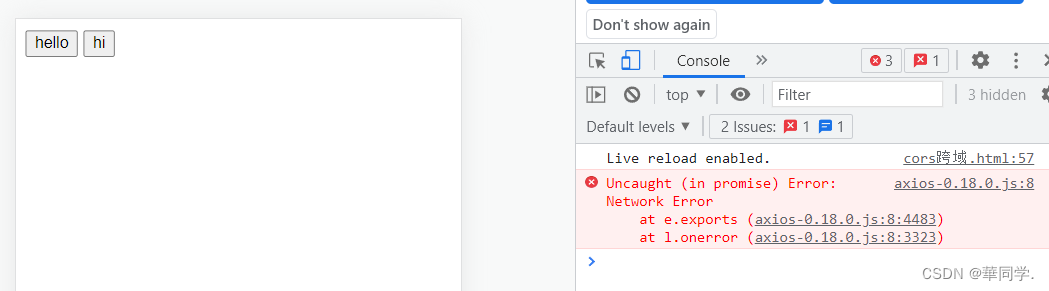
首先肯定是跨域,点击hi 的话会报错,当hiController中添加@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")
就ok了
2.通过全局配置解决跨域请求
如果说你有好多Controller 每一个都要配置,那么不值当的,所有可以用这种方法
@Configuration
public class DemoWebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**") // 匹配了所有的URL
.allowedHeaders("*") // 允许跨域请求包含任意的头信息
.allowedMethods("*") // 设置允许的方法
.allowedOrigins("*") // 设置允许跨域请求的域名
.allowCredentials(false); // 是否允许证书,默认false
}
}