文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Springboot快速入门
- 1.1 实例
- 1.2 总结:
- 1.2.1 什么是starter启动器
- 1.2.2 @SpringBootApplication注解的功效
- 二、springboot3 统一配置文件
- 1.概述
- 2、属性配置文件使用简单案例
- 3、yaml配置介绍和说明
- 4、批量配置文件的读取
- 5、多环境配置和激活
- 三、springboot 整合springmvc
- 1、导入依赖
- 2、创建启动类、编写Contorllor等
- 3、 web相关配置
- 4、 静态资源配置
- 4.1. 默认路径
- 4.2 覆盖路径
- 5、拦截器配置
- 四、springboot配置druid连接池
- 1.创建项目
- 2、添加依赖
- 3、编写启动类
- 4、创建实体类
- 5、编写Controller
- 6、编写配置类
- 五、springboot整合mybatis
- 1、添加依赖
- 2、配置文件
- 3、实体类准备
- 4、mapper接口
- 5、mapper接口实现(xml)
- 6、contorller
- 7.启动类和接口扫描
- 五、springboot 项目打包和运行
- 5.1 添加打包插件
- 5.2 执行打包
- 5.3 命令启动和参数说明
前言
通过之前springmvc,mhbatis等的配置文件,不管是xml方式,配置类方式还是其他的我们都会发现配置很复杂。所以就出现了springboot,springboot方式会简化我们的配置,但根本还是使用的ssm框架。
一、Springboot快速入门
1.1 实例
1、首先创建一个空项目
注意:这里创建的是空工程,而不是一个maven项目,因为任何一个项目都有其父工程,我们需要使用springboot作为父工程。
2、创建一个maven项目,添加进springboot父工程以及对应的气功依赖
在maven项目的pom.xml里
添加parent和dependency
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
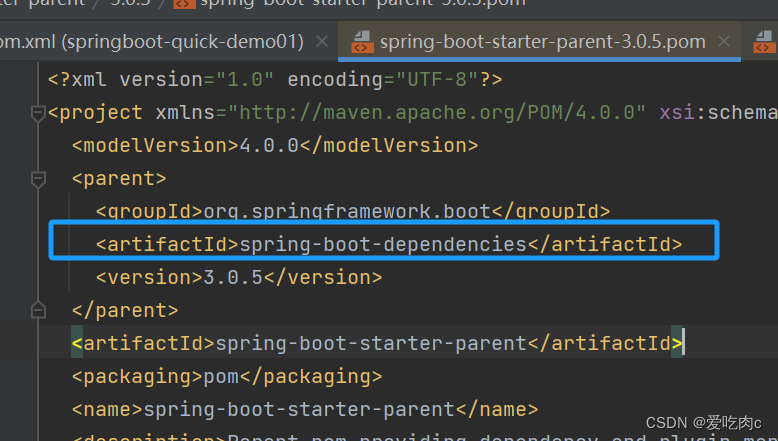
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.cky</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-quick-demo01</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
注意
这里依赖的spring-boot-starter-web没有写版本号,是因为我的父工程的父工程中有版本依赖,防止依赖冲突。
3 、启动类
package com.cky;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(Main.class,args);
}
}
4、编写一个controllor
package com.cky.Controllor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("hello")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("spring")
public String hello(){
return "hello springboot3";
}
}
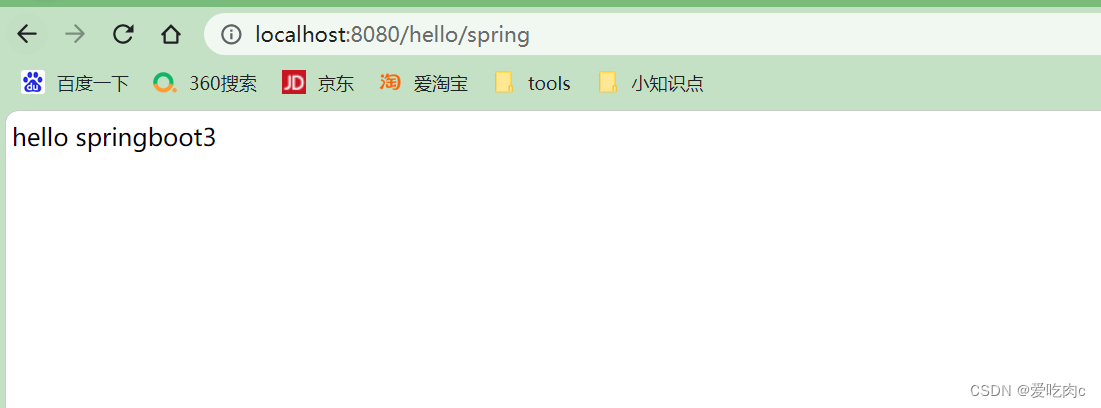
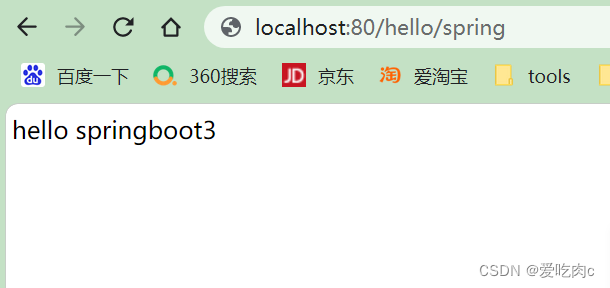
5、测试:
1.2 总结:
1.2.1 什么是starter启动器
Spring Boot提供了一种叫做Starter的概念,它是一组预定义的依赖项集合,旨在简化Spring应用程序的配置和构建过程。Starter包含了一组相关的依赖项,以便在启动应用程序时自动引入所需的库、配置和功能。
使用starter启动器可以帮助我们导入相对应的依赖以及配置文件等信息,大大简化了我们的操作
Spring Boot提供了许多预定义的Starter,例如spring-boot-starter-web用于构建Web应用程序,spring-boot-starter-data-jpa用于使用JPA进行数据库访问,spring-boot-starter-security用于安全认证和授权等等。
使用Starter非常简单,只需要在项目的构建文件(例如Maven的pom.xml)中添加所需的Starter依赖,Spring Boot会自动处理依赖管理和配置。
通过使用Starter,开发人员可以方便地引入和配置应用程序所需的功能,避免了手动添加大量的依赖项和编写冗长的配置文件的繁琐过程。同时,Starter也提供了一致的依赖项版本管理,确保依赖项之间的兼容性和稳定性。
spring boot提供的全部启动器地址:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using.html#using.build-systems.starters
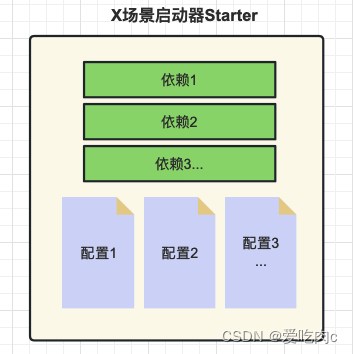
在案例中我们导入了web启动器,相对应的就可以导入对应的tomcat,json,springmvc等依赖,同时也会帮我们提供相应的配置类,比如springmvc需要配置类,添加handeler等,但是导入web启动器自带配置类,在之后我们添加完启动类之后就会自动将这些配置类添加进去。
1.2.2 @SpringBootApplication注解的功效
在上边案例中,我们有一个main方法,用来启动该工程。
@SpringBootApplication添加到启动类上,是一个组合注解,他的功效有具体的子注解实现!
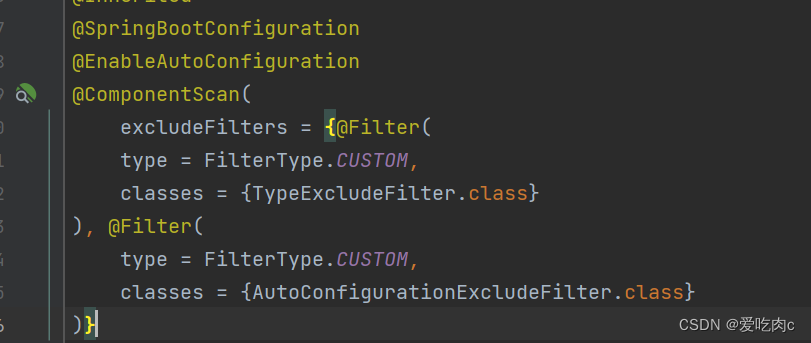
①首先是@SpringBootConfiguration 这表明它自己是一个配置类。
②@EnableAutoConfiguration 这个表明自动添加上其他配置类,比如上边我们提到的springmvc配置类。
③@ComponentScan表明可以自动扫描包,它默认会扫描@SpringBootApplication注解所在类的包及其子包中的组件,并将它们纳入Spring Boot应用程序的上下文中,使它们可被自动注入和使用。
@SpringBootApplication注解是Spring Boot框架中的核心注解,它的主要作用是简化和加速Spring Boot应用程序的配置和启动过程。
具体而言,@SpringBootApplication注解起到以下几个主要作用:
- 自动配置:@SpringBootApplication注解包含了@EnableAutoConfiguration注解,用于启用Spring Boot的自动配置机制。自动配置会根据应用程序的依赖项和类路径,自动配置各种常见的Spring配置和功能,减少开发者的手动配置工作。它通过智能地分析类路径、加载配置和条件判断,为应用程序提供适当的默认配置。
- 组件扫描:@SpringBootApplication注解包含了@ComponentScan注解,用于自动扫描并加载应用程序中的组件,例如控制器(Controllers)、服务(Services)、存储库(Repositories)等。它默认会扫描@SpringBootApplication注解所在类的包及其子包中的组件,并将它们纳入Spring Boot应用程序的上下文中,使它们可被自动注入和使用。
- 声明配置类:@SpringBootApplication注解本身就是一个组合注解,它包含了@Configuration注解,将被标注的类声明为配置类。配置类可以包含Spring框架相关的配置、Bean定义,以及其他的自定义配置。通过@SpringBootApplication注解,开发者可以将配置类与启动类合并在一起,使得配置和启动可以同时发生。
总的来说,@SpringBootApplication注解的主要作用是简化Spring Boot应用程序的配置和启动过程。它自动配置应用程序、扫描并加载组件,并将配置和启动类合二为一,简化了开发者的工作量,提高了开发效率。
二、springboot3 统一配置文件
1.概述
SpringBoot工程下,进行统一的配置管理,你想设置的任何参数(端口号、项目根路径、数据库连接信息等等)都集中到一个固定位置和命名的配置文件(application.properties或application.yml)中!
配置文件应该放置在Spring Boot工程的src/main/resources目录下。这是因为src/main/resources目录是Spring Boot默认的类路径(classpath),配置文件会被自动加载并可供应用程序访问。
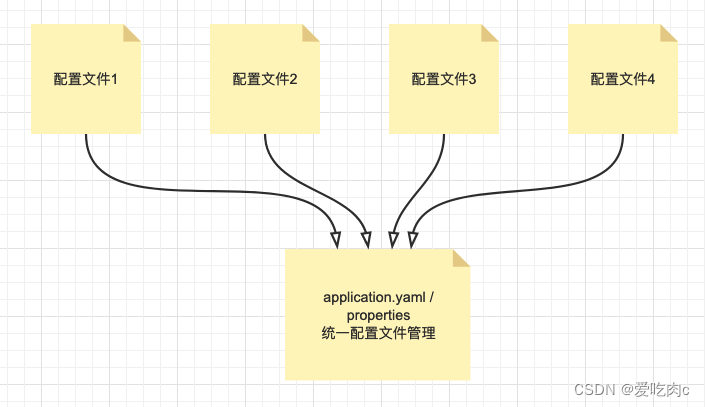
我们可以看到在springboot parent 父工程中 会自动将我们resoueces文件夹下的该配置类 添加进去’
这也是为什么我们的配置文件和配置文件的路径要放在一个固定的地方。
 功能配置参数说明:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/application-properties.html#appendix.application-properties
功能配置参数说明:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/application-properties.html#appendix.application-properties
细节总结:
- 集中式管理配置。统一在一个文件完成程序功能参数设置和自定义参数声明 。
- 位置:resources文件夹下,必须命名application 后缀 .properties / .yaml / .yml 。
- 如果同时存在application.properties | application.yml(.yaml) , properties的优先级更高。
- 配置基本都有默认值。
- 我们也可以自定义key 通过@value(${})在文件中读取。我们不需要资源加载,springbootparent会自动查看我们是否有配置类,然后自动加载进去。
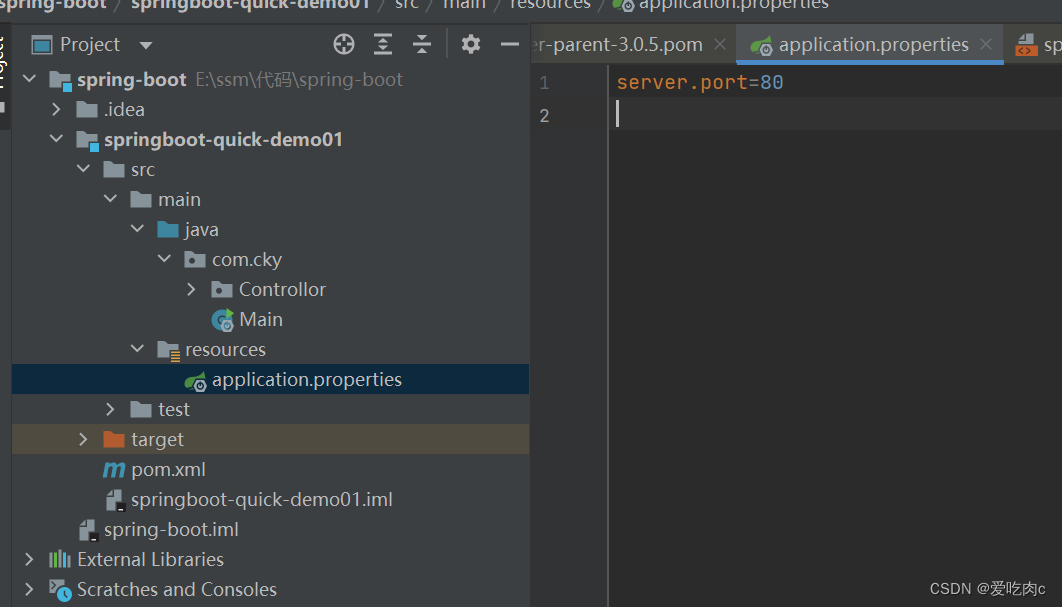
2、属性配置文件使用简单案例
我们在项目下添加上application.properties配置文件 将端口号改为80,然后测试
server.port 是springboot 提供的固定的key 我们可以通过该key 配置端口号
该配置文件会自动添加,不用我们手动配置加载。
3、yaml配置介绍和说明
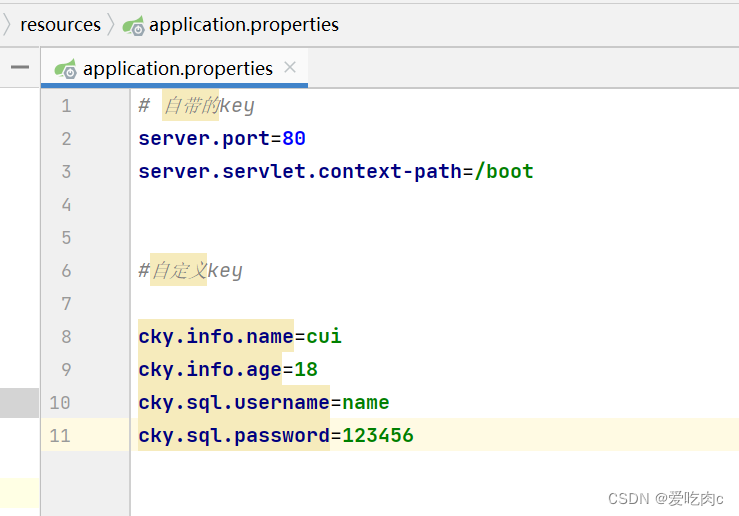
同一个配置:我们可以观察一下yaml/yml 与properties 的区别:
application.properties
application.yaml
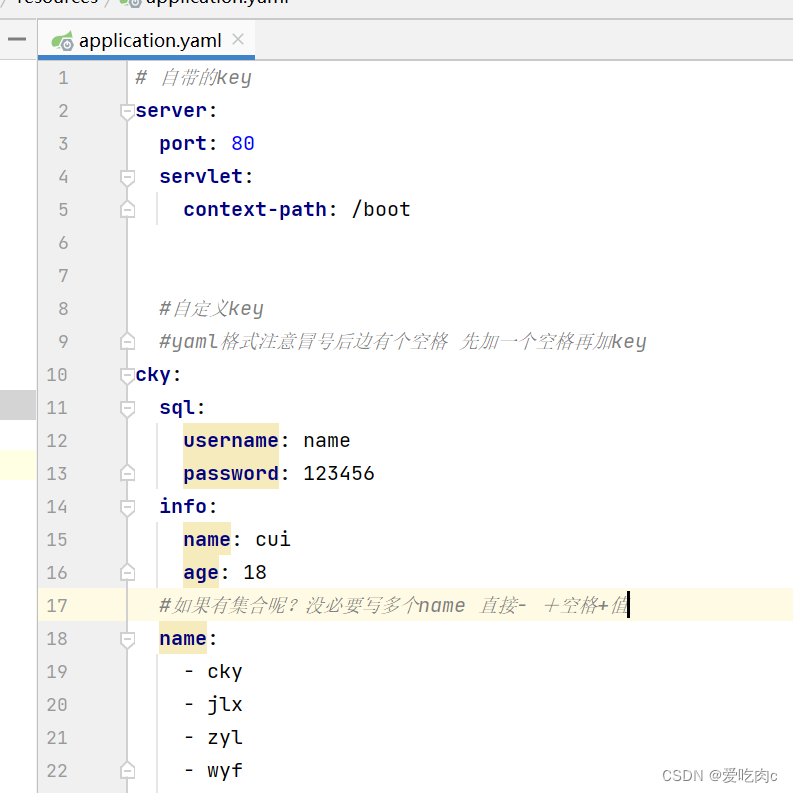
从上边两张图我们可以比较出来 yaml格式更具有层次感,没必要写重复的key,springboot配置属性命名时本来就是按照层次结构来的,如果只是添加简单的配置类,我们可以使用properties配置,如果是复杂的配置类,我们就可以使用yaml配置。
yaml语法说明
- 数据结构用树形结构呈现,通过缩进来表示层级,
- 连续的项目(集合)通过减号 ” - ” 来表示
- 键值结构里面的key/value对用冒号 ” : ” 来分隔。
- YAML配置文件的扩展名是yaml 或 yml
4、批量配置文件的读取
对于配置文件的读取,’
我们可以使用@Value(“$()”)注解的方式
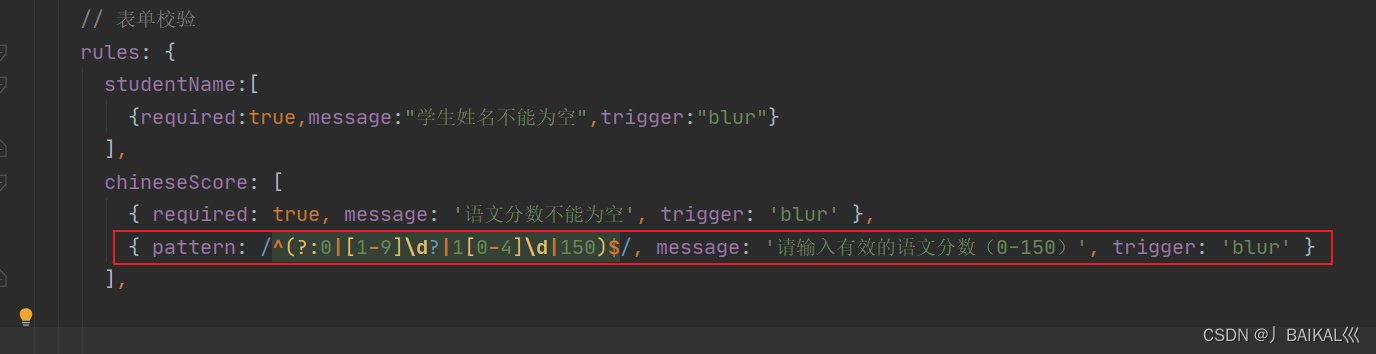
但是该注解有一个问题就是①不能读取集合类,只能读取单个值②每次都要写清楚属性对应的key值比较麻烦
批量配置读取:@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “xxx”) 通用的前缀
实体类
属性名=最后一个key的值
优势1:方便 不用一个一个读取
优势2:可以给集合类型赋值。
这时候我们就可以采取批量配置文件的方式来进行读取。

我们的applicacation.yaml
# 自带的key
server:
port: 80
servlet:
context-path: /boot
#自定义key
#yaml格式注意冒号后边有个空格 先加一个空格再加key
#如果有集合呢?没必要写多个name 直接- +空格+值
cky:
sql:
username: name
password: 123456
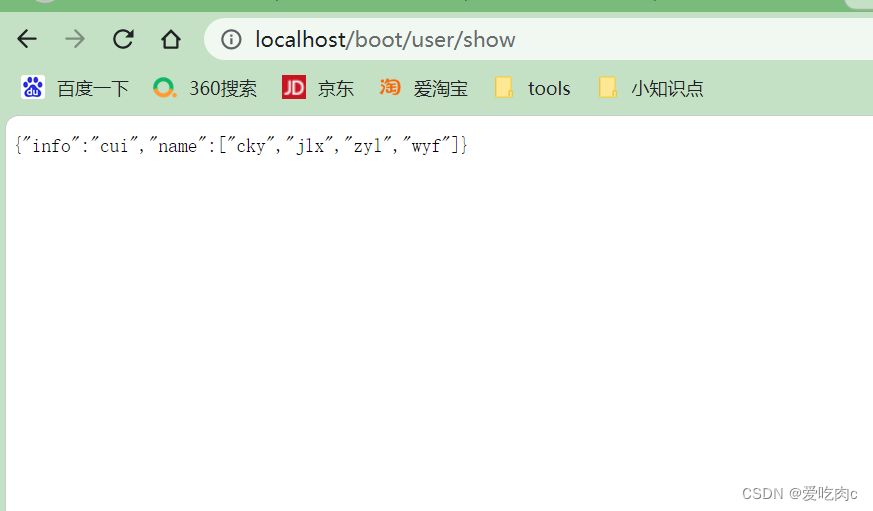
info: cui
name:
- cky
- jlx
- zyl
- wyf
我们创建一个User类
package com.cky.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Component
@Data //自动添加get set方法
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cky") //这是我们配置文件的key的前缀
有了前缀,我们只要保证我们的变量名与属性值的最后名字相同 就可以自动读取我们配置文件里边的值了
//一定要有set和get方法
public class User {
private String info;
private List<String> name;
}
Controller类
package com.cky.Controllor;
import com.cky.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired //自动注入
private User user;
@GetMapping("show")
public User show(){
return user;
}
}
结果:
5、多环境配置和激活
在实际项目中,往往会有测试开发维护等过程,比如测试和开发用的数据库可能就不一样,但是我们又不能在一个配置文件中写不同的数据库属性,这时候就需要多环境配置了。
虽然在springboot中 只会整合application.yaml/properties 这一个配置文件,但是我们可以通过配置规则,在该配置文件中激活其他配置文件,但是对于其他配置文件也是有要求的,命名必须符合 application-{key}
之后我们可以在主配置文件中去激活其他配置文件。
在这里我添加了一个application-dev.yaml 配置文件
cky:
name:
- dev1
- dev2
又添加了一个 application-text.yaml 配置文件
cky:
info: test
同时主配置文件application.yaml中激活这两个配置文件
cky:
sql:
username: name
password: 123456
info: cui
name:
- cky
- jlx
- zyl
- wyf
spring:
profiles:
active: dev,text
测试结果:
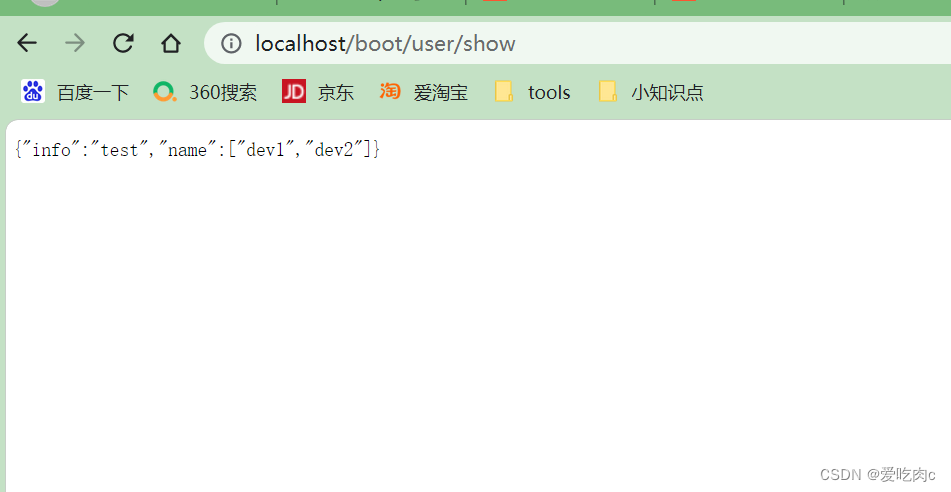
我们注意到虽然主配置文件(application.yaml)中也有cky-info 值和cky-name值,但是输出的并不是主文件属性值,首先会从激活的配置文件中找。
如果设置了spring.profiles.active,并且和application有重叠属性,以active设置优先。
如果设置了spring.profiles.active,和application无重叠属性,application设置依然生效
三、springboot 整合springmvc
1、导入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!-- 变为一个springboot3 程序-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.atguigu</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-starter-springmvc-03</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- web开发的场景启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2、创建启动类、编写Contorllor等
3、 web相关配置
位置 :application.yaml
比如:修改端口号,项目根路径等
# web相关的配置
# https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/application-properties.html#appendix.application-properties.server
server:
# 端口号设置
port: 80
# 项目根路径
servlet:
context-path: /boot
当涉及Spring Boot的Web应用程序配置时,以下是五个重要的配置参数:
server.port: 指定应用程序的HTTP服务器端口号。默认情况下,Spring Boot使用8080作为默认端口。您可以通过在配置文件中设置server.port来更改端口号。server.servlet.context-path: 设置应用程序的上下文路径。这是应用程序在URL中的基本路径。默认情况下,上下文路径为空。您可以通过在配置文件中设置server.servlet.context-path属性来指定自定义的上下文路径。spring.mvc.view.prefix和spring.mvc.view.suffix: 这两个属性用于配置视图解析器的前缀和后缀。视图解析器用于解析控制器返回的视图名称,并将其映射到实际的视图页面。spring.mvc.view.prefix定义视图的前缀,spring.mvc.view.suffix定义视图的后缀。spring.resources.static-locations: 配置静态资源的位置。静态资源可以是CSS、JavaScript、图像等。默认情况下,Spring Boot会将静态资源放在classpath:/static目录下。您可以通过在配置文件中设置spring.resources.static-locations属性来自定义静态资源的位置。spring.http.encoding.charset和spring.http.encoding.enabled: 这两个属性用于配置HTTP请求和响应的字符编码。spring.http.encoding.charset定义字符编码的名称(例如UTF-8),spring.http.encoding.enabled用于启用或禁用字符编码的自动配置。
这些是在Spring Boot的配置文件中与Web应用程序相关的一些重要配置参数。根据您的需求,您可以在配置文件中设置这些参数来定制和配置您的Web应用程序
4、 静态资源配置
在WEB开发中我们需要引入一些静态资源 , 例如 : HTML , CSS , JS , 图片等 , 如果是普通的项目静态资源可以放在项目的webapp目录下。现在使用Spring Boot做开发 , 项目中没有webapp目录 , 我们的项目是一个jar工程,那么就没有webapp,我们的静态资源该放哪里呢?
4.1. 默认路径
在springboot中就定义了静态资源的默认查找路径:
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web;
//..................
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
private boolean addMappings;
private boolean customized;
private final Chain chain;
private final Cache cache;
public Resources() {
this.staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
this.addMappings = true;
this.customized = false;
this.chain = new Chain();
this.cache = new Cache();
}
//...........
默认的静态资源路径为:
· classpath:/META-INF/resources/
· classpath:/resources/
· classpath:/static/
· classpath:/public/
我们只要静态资源放在这些目录中任何一个,SpringMVC都会帮我们处理。 我们习惯会把静态资源放在classpath:/static/ 目录下。在resources目录下创建index.html文件
这里 classpath 指的是 resourses资源 **· classpath:/resources/**指的是在resources资源下在添加一个resources文件夹。
举例
在这里:我在classpath 下创建了一个static文件夹,之后又创建了一个index.html
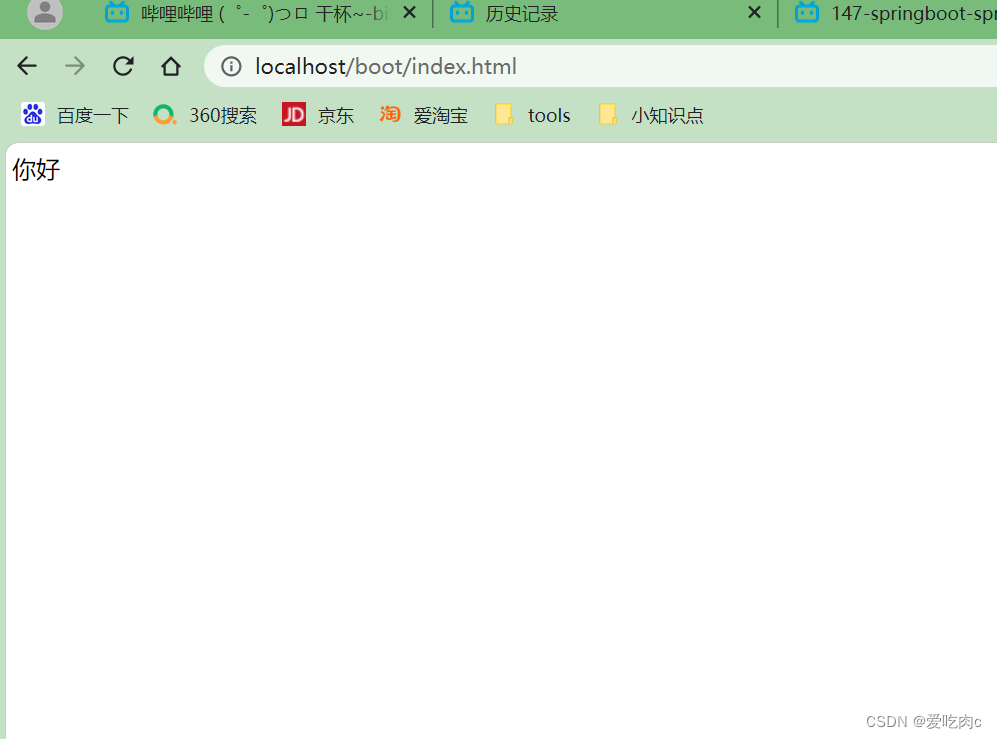
我们启动项目,在浏览器中搜索http://localhost/boot/index.html
便可看到: 静态资源访问成功
4.2 覆盖路径
除了默认路径,我们可以自定义路径,然后在配置文件中覆盖原始默认路径
在这里插入代码片# web相关的配置
# https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/application-properties.html#appendix.application-properties.server
server:
# 端口号设置
port: 80
# 项目根路径
servlet:
context-path: /boot
spring:
web:
resources:
# 配置静态资源地址,如果设置,会覆盖默认值
static-locations: classpath:/webapp
再次浏览http://localhost/boot/index.html
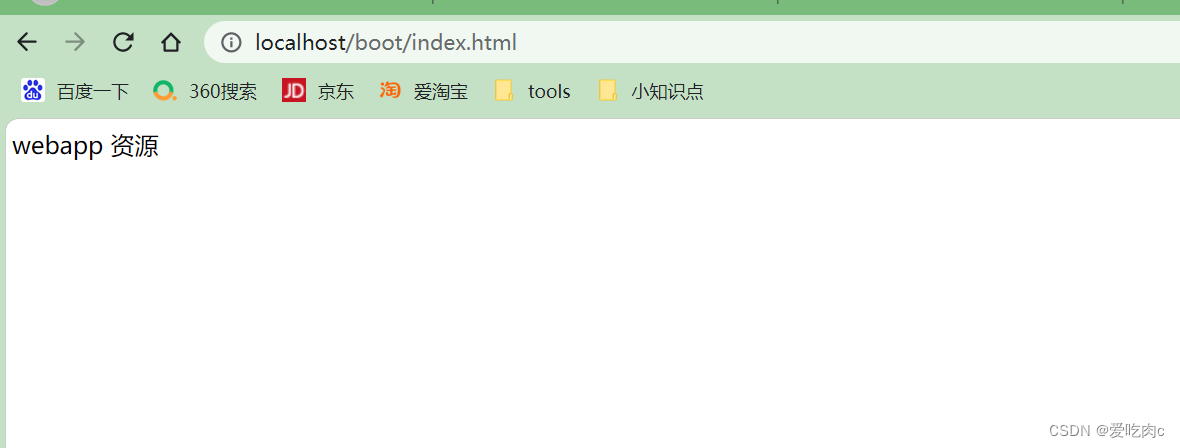
可以看到 会将原始默认路径下的index.html覆盖
5、拦截器配置
拦截器配置和普通的springmvc一样
首先我们写一个类定义我们的拦截器
package com.cky.interpetor;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Component
public class Myinterpetor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
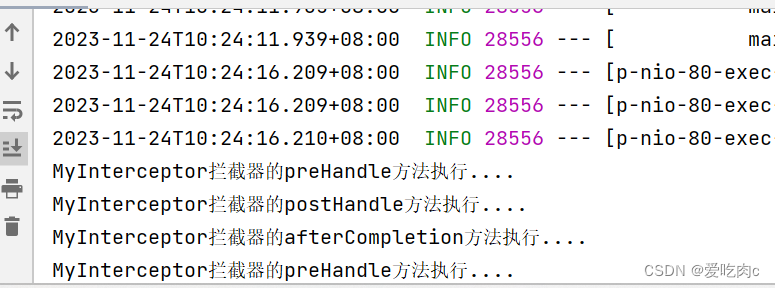
System.out.println("MyInterceptor拦截器的preHandle方法执行....");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor拦截器的postHandle方法执行....");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor拦截器的afterCompletion方法执行....");
}
}
接着写配置类
正常使用配置类,只要保证,配置类要在启动类的同包或者子包方可生效!
springboot 会自动加载属于启动类的同包或子包位置下的配置类
package com.cky.config;
import com.cky.interpetor.Myinterpetor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class Myconfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private Myinterpetor myinterpetor;
/**
* /** 拦截当前目录及子目录下的所有路径 /user/** /user/findAll /user/order/findAll
* /* 拦截当前目录下的以及子路径 /user/* /user/findAll
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(myinterpetor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}
四、springboot配置druid连接池
1.创建项目
2、添加依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cky</groupId>
<artifactId>demo02</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库相关配置启动器 jdbctemplate 事务相关-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- druid启动器的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-3-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.20</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 驱动类-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3、编写启动类
package com.cky;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(Main.class,args);
}
}
4、创建实体类
记得写@Data 即配置get set方法 不然会出错
package com.cky.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
}
5、编写Controller
package com.cky.Controller;
import com.cky.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired(required = false)
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
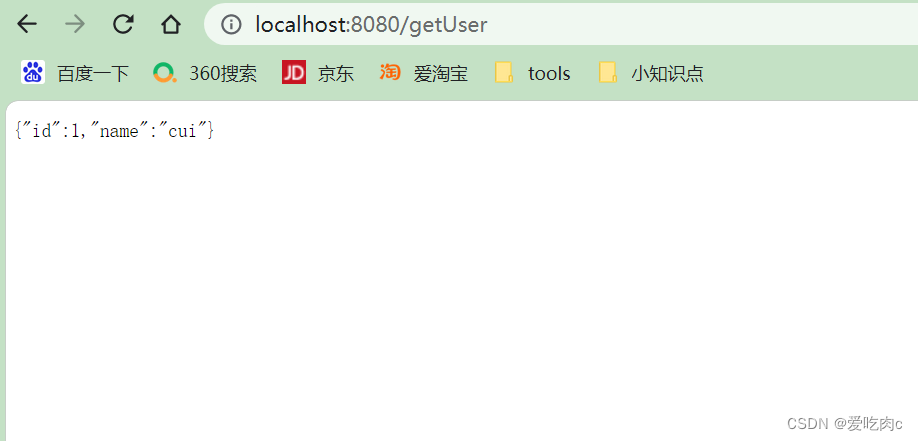
@GetMapping("/getUser")
@ResponseBody
public User show(){
String sql = "select * from test where id = ? ; ";
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 1);
return user;
}}
6、编写配置类
spring:
datasource:
# 连接池类型
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# Druid的其他属性配置 springboot3整合情况下,数据库连接信息必须在Druid属性下!
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://47.115.213.172:3306/school ## 自己的数据库
username: root
password: xxx //自己的密码
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 初始化时建立物理连接的个数
initial-size: 5
# 连接池的最小空闲数量
min-idle: 5
# 连接池最大连接数量
max-active: 20
# 获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒
max-wait: 60000
# 申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
test-while-idle: true
# 既作为检测的间隔时间又作为testWhileIdel执行的依据
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
# 销毁线程时检测当前连接的最后活动时间和当前时间差大于该值时,关闭当前连接(配置连接在池中的最小生存时间)
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 30000
# 用来检测数据库连接是否有效的sql 必须是一个查询语句(oracle中为 select 1 from dual)
validation-query: select 1
# 申请连接时会执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,开启会降低性能,默认为true
test-on-borrow: false
# 归还连接时会执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,开启会降低性能,默认为true
test-on-return: false
# 是否缓存preparedStatement, 也就是PSCache,PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle,在mysql下建议关闭。
pool-prepared-statements: false
# 要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: -1
# 合并多个DruidDataSource的监控数据
use-global-data-source-stat: true
logging:
level:
root: debug
五、springboot整合mybatis
springboot整合mybatis没必要让接口和接口实现类的xml文件放在同级目录下 因为接口扫描是在启动类上 而接口实现类的xml文件扫描是在配置文件application.yaml中
1、添加依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库相关配置启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- druid启动器的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-3-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.18</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 驱动类-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、配置文件
**server:
port: 80
servlet:
context-path: /
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql:///day01
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
configuration: # setting配置
auto-mapping-behavior: full
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.slf4j.Slf4jImpl
type-aliases-package: com.atguigu.pojo # 配置别名
mapper-locations: classpath:/mapper/*.xml # mapperxml位置**
3、实体类准备
package com.atguigu.pojo;
public class User {
private String account ;
private String password ;
private Integer id ;
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"account='" + account + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
4、mapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> queryAll();
}
5、mapper接口实现(xml)
位置:resources/mapper/UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace = 接口的全限定符 -->
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="queryAll" resultType="user">
select * from users
</select>
</mapper>
6、contorller
package com.cky.Controller;
import com.cky.mappers.Usermapper;
import com.cky.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired(required = false)
private Usermapper usermapper;
@GetMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> show(){
return usermapper.queryAll();
}}
7.启动类和接口扫描
@MapperScan("com.atguigu.mapper") //mapper接口扫描配置
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}
五、springboot 项目打包和运行
5.1 添加打包插件
在Spring Boot项目中添加
spring-boot-maven-plugin插件是为了支持将项目打包成可执行的可运行jar包。如果不添加spring-boot-maven-plugin插件配置,使用常规的java -jar命令来运行打包后的Spring Boot项目是无法找到应用程序的入口点,因此导致无法运行。
<!-- SpringBoot应用打包插件-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
5.2 执行打包
在idea点击package进行打包
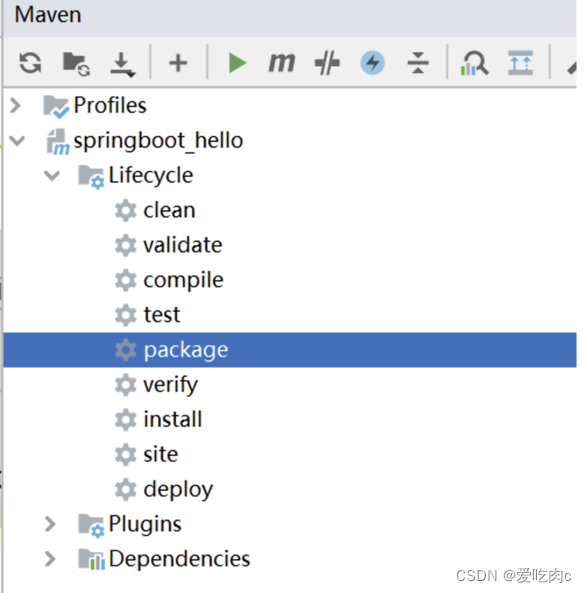
可以在编译的target文件中查看jar包
5.3 命令启动和参数说明
java -jar命令用于在Java环境中执行可执行的JAR文件。下面是关于java -jar命令的说明:
命令格式:java -jar [选项] [参数] <jar文件名>
-D<name>=<value>:设置系统属性,可以通过System.getProperty()方法在应用程序中获取该属性值。例如:java -jar -Dserver.port=8080 myapp.jar。-X:设置JVM参数,例如内存大小、垃圾回收策略等。常用的选项包括:-Xmx<size>:设置JVM的最大堆内存大小,例如-Xmx512m表示设置最大堆内存为512MB。-Xms<size>:设置JVM的初始堆内存大小,例如-Xms256m表示设置初始堆内存为256MB。
-Dspring.profiles.active=<profile>:指定Spring Boot的激活配置文件,可以通过application-<profile>.properties或application-<profile>.yml文件来加载相应的配置。例如:java -jar -Dspring.profiles.active=dev myapp.jar。
启动和测试:
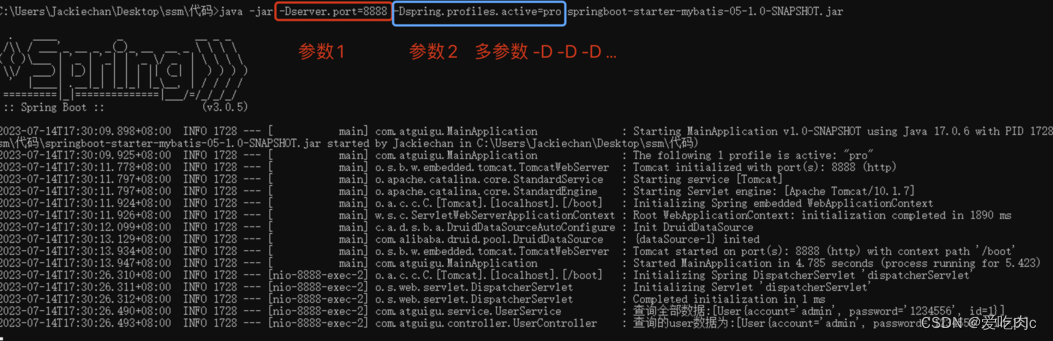
注意: -D 参数必须要在jar之前!否者不生效!