一. 引言
一. 引言
在 JavaScript 编程中,我们经常遇到类数组对象,它们拥有类似数组的结构和行为,但却不具备真正的数组方法和属性。常见的类数组对象包括 DOM 集合、函数的 arguments 对象和字符串等。如果我们想对这些类数组对象进行操作和处理,我们需要掌握一些优雅的技巧。
处理类数组对象的见方法有循环迭代、转换为数组、使用数组方法、使用 Array.prototype 方法、使用解构赋值以及其他一些殊情况的处理。本篇文章中,我们将介绍这些方法,并给出一些实用的示例。
通过优雅地处理类数组对象,我们可以更加灵活地操作和处理数据,从而提高开发效率和代码质量。无论是处理 DOM 元素、函数参数还是字符串,了解这些优雅的技巧都能让我们更游刃有余。
接下来让我们一起来认识如何优雅地处理类数组对象,实现 JavaScript 神奇的转变!
二. 了解类数组对象
1. 什么是类数组对象
类数组对象是指在 JavaScript 中具有类似数组的特点,但并非真正的数组。它们与数组相似,可以通过索引访问元素,并且具有length属性来表示元素的个数。但与真正的数组不同,类数组对象不具备数组原型链上的方法和属性。
例如:
const obj = {
0: "apple",
1: "banana",
2: "orange",
length: 3,
};
console.log(obj.length); // 输出: 32. 常见的类数组对象
(1)arguments对象:在函数内部可用的特殊对象,存储了函数参数的类数组对象。
function sum() {
console.log(arguments);
}
sum(1, 2, 3); // Arguments(3) [1,2, 3, callee: f, Symbol(Symbol.iterator): f]
(2)NodeList对象:DOM 元素的集合,通过像document.querySelectorAll()方法获取
<ul id="list" style="width: 100px; margin: 0; float: left">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
</ul>
<script>
const paragraphs = document.querySelectorAll("li");
console.log(paragraphs.length); // 输出: 指定选择器的li元素个数
console.log(paragraphs); // 输出: 指定选择器的li元素
console.log(paragraphs[0]); // 输出: 第一个li元素
</script>
(3)HTMLCollection对象:表示一组 DOM 元素的集合,例如通过类似getElementsByClassName、getElementsByTagName等方法获取的元素集合。
<button class="btn">第一个按钮</button>
<button class="btn">第二个按钮</button>
<script>
const buttons = document.getElementsByClassName("btn");
console.log(buttons.length); // 输出: 指定类名的按钮元素个数
console.log(buttons); // 输出: 指定类名的按钮元素
console.log(buttons[0]); // 输出: 指定索引的按钮元素
</script>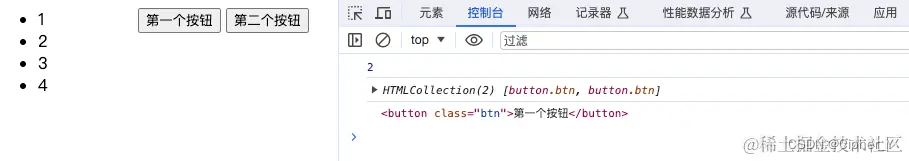
(4)TypedArray对象:表示一定长度的二进制数据缓冲区的类数组对象,例如Int8Array、Uint8Array等。
const buffer = new ArrayBuffer(8); // 创建一个8字节的缓冲区
const intArray = new Int32Array(buffer); // 使用Int32Array视图包装缓冲区
console.log(intArray);
console.log(intArray[0]); // 输出: 0
intArray[0] = 42;
console.log(intArray);
console.log(intArray[0]); // 输出: 42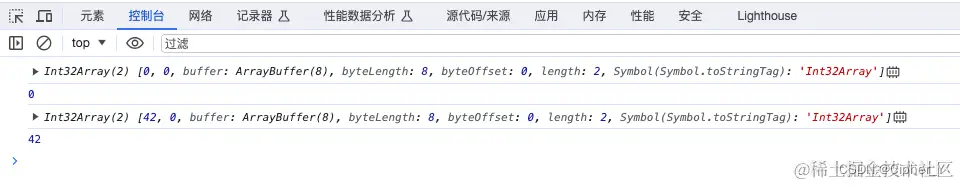
(5)FileList:表示一组文件的集合,通常来自于文件上传 input 元素
<input type="file" multiple="true" />
<script>
window.onload = function (event) {
init();
};
function init() {
const fileInput = document.querySelector('input[type="file"]');
fileInput.onchange = onFileChange;
}
function onFileChange(event) {
const files = event.target.files;
console.log(files.length); // 输出: 选择的文件数量
console.log(files); // 输出: 所有文件对象
console.log(files[0]); // 输出: 第一个文件对象
}
</script> 这些类数组对象都可以通过索引访问元素,并且具有length属性,但不具备数组原型链上的方法和属性。如果需要使用数组的方法和属性,可以将类数组对象转换为真正的数组,例如通过Array.from、Array.prototype.slice.call、Array.prototype.concat等方法。
这些类数组对象都可以通过索引访问元素,并且具有length属性,但不具备数组原型链上的方法和属性。如果需要使用数组的方法和属性,可以将类数组对象转换为真正的数组,例如通过Array.from、Array.prototype.slice.call、Array.prototype.concat等方法。
三. 类数组对象的特性
这些特性使得类数组对象在某些场景下非常有用,例如处理函数参数(arguments对象),DOM 操作中获取的元素集合(HTMLCollection对象和NodeList对象)等。
1. 索引访问和写入
类数组对象可以通过索引访问元素,读取或者写入数据。可以使用中括号([])操作符来读写类数组对象中的元素。
示例代码:
const obj = {
0: "apple",
1: "banana",
2: "orange",
length: 3,
};
console.log(obj[0]); // 输出: "apple"
console.log(obj[1]); // 输出: "banana"
obj[2] = "grape";
console.log(obj[2]); // 输出: "grape"2. 长度属性
类数组对象具有length属性,用于表示对象中元素的个数。可以通过访问length属性来获取类数组对象中元素的数量。
示例代码:
const obj = {
0: "apple",
1: "banana",
2: "orange",
length: 3,
};
console.log(obj.length); // 输出: 33. 迭代类数组对象
类数组对象可以使用迭代方法进行遍历操作,可以使用for循环对其进行迭代操作。或者通过一些方法先将其转换成数组,在对其进行迭代也是可以的!
示例代码:
const obj = {
0: "apple",
1: "banana",
2: "orange",
length: 3,
};
for (let index = 0; index < obj.length; index++) {
const element = obj[index];
console.log(element);
}使用 for 循环迭代类数组的输出入下图所示:

注意:通过迭代方法进行遍历操作时,最好先将类数组对象转换为真正的数组,以避免出现一些问题。
四. 类数组对象 VS 真正的数组
类数组对象与真正的数组在以下两个方面存在区别:
1. 原型链上的方法和属性
真正的数组具有数组对象的原型链,因此具有丰富的方法和属性,如push、pop、shift、unshift等用于操作数组的方法,以及length、concat、slice等用于处理数组的属性和方法。而类数组对象并没有这些原型方法和属性,使用类数组对象时不能直接调用数组的方法和属性。
示例代码:
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const obj = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
2: 3,
length: 3,
};
console.log(arr.push(4)); // 输出: 4
console.log(obj.push(4)); // 报错: obj.push is not a function
console.log(arr.length); // 输出: 4
console.log(obj.length); // 输出: 32. 结构差异
类数组对象与真正的数组在内部结构上存在差异。真正的数组是一段连续的内存空间,可以直接通过索引访问到每个元素,而类数组对象并非连续的内存空间,且可能具有非数字索引。类数组对象通常是基于对象实现的,使用非数字索引作为键来存储元素。因此,类数组对象的内部结构与真正的数组不同。
示例代码:
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const obj = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
2: 3,
length: 3,
};
console.log(arr[0]); // 输出: 1
console.log(obj[0]); // 输出: 1
console.log(arr[3]); // 输出: undefined
console.log(obj[3]); // 输出: undefined
console.log(arr); // 输出: [1, 2, 3]
console.log(obj); // 输出: {0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3, length: 3}总结:尽管类数组对象与真正的数组在某些方面类似,但在原型链上的方法和属性、内部结构方面存在差异。因此,在使用类数组对象时需要注意这些区别,需要根据实际需求进行相应的处理。如有需要,可以将类数组对象转换为真正的数组,以便能够使用数组的方法和属性来操作数据。
五. 处理类数组对象的常见方法
假如有一个类数组对象,如下所示:
const obj = {
0: "apple",
1: "banana",
2: "orange",
length: 3,
};下面总结处理以上这个类数组对象的几种方式:
1. 使用数组展开运算符(...)
const arr = [...obj];
console.log(arr); // 输出: ["apple", "banana", "orange"]2. 使用 Array.from()方法
const arr = Array.from(obj);
console.log(arr); // 输出: ["apple", "banana", "orange"]3. 使用 Array.prototype.slice.call()方法
const arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(obj);
console.log(arr); // 输出: ["apple", "banana", "orange"]4. 使用 Array.prototype.map.call()方法
const arr = Array.prototype.map.call(obj, (item) => item);
console.log(arr); // 输出: ["apple", "banana", "orange"]5. 使用 ES6 的 Array.from()方法与箭头函数
const arr = Array.from(obj, (item) => item);
console.log(arr); // 输出: ["apple", "banana", "orange"]以上的这些方法可以将类数组对象转换为真正的数组,并可以使用数组的方法和属性对其进行操作。根据实际需求选择适合的方式进行处理。
六. 总结
通过本篇文章,我们了解了在 JavaScript 中处理类数组对象的一些优雅的技巧。这些技巧可以帮助我们更加灵活地操作和处理数据,提高开发效率和代码质量。
首先,我们学习了几种在前端开发中常见的类数组对象。包括:arguments对象、NodeList对象、HTMLCollection对象、TypedArray对象,以及FileList等。
其次,我们了解了如何将类数组对象转换为真正的数组。可以使用 Array.from() 方法、Array.prototype 方法或者扩展运算符(...)来实现转换。这些方法可以让我们方便地使用数组的方法和属性进行处理。
总结来说,处理类数组对象对于 JavaScript 开发者来说是非常重要的,在实际开发中,我们经常遇到类数组对象,只有了解这些处理技巧,我们才能更加轻松地处理数据,编写高效、干净的代码。加油!