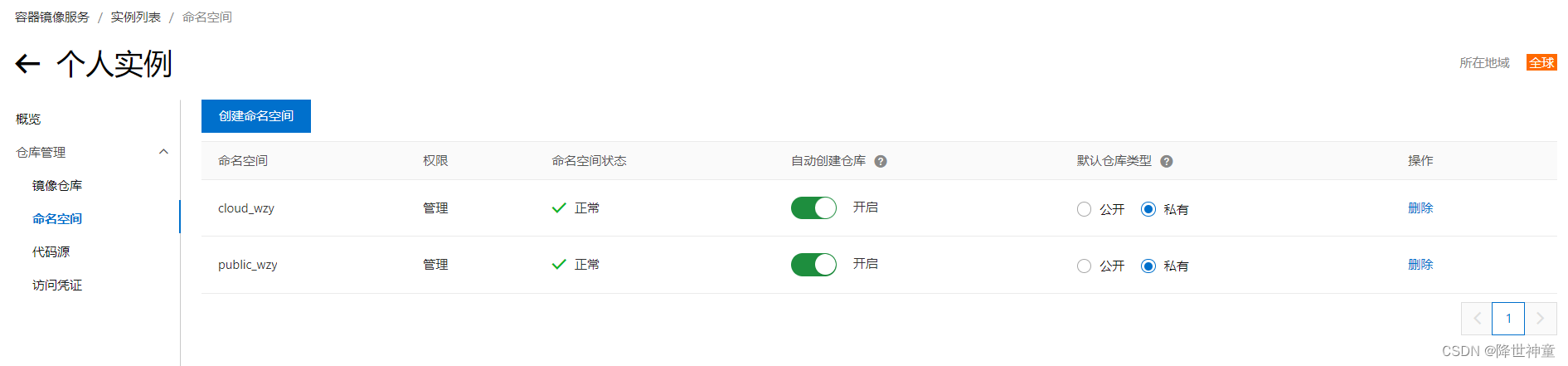
这篇文章发布于2023年10月nature。通讯作者是来自于 DOE Joint Genome Institute, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, USA.
背景介绍&目标
作者首先背景介绍了两种主流宏基因组分析方法,包括reads-based reference mapping(eg. MG-RAST)和assembled-based de novo(Integrated Microbial Genomes & Microbiomes (IMG/M) and MGnify)两种.
又提到目前无论哪种方法下游分析中对基因组的功能注释都依赖于现有的库,这种分析方法会去除掉一些未知的基因。所以一个全面的基因组比对以解释未知功能的分析是非常需要的。那这个未知功能作者援引为functional dark matters。
原文:‘
Same major limitation with respect to gene functional annotation, which relies on predicting function by homology searching against reference protein databases, such as COG, Pfam and KEGG Orthology. As a result, any genes predicted in assembled metagenomic data that do not map to reference protein families are typically ignored and dropped from subsequent comparative analysis.
To estimate the breadth of unexplored functional diversity, referred to as the functional dark matter an all-versus-all metagenomic comparison is required.’
这些reference database都是做功能注释非常常用的库。
-
COG-Database: The Clusters of Orthologous Genes (COGs) database
-
Pfam: a complete and accurate classification of protein families and domains.
-
KEGG Orthology: molecular functions represented in terms of functional orthologs.
为了揭示这个位置的dark matters(功能),总结来说这篇文章主要做了以下工作
-
They present a scalable computational approach 他们提出了一种可扩展的计算方法,用于识别和表征宏基因组中发现的功能性暗物质。
-
They identified the novel protein space (after removing all reference matched genes) and clustered them into families首先,在删除与超过 100,000 个参考基因组或 Pfam 的 IMG 数据库匹配的所有基因后,我们确定了 IMG/M 的 26,931 个宏基因组数据集中存在的新蛋白质空间。接下来,我们将剩余的序列聚集到蛋白质家族中。
-
They explored their taxonomic and biome distributions 他们探索了这些未知cluster的分类学和生物群落分布
-
They predicted their three-dimensional (3D) structures他们预测了它们的三维结构
数据来源和数据处理Data source and preprocess of the data
Environmental dataset 来源于:数据来源:来自IMG/M平台托管的所有公共参考基因组和组装的宏基因组和元转录组的所有蛋白质序列(超过35个氨基酸残基)
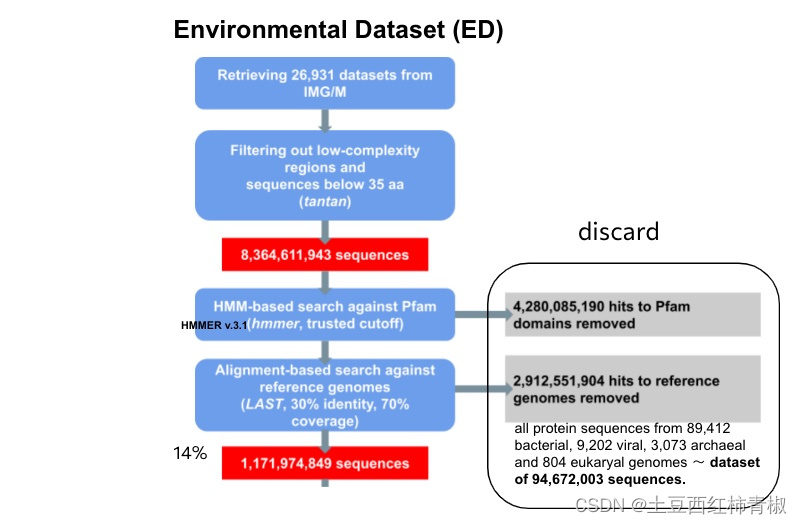
这个来自于supplementary的图片说明整个流程更加的清晰。可以看到首先去除一些低复杂度的序列,拿到>35bp的序列,作者用hmm比对pfam数据库去除map上的hits,后面又使用LAST比对工具再次过滤reference genomes。最后仅仅得到最初序列的14%,即1,171,974,849序列,这些序列被称为novel protein sequences。
tips:
文章中去除低复杂度序列应该是处于低复杂度区域通常包含一些高度重复的序列,这些重复序列可能对分析和解释基因组和转录组数据造成干扰,因此去除它们有助于减少噪音和提高数据的可信度。
文章中提到提取reference genomes方法:
Reference Genomes: In total, we extracted all protein sequences from 89,412 bacterial, 9,202 viral, 3,073 archaeal and 804 eukaryal genomes, resulting in a final dataset of 94,672,003 sequences. The reference genomes included in this study consisted solely of isolate genomes, not MAGs or single-amplified genomes.

那么接下来拿到这些novel protein sequences 之后作者又用LAST对蛋白质序列之间做相似性比较(an all-versus-all similarity matrix was built for each of the two gene catalogues by calculating all significant pairwise sequence similarities.),生成一个相似性矩阵,然后根据相似性矩阵用HipMCL进行聚类得到最后的蛋白质clusters。作者同样对reference genomes也进行了类似的操作,以便后续比较。整个过程结合图1a和supp figure更加清楚
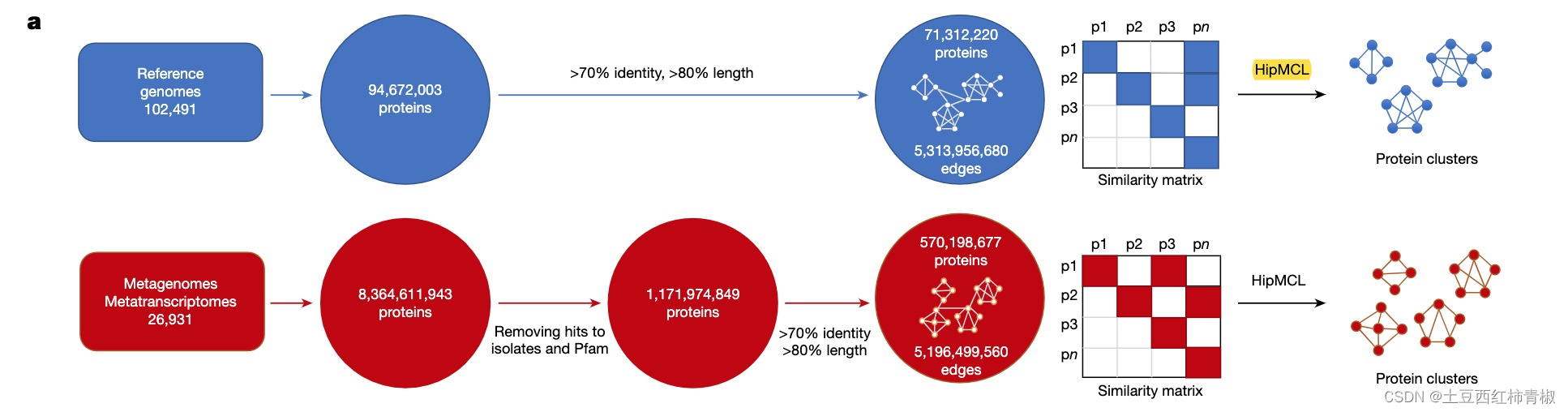

原文细节描述(具体node和edges数目)如下
We next clustered the 1.1 billion ED proteins using a graph-based approach. For comparative purposes, we followed the same approach for the 94 million proteins from reference genomes.
First, an all-versus-all similarity matrix was built for each of the two gene catalogues (that is, proteins from reference genomes and those from the ED) by calculating all significant pairwise sequence similarities.
The all-versus-all pairwise alignments were calculated using LAST (70% sequence identity, 80% alignment coverage). The reference genome graph consisted of 71,312,220 nodes (proteins) and 5,313,956,680 edges (pairwise similarities). The graph for the ED proteins consisted of 570,198,677 nodes and 5,196,499,560 edges.
下面作者进一步移走了一些只有少数蛋白序列的cluster以及和pfam有weak hits的cluster,只留下包含有至少100个memeber的cluster,我认为这部是为了保证这个novel。这个部分就是novel protein families,也就是全文通篇在提的NMPFs(novel metagenome protein families)

结果1: ED has more clusters than reference genomes
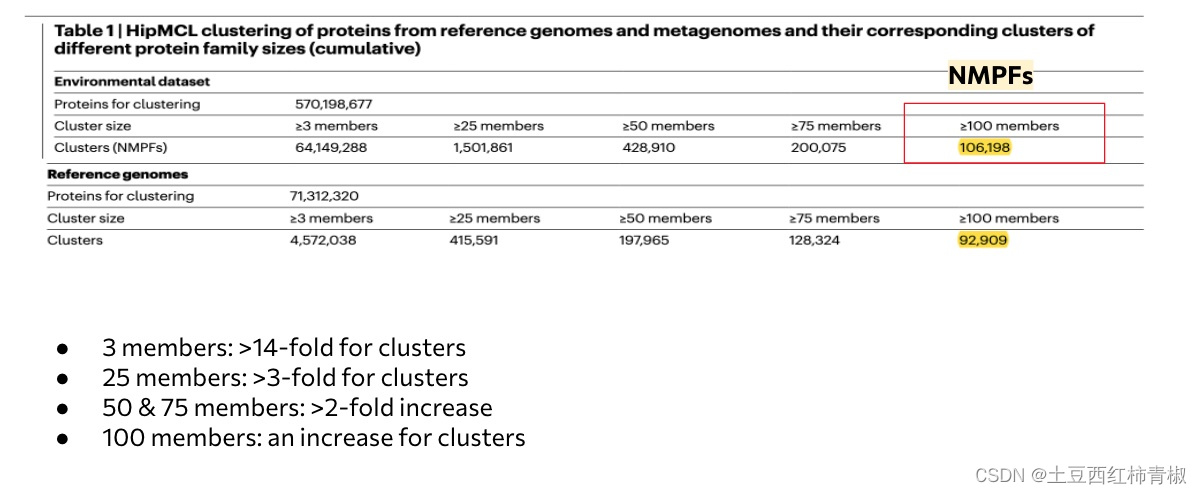
文章这里的图是说明与reference genome的cluster相比,NMPFs包含的蛋白序列更加的多,不仅仅是有3个members的cluster多,从3-100都多。
In total, we identified 106,198 families with at least 100 members that will be referred to as novel metagenome protein families (NMPFs) (Table 1 (right column)).
For comparison, we identified 92,909 protein clusters in the corresponding set of protein clusters with at least 100 members from reference genomes.
We observed an increase in the ED protein clusters by greater than 14-fold for clusters with at least 3 members, greater than 3-fold for clusters with at least 25 members, around a 2-fold increase for clusters with at least 50 and 75 members as well as an increase for clusters with at least 100 members.
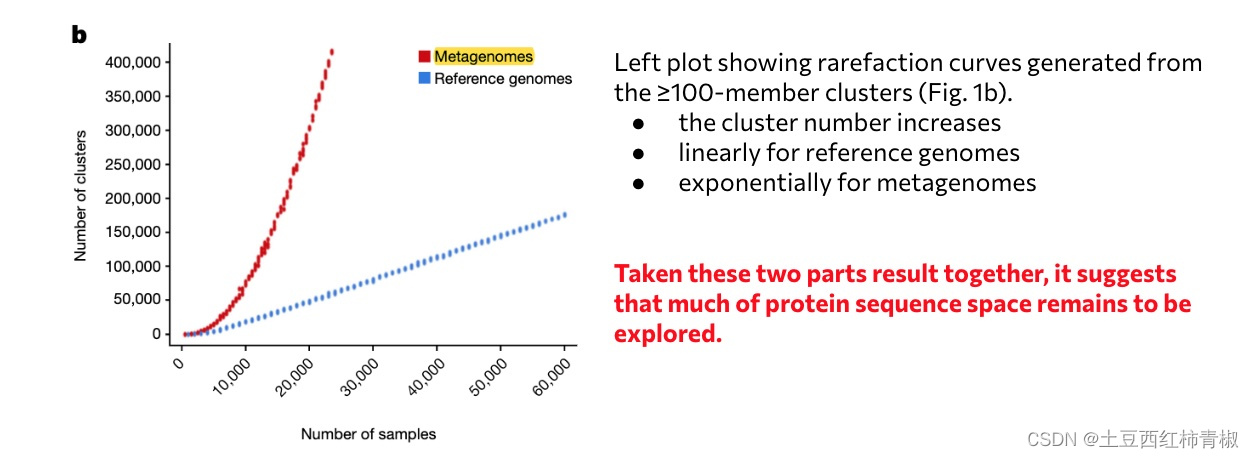
下面作者又做了一个稀释曲线,可以发现ED组相比较reference genomes的斜率更大,说明随着sample数目的增加,还可能有更多的cluster被发现。这进一步说明这些unknown protein sequence是未知的,非常值得探索的,是比reference genomes更多未知的更丰富的功能序列。
结果2:biome distribution(未完待续。会明天补全。)
reference
Unraveling the functional dark matter through global metagenomics | Nature