gin官方文档
https://gin-gonic.com/docs/quickstart/
1. 安装
go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin
简单入门
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func pong(c *gin.Context) {
//c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
// "message": "pong",
//})
//第二种
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]string{
"message": "pong",
})
}
func main() {
//实例化一个gin的server对象
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/ping", pong)
r.Run(":8084") // listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 (for windows "localhost:8080")
}
//restful 的开发中
router.GET("/someGet", getting)
router.POST("/somePost", posting)
router.PUT("/somePut", putting)
router.DELETE("/someDelete", deleting)
router.PATCH("/somePatch", patching)
router.HEAD("/someHead", head)
router.OPTIONS("/someOptions", options)
1. 路由分组
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// Simple group: v1
v1 := router.Group("/v1")
{
v1.POST("/login", loginEndpoint)
v1.POST("/submit", submitEndpoint)
v1.POST("/read", readEndpoint)
}
// Simple group: v2
v2 := router.Group("/v2")
{
v2.POST("/login", loginEndpoint)
v2.POST("/submit", submitEndpoint)
v2.POST("/read", readEndpoint)
}
router.Run(":8082")
}
2. 带参数的url
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
r.GET("/user/:name/:action/", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Param("name")
action := c.Param("action")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "%s is %s", name, action)
})
r.GET("/user/:name/*action", func(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.Param("name")
action := c.Param("action")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "%s is %s", name, action)
})
r.Run(":8082")
}
案例源码
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
goodsGroup := router.Group("/goods")
//不需要依附于任何函数体
{
goodsGroup.GET("/list", goodsList)
//goodsGroup.GET("/1", goodsDetail) //获取商品id为1的详细信息
//带参的url
//goodsGroup.GET("/:id/:action", goodsDetail) //获取商品id为1的详细信息
goodsGroup.GET("/:id/*action", goodsDetail) //获取商品id为1的详细信息 带*就会把id后面全部的路径全部取出来
goodsGroup.POST("/add", createGoods)
}
router.Run(":8082")
}
func createGoods(context *gin.Context) {
}
func goodsDetail(context *gin.Context) {
id := context.Param("id")
action := context.Param("action")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"id": id,
"action": action,
})
}
func goodsList(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": "goodlist",
})
}
3. 获取路由分组的参数
package main
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
type Person struct {
ID string `uri:"id" binding:"required,uuid"`
Name string `uri:"name" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
route := gin.Default()
route.GET("/:name/:id", func(c *gin.Context) {
var person Person
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(&person); err != nil {
c.JSON(400, gin.H{"msg": err})
return
}
c.JSON(200, gin.H{"name": person.Name, "uuid": person.ID})
})
route.Run(":8088")
}
案例代码
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
// Person 这是来约束参数是什么类型
type Person struct {
//Id string `uri:"id" binding:"required,uuid"` //这里必须是uuid http://127.0.0.1:8083/bobby/6e4e2015-a5c2-9279-42a6-6b70478276bc
Id int `uri:"id" binding:"required"`
Name string `uri:"name" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/:name/:id", func(context *gin.Context) {
var person Person
if err := context.ShouldBindUri(&person); err != nil {
context.Status(404)
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": person.Name,
"id": person.Id,
})
})
router.Run(":8083")
}
1. 获取get参数
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// 匹配的url格式: /welcome?firstname=Jane&lastname=Doe
router.GET("/welcome", func(c *gin.Context) {
firstname := c.DefaultQuery("firstname", "Guest")
lastname := c.Query("lastname") // 是 c.Request.URL.Query().Get("lastname
c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello %s %s", firstname, lastname)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
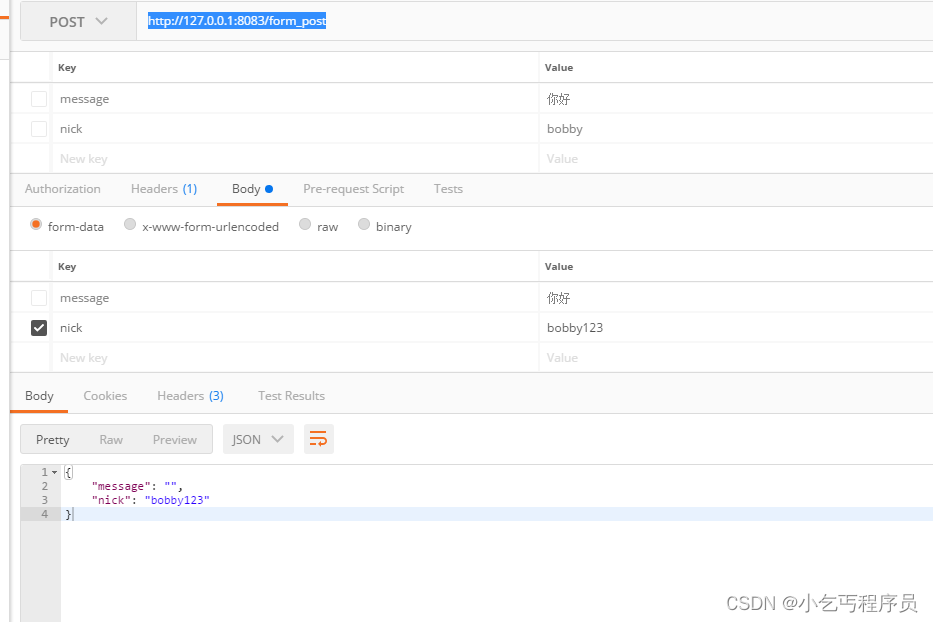
2. 获取post参数
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/form_post", func(c *gin.Context) {
message := c.PostForm("message")
nick := c.DefaultPostForm("nick", "anonymous") // 此⽅法可以设置默认值
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"status": "posted",
"message": message,
"nick": nick,
})
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
3. get、post混合
POST /post?id=1234&page=1 HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
name=manu&message=this_is_great
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/post", func(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Query("id")
page := c.DefaultQuery("page", "0")
name := c.PostForm("name")
message := c.PostForm("message")
fmt.Printf("id: %s; page: %s; name: %s; message: %s", id, page, name, mes
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
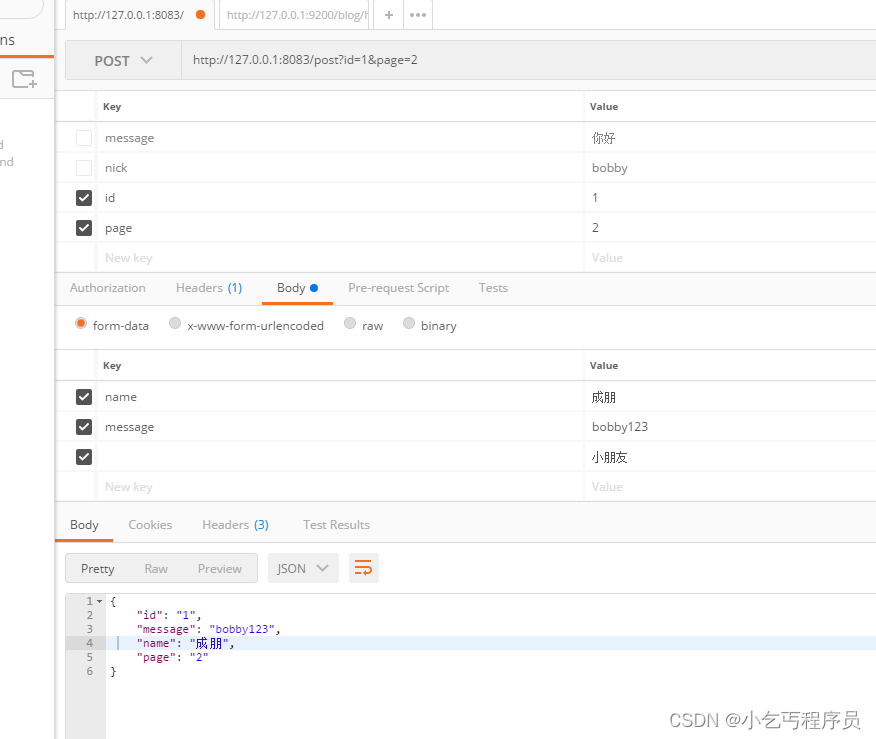
案例源码
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
//GET请求获取参数
router.GET("/welcome", welcome)
//POST获取参数
router.POST("/form_post", formPost)
//get和post请求混合使用
router.POST("/post", getPost)
router.Run(":8083")
}
func getPost(context *gin.Context) {
id := context.Query("id")
page := context.DefaultQuery("page", "0")
name := context.PostForm("name")
message := context.DefaultPostForm("message", "信息")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"id": id,
"page": page,
"name": name,
"message": message,
})
}
// http://127.0.0.1:8083/form_post 然后在body写入参数
func formPost(context *gin.Context) {
message := context.PostForm("message")
nick := context.DefaultPostForm("nick", "anonymous")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": message,
"nick": nick,
})
}
// http://127.0.0.1:8083/welcome
// 如果什么都不写取默认值 为bobby 和chengpeng
// http://127.0.0.1:8083/welcome?firstname=chengpeng2&lastname=llAS
// 如果这种写法 得到的就是chengpeng2 和llAS
func welcome(context *gin.Context) {
firstName := context.DefaultQuery("firstname", "bobby")
lastName := context.DefaultQuery("lastname", "chengpeng")
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"first_name": firstName,
"last_name": lastName,
})
}
1. 输出json和protobuf
新建user.proto文件
syntax = "proto3";
option go_package = ".;proto";
message Teacher {
string name = 1;
repeated string course = 2;
}
protoc --go_out=. --go-grpc_out=. .\user.proto
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"start/gin_t/proto"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// gin.H is a shortcut for map[string]interface{}
r.GET("/someJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hey", "status": http.StatusOK})
})
r.GET("/moreJSON", func(c *gin.Context) {
// You also can use a struct
var msg struct {
Name string `json:"user"` //转义
Message string
Number int
}
msg.Name = "Lena"
msg.Message = "hey"
msg.Number = 123
// Note that msg.Name becomes "user" in the JSON
// Will output : {"user": "Lena", "Message": "hey", "Number": 123}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, msg)
})
r.GET("/someProtoBuf", func(c *gin.Context) {
courses := []string{"python", "django", "go"}
data:&proto.Teacher{
Name: "bobby",
Course: courses,
}
// Note that data becomes binary data in the response
// Will output protoexample.Test protobuf serialized data
c.ProtoBuf(http.StatusOK, data)
})
// Listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8083")
}
2. PureJSON
通常情况下,JSON会将特殊的HTML字符替换为对应的unicode字符,比如 < 替换为 \u003c ,如果想原样输出html,则使用PureJSON
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
// Serves unicode entities
r.GET("/json", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"html": "<b>Hello, world!</b>",
})
})
// Serves literal characters
r.GET("/purejson", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.PureJSON(200, gin.H{
"html": "<b>Hello, world!</b>",
})
})
// listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080
r.Run(":8080")
}
源码案例
package main
import (
proto1 "GormStart/gin_start/ch05/proto"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
//JSON
router.GET("/moreJSON", moreJSON)
//proto
router.GET("/someProtoBuf", returnProto)
router.Run(":8083")
}
func returnProto(context *gin.Context) {
course := []string{"python", "go", "微服务"}
user := &proto1.Teacher{
Name: "bobby",
Course: course,
}
context.ProtoBuf(http.StatusOK, user)
}
// {
// "user": "bobby",
// "Message": "这是测试一个json",
// "Number": 20
// }
//
// http://127.0.0.1:8083/moreJSON
func moreJSON(context *gin.Context) {
var msg struct {
Name string `json:"user"`
Message string
Number int
}
msg.Name = "bobby"
msg.Message = "这是测试一个json"
msg.Number = 20
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, msg)
}
客户端反解码
package main
import (
proto1 "GormStart/gin_start/ch05/proto"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/proto"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
resp, _ := http.Get("http://127.0.0.1:8083/someProtoBuf")
bytes, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
var res proto1.Teacher
_ = proto.Unmarshal(bytes, &res)
fmt.Println(res.Name, res.Course)
}
1. 表单的基本验证
若要将请求主体绑定到结构体中,请使用模型绑定,目前支持JSON、XML、YAML和标准表单值(foo=bar&boo=baz)的绑定。
Gin使用 go-playground/validator和https://github.com/go-playground/validator 验证参数,查看完整文档(https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/go-playground/validator/v10)。
需要在绑定的字段上设置tag,比如,绑定格式为json,需要这样设置 json:“fieldname” 。此外,Gin还提供了两套绑定方法:
Must bind
- Methods - Bind , BindJSON , BindXML , BindQuery , BindYAML
Behavior - 这些方法底层使用 MustBindWith ,如果存在绑定错误,请求将被以下指令中c.AbortWithError(400,err).SetType(ErrorTypeBind) ,响应状态代码会被设置为400,请求头 Content-Type 被设置为 text/plain;charset=utf-8 。注意,如果你试图在此之后设置响应代码,将会发出一个警告 [GIN-debug] [WARNING] Headers were already written. Wanted to override status code 400 with 422 ,如果你希望更好地控制行为,请使用 ShouldBind 相关的方法
Should bind
- Methods - ShouldBind(动态决定JSON,XML等等) , ShouldBindJSON , ShouldBindXML ,ShouldBindQuery , ShouldBi ndYAML
- Behavior - 这些方法底层使用 ShouldBindWith ,如果存在绑定错误,则返回错误,开发人员 可以正确处理请求和错误。
当我们使用绑定方法时,Gin会根据Content-Type推断出使用哪种绑定器,如果你确定你绑定的是什么,你可以使用 MustBindWith 或者 BindingWith 。
你还可以给字段指定特定规则的修饰符,如果一个字段用 binding:“required” 修饰,并且在绑定时该字段的值为空,那么将返回一个错误。
validator支持中文==>国际化
go语言实现翻译解释器
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/binding"
"github.com/go-playground/locales/en"
"github.com/go-playground/locales/zh"
ut "github.com/go-playground/universal-translator"
"github.com/go-playground/validator/v10"
en_translations "github.com/go-playground/validator/v10/translations/en"
zh_translations "github.com/go-playground/validator/v10/translations/zh"
var trans ut.Translator
// InitTrans 翻译
func InitTrans(locale string) (err error) {
//修改gin框架中的validator引擎属性,实现定制
//Engine返回为StructValidator实现提供动力的底层验证器引擎。
if v, ok := binding.Validator.Engine().(*validator.Validate); ok {
zhT := zh.New() //中文翻译器
enT := en.New() //英文翻译器
// 第一个参数是备用(fallback)的语言环境 // 后面的参数是应该支持的语言环境(支持多个)
uni := ut.New(enT, zhT, enT) //后面可以重复放
// locale 通常取决于 http 请求头的 'Accept-Language'
//根据参数取翻译器实例
// 也可以使用 uni.FindTranslator(...) 传入多个locale进行查找
trans, ok = uni.GetTranslator(locale) //拿到Translator
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("uni.GetTranslator(%s)", locale)
}
// 注册翻译器
switch locale {
case "en":
en_translations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(v, trans) //使用英文的注册器
case "zh":
zh_translations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(v, trans) //使用中文注册器
default:
en_translations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(v, trans)
}
return
}
return
}
案例整体源码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin/binding"
"github.com/go-playground/locales/en"
"github.com/go-playground/locales/zh"
ut "github.com/go-playground/universal-translator"
"github.com/go-playground/validator/v10"
en_translations "github.com/go-playground/validator/v10/translations/en"
zh_translations "github.com/go-playground/validator/v10/translations/zh"
"net/http"
"reflect"
"strings"
)
// LoginForm 绑定为json
type LoginForm struct {
//form json xml
User string `form:"user" json:"user" xml:"user" binding:"required,min=3,max=10"` //required必填最短长度
Password string `form:"password" json:"password" xml:"password" binding:"required"`
}
// SignUpForm 注册
type SignUpForm struct {
Age uint8 `json:"age" binding:"gte=1,lte=130"`
Name string `json:"name" binding:"required,min=3"`
Email string `json:"email" binding:"required,email"` //email是否是合法的格式
Password string `json:"password" binding:"required"`
RePassword string `json:"re_password" binding:"required,eqfield=Password"` //跨字段验证 eqfield指定上面的字段和它相等
}
var trans ut.Translator
// InitTrans 翻译
func InitTrans(locale string) (err error) {
//修改gin框架中的validator引擎属性,实现定制
//Engine返回为StructValidator实现提供动力的底层验证器引擎。
if v, ok := binding.Validator.Engine().(*validator.Validate); ok {
//注册一个获取json的tag的自定义方法
v.RegisterTagNameFunc(func(field reflect.StructField) string {
//name1 := strings.SplitN(field.Tag.Get("json"), ",", 2)
//fmt.Println("chengpeng", name1)
//a := field.Tag.Get("form")
//fmt.Println("chengpeng", a)
name := strings.SplitN(field.Tag.Get("json"), ",", 2)[0]
if name == "_" {
return ""
}
return name
})
zhT := zh.New() //中文翻译器
enT := en.New() //英文翻译器
// 第一个参数是备用(fallback)的语言环境 // 后面的参数是应该支持的语言环境(支持多个)
uni := ut.New(enT, zhT, enT) //后面可以重复放
// locale 通常取决于 http 请求头的 'Accept-Language'
//根据参数取翻译器实例
// 也可以使用 uni.FindTranslator(...) 传入多个locale进行查找
trans, ok = uni.GetTranslator(locale) //拿到Translator
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("uni.GetTranslator(%s)", locale)
}
// 注册翻译器
switch locale {
case "en":
en_translations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(v, trans) //使用英文的注册器
case "zh":
zh_translations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(v, trans) //使用中文注册器
default:
en_translations.RegisterDefaultTranslations(v, trans)
}
return
}
return
}
// "msg": { "LoginForm.user": "user长度必须至少为3个字符" }
//
// 去掉LoginForm
func removeTopStruct(fileds map[string]string) map[string]string {
rsp := map[string]string{}
for filed, err := range fileds {
//要查找的字符串.的位置strings.Index(filed, ".")
rsp[filed[strings.Index(filed, ".")+1:]] = err
}
return rsp
}
func main() {
err := InitTrans("zh")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("获取翻译器错误")
return
}
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/loginJSON", func(context *gin.Context) {
var loginForm LoginForm
//你应该这样 获取参数
err := context.ShouldBind(&loginForm)
if err != nil {
errs, ok := err.(validator.ValidationErrors) //转换为FieldError
if !ok {
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"msg": err.Error(),
})
}
//fmt.Println(err.Error())
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
//"msg": err.Error(),
//"msg": errs.Translate(trans),
"msg": removeTopStruct(errs.Translate(trans)),
})
return
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"msg": "登录成功",
})
})
router.POST("/signup", func(context *gin.Context) {
var signUpForm SignUpForm
//你应该这样 获取参数
err := context.ShouldBind(&signUpForm)
if err != nil {
errs, ok := err.(validator.ValidationErrors) //转换为FieldError
//不能转换成功
if !ok {
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"msg": err.Error(),
})
}
context.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
//"msg": err.Error(),
//"msg": errs.Translate(trans),
"msg": removeTopStruct(errs.Translate(trans)),
})
return
}
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"msg": "注册成功",
})
})
_ = router.Run(":8083")
}
中间件==>自定义gin中间件
是一类能够为一种或多种应用程序合作互通、资源共享,同时还能够为该应用程序提供相关的服务的软件。中间件是一类软件统称,而非一种软件;中间件不仅仅实现互连,还要实现应用之间的互操作。
中间件与操作系统和数据库共同构成基础软件三大支柱,是一种应用于分布式系统的基础软件,位于应用与操作系统、数据库之间,为上层应用软件提供开发、运行和集成的平台。中间件解决了异构网络环境下软件互联和互操作等共性问题,并提供标准接口、协议,为应用软件间共享资源提供了可复用的“标准件”。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"time"
)
// MyLogger 自定义中间件
func MyLogger() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(context *gin.Context) {
now := time.Now()
// 设置变量到Context的key中,可以通过Get()取
context.Set("example", "123456")
//让原本该执行的逻辑继续执行
context.Next()
//把开始的时间给我去计算时长
end := time.Since(now)
//拿到状态信息 // 中间件执行完后续的一些事情
status := context.Writer.Status()
//[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8083
//耗时:%!V(time.Duration=610500)
//状态 200
fmt.Printf("耗时:%V\n", end)
fmt.Println("状态", status)
}
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.Use(MyLogger())
router.GET("/ping", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
router.Run(":8083")
}
//func main() {
// //engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery()) 默认使用这两个中间件
// //router := gin.Default()
// router := gin.New()
// //使用logger中间件和recovery(恢复)中间件 全局使用
// router.Use(gin.Logger(), gin.Recovery())
//
// //某一组url 这样配置这个中间件只有这样开始的时候,这个url才会影响
// authrized := router.Group("/goods")
// authrized.Use(AuthRequired)
//
//}
//
AuthRequired 中间件
//func AuthRequired(context *gin.Context) {
//
//}
终止中间件后续的逻辑的执行
//如果你想不执行后面的逻辑
context.Abort()
为什么连return都阻止不了后续逻辑的执行?
那是因为Use或者GET等等里面有一个HandlersChain的切片(type HandlersChain []HandlerFunc)添加到切片中去,如果使用return只是返回这个函数,并不会结束全部的接口。使用Next函数,index只是跳转到下个函数里面,如果使用Abort他会把index放到切片最后,那么全部都会结束。
案例源码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"time"
)
// MyLogger 自定义中间件
func MyLogger() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(context *gin.Context) {
now := time.Now()
// 设置变量到Context的key中,可以通过Get()取
context.Set("example", "123456")
//让原本该执行的逻辑继续执行
context.Next()
//把开始的时间给我去计算时长
end := time.Since(now)
//拿到状态信息 // 中间件执行完后续的一些事情
status := context.Writer.Status()
fmt.Printf("耗时:%V\n", end)
fmt.Println("状态", status)
}
}
func TokenRequired() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(context *gin.Context) {
var token string
//token放到了Header里面
for k, v := range context.Request.Header {
if k == "X-Token" {
token = v[0]
fmt.Println("chengpeng", token)
} else {
fmt.Println(k, v)
}
//fmt.Println(k, v, token)
}
if token != "bobby" {
context.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, gin.H{
"msg": "未登录",
})
//return结束不了
//return
//如果你想不执行后面的逻辑
context.Abort()
}
context.Next()
}
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
//router.Use(MyLogger())
router.Use(TokenRequired())
router.GET("/ping", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
router.Run(":8083")
}
//func main() {
// //engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery()) 默认使用这两个中间件
// //router := gin.Default()
// router := gin.New()
// //使用logger中间件和recovery(恢复)中间件 全局使用
// router.Use(gin.Logger(), gin.Recovery())
//
// //某一组url 这样配置这个中间件只有这样开始的时候,这个url才会影响
// authrized := router.Group("/goods")
// authrized.Use(AuthRequired)
//
//}
//
AuthRequired 中间件
//func AuthRequired(context *gin.Context) {
//
//}
gin返回html
官方地址:https://golang.org/pkg/html/template/
翻 译 : https://colobu.com/2019/11/05/Golang-Templates-Cheatsheet/#if/else_%E8%AF%AD%E5%8F%A5
1. 设置静态文件路径
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
// 创建⼀个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
// 配置模板
r.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/**/*")
//router.LoadHTMLFiles("templates/template1.html", "templates/template2.html
// 配置静态⽂件夹路径 第⼀个参数是api,第⼆个是⽂件夹路径
r.StaticFS("/static", http.Dir("./static"))
// GET:请求⽅式;/hello:请求的路径
// 当客户端以GET⽅法请求/hello路径时,会执⾏后⾯的匿名函数
r.GET("/posts/index", func(c *gin.Context) {
// c.JSON:返回JSON格式的数据
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "posts/index.tmpl", gin.H{
"title": "posts/index",
})
})
r.GET("gets/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "posts/login.tmpl", gin.H{
"title": "gets/login",
})
})
// 启动HTTP服务,默认在0.0.0.0:8080启动服务
r.Run()
}
2. index.html内容
<html>
<h1>
{{ .title }}
</h1>
</html>
3. templates/posts/index.tmpl
{{ define "posts/index.tmpl" }}
<html><h1>
{{ .title }}
</h1>
<p>Using posts/index.tmpl</p>
</html>
{{ end }}
4. templates/users/index.tmpl
{{ define "users/index.tmpl" }}
<html><h1>
{{ .title }}
</h1>
<p>Using users/index.tmpl</p>
</html>
{{ end }}
案例源码
{{define "goods/list.html"}}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>商品名称</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>商品列表页</h1>
</body>
</html>
{{end}}
{{define "users/list.html"}}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>用户列表页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户列表页</h1>
</body>
</html>
{{end}}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
{{.name}}
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
{{.title}}
</h1>
</body>
</html>
优雅退出: https://gin-gonic.com/zh-cn/docs/examples/graceful-restart-or-stop/
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"os"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
)
func main() {
//优雅退出,当我们关闭程序的时候,应该做的后续处理
//微服务 启动之前或者启动之后会做一件事,将当前的服务的ip地址和端口号注册到注册中心
//我们当前的服务停止了以后并没有告知注册中心
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"msg": "pong",
})
})
go func() {
router.Run(":8083") //启动以后会一直停在这里
}()
//如果想要接收到信号 kill -9 强杀命令
quit := make(chan os.Signal)
signal.Notify(quit, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-quit
//处理后续的逻辑
fmt.Println("关闭server中...")
fmt.Println("注销服务...")
}
设置静态文件
router.Static("/static", "./static")