系列文章目录
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(一):FFMPEG + Conan 环境集成
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(二):基础知识和解封装(demux)
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(三):视频解码
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(四):像素格式与格式转换
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(五):使用 SDL 播放视频
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(六):使用 SDL 播放音频和视频
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(七):使用多线程解码视频和音频
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(八):音画同步
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(九):Seek 策略
- 基于 FFmpeg 的跨平台视频播放器简明教程(十):在 Android 运行 FFmpeg
前言
一个视频播放器需要的模块大致包括:
- 视频解码
- 音频解码
- 视频画面输出
- 音频播放
- 图像格式转换
- 音频重采样
- 音画同步
经过前九章的学习,我们已经对以上模块有了深入的理解和实践。然而,目前的代码实现较为零散,缺乏统一的组织和抽象。
接下来,我们将进入移动端播放器的设计与开发阶段。为了能够最大限度地复用现有的模块和代码,我们需要对现有的代码进行整理和优化,形成一种有效的架构。本文将介绍一种简单但实用的架构,它能够满足我们的需求。
这种架构虽然简单,但是能够满足我们的需求。
架构介绍
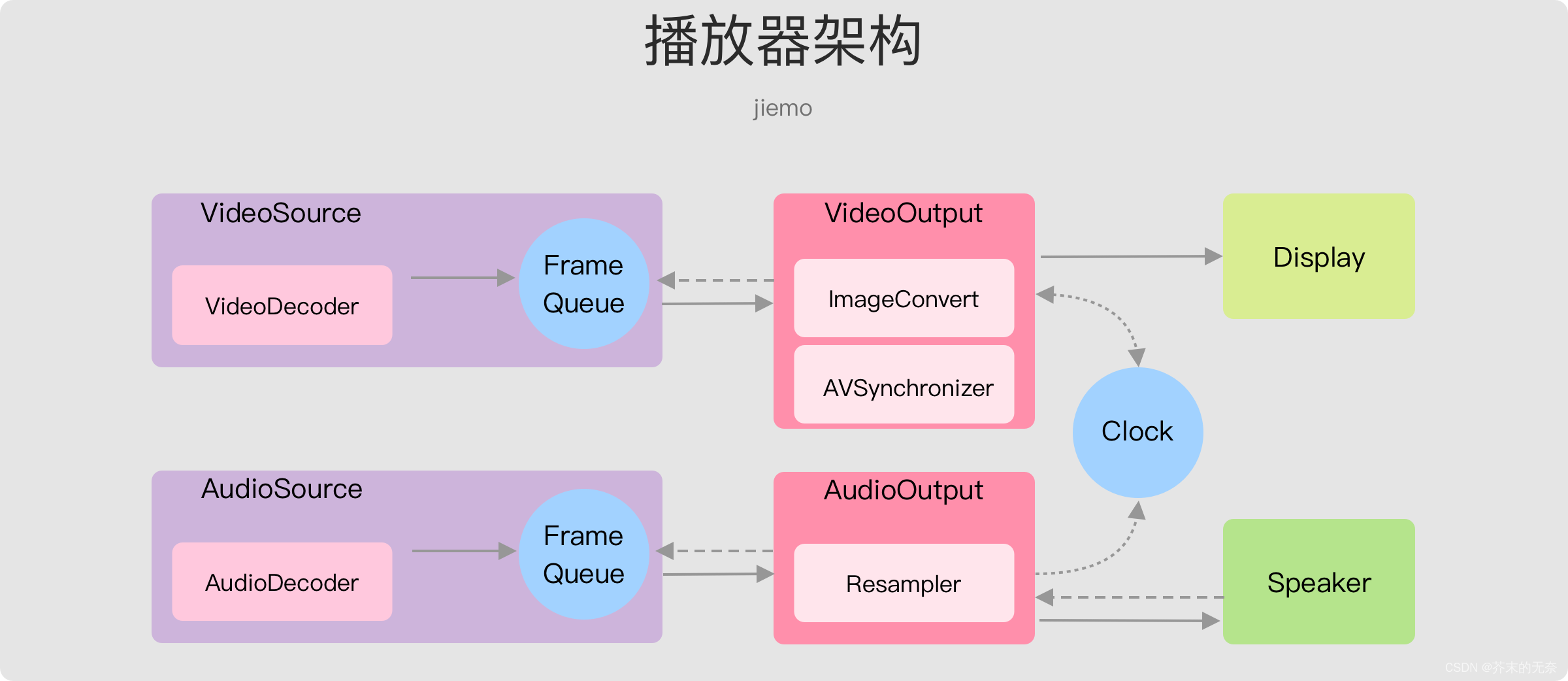
整体框架如上图,每个模块职责清晰,其中:
- Decoder,负责解码音视频数据
- Source,负责提供音频/视频数据
- Output,负责显示画面,和播放音频
接下来对各个模块做详细说明。
音频/视频解码,Audio/Video Decoder
namespace j_video_player {
class IVideoDecoder {
public:
virtual ~IVideoDecoder() = default;
/**
* open a video file
* @param file_path video file path
* @return 0 if success, otherwise return error code
*/
virtual int open(const std::string &file_path) = 0;
/**
* check if the decoder is valid
* @return true if valid, otherwise return false
*/
virtual bool isValid() = 0;
/**
* close the decoder
*/
virtual void close() = 0;
/**
* decode next frame
* @return a shared_ptr of VideoFrame if success, otherwise return nullptr
*/
virtual std::shared_ptr<Frame> decodeNextFrame() = 0;
/**
* seek to a timestamp quickly and get the video frame
*
* @param timestamp the timestamp(us) to seek
* @return video frame if success, otherwise return nullptr
*/
virtual std::shared_ptr<Frame> seekFrameQuick(int64_t timestamp) = 0;
/**
* seek to a timestamp precisely and get the video frame
* @param timestamp the timestamp(us) to seek
* @return video frame if success, otherwise return nullptr
*/
virtual std::shared_ptr<Frame> seekFramePrecise(int64_t timestamp) = 0;
/**
* get the current position of the decoder
* @return the current position(us)
*/
virtual int64_t getPosition() = 0;
virtual MediaFileInfo getMediaFileInfo() = 0;
};
} // namespace j_video_player
视频解码接口如上,其中
open(),即打开文件。打开后可以通过getMediaFileInfo获取文件的媒体信息,例如视频宽高、音频采样率等等decodeNextFrame,顺序解码,获取下一帧数据seekFrameQuick,快速 seek,但不保证精确seekFramePrecise,精确 seek,可能更加耗时getPosition,获取当前解码的位置,单位微妙(us)
音频解码接口与视频的一模一样,这是因为对于解码器而言,无论音频帧还是视频帧都是 frame,因此两边接口是一致的。
在实现上,我们使用 ffmpeg 实现了上述音频/视频解码接口。
具体实现请参考 FFmpegAVDecoder 源码
音频/视频源,Audio/Video Source
namespace j_video_player {
enum class SourceState {
kIdle,
kStopped,
kPlaying,
kSeeking,
kPaused,
};
class ISource {
public:
virtual ~ISource() = default;
virtual int open(const std::string &file_path) = 0;
virtual MediaFileInfo getMediaFileInfo() = 0;
virtual int play() = 0;
virtual int pause() = 0;
virtual int stop() = 0;
virtual int seek(int64_t timestamp) = 0;
virtual SourceState getState() = 0;
virtual int64_t getDuration() = 0;
virtual int64_t getCurrentPosition() = 0;
virtual std::shared_ptr<Frame> dequeueFrame() = 0;
virtual int getQueueSize() = 0;
};
class IVideoSource : public ISource {
public:
std::shared_ptr<Frame> dequeueFrame() override { return dequeueVideoFrame(); }
virtual std::shared_ptr<Frame> dequeueVideoFrame() = 0;
};
class IAudioSource : public ISource {
public:
std::shared_ptr<Frame> dequeueFrame() override { return dequeueAudioFrame(); }
virtual std::shared_ptr<Frame> dequeueAudioFrame() = 0;
};
} // namespace j_video_player
ISource 类负责生产音频/视频帧,其中:
open即打开文件。打开后可以通过getMediaFileInfo获取文件的媒体信息,例如视频宽高、音频采样率等等play、pause和stop负责 Source 的转态流转dequeueFrame从队列中获取一个 Frame,通过这个接口,下游的消费者可以对音频/视频帧进行消费。- IVideoSource 和 IAudioSource 继承自 ISource,并提供了额外的
dequeueVideoFrame和dequeueAudioFrame方法
我们代码中的 SimpleSource 类是对 IVideoSource 和 IAudioSource 的具体实现。具体的:
SimpleSource持有一个 Decoder(VideoDecoder 或者 AudioDecoder ),内部使用 Decoder 进行音视频的解码。SimpleSource拥有自己的解码线程,在调用play时将启动该线程。SimpleSource拥有一个 Frame queue,默认大小为 3,也就是最多存放 3 帧数据,如果 queue 满了,则阻塞解码线程,等待消费者调用dequeueFrame消费数据
具体实现请参考 SimpleSource 源码
视频画面输出,VideoOutput
namespace j_video_player {
class VideoOutputParameters {
public:
int width{0};
int height{0};
int fps{0};
int pixel_format{0}; // AVPixelFormat
};
enum class OutputState { kIdle, kPlaying, kPaused, kStopped };
class IVideoOutput {
public:
virtual ~IVideoOutput() = default;
virtual int prepare(const VideoOutputParameters ¶meters) = 0;
virtual void attachVideoSource(std::shared_ptr<IVideoSource> source) = 0;
virtual void attachImageConverter(
std::shared_ptr<ffmpeg_utils::FFMPEGImageConverter> converter) = 0;
virtual void
attachAVSyncClock(std::shared_ptr<utils::ClockManager> clock) = 0;
virtual int play() = 0;
virtual int pause() = 0;
virtual int stop() = 0;
virtual OutputState getState() const = 0;
};
} // namespace j_video_player
IVideoOutput 类负责消费 Source 生产的视频帧,将其显示在窗口上。其中:
prepare用于进行一些初始化操作,例如根据VideoOutputParameters参数来设置输出窗口大小、像素格式等attachVideoSource,绑定一个 IVideoSource,意味着将从这个 Source 中获取数据(调用dequeueVideoFrame方法)attachImageConverter方法用于绑定一个负责像素格式转换的类。这个类将无条件地将源发送过来的帧进行像素格式转换。从IVideoOutput的视角来看,它只知道要输出的格式,而无法知道源格式。因此,需要在外部设置转换器的参数。设置完成后,再将其附加到 IVideoOutput 上。attachAVSyncClock方法用于绑定一个时钟对象,它负责纪录视频流和音频流的时间,IVideoOutput可以利用时钟进行音画同步。
BaseVideoOutput 继承自 IVideoOutput,BaseVideoOutput 内部启动另一个线程用于从 Source 中获取音频数据,并提供了 drawFrame 的虚方法用于图像上屏显示,具体实现细节参考 BaseVideoOutput,我们重点看线程做了啥:
void startOutputThread() {
output_thread_ = std::make_unique<std::thread>([this]() {
for (;;) {
if (state_ == OutputState::kStopped || state_ == OutputState::kIdle) {
break;
} else if (state_ == OutputState::kPaused) {
continue;
} else if (state_ == OutputState::kPlaying) {
if (source_ == nullptr) {
LOGW("source is null, can't play. Please attach source first");
break;
}
auto frame = source_->dequeueVideoFrame();
if (frame == nullptr) {
continue;
}
std::shared_ptr<Frame> frame_for_draw = convertFrame(frame);
if (frame_for_draw != nullptr) {
drawFrame(frame_for_draw);
doAVSync(frame_for_draw->pts_d());
}
}
}
});
}
当正在播放时,调用 source_->dequeueVideoFrame() 向源索取一帧;接着调用 convertFrame 方法将视频帧格式转换为预期的格式;然后,使用 drawFrame 方法将改帧渲染至屏幕;最后进行音画同步。
我们的代码中 SDL2VideoOutput 是对 BaseVideoOutput 的具体实现,具体细节请参考源码。
音频播放,AudioOutput
namespace j_video_player {
enum class AudioOutputState { kIdle, kPlaying, kStopped };
class AudioOutputParameters {
public:
int sample_rate{44100};
int channels{2};
int num_frames_of_buffer{1024};
bool isValid() const {
return sample_rate > 0 && channels > 0 && num_frames_of_buffer > 0;
}
};
class IAudioOutput {
public:
virtual ~IAudioOutput() = default;
virtual int prepare(const AudioOutputParameters ¶ms) = 0;
virtual void attachAudioSource(std::shared_ptr<IAudioSource> source) = 0;
virtual void attachResampler(
std::shared_ptr<ffmpeg_utils::FFmpegAudioResampler> resampler) = 0;
virtual void
attachAVSyncClock(std::shared_ptr<utils::ClockManager> clock) = 0;
virtual int play() = 0;
virtual int stop() = 0;
virtual AudioOutputState getState() const = 0;
};
} // namespace j_video_player
IAudioOutput 负责播放音频,其中:
prepare,用于一些初始化的操作,例如打开音频设备等attachAudioSource,绑定一个 Audio SourceattachResampler绑定一个 resampler 进行音频重采样。这个类将无条件地将源发送过来的音频进行重采样。从IAudioOutput的视角来看,它只知道要输出的格式,而无法知道源格式。因此,需要在外部设置重采样的参数。设置完成后,再将其附加到 IAudioOutput 上。
我们的代码中 SDL2AudioOutput 是对 BaseVideoOutput 的具体实现,具体细节请参考源码。
组成播放器
各个模块已经讲解完毕,接下来只需要将他们组装起来,屏蔽一些细节就可以了。我们封装了一个 SimplePlayer 来做这样的事情,它使用起来非常简单,参考 my_tutorial08 :
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
printHelpMenu();
return -1;
}
std::string in_file = argv[1];
auto video_decoder = std::make_shared<FFmpegVideoDecoder>();
auto audio_decoder = std::make_shared<FFmpegAudioDecoder>();
auto video_source = std::make_shared<SimpleVideoSource>(video_decoder);
auto audio_source = std::make_shared<SimpleAudioSource>(audio_decoder);
auto video_output = std::make_shared<SDL2VideoOutput>();
auto audio_output = std::make_shared<SDL2AudioOutput>();
auto player =
SimplePlayer{video_source, audio_source, video_output, audio_output};
int ret = player.open(in_file);
RETURN_IF_ERROR_LOG(ret, "open player failed, exit");
auto media_file_info = player.getMediaFileInfo();
VideoOutputParameters video_output_param;
video_output_param.width = media_file_info.width;
video_output_param.height = media_file_info.height;
video_output_param.pixel_format = AVPixelFormat::AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
AudioOutputParameters audio_output_param;
audio_output_param.sample_rate = 44100;
audio_output_param.channels = 2;
audio_output_param.num_frames_of_buffer = 1024;
ret = player.prepare(video_output_param, audio_output_param);
RETURN_IF_ERROR_LOG(ret, "prepare player failed, exit");
player.play();
// ....
}
- 创建好 Audio/VideoSource 和 Audio/VideoOutput 后,将他们塞到 SimplePlayer 构造函数即可
player.open()打开文件- 设置 VideoOutputParameters 和 AudioOutputParameters,调用
prepare函数进行一些初始化操作 - 使用
play/pause/stop/seek等函数操作视频播放
SimplePlayer 具体实现请参考源码。
总结
本文对一种简易的播放器架构进行了说明,该架构下播放器被分为若干模块,包括 Audio/VideoSource,Audio/VideoOutput 等。通过该架构设计我们能够灵活的扩展解码、上屏、音频播放等模块。
参考
- FFmpegAVDecoder
- SimpleSource
- SDL2VideoOutput
- BaseVideoOutput
- SDL2AudioOutput
- my_tutorial08
- SimplePlayer


![[AutoSar]导出task mapping 表到excel](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/af7b6b3dbe9a493e913fce3af7d83a7e.png)


![[oeasy]python001_先跑起来_python_三大系统选择_windows_mac_linux](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f8a356f9bd35227eda97ec6b1151e81e.png)

