专栏简介 :MySql数据库从入门到进阶.
题目来源:leetcode,牛客,剑指offer.
创作目标:记录学习MySql学习历程
希望在提升自己的同时,帮助他人,,与大家一起共同进步,互相成长.
学历代表过去,能力代表现在,学习能力代表未来!
目录
1.新增
2. 聚合查询
2.1 聚合函数
3. 分组查询(grop by)
4. having
5. 联合查询
5.1 内连接
5.2 外连接
5.3 自连接
6. 子查询
7. 合并查询
1.新增
将查询结果作为values, 插入到指定表中.
语法:
insert into 表1 select * from 表2;示例:
将学生表1中的数据插入到学生表2中.
mysql> insert into student1 select * from student2;
mysql> select * from student1;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
| 4 | 老六 |
+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student2;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
| 4 | 老六 |
+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)Tips:
- 查询表与插入表的列数和类型要匹配.
- 所有select查询都可以和该操作组合使用.
2. 聚合查询
之前提到的条件查询都是基于列和列之间的查询, 而聚合查询针对某个列中所有的行来运算.
2.1 聚合函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
| count | 返回查询到的数据的数量 |
| sum | 返回查询到数据的总和 (不是数字没有意义) |
| avg | 返回查询到数据的平均值 (不是数字没有意义) |
| max | 返回查询到数据的最大值 (不是数字没有意义) |
| min | 返回查询到数据的最小值 (不是数字没有意义) |
- count
语法:
select count(表达式) from 表名;
- Tips: count(*)包含null所在的行.
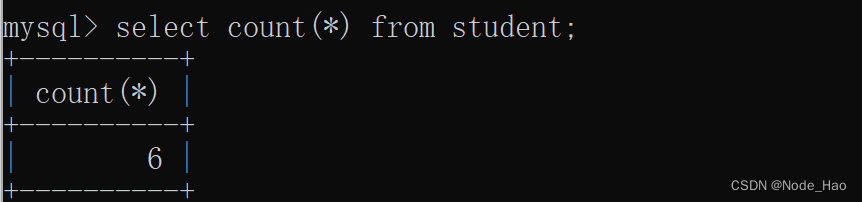
示例:
统计班级有多少学生
- sum
语法:
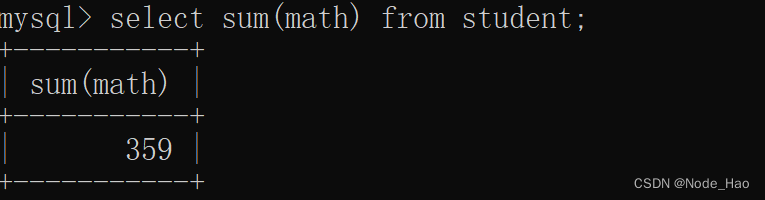
select sum(表达式) from 表名示例:
统计数学总分
- avg
语法:
select avg(表达式) from student;示例:
统计平均总分

- max
语法:
select max(表达式) from 表名;示例:
返回英语最高分

- min
语法:
select min(表达式) from 表名;示例:
返回大于60分以上的数学最低分

3. 分组查询(grop by)
语法:
select 字段 from 表名 group by 字段示例:

- 单个字段分组
查出学生等级的种类:(按等级划分,去除重复的)
select grade from student group by grade; 
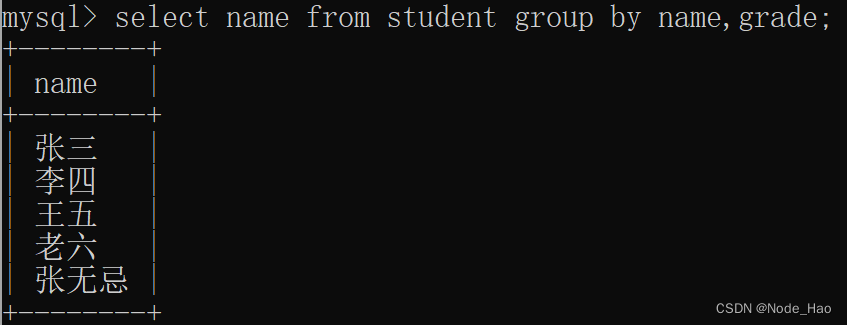
- 多个字段分组
按名字和等级划分去除重复的同学:
select name from student group by name,grade;Tip:此时将名字和等级看做是一个整体, 只有名字和等级都相同的才能分成一组, 其中一个不同就不是一组.
- 搭配聚合函数分组
查看表中相同人名的个数:
select name,count(*) from student group by name;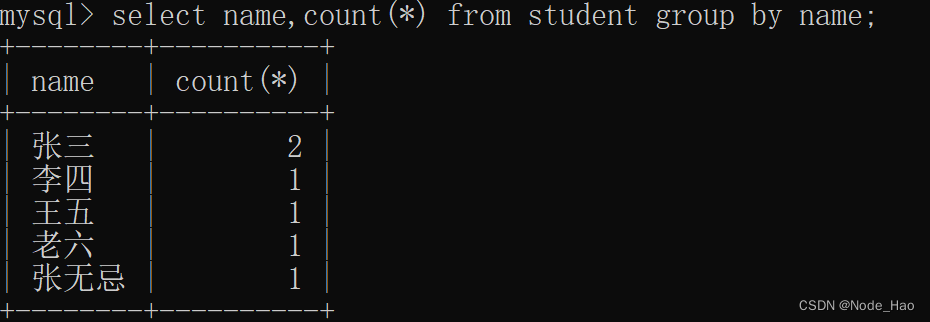
4. having
where 与having都是设定筛选条件的语句,有相似点也有不同点.
- group by子句进行分组以后,, 分组之前筛选用where, 分组之后筛选用having.
- having必须和group by 一起使用.
- where之后不能使用聚合函数, having之后可以使用聚合函数.
- having可以看做是对where的补充, where筛选出合适的数据having才能进行聚合操作.
| 字名 | 作用 |
| where 子句 | 1)对查询结果进行分组前, 将不符合where条件的行去掉, 即在分组之前过滤数据. 2)where 后面不可以使用聚合函数 3)过滤行 |
| having 子句 | 1)having 子句的作用是筛选满足条件的组, 即在分组之后过滤数据,. 2)having 后面可以使用聚合函数 3)过滤组 4)支持所有的where操作. |
MySQL语句执行顺序:
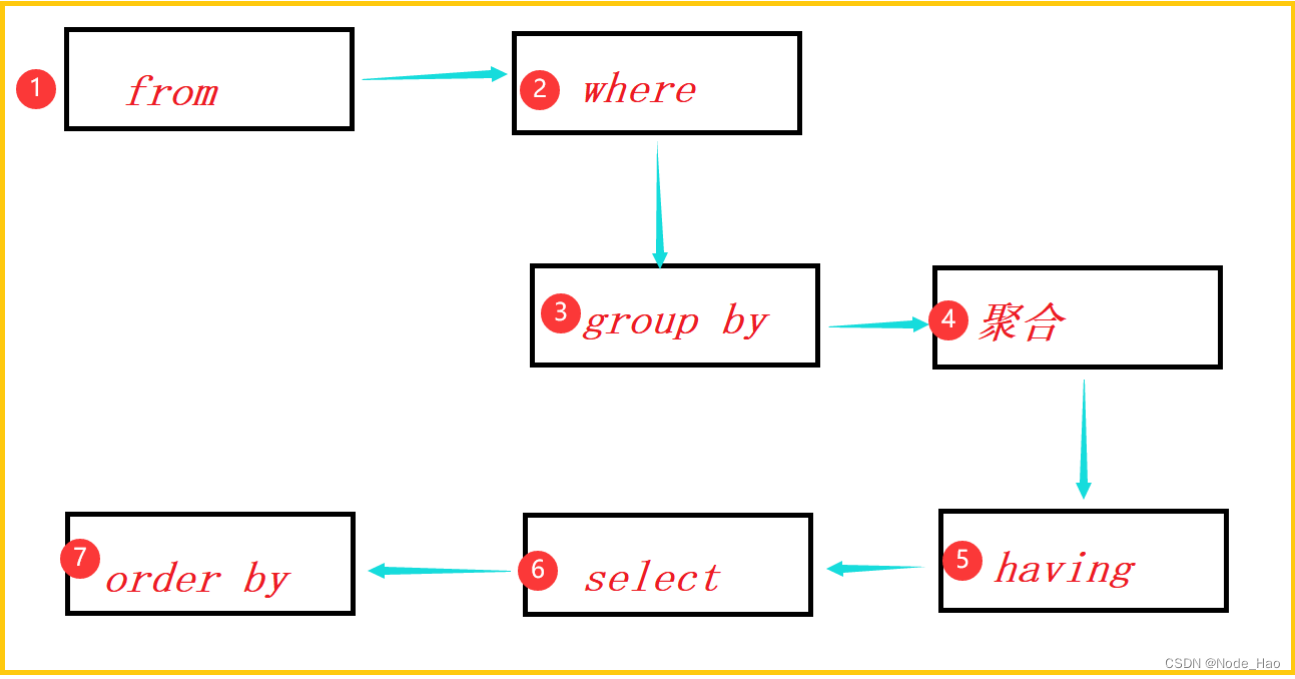
示例:
显示平均工资高于1500的人的平均工资.
select name,avg(salary) from student group by name having avg(salary)>1500;
5. 联合查询
实际开发中数据往往来自不同的表, 所以需要多表联合查询, 多表联合查询本质是对多张表的数据取笛卡尔积(也就是全排列).列数是两个表列数之和, 行数是两个表行数之和.因此其中只有一部分数据是有效的, 需要后续相关操作进行筛选.

Tips:关联表查询时可以对关联表使用别名, 更加直观.
筛选前:
 筛选后:
筛选后:
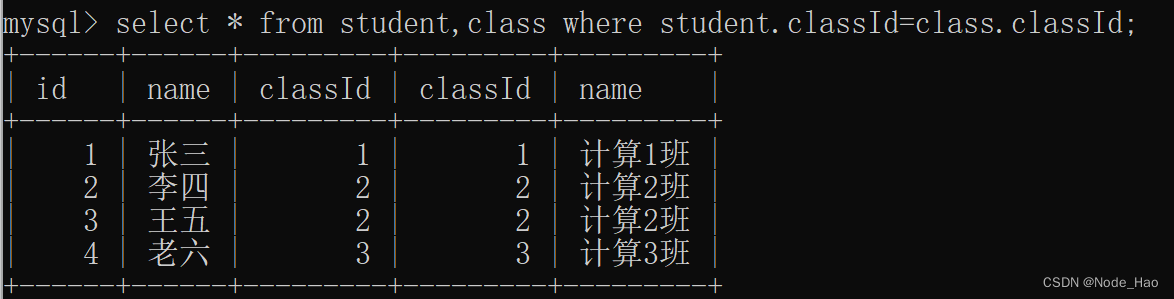
Tips:如果两张表中字段重名, 不加成员访问修饰符" . ", 会报错 ambigous(模糊不清的)
 为了使查询数据更加直观明了, 本文提供以下代码供后续案例使用.
为了使查询数据更加直观明了, 本文提供以下代码供后续案例使用.
drop table if exists classes;
drop table if exists student;
drop table if exists course;
drop table if exists score;
create table classes (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), `desc` varchar(100));
create table student (id int primary key auto_increment, sn varchar(20), name varchar(20), qq_mail varchar(20) ,
classes_id int);
create table course(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
create table score(score decimal(3, 1), student_id int, course_id int);
insert into classes(name, `desc`) values
('计算机系2019级1班', '学习了计算机原理、C和Java语言、数据结构和算法'),
('中文系2019级3班','学习了中国传统文学'),
('自动化2019级5班','学习了机械自动化');
insert into student(sn, name, qq_mail, classes_id) values
('09982','张三','zhangsan@qq.com',1),
('00835','李四',null,1),
('00391','王五',null,1),
('00031','老六','xuxian@qq.com',1),
('00054','老师我作业忘带了',null,1),
('51234','芝士雪豹','xuebao@qq.com',2),
('83223','tellme',null,2),
('09527','老外学英文','foreigner@qq.com',2);
insert into course(name) values
('Java'),('中国传统文化'),('计算机原理'),('语文'),('高等数学'),('英语');
insert into score(score, student_id, course_id) values
-- 张三
(70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(33, 1, 5),(98, 1, 6),
-- 李四
(60, 2, 1),(59.5, 2, 5),
-- 王五
(33, 3, 1),(68, 3, 3),(99, 3, 5),
-- 老六
(67, 4, 1),(23, 4, 3),(56, 4, 5),(72, 4, 6),
-- 老师我作业忘带了
(81, 5, 1),(37, 5, 5),
-- 芝士雪豹
(56, 6, 2),(43, 6, 4),(79, 6, 6),
-- 老外学英文
(80, 7, 2),(92, 7, 6);5.1 内连接
内连接就是指结果仅包含符合连接条件的行, 参与连接的两个表都应符合连接条件.

语法:
1.from多个表简单明了,但只能实现内连接不能实现外连接.
select * from 表1,表2...;2.join on可以既可以实现内连接也可以实现外连接.
select * from 表1 join 表2 on...;select * from 表1 inner join 表2 on...;示例:
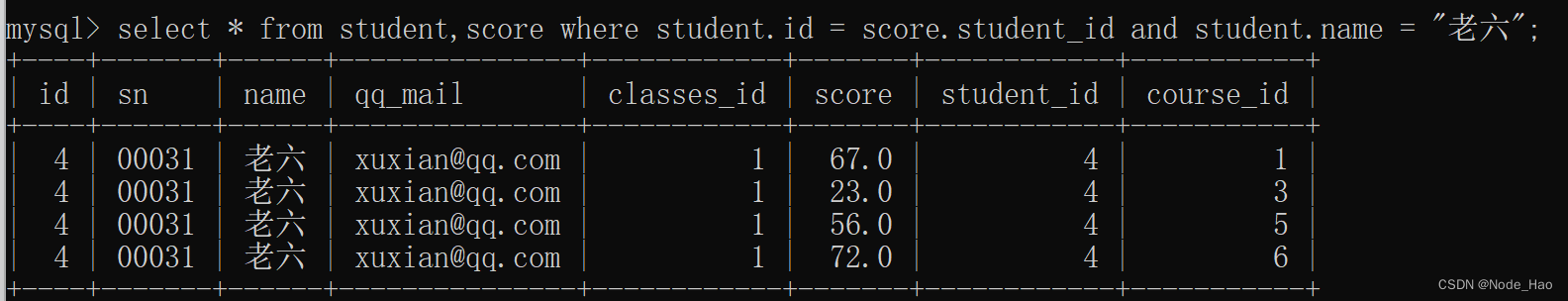
查询老六同学的全科成绩.
查询步骤:
- 分析需要联合的表(学生表和分数表), 然后计算笛卡尔积.
- 合法性筛选(分数表id对应学生id).
- 根据需求加入必要条件.xue
- 去要的列.
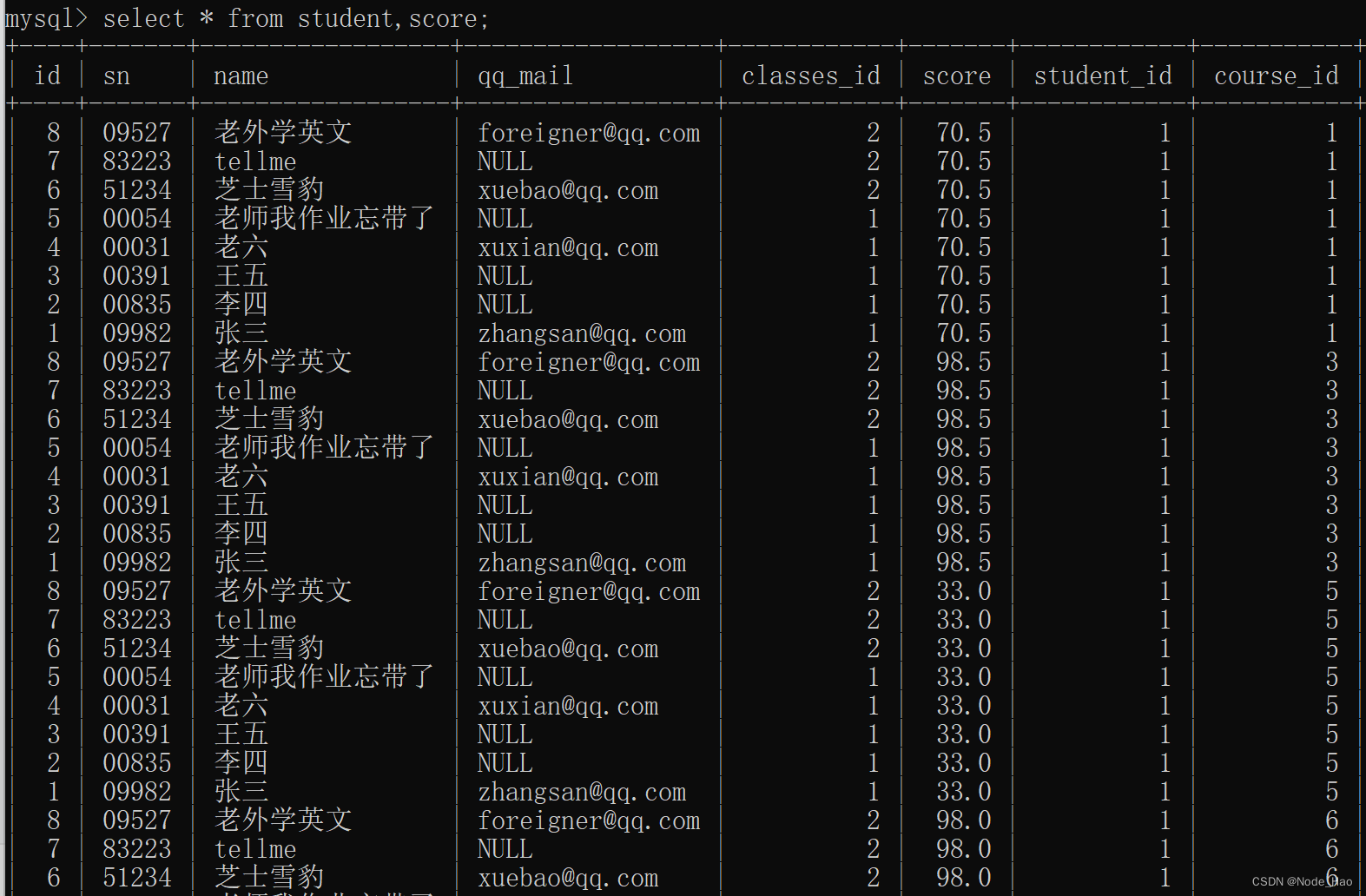
1.计算学生表和分数表的笛卡尔积.(160多行数据, 大部分无效)
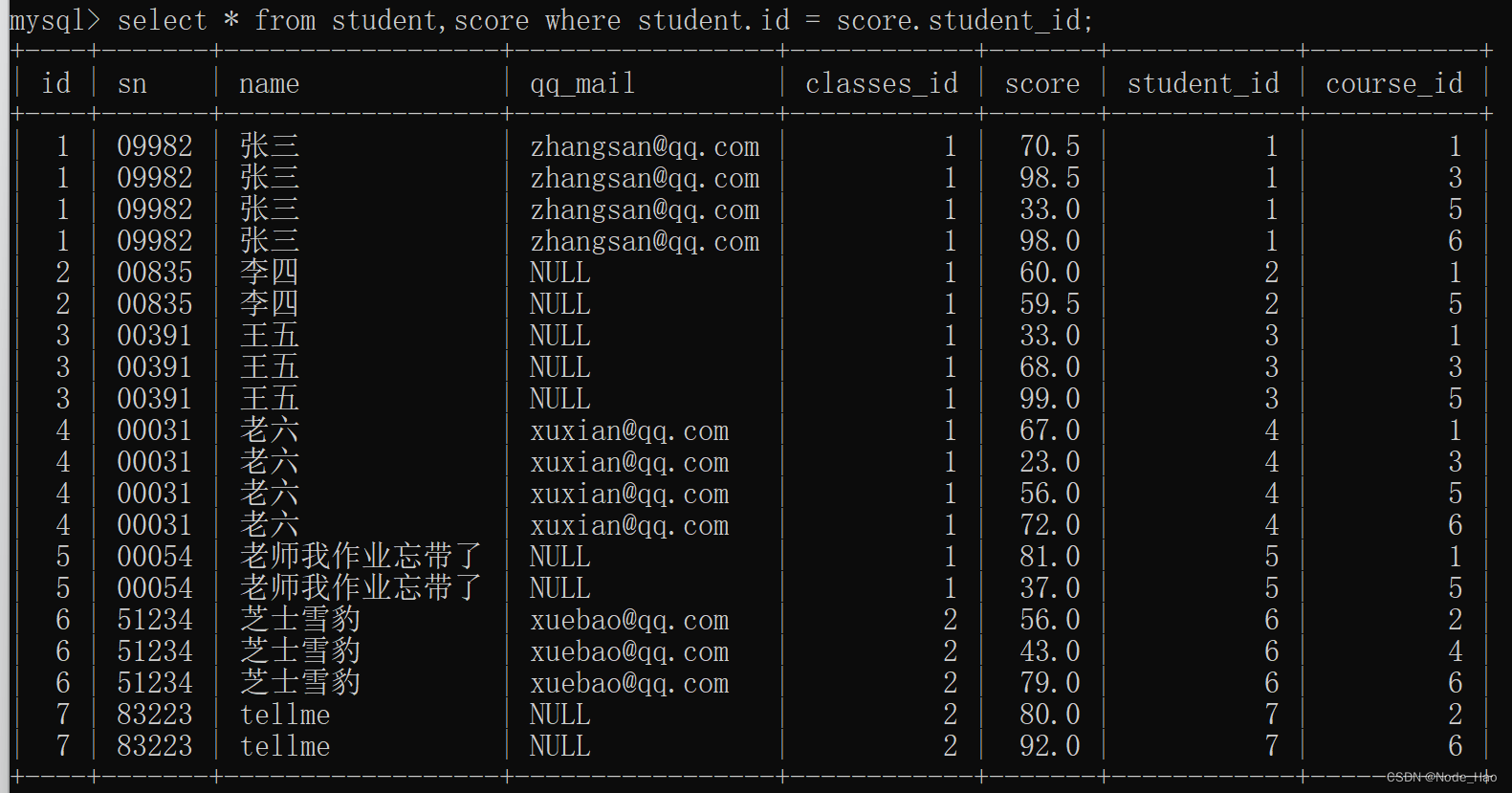
2.分数表中id对应学生表中id
3.学生姓名为老六
4.去除不必要的列
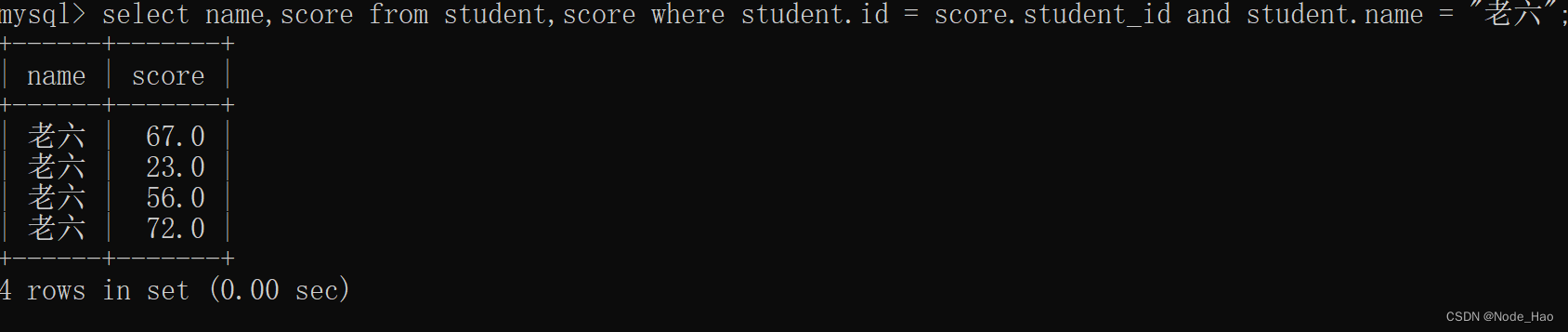
查询所有同学的成绩, 及同学的个人信息.(学生表,课程表,分数表)
select student.name as 姓名,course.name as 课程名称,score.score from student,course,score where student.id = score.student_id and score.course_id = course.id;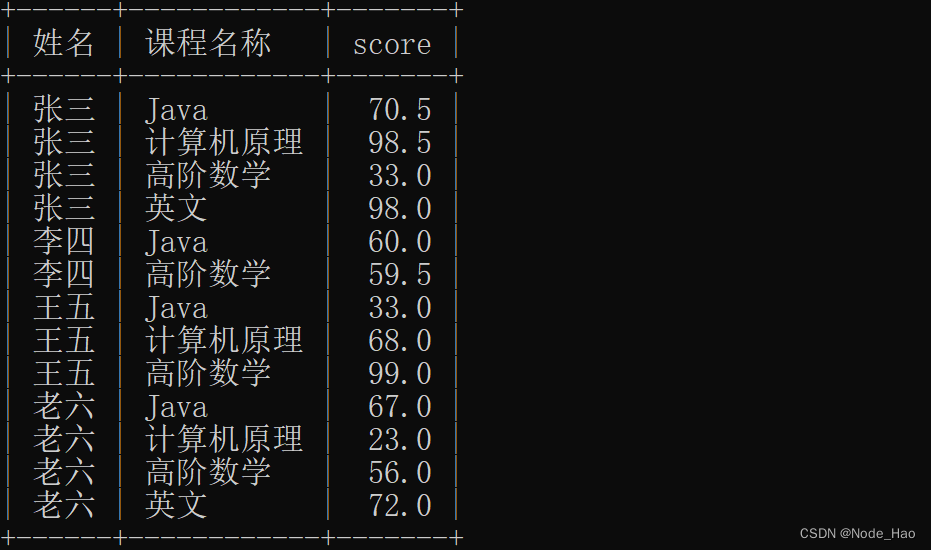
5.2 外连接
连接结果不仅包含符合连接条件的行, 同时也包含不符合连接条件的行, 分为左外连接和右外连接.
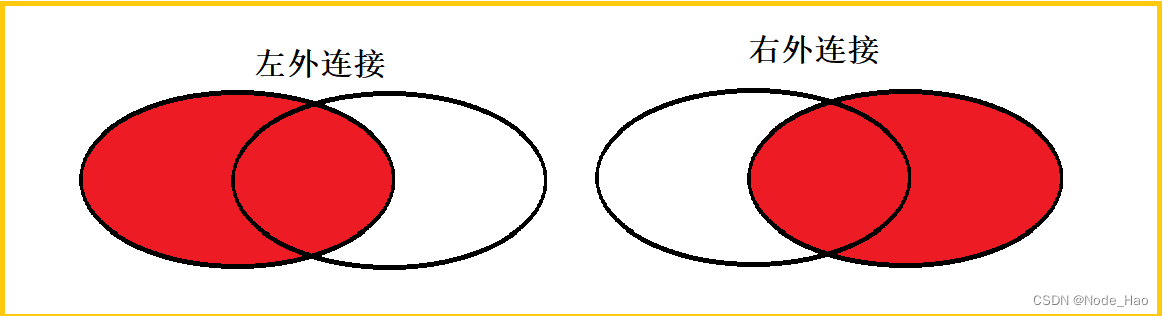
语法:
左外连接:左表有多少数据就显示多少数据, 右边没有的就用null表示
select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 连接条件;右外连接:右表有多少数据就显示多少数据, 左表没有的就用null表示
select * from 表1 right join 表2 on 条件;示例:
假如王五同学转专业, 数据表还未同步他的成绩信息.
mysql> select * from student;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| 2 | 李四 |
| 3 | 王五 |
+------+------+
mysql> select * from score;
+------------+-------+
| student_id | score |
+------------+-------+
| 1 | 90 |
| 2 | 89 |
| 4 | 77 |
+------------+-------+
--左外连接
mysql> select * from student left join score on student.id = score.student_id;
+------+------+------------+-------+
| id | name | student_id | score |
+------+------+------------+-------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 90 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 89 |
| 3 | 王五 | NULL | NULL |
+------+------+------------+-------+
--右外连接
mysql> select * from student right join score on student.id = score.student_id;
+------+------+------------+-------+
| id | name | student_id | score |
+------+------+------------+-------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 90 |
| 2 | 李四 | 2 | 89 |
| NULL | NULL | 4 | 77 |
+------+------+------------+-------+5.3 自连接
自连接顾名思义就是自己和自己笛卡尔积, 自连接的效果就是把行转成列.不管和where子句还是having子句都是针对不同列之间的行进行操作, 如果只有一个列并且想要行与行之间进行比较, 就必须自连接.
语法:
select * from 表名 as 别名1,表名 as 别名2;Tips:自连接必须给表起个别名, 否则两个相同的表连接会报错.

示例:
查询java成绩高于计算机原理成绩的同学.
由图可以看出, java成绩和计算机原理成绩之间的比较在同一列, 所以需要行转列.

自连接之后可以发现, 可以进行列与列之间的比较了, 本题针对的是同一同学不同课程, 所以筛选条件是两表的学生id相同.
mysql> select * from score as s1, score as s2 where s1.student_id = s2.student_id; 最后添加条件完成比较.
最后添加条件完成比较.
mysql> select * from score as s1, score as s2 where s1.student_id = s2.student_id and s1.course_id = 3 and s2.course_id = 1 and s1.score>s2.score;
+-------+------------+-----------+-------+------------+-----------+
| score | student_id | course_id | score | student_id | course_id |
+-------+------------+-----------+-------+------------+-----------+
| 98.5 | 1 | 3 | 70.5 | 1 | 1 |
| 68.0 | 3 | 3 | 33.0 | 3 | 1 |
+-------+------------+-----------+-------+------------+-----------+6. 子查询
子查询是指嵌套在其他sql语句中的select语句, 也叫嵌套查询.(本质上就是套娃)
- 单行子查询:返回一行记录的子查询
示例:
返回与"老六"同学同班的同学.
--分步骤
mysql> select * from student where name = "老六";
+----+-------+------+---------------+------------+
| id | sn | name | qq_mail | classes_id |
+----+-------+------+---------------+------------+
| 4 | 00031 | 老六 | xuxian@qq.com | 1 |
+----+-------+------+---------------+------------+
mysql> select * from student where classes_id = 1 and name!="老六";
+----+-------+------------------+-----------------+------------+
| id | sn | name | qq_mail | classes_id |
+----+-------+------------------+-----------------+------------+
| 1 | 09982 | 张三 | zhangsan@qq.com | 1 |
| 2 | 00835 | 李四 | NULL | 1 |
| 3 | 00391 | 王五 | NULL | 1 |
| 5 | 00054 | 老师我作业忘带了 | NULL | 1 |
+----+-------+------------------+-----------------+------------+
--子查询一步完成
mysql> select * from student where classes_id = (select classes_id from student where name = "老六" ) and name!="老六";
+----+-------+------------------+-----------------+------------+
| id | sn | name | qq_mail | classes_id |
+----+-------+------------------+-----------------+------------+
| 1 | 09982 | 张三 | zhangsan@qq.com | 1 |
| 2 | 00835 | 李四 | NULL | 1 |
| 3 | 00391 | 王五 | NULL | 1 |
| 5 | 00054 | 老师我作业忘带了 | NULL | 1 |
+----+-------+------------------+-----------------+------------+- 多行子查询:返回多行记录的子查询
示例:
查询语文或英语课程的成绩信息.
1. (not) in 关键字
--分步骤查询
mysql> select * from course where name = "语文" or name = "英语";
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 4 | 语文 |
| 6 | 英语 |
+----+------+
mysql> select * from score where course_id = 4 or course_id = 6;
+-------+------------+-----------+
| score | student_id | course_id |
+-------+------------+-----------+
| 98.0 | 1 | 6 |
| 72.0 | 4 | 6 |
| 43.0 | 6 | 4 |
| 79.0 | 6 | 6 |
| 92.0 | 7 | 6 |
+-------+------------+-----------+
--多行子查询
mysql> select * from score where course_id in (select id from course where name = "语文" or name = "英语");
+-------+------------+-----------+
| score | student_id | course_id |
+-------+------------+-----------+
| 98.0 | 1 | 6 |
| 72.0 | 4 | 6 |
| 43.0 | 6 | 4 |
| 79.0 | 6 | 6 |
| 92.0 | 7 | 6 |
+-------+------------+-----------+2. (not) exists 关键字
由于 in 关键字查询结果在内存中, 如果内存中存不下可以考虑使用exists关键字, 但exists关键字执行效率低下, 且可读性差.不如分步查询.
7. 合并查询
在实际应用中, 为了合并多个select的执行结果, 可以使用集合操作符 union, union all, 使用union和union all时, 前后查询结果集中, 字段要一致.
Tips:
- union查询结果会去重, union all 可以保留多份.
- or 只能联合一个表中的结果, union 可以联合多个表中的.
- union
示例:
查询id<3 或者名字为"英文"的课程
mysql> select * from course where id<3 union select * from course where name = "英语";
+----+--------------+
| id | name |
+----+--------------+
| 1 | Java |
| 2 | 中国传统文化 |
| 6 | 英语 |
+----+--------------+- union all
示例:
查询id<3 或者名字为"java"的课程
mysql> select * from course where id<3 union all select * from course where name = "Java";
+----+--------------+
| id | name |
+----+--------------+
| 1 | Java |
| 2 | 中国传统文化 |
| 1 | Java |
+----+--------------+