AVL树和红黑树
- 一、AVL树
- 1. 概念
- 2. 原理
- AVL树节点的定义
- 插入
- 不违反AVL树性质
- 违反AVL树性质
- 左单旋
- 右单旋
- 左右双旋
- 右左双旋
- 总结
- 删除
- 3. 验证代码
- 4. AVL树完整实现代码
- 二、红黑树
- 1. 概念
- 2. 性质
- 3. 原理
- 红黑树节点的定义
- 默认约定
- 插入
- 情况一 (u存在且为红)
- 情况二(u不存在或u存在且为黑)
- 删除
- 4. 相关的验证测试代码
- 5. 红黑树完整实现代码
- 三、总结
一、AVL树
1. 概念
AVL树又称高度平衡二叉搜索树:
- 它的左右子树都是AVL树
- 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1(1, 0, -1)。

2. 原理
AVL树是在二叉搜索树的基础上引入平衡因子,借助平衡因子调节AVL树高度。(注意:也可以使用高度,来调节AVL树)
AVL树节点的定义
template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
int _bf; //平衡因子 -- balance factor
AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _bf(0)
{}
};
插入
- 按照二叉树的方式插入新节点
- 调节平衡因子
a. 旋转
b. 结束
不违反AVL树性质
不违反AVL树性质的平衡因子调整的情况:
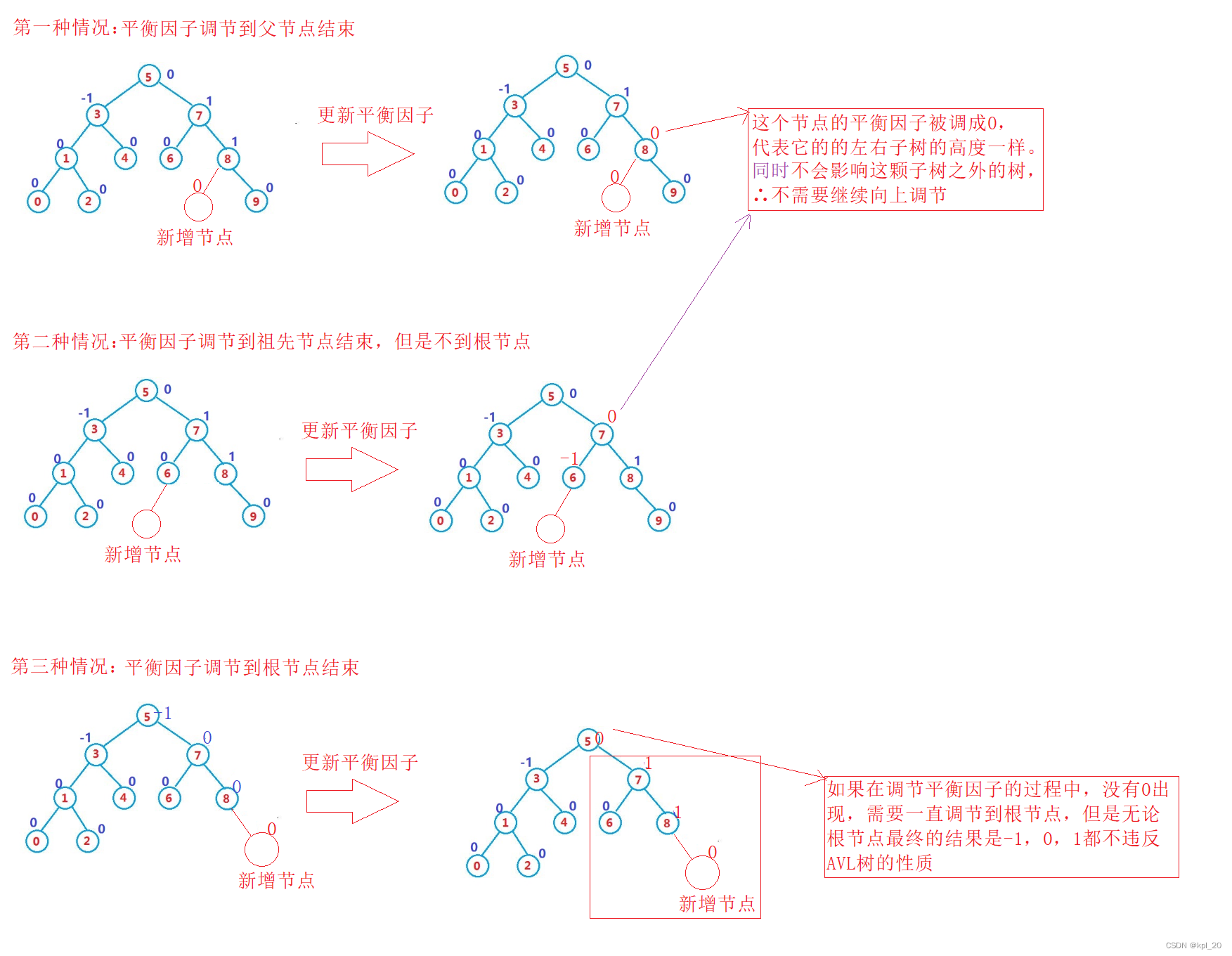
根据上述平衡因子的调整情况得出结论:新增节点,影响了被调整子树的高度,需要沿着祖先路径向上调节,直到调节到平衡因子为0的节点或者根节点,只要平衡因子的绝对值不超过1就符合AVL树的性质。
代码实现:
//控制平衡因子
while (parent)
{
//新增节点在父节点的左,则--。在右则++
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_bf--;
}
else
{
parent->_bf++;
}
//向上更新平衡因子
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
//树平衡的,平衡因子更新完成
break;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
//继续向上更新
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
//树不平衡了,需要旋转
//...
break;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
违反AVL树性质
违反AVL树性质的平衡因子调整的情况:
这种情况就是平衡因子在调整的过程中出现绝对值大于1的情况 --> 需要进行旋转
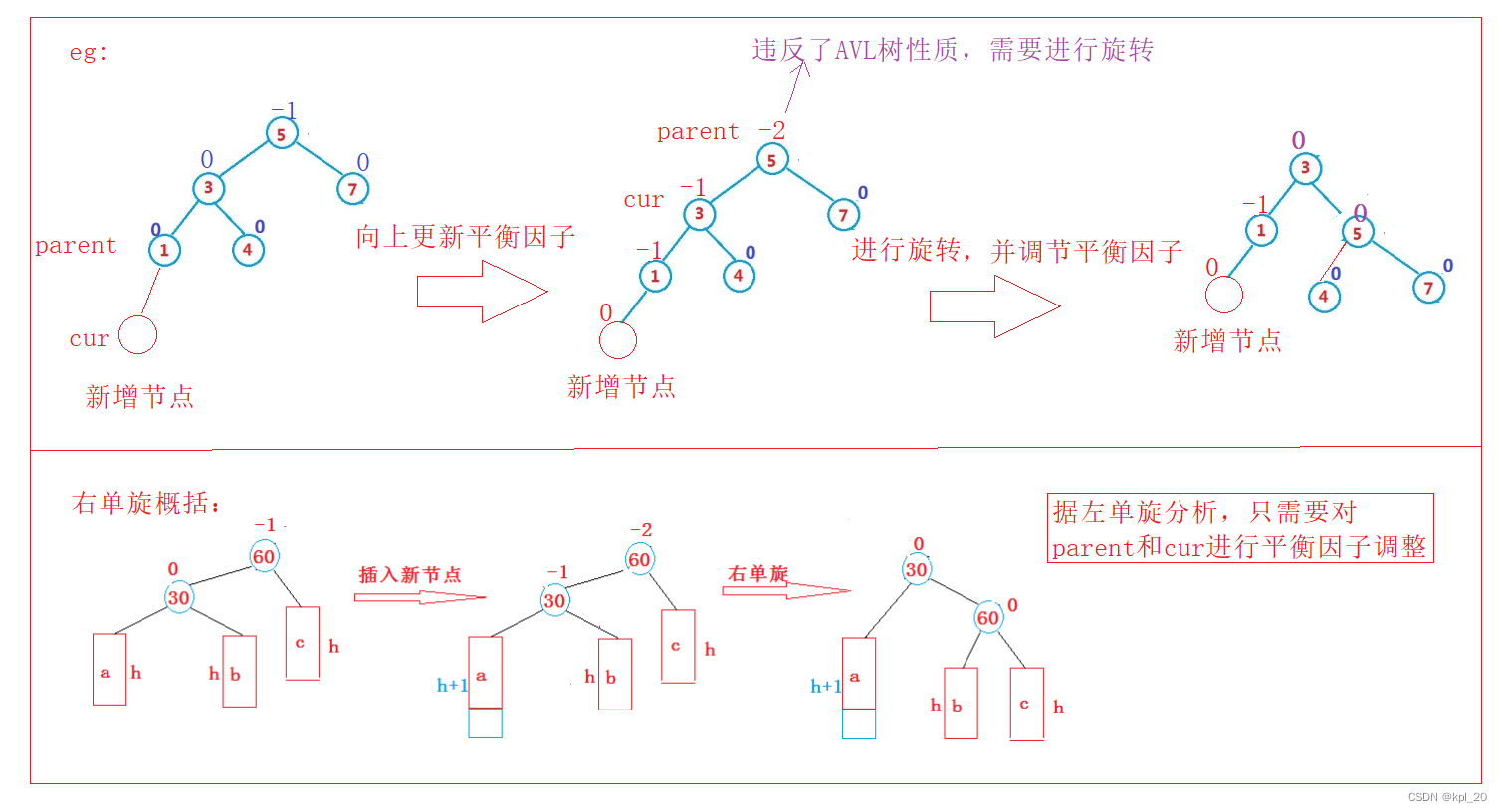
左单旋
逻辑分析:

代码实现:
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
//重新链接
parent->_right = curleft;
if(curleft)
curleft->_parent = parent;
cur->_left = parent;
//提前保存parent->_parent,可能是根节点,也可能是子树的根节点
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
parent->_bf = cur->_bf = 0; //根据上面的分析,不平衡的AVL树,在完成旋转后只需要在这两个节点更改平衡因子
}
右单旋
逻辑分析:
代码实现:
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
parent->_left = curright;
if (curright)
curright->_parent = parent;
//提前保存parent->_parent,可能是根节点,也可能是子树的根节点
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
cur->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
parent->_bf = cur->_bf = 0;
}
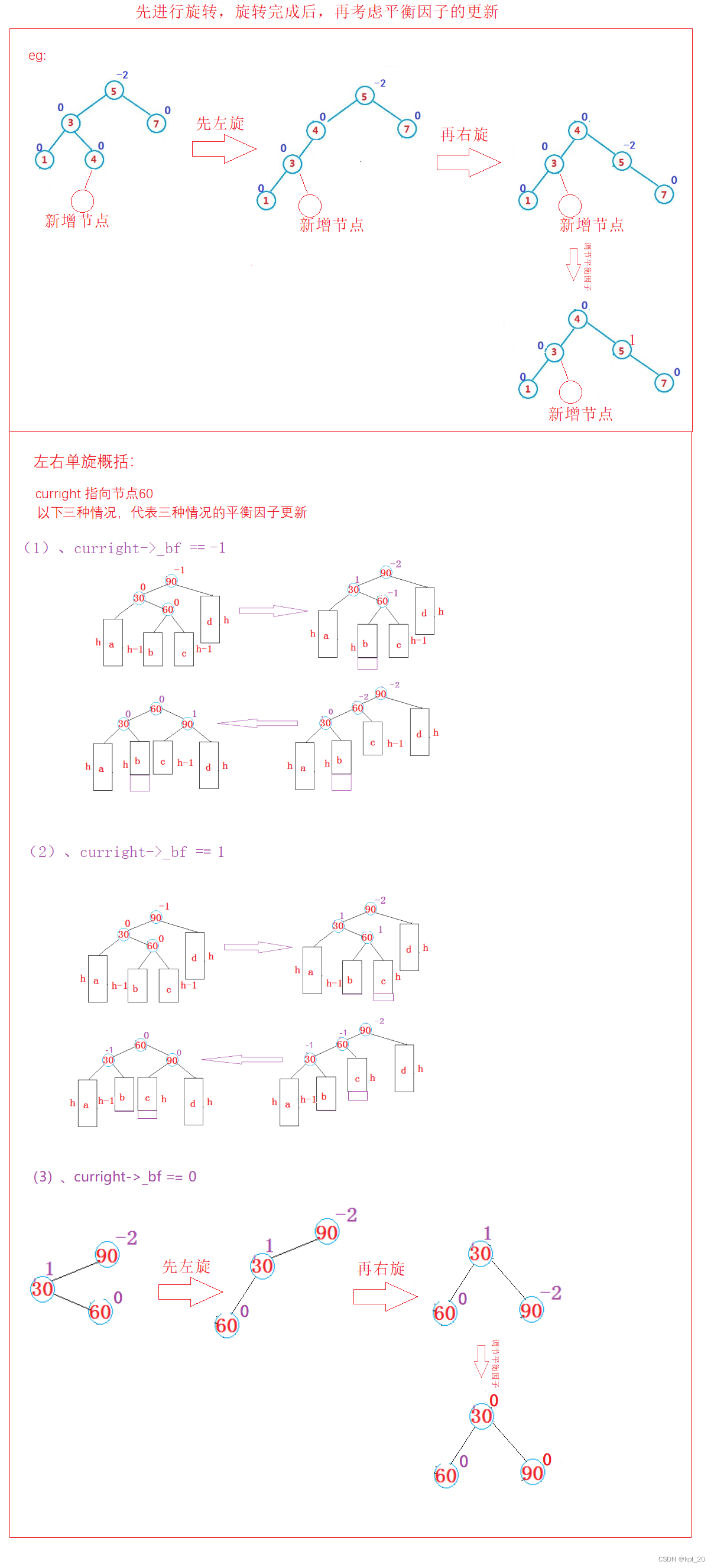
左右双旋
逻辑分析:
代码实现:
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
int bf = curright->_bf;
//在调用完成这两个函数时,改动了parent和cur的影响因子
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
//调节平衡因子
if (bf == -1)
{
parent->_bf = 1;
cur->_bf = 0;
curright->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = -1;
curright->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 0)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = 0;
curright->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
右左双旋
逻辑分析:
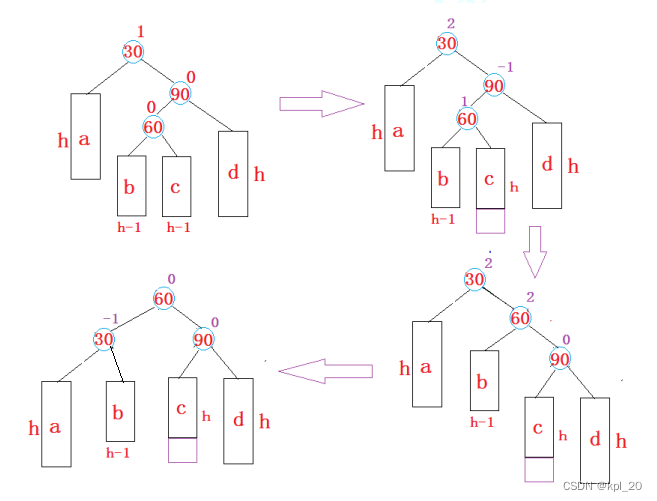
基本原理同左右双旋
代码实现:
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
int bf = curleft->_bf;
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
if (bf == 1)
{
parent->_bf = -1;
cur->_bf = 0;
curleft = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = 1;
curleft->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 0)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = 0;
curleft->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
总结
通过parent和cur的平衡因子,来判断是怎么旋转。旋转完成后,高度降低,AVL树平衡,所以不需要继续向上更新
代码:
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
//树不平衡了,需要旋转
if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateLR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateRL(parent);
}
break;
}
删除
类似二叉搜索树的删除。这里不进行介绍
- 寻找删除目标(是否存在,存在的位置)
- 判断删除目标的结构,使用二叉搜索树的转换思路,将其转为叶子节点
- 将删除目标与AVL树断开,调整平衡。
3. 验证代码
验证该树是否是AVL树
代码:
//判断是不是AVLTree
bool IsBalance()
{
return _IsBalance(_root);
}
//树的高度
int Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
bool _IsBalance(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
int leftHight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHight = Height(root->_right);
if (rightHight - leftHight != root->_bf)
{
cout << "平衡因子异常:" << root->_kv.first << "->" << root->_bf << endl;
return false;
}
return abs(rightHight - leftHight) < 2 && _IsBalance(root->_left) && _IsBalance(root->_right);
}
4. AVL树完整实现代码
//AVL树的节点定义
template<class K, class V>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
int _bf; //平衡因子 -- balance factor
AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _bf(0)
{}
};
template <class K, class V>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//链接新增节点
cur = new Node(kv);
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//控制平衡因子
while (parent)
{
//新增节点在父节点的左,则--。在右则++
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_bf--;
}
else
{
parent->_bf++;
}
//向上更新平衡因子
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
//树平衡的,平衡因子更新完成
break;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
//继续向上更新
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
//树不平衡了,需要旋转
if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
RotateLR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
RotateRL(parent);
}
break;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
return true;
}
//判断是不是AVLTree
bool IsBalance()
{
return _IsBalance(_root);
}
private:
//树的高度
int Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
bool _IsBalance(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
int leftHight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHight = Height(root->_right);
if (rightHight - leftHight != root->_bf)
{
cout << "平衡因子异常:" << root->_kv.first << "->" << root->_bf << endl;
return false;
}
return abs(rightHight - leftHight) < 2 && _IsBalance(root->_left) && _IsBalance(root->_right);
}
//旋转
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
parent->_left = curright;
if (curright)
curright->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
cur->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
parent->_bf = cur->_bf = 0;
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
//重新链接
parent->_right = curleft;
if(curleft)
curleft->_parent = parent;
cur->_left = parent;
//提前保存parent->_parent,可能是根节点,也可能是子树的根节点
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
parent->_bf = cur->_bf = 0;
}
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
int bf = curright->_bf;
//在调用完成这两个函数时,改动了parent和cur的影响因子
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
//调节平衡因子
if (bf == -1)
{
parent->_bf = 1;
cur->_bf = 0;
curright->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = -1;
curright->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 0)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = 0;
curright->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
int bf = curleft->_bf;
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
if (bf == 1)
{
parent->_bf = -1;
cur->_bf = 0;
curleft = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = 1;
curleft->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 0)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
cur->_bf = 0;
curleft->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
二、红黑树
1. 概念
二叉搜索树的一种,每个节点增加一个存储位表示节点标识的颜色(Red或Black),通过每条路径的每个节点的着色方式的限制,红黑树保证没有一条路径会比其它路径长出两倍。(趋近平衡)
2. 性质
- 每个节点只能是红色或黑色
- 根节点是黑色
- 任何路径没有连续的节点是红色的
- 每条路径黑色节点的数量相等
根据性质3和4,保证了红黑树最长路径的节点个数不超过最短路径节点个数的两倍。
eg1(图):
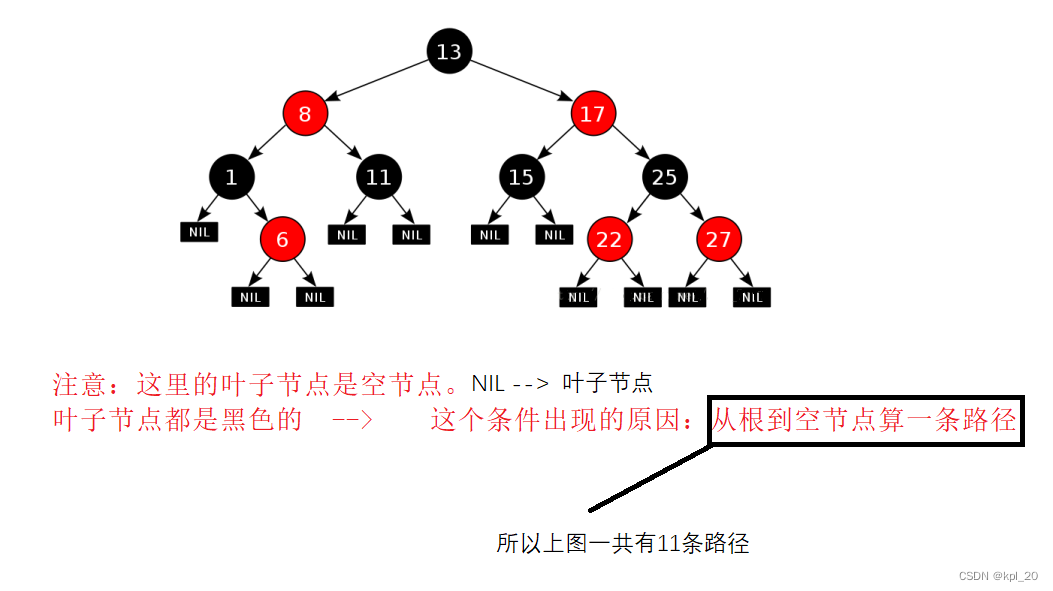
eg2(图):证明没有一条路径会比其它路径长出两倍
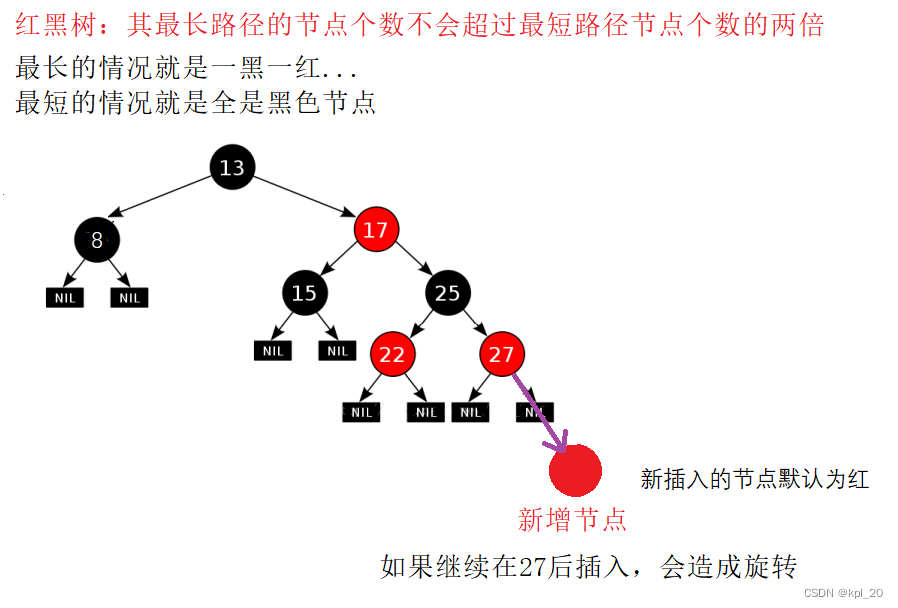
3. 原理
红黑树节点的定义
//节点的颜色
enum Color
{
RED, //红
BLACK //黑
};
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
pair<K, V> _kv;
Color _color;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
,_color(RED)
{}
};
默认约定
新插入的节点,颜色默认为红色
- 不需要调整
如果新插入节点的双亲节点的颜色为黑色,则没有违反红黑树的任何性质。- 需要调整
当新插入节点的双亲节点颜色为红色,违反了红黑树的性质3。
默认约定1:cur为当前节点,p为双亲节点,g为祖父节点,u为叔叔节点
默认约定2:被调节的树,可能是一颗完整的树,也可能是一颗子树。
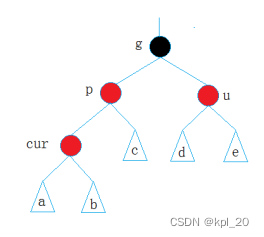
eg: (a,b,c,d,e理解成子树即可)该例符合下述插入的情况一
插入
注意: 如果不违反红黑树规则直接寻找位置插入即可,所以这里只介绍违反规则的情况。
违反规则的情况只需要判断u节点的状态。
原因:插入一个节点受影响的节点有cur,p,g,u四个节点,但是前三个节点的颜色是固定的,cur默认是红色。p如果为黑则不违反规则,所以不需要进行调整。g如果为红则证明插入cur之前这棵树就已经不是红黑树。
情况一 (u存在且为红)
- 被调节的树是一颗完整的树
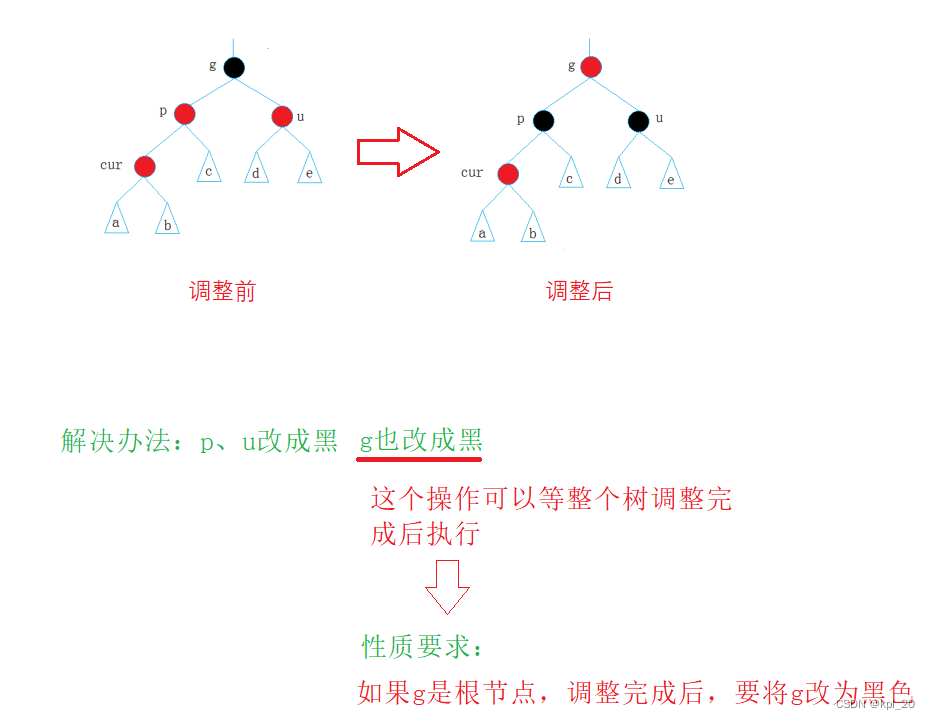
- 被调节的树是一颗子树
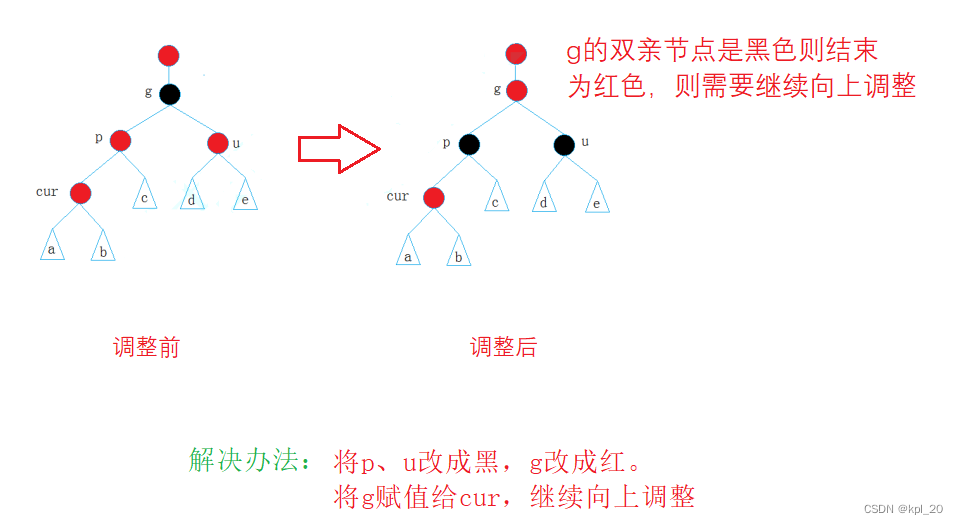
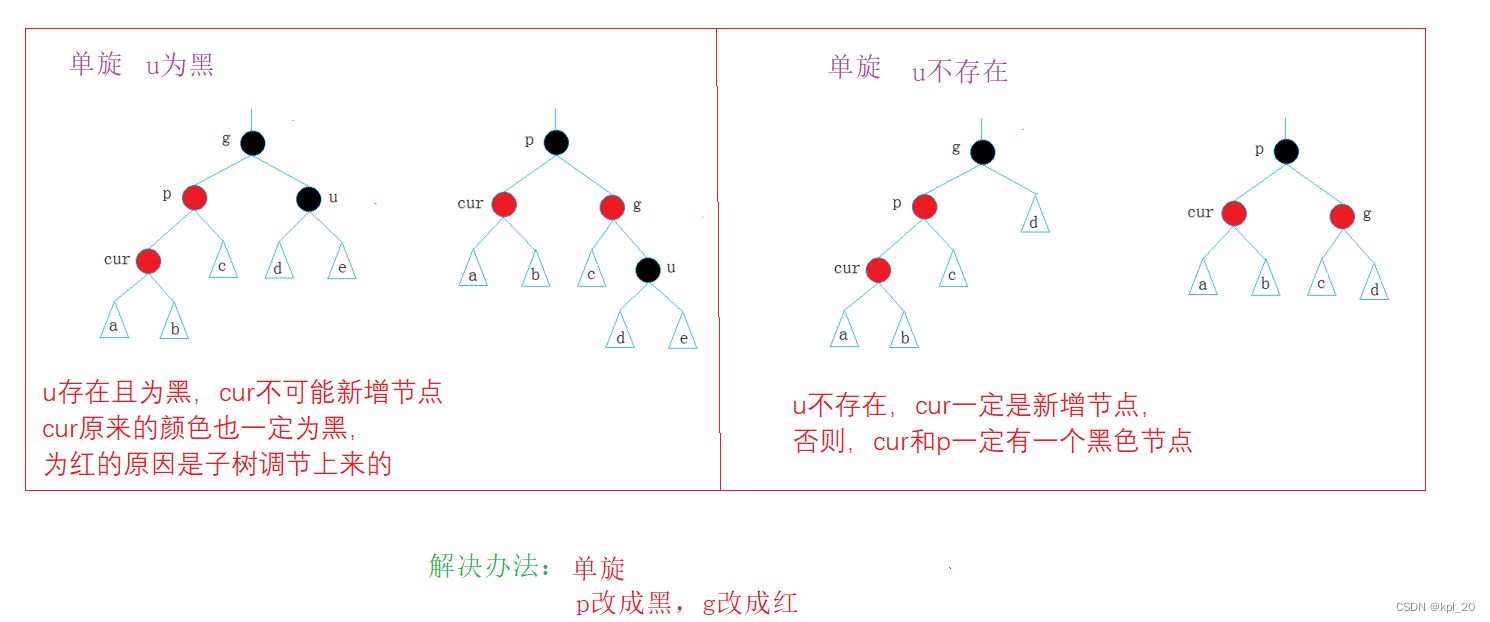
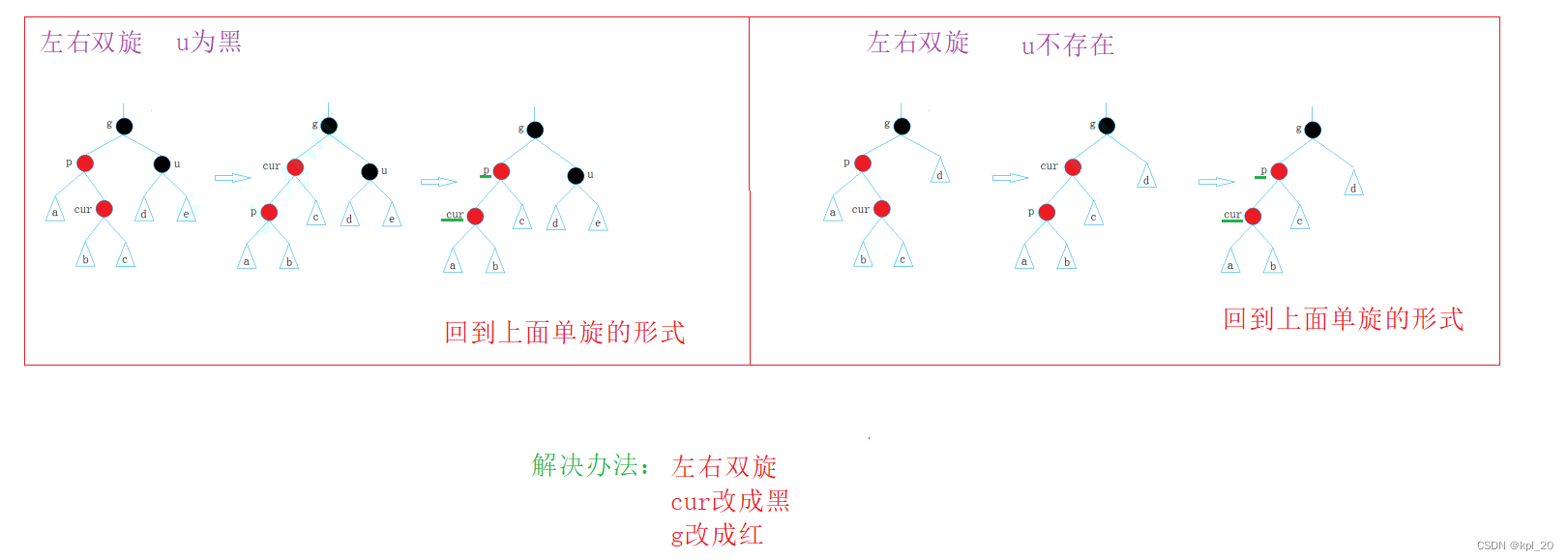
情况二(u不存在或u存在且为黑)
这里只对左单旋进行介绍,右单旋情况同理
这里只对左右双旋进行介绍,右左双旋情况同理
删除
红黑树的删除原理:根据其子节点的情况进行分类讨论。
- 要删除的节点没有子节点,直接将其删除即可。
- 要删除的节点只有一个子节点,将其子节点替代要删除的节点,并将替代节点染成黑色,以保持红黑树的性质。
- 要删除的节点有两个子节点,需要找到其后继节点(即大于该节点值的最小节点)或前驱节点(即小于该节点值的最大节点)来替代要删除的节点。将后继节点或前驱节点的值复制到要删除的节点,并将要删除的节点指向后继节点或前驱节点。接下来,将删除后继节点或前驱节点的问题转化为删除拥有一个或没有儿子节点的情况。在删除后继节点或前驱节点时,如果删除的节点是黑色的,则可能破坏红黑树的性质。为了维持红黑树的性质,需要进行调整操作。
- 根据删除节点的兄弟节点的情况,通过旋转和重新着色等操作重新调整树的结构,即保持红黑树的性质。 在进行旋转和重新着色等调整操作后,最后再删除要删除的节点。
4. 相关的验证测试代码
验证该树是否是红黑树
代码:
//判断该树是不是红黑树
bool IsBalance()
{
return IsBalance(_root);
}
//计算红黑树的高度
int Height()
{
return Height(_root);
}
int Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
//检查颜色
bool CheckColor(Node* root, int blacknum, int benchmark)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (blacknum != benchmark)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//计算每条路径的黑色节点
if (root->_color == BLACK)
{
++blacknum;
}
if (root->_color == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_color == RED)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "出现连续红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return CheckColor(root->_left, blacknum, benchmark)
&& CheckColor(root->_right, blacknum, benchmark);
}
bool IsBalance(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_color != BLACK)
{
return false;
}
//基准值 --> 用于比较别的路径黑色节点个数
int benchmark = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_color == BLACK)
benchmark++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return CheckColor(root, 0, benchmark);
}
5. 红黑树完整实现代码
//节点的颜色
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
pair<K, V> _kv;
Color _color;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
,_color(RED)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_color = BLACK;
return true;
}
//寻找要链接新节点的位置
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//插入节点 + 链接
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_color = RED;
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//调整 这里parent是否为空,是为了下一次循环判断
// 如果parent->_color == BLACK也不用玩了
while (parent && parent->_color == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//u为红
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED)
{
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
//继续向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //u不存在 或 存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p
//c
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
//调整完之后,就不需要继续改变了
break;
}
}
else //grandfather->_right == parent
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//u为红
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED)
{
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
//继续向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //u不存在 或 存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
//g
// p
// c
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
else
{
//g
// p
//c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
//调整完之后,就不需要继续改变了
break;
}
}
}
//根节点的颜色改成黑色
_root->_color = BLACK;
return true;
}
//判断该树是不是红黑树
bool IsBalance()
{
return IsBalance(_root);
}
//计算红黑树的高度
int Height()
{
return Height(_root);
}
private:
int Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
bool CheckColor(Node* root, int blacknum, int benchmark)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (blacknum != benchmark)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//计算每条路径的黑色节点
if (root->_color == BLACK)
{
++blacknum;
}
if (root->_color == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_color == RED)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "出现连续红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return CheckColor(root->_left, blacknum, benchmark)
&& CheckColor(root->_right, blacknum, benchmark);
}
bool IsBalance(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_color != BLACK)
{
return false;
}
//基准值 --> 用于比较别的路径黑色节点个数
int benchmark = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_color == BLACK)
benchmark++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return CheckColor(root, 0, benchmark);
}
//旋转
//都是二叉树的旋转,所以和AVLTree的旋转一样,只不过这里没有平衡因子
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
_rotateCount++;
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
parent->_left = curright;
if (curright)
curright->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
cur->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
_rotateCount++;
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
//重新链接
parent->_right = curleft;
if (curleft)
curleft->_parent = parent;
cur->_left = parent;
//提前保存parent->_parent,可能是根节点,也可能是子树的根节点
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
三、总结
红黑树和AVL树都是高效的平衡二叉树,增删查改的效率都是O(logN),红黑树不追求绝对平衡,只需要保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,相对而言降低了旋转次数。所以红黑树更优一些

![[AI]ChatGPT4 与 ChatGPT3.5 区别有多大](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fa98ee2c1eef427a88412f9bc6483e55.png)