✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌟🌟 无人扶我青云志 🌟🌟
🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀🍀
🌟🌟 我自踏雪之山巅🌟🌟
🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿🌿
✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨✨
✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅✅
🍋顺序表
- 🍌顺序表的定义
- 🍌顺序表的结构
- 🍍静态顺序表
- 🍍动态顺序表
- 🍌顺序表接口的实现(增删查改)
- 🍍其它接口
- 🍍顺序表初始化
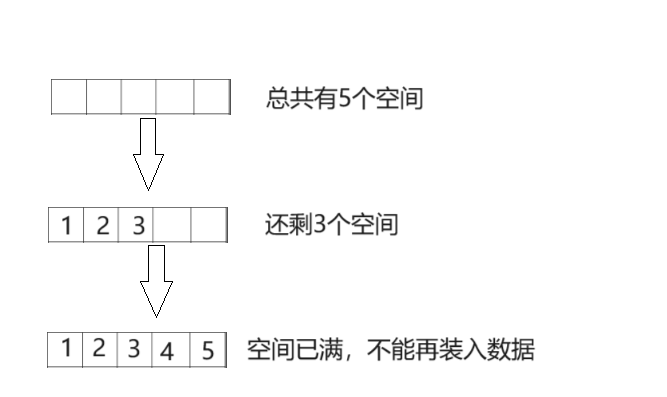
- 🍍检查空间是否增容(空间满了就增容)
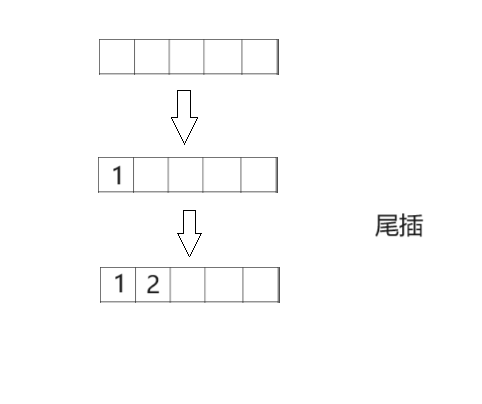
- 🍍顺序表尾插
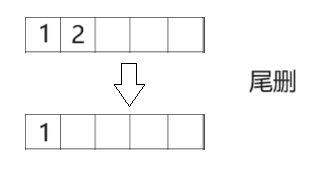
- 🍍顺序表尾删
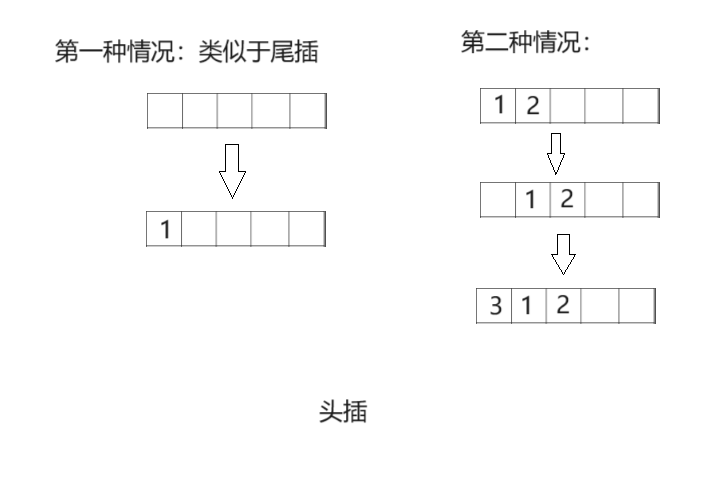
- 🍍顺序表头插
- 🍍顺序表头删
- 🍍顺序表查找
- 🍍顺序表在pos位置插入x
- 🍍顺序表删除pos位置的值
- 🍍顺序表修改pos位置的值
- 🍍顺序表销毁
- 🍍顺序表打印
- 🍌顺序表整体代码的实现
🍌顺序表的定义
顺序表是在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表,线性表的顺序存储是指用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中的各个元素、使得线性表中在逻辑结构上相邻的数据元素存储在相邻的物理存储单元中,即通过数据元素物理存储的相邻关系来反映数据元素之间逻辑上的相邻关系,采用顺序存储结构的线性表通常称为顺序表。顺序表是将表中的结点依次存放在计算机内存中一组地址连续的存储单元中。

线性表:线性表是最基本、最简单、也是最常用的一种数据结构。大部分线性表除了第一个和最后一个数据元素之外,其它数据元素都是首尾相接的。而又一些小部分,比如,循环链表逻辑层次上也是一种线性表(存储层次上属于链式存储,但是把最后一个数据元素的尾指针指向了首位结点
🍌顺序表的结构
🍍静态顺序表
静态顺序表就是以一定长度的数组来存储元素
//静态存储
#define N 5
typedef int SLDetatype ;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDetatype a[N] ;//有限空间的数组
int size ;//有效的数据个数
}SeqList;
🍍动态顺序表
动态顺序表使用动态开辟的数组来存储元素
//动态存储
typedef int SLDetatype ;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDetatype *a ; //指向动态开辟的数组
int size ; //有效的数据个数
int capicity ; //空间的容量
}SeqList;

🍌顺序表接口的实现(增删查改)
🍍其它接口
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDatatype* a;
int capacity;
int size;
}SeqList;
🍍顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
//在初始情况我们可以直接置空
//当然也可以创建空间,看自己习惯
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
🍍检查空间是否增容(空间满了就增容)
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//在两个相等时,空间可能会满,还可能空间为0,这是因为我们在初始化没有创建空间导致
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
if (ps->capacity == 0)
ps->capacity = 2;
else
ps->capacity *= 2;
int newcapacity = ps->capacity;
//在扩容时,我们都是利用realloc,创建空间利用malloc
SLDatatype* cur = (SLDatatype*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDatatype) * newcapacity);
if (cur == NULL)
{
perror("realloc faild");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = cur;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
大家如果对于malloc和realloc以及空间的创建的用法有些遗忘,可以看我这篇博客:动态内存管理(这是一个链接,有需要的朋友可以直接点进去)
🍍顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps); //需要检查空间是否满或者空
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
🍍顺序表尾删
//顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0); //检查数据个数是否为0,如果为0就不执行,反之亦然
(ps->size)--;
}
🍍顺序表头插
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);//判断空间是否满还是空
//注意头插要分两种情况
//第一种是数组里没有元素,此时头插就是相当于尾插
//第二种是数组里有元素,这时就先把整体元素往后移动一位
if (ps->size - 1 == 0)
{
ps->a[ps->size -1] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
else
{
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
}
注意:
注意头插要分两种情况
(1)第一种是数组里没有元素,此时头插就是相当于尾插
(2)第二种是数组里有元素,这时就先把整体元素往后移动一位
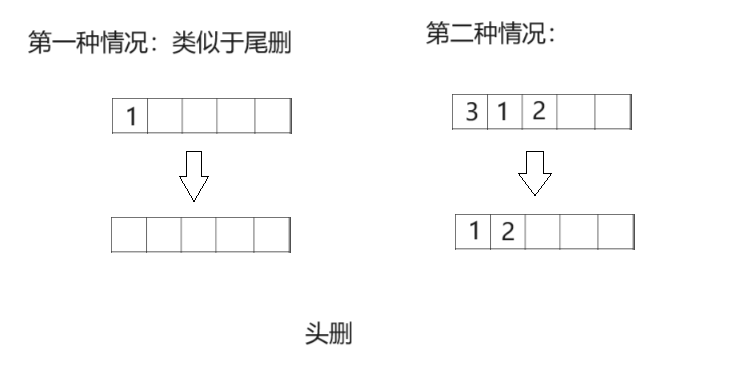
🍍顺序表头删
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
//注意头删要分两种情况
//第一种是数组里没有元素,此时头删就是相当于尾删
//第二种是数组里有元素,这时就需要把除了第一个元素外的所有元素往前移动一位,把原来的第一位元素覆盖
if (ps->size - 1 == 0)
{
(ps->size)--;
}
else
{
int end = 0;
while (end < ps->size - 1)
{
ps->a[end] = ps->a[end + 1];
end++;
}
(ps->size)--;
}
}
注意:
注意头删要分两种情况
(1)第一种是数组里没有元素,此时头删就是相当于尾删
(2)第二种是数组里有元素,这时就需要把除了第一个元素外的所有元素往前移动一位,把原来的第一位元素覆盖
🍍顺序表查找
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
return 1;
}
return -1;
}
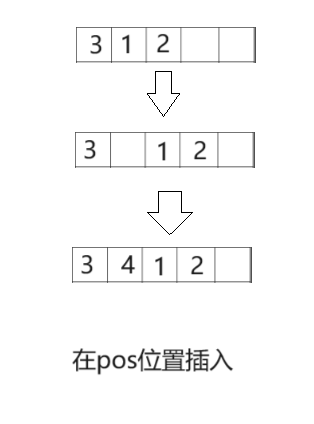
🍍顺序表在pos位置插入x
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
CheckCapacity(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos - 1; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i + 1] = ps->a[i];
}
ps->a[pos-1] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
注意:pos必须在0到ps->size之间
🍍顺序表删除pos位置的值
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos - 1; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
(ps->size)--;
}
注意:pos必须在0到ps->size之间
🍍顺序表修改pos位置的值
//顺序表修改pos位置的值
void SeqModify(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
ps->a[pos - 1] = x;
}
🍍顺序表销毁
// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
🍍顺序表打印
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
🍌顺序表整体代码的实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDatatype* a;
int capacity;
int size;
}SeqList;
//顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
//检查空间,如果满了就增容
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
if (ps->capacity == 0)
ps->capacity = 2;
else
ps->capacity *= 2;
int newcapacity = ps->capacity;
SLDatatype* cur = (SLDatatype*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDatatype) * newcapacity);
if (cur == NULL)
{
perror("realloc faild");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = cur;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
//顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
//顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
(ps->size)--;
}
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
if (ps->size == 0)
{
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
else
{
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
}
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
if (ps->size - 1 == 0)
{
(ps->size)--;
}
else
{
int end = 0;
while (end < ps->size - 1)
{
ps->a[end] = ps->a[end + 1];
end++;
}
(ps->size)--;
}
}
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
return 1;
}
return -1;
}
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
CheckCapacity(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos - 1; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i + 1] = ps->a[i];
}
ps->a[pos-1] = x;
(ps->size)++;
}
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos - 1; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
(ps->size)--;
}
// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//顺序表修改pos位置的值
void SeqModify(SeqList* ps, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
ps->a[pos - 1] = x;
}
void test1()
{
SeqList cur;
SeqListInit(&cur);
SeqListPushBack(&cur, 500);//尾插
SeqListPushBack(&cur, 400);//尾插
SeqListPushBack(&cur, 300);//尾插
SeqListPrint(&cur);
SeqListPopBack(&cur);//尾删
SeqListPrint(&cur);
SeqListPushFront(&cur, 100);//头插
SeqListPushFront(&cur, 200);//头插
SeqListPushFront(&cur, 600);//头插
SeqListPrint(&cur);
SeqListPopFront(&cur); //头删
SeqListPrint(&cur);
if (SeqListFind(&cur,200) == 1)//元素查找
printf("找到了\n");
else
{
printf("没有找到\n");
}
SeqListInsert(&cur, 3, 999);//在pos位置插入x
SeqListPrint(&cur);
SeqListErase(&cur, 3);//删除pos位置的值
SeqListPrint(&cur);
SeqModify(&cur, 3, 666); //修改pos位置的值
SeqListPrint(&cur);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}