目录
一、ransac算法原理
1.1、算法概念
1.2、图解
二、c++实现ransac
2.1、设置随机样本和离群点
2.2、随机抽取样本
2.3、内点计算
2.4、更新参数
2.2、完整代码
一、ransac算法原理
1.1、算法概念
随机抽样一致性 (RANSAC) 是一种迭代方法,用于根据一组包含异常值的观测数据来估计数学模型的参数,此时异常值不会对估计值产生影响。 因此,它也可以解释为一种异常值检测方法,说白了就是能剔除异常的、离群的样本。 它是一种非确定性算法,因为它仅以一定的概率产生合理的结果,并且随着允许更多迭代,该概率会增加,说白了就是由于每次随机抽取样本,最终都会得到更好的结果,但是每次执行整个ransac算法,最终结果会有略微差异。 该算法最初由 Fischler 和 Bolles 在 SRI International 于 1981 年发布。他们使用 RANSAC 来解决位置确定问题 (LDP),其目标是确定空间中投影到图像上的点,形成一组地标 已知地点。
一个基本假设是数据由“内点”和“离群值”组成,“内点”是指其分布可以通过某些模型参数集来解释的数据,尽管可能会受到噪声的影响;“离群值”是不适合模型的数据。 例如,异常值可能来自噪声的极值、错误的测量或有关数据解释的错误假设。 RANSAC 还假设,给定一组(通常很小的)内点,存在一个可以估计模型参数的过程,该模型可以最佳地解释或拟合该数据。
伪代码:
Given:
data – a set of observations
model – a model to explain observed data points
n – minimum number of data points required to estimate model parameters
k – maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm
t – threshold value to determine data points that are fit well by model
d – number of close data points required to assert that a model fits well to data
Return:
bestFit – model parameters which best fit the data (or nul if no good model is found)
iterations = 0
bestFit = nul
bestErr = something really large
while iterations < k {
maybeInliers = n randomly selected values from data
maybeModel = model parameters fitted to maybeInliers
alsoInliers = empty set
for every point in data not in maybeInliers {
if point fits maybeModel with an error smaller than t
add point to alsoInliers
}
if the number of elements in alsoInliers is > d {
% this implies that we may have found a good model
% now test how good it is
betterModel = model parameters fitted to all points in maybeInliers and alsoInliers
thisErr = a measure of how well betterModel fits these points
if thisErr < bestErr {
bestFit = betterModel
bestErr = thisErr
}
}
increment iterations
}
return bestFit1.2、图解
如下图,以直线拟合为例子,假如给定N个点,求解直线方程y=kx+b。这里使用ransac算法求解直线方程参数k、b,主要思想如下:
- step1:随机选取两个样本点,如图红点
- step2:计算直线方程参数ki、bi,得到直线记为Li,此时有k=ki,b=bi
- step3:计算其余所有点到直线Li的距离,距离Li足够近的点为内点(inliers),比较远的点为外点(outliers)
- step4:执行step1、step2得到直线Lj(对应方程参数kj、bj);执行step3得到的inliers如果大于直线Li,那么更新参数为:k=kj,b=bj。
依次类推,最多循环迭代100次,只要下一次计算得到直线比上一次更优,那就更新参数k、b;直到内点比例足够高或者循环到100次了为止。

二、c++实现ransac
依赖opencv的一点点数据结构,你也可以自己去掉。
2.1、设置随机样本和离群点
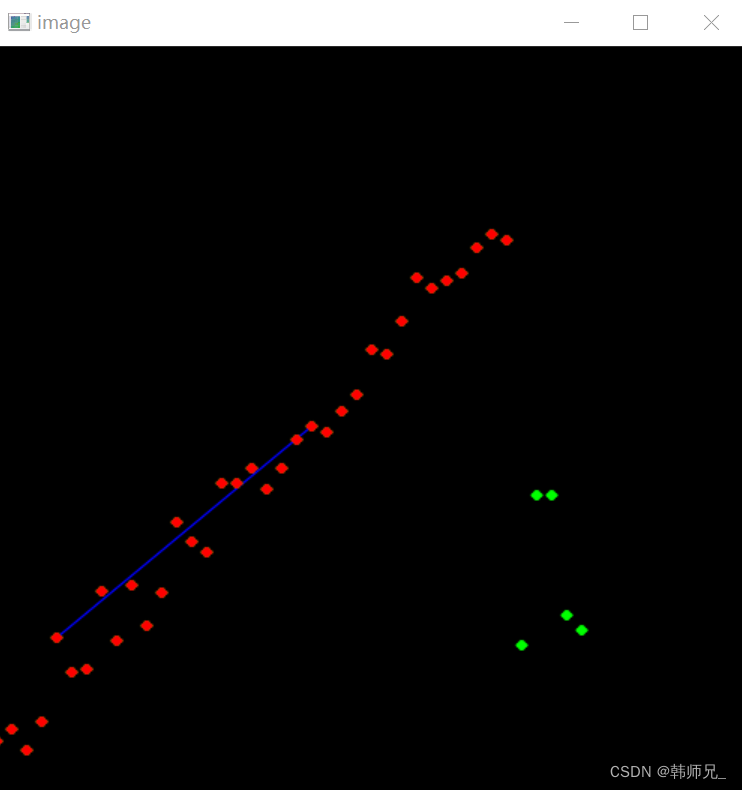
如下图,红色点就是样本点,绿色的就是离群点
// time seed
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr));
// <1>产生随机数
vector<Point2d> points;
// 精确解
const int k = 1;
const int b = 10;
// x [0, 390]; y [10, 400] total_numbers = 40
for (int x = 0; x < 400; x += 10)
{
points.push_back(Point2d(x, k * x + b + Ransac::getRand(0, 60)));
}
//添加离群点
points[35].y = 100;
points[36].y = 200;
points[37].y = 200;
points[38].y = 120;
points[39].y = 110;2.2、随机抽取样本
随机选取两个样本点的索引。
// <1>、随机抽取两个样本
int index_first = Ransac::getRand(0, points.size() - 2);
int index_second = Ransac::getRand(0, points.size() - 2);
sample_first = points[index_first];
sample_second = points[index_second];2.3、内点计算
y_error实在计算点到直线距离,如果小于y_threshold,也就是内点inliers。
// <2>、根据距离,来找出所有样本点中的内点,并统计数量
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
// delta = k * x + b - y
double y_error = abs(k_estimate * points[i].x + b_estimate - points[i].y) / sqrt((pow(k_estimate, 2) + 1));
//cout << "y_error = " << y_error << endl;
if (y_error < y_threshold)
{
count++;
}
}2.4、更新参数
如果当前迭代比上一轮内点要多,那直接当当前迭代对应参数更新为最优解
// <3>、找出内点数量最多的那一组
if (count > total)
{
total = count;
best_sample_first = sample_first;
best_sample_second = sample_second;
best_parameters.x = k_estimate;
best_parameters.y = b_estimate;
}2.2、完整代码
需要说明:
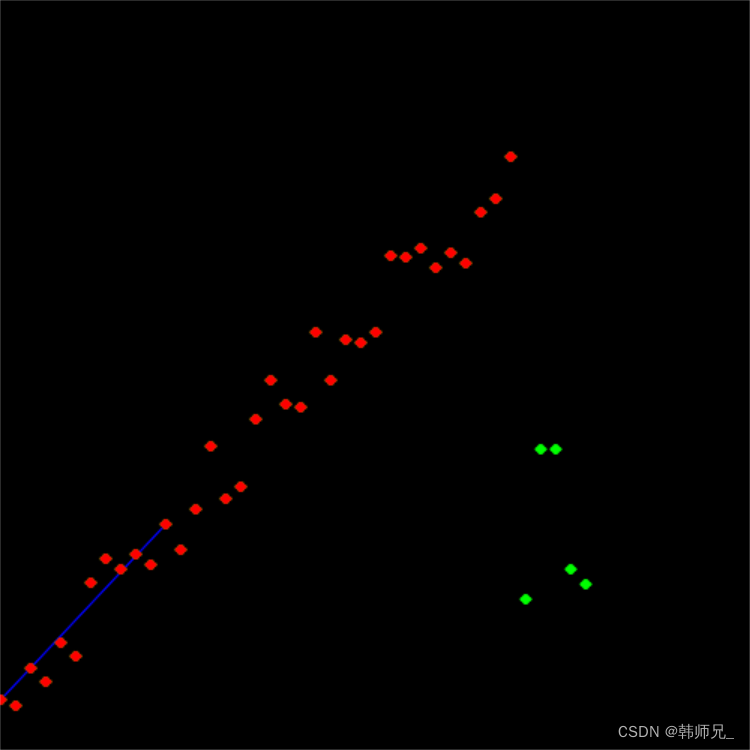
- ransac每次结果不一样,但是总是能计算得到好的解;
- 以下代码在画直线的时候没有画得很长,并不影响算法,只是懒得画而已。

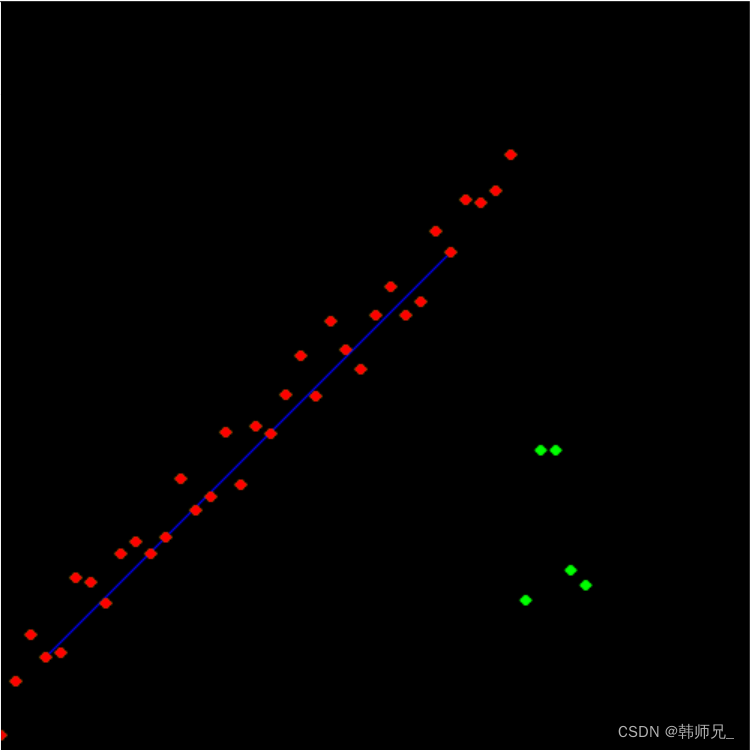
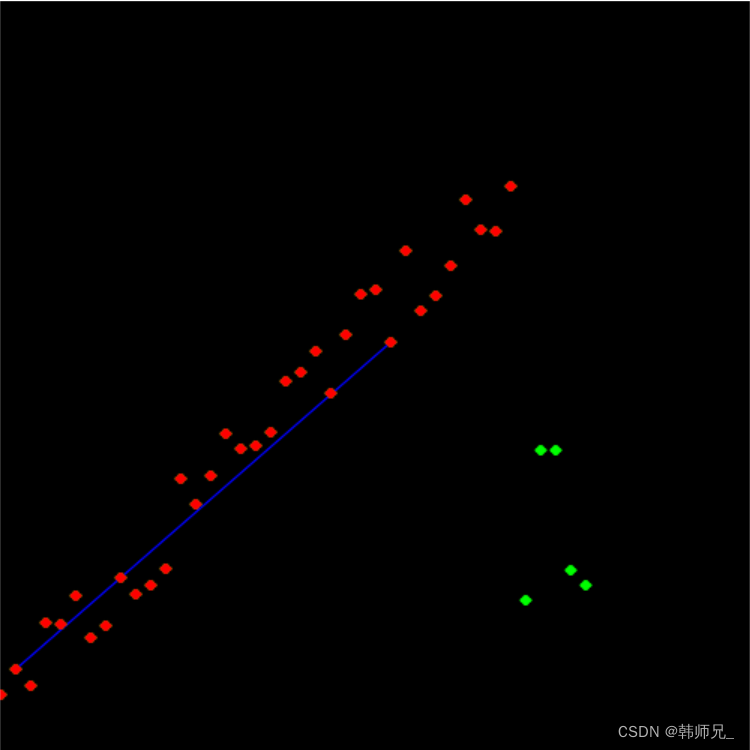
完整代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
// 功能:画点
void drawPoints(vector<Point2d> points, Mat& image, bool is_green)
{
if (is_green)
{
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
circle(image, Point2i(int(points[i].x), int(points[i].y)), 2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, LINE_AA);
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
circle(image, Point2i(int(points[i].x), int(points[i].y)), 2, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA);
}
}
}
// 功能:画线
void drawLine(Point2d begin, Point2d end, Mat& image)
{
line(image, Point2i(int(begin.x), int(begin.y)),
Point2i(int(end.x), int(end.y)), Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, LINE_AA);
}
// 功能:将一张图经行纵向镜像
void upDownMirror(Mat& image)
{
Mat image_cpy = image.clone();
for (int j = 0; j < image.rows; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < image.cols; i++)
{
image.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(j)[i] = image_cpy.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(image.rows - 1 - j)[i];
}
}
}
// 功能:最简单的直线拟合 Ransac 框架
class Ransac
{
public:
Ransac(vector<double> x, vector<double> y);
~Ransac();
static int getRand(int min, int max);//[min, min + max - 1]
public:
vector<double> x_, y_;
};
Ransac::Ransac(vector<double> x, vector<double> y) :x_(x), y_(y)
{
}
Ransac::~Ransac()
{
}
int Ransac::getRand(int min, int max)//[min, min + max - 1]
{
return rand() % max + min;
}
int main()
{
// time seed
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr));
// <1>产生随机数
vector<Point2d> points;
// 精确解
const int k = 1;
const int b = 10;
// x [0, 390]; y [10, 400] total_numbers = 40
for (int x = 0; x < 400; x += 10)
{
points.push_back(Point2d(x, k * x + b + Ransac::getRand(0, 60)));
}
//添加离群点
points[35].y = 100;
points[36].y = 200;
points[37].y = 200;
points[38].y = 120;
points[39].y = 110;
const int itr_nums = 300;
double k_estimate = 0;
double b_estimate = 0;
Point2d best_parameters; // [k, b]
// 统计纵向距离 y
int count = 0; // 内点计数器
int y_threshold = 50; // 判定内点的阈值
int total = 0; // 内点总数
//样本点
Point2d sample_first;
Point2d sample_second;
// 最佳样本点
Point2d best_sample_first;
Point2d best_sample_second;
for (int i = 0; i < itr_nums; i++)
{
// <1>、随机抽取两个样本
int index_first = Ransac::getRand(0, points.size() - 2);
int index_second = Ransac::getRand(0, points.size() - 2);
sample_first = points[index_first];
sample_second = points[index_second];
if (sample_first == sample_second)
{
continue;
}
// 计算斜率 k = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)
k_estimate = (sample_second.y - sample_first.y) / (sample_second.x - sample_first.x);
// 计算截距 b = y1 - k * x1
b_estimate = sample_first.y - k_estimate * sample_first.x;
// <2>、根据距离,来找出所有样本点中的内点,并统计数量
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
// delta = k * x + b - y
double y_error = abs(k_estimate * points[i].x + b_estimate - points[i].y) / sqrt((pow(k_estimate, 2) + 1));
//cout << "y_error = " << y_error << endl;
if (y_error < y_threshold)
{
count++;
}
}
// <3>、找出内点数量最多的那一组
if (count > total)
{
total = count;
best_sample_first = sample_first;
best_sample_second = sample_second;
best_parameters.x = k_estimate;
best_parameters.y = b_estimate;
}
count = 0;
}
cout << "内点数 = " << total << endl;
cout << "斜率 k = " << best_parameters.x << "截距 b = " << best_parameters.y << endl;
// 统计内点
vector<Point2d> inliners_points;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
// delta = k * x + b - y
double y_error = abs(best_parameters.x * points[i].x + best_parameters.y - points[i].y) / sqrt((pow(k_estimate, 2) + 1));
//cout << "y_error = " << y_error << endl;
if (y_error < y_threshold)
{
inliners_points.push_back(points[i]);
}
}
Mat image = Mat::zeros(500, 500, CV_8UC3);
drawLine(best_sample_first, best_sample_second, image);
drawPoints(points, image, true);
drawPoints(inliners_points, image, false); //画内点
upDownMirror(image);
imshow("image", image);
waitKey(0);
return 1;
}