目录
前言:
一:单链表的特点
编辑 二:单链表实现
单链表定义
2.1申请节点(初始化)
2.2单链表尾插
编辑 2.3单链表打印
2.4单链表头插
2.5单链表尾删
2.6单链表头删
2.7单链表查找
2.8在目标位置后面插入
2.9删除目标位置后面的值
2.10在目标位置前插入
2.11删除目标位置
2.12单链表销毁
总代码
test.c
SList.c
SList.h
前言:
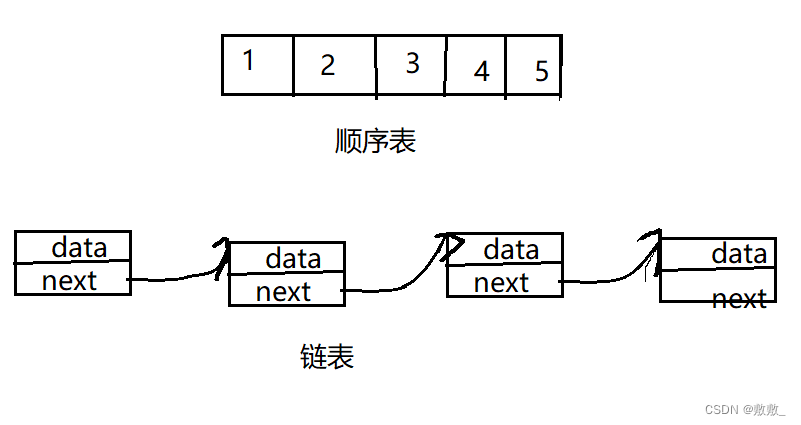
因为顺序进行插入删除时,有时候需要移动大量数据,造成不便,影响了运行效率。这时候引出了它的黄金搭档 单链表;
单链表:通过一组任意的存储单元来存储线性表中的数据元素,不需要使用地址连续的存储单元,因此它不要求在逻辑上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻。
一:单链表的特点
- 单链表不要求逻辑上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻,因此不需要连续的存储空间。
- 单链表是非随机的存储结构,即不能直接找到表中某个特定的结点。查找某个特定的结点时,需要从表头开始遍历,依次查找。
- 优点:支持动态内存分配。由于单链表不需要预先分配一段连续的空间,因此可以根据实际需求动态地申请、释放节点空间,避免浪费内存。支持高效的插入、删除操作。由于单链表中的节点是通过指针相连的,因此在插入、删除一个节点时,只需要修改其前驱节点或后继节点的指针即可,时间复杂度为O ( 1 )
- 缺点:不支持随机访问。由于单链表中的节点不是连续存储的,因此不能像数组一样通过下标来直接访问一个元素,需要从头节点开始遍历整个链表才能访问任意位置的元素。
 二:单链表实现
二:单链表实现
单链表定义
每个链表结点,除了存放元素自身的信息外,还需要存放一个指向其后继的指针
单链表功能实现中,需要考虑三种情况:链表为空,一个节点,多个节点
typedef int SLNDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode //定义单链表结点类型
{
struct SListNode* next; //数据域,可以是别的各种数据类型
SLNDatatype val; //指针域
}SLNode;
2.1申请节点(初始化)
malloc出来一块地址,将有效值赋给val,next给NULL
malloc动态开辟的地址,在程序结束前,都需要进行free释放;
然会该节点的地址
//申请一个节点
SLNode* CreateNode(SLNDatatype x)
{
SLNode* newnode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}2.2单链表尾插
我们需要改变该链表,传的是地址,形参接受应该为二级指针;
单链表功能实现中,需要考虑三种情况:链表为空,一个节点,多个节点
如果是空,直接将新节点赋给第一个节点
如果是一个及以上节点,找到链表尾部后,指针域next链接新节点数据域data
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pplist, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pplist);
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = newnode;
}
else
{
//找尾
SLNode* tail = *pplist;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
} 2.3单链表打印
2.3单链表打印
在【C】系列中,讲过结构体不管是修改还是打印,最好都传地址来操作,这样不需要额外开辟空间
assert():
断言判断中,其实pplist这个不会为NULL,因为*pplist是地址,哪怕这个地址指向的也是NULL,但是该pplist不为NULL;
assert():
断言是判断不允许为NULL的情况,比如链表为空,还要删除的这类情况;
在打印中:
将下一个地址赋给当前地址,进行遍历操作,和之前的自增++这类不同,因为链表空间不是连续存放的
//打印单链表
void SListPrint(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
//遍历打印
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
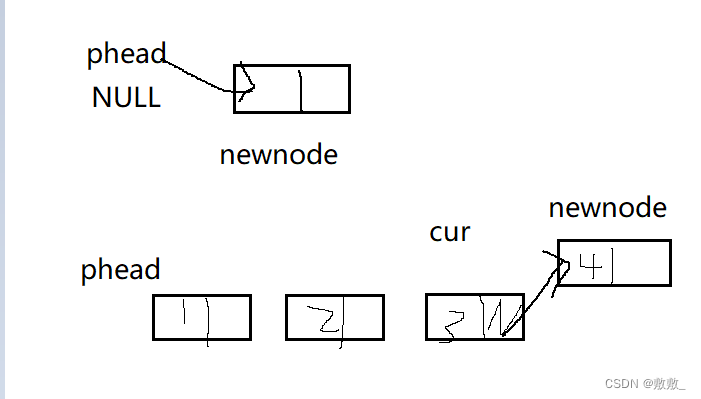
}2.4单链表头插
头部插入不管是空链表还是多个节点,将新链表链接到第一个节点即可
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pplist, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pplist);
SLNode* phead = *pplist;
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
newnode->next = *pplist;
*pplist = newnode;
}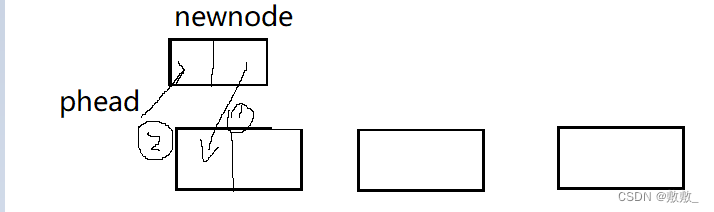
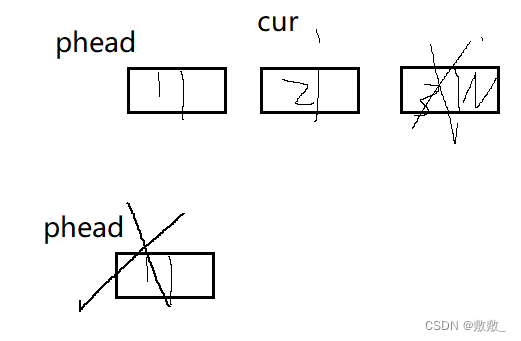
2.5单链表尾删
需要考虑两种情况
一个节点:将该节点删除释放即可;
两个及以上节点:循环找到下下个节点为空的节点,将其删除释放;
也可以定义一个指针 prev:该指针作用是 当cur的下一个节点不等于空时, 记录此位置,如此循环直到找到下一个节点为空,将其cur释放删除,再将prev定义为新的尾,next置NULL;
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
assert(*pplist);
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
//1.一个节点
if ((*pplist)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pplist);
*pplist = NULL;
}
//2.一个以上的节点
else
{
// 找尾
/*SLNode* prev = NULL;
SLNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;*/
while (cur->next->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
free(cur->next);
cur->next = NULL;
}
}
2.6单链表头删
检查断言后,记录第一个节点位置,将第二个节点赋给第一个节点,再释放记录的位置;
可满足一个节点和多个节点
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
assert(*pplist);
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
*pplist = (*pplist)->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
2.7单链表查找
查找单链表是否存在此val,存在返回该指针,不存在返回null;
需要注意的是返回的是该指针,而不是该值;后面功能用指针传递更好,在C++库中也是这样定义的,我们可以统一
// 单链表查找
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* plist, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(plist);
SLNode* cur= plist;
while (cur) //遍历查找
{
if (cur->val == x)
{
return cur;
}
else
{
cur= cur->next;
}
}
return NULL;
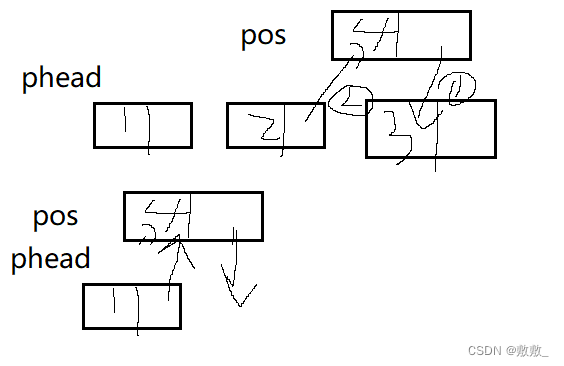
}2.8在目标位置后面插入
创建新节点空间后,将newnode链接到原链表尾,这里需要顺序关系,先链接尾部,再将newnode地址链接到原链表尾部
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pos);
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
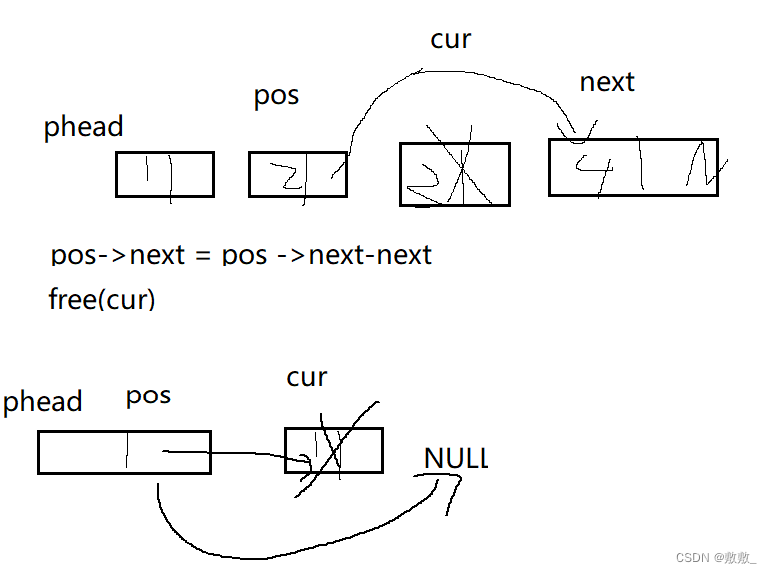
2.9删除目标位置后面的值
删除pos后面,将pos的next记录,再将链表跨过链接,释放记录值
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
pos位置后还有两个及以上值
//if (pos->next->next != NULL)
//{
// SLNode* cur = pos->next; //cur是要删除的位置
// SLNode * next = pos->next->next; //pos链接下一个位置
//
// pos->next = next;
// free(cur);
// cur = NULL;
//}
pos位置后只有一个或者没有值
//else
//{
// free(pos->next);
// pos->next = NULL;
//}
SLNode* cur = pos->next;
pos->next = pos->next->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
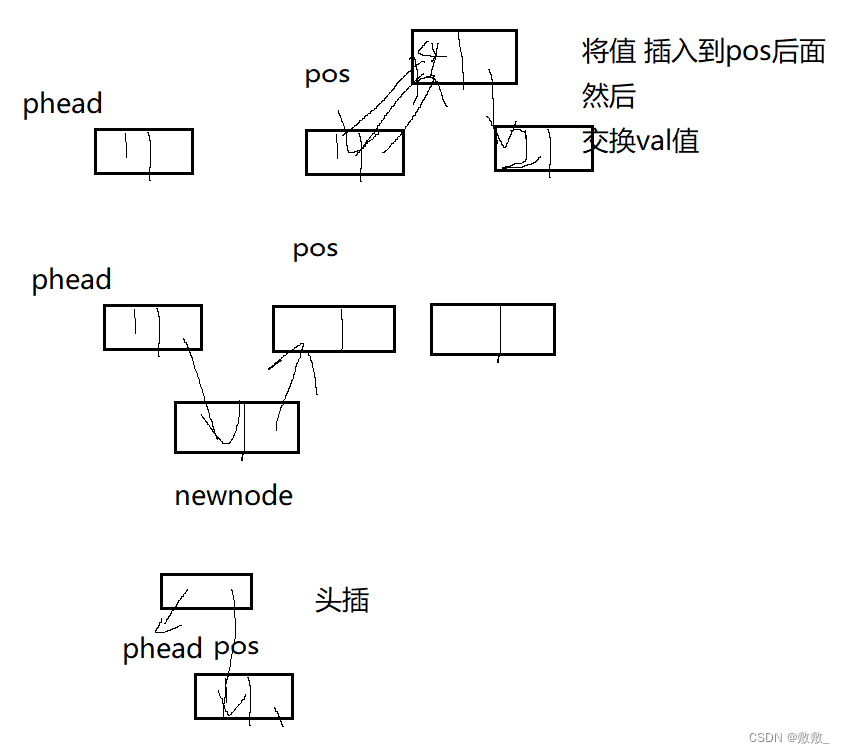
2.10在目标位置前插入
精确断言判定后,分成两种情况;
pos为第一个节点: 该操作类似 单链表头插入,调用该函数即可;
pos在链表其他位置:先循环next找,与上同理,注意链接的先后顺序;
这里其实还有一种方式,就是将新节点插入到pos位置后,然后将pos的val值和newnode的val值进行交换即可;
// 在pos的前面插入
void SLTInsert(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
//pos在头节点
if (pos == cur)
{
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
while (cur)
{
if (cur->next == pos) //找到pos位置 前
{
newnode->next = pos;
cur->next = newnode;
return;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
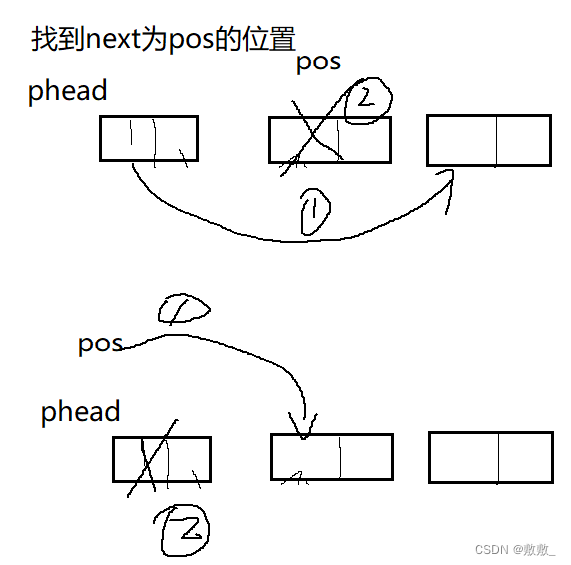
2.11删除目标位置
与上同理分两种情况:
pos为第一个节点:类似头删除;
pos在其他位置:记录覆盖即可
// 删除pos位置
void SLTErase(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
//
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
//while (cur)
//{
// if (pos == cur)
// {
// cur = cur->next;
// free(pos);
// pos = NULL;
// return;
// }
// if (cur->next == pos)
// {
// cur->next = cur->next->next;
// free(pos);
// pos = NULL;
// return;
// }
// else
// {
// cur = cur->next;
// }
//}
if (pos == *pphead)
{
//头删
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}
2.12单链表销毁
因为链表是动态开辟空间,在最后需要释放置NULL;
void SLTDestroy(SLNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
SLNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}总代码
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SList.h"
void test1()
{
SLNode* s = NULL;
SListPushBack(&s, 1);
SListPushBack(&s, 2);
SListPushBack(&s, 3);
SListPrint(&s);
SListPushFront(&s, 5);
SListPrint(&s);
}
void test2()
{
SLNode* s = NULL;
SListPushBack(&s, 1);
SListPushBack(&s, 2);
SListPushBack(&s, 3);
SListPrint(&s);
SListPopBack(&s);
SListPrint(&s);
SListPopFront(&s);
SListPrint(&s);
SListPopFront(&s);
SListPrint(&s);
}
void test3()
{
SLNode* s = NULL;
SListPushBack(&s, 1);
SListPushBack(&s, 2);
SListPushBack(&s, 3);
SListPrint(&s);
SLNode* pos = SListFind(s, 1);
SListInsertAfter(pos, 4);
SListPrint(&s);
}
void test4()
{
SLNode* s = NULL;
SListPushBack(&s, 1);
SListPushBack(&s, 2);
SListPushBack(&s, 3);
SListPushBack(&s, 4);
SListPushBack(&s, 5);
SListPrint(&s);
SLNode* pos = SListFind(s, 2);
SListEraseAfter(pos);
SListPrint(&s);
}
void test5()
{
SLNode* s = NULL;
SListPushBack(&s, 1);
SListPushBack(&s, 2);
SListPushBack(&s, 3);
SListPrint(&s);
SLNode* pos = SListFind(s, 2);
SLTInsert(&s,pos,6);
SListPrint(&s);
SLTErase(&s,pos);
SListPrint(&s);
}
int main()
{
//test1();
//test2();
//test3();
//test4();
test5();
return 0;
}SList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SList.h"
//申请一个节点
SLNode* CreateNode(SLNDatatype x)
{
SLNode* newnode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pplist, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pplist);
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = newnode;
}
else
{
//找尾
SLNode* tail = *pplist;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
//打印单链表
void SListPrint(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
//遍历打印
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pplist, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pplist);
SLNode* phead = *pplist;
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
newnode->next = *pplist;
*pplist = newnode;
}
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
assert(*pplist);
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
//1.一个节点
if ((*pplist)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pplist);
*pplist = NULL;
}
//2.一个以上的节点
else
{
// 找尾
/*SLNode* prev = NULL;
SLNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;*/
while (cur->next->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
free(cur->next);
cur->next = NULL;
}
}
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pplist)
{
assert(pplist);
assert(*pplist);
SLNode* cur = *pplist;
*pplist = (*pplist)->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
// 单链表查找
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* plist, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(plist);
SLNode* cur = plist;
while (cur) //遍历查找
{
if (cur->val == x)
{
return cur;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pos);
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
pos位置后还有两个及以上值
//if (pos->next->next != NULL)
//{
// SLNode* cur = pos->next; //cur是要删除的位置
// SLNode * next = pos->next->next; //pos链接下一个位置
//
// pos->next = next;
// free(cur);
// cur = NULL;
//}
pos位置后只有一个或者没有值
//else
//{
// free(pos->next);
// pos->next = NULL;
//}
SLNode* cur = pos->next;
pos->next = pos->next->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
// 在pos的前面插入
void SLTInsert(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos, SLNDatatype x)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
SLNode* newnode = CreateNode(x);
//pos在头节点
if (pos == cur)
{
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
while (cur)
{
if (cur->next == pos) //找到pos位置 前
{
SLNode* prev = cur;
newnode->next = pos;
cur->next = newnode;
return;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
// 删除pos位置
void SLTErase(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
//
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
//while (cur)
//{
// if (pos == cur)
// {
// cur = cur->next;
// free(pos);
// pos = NULL;
// return;
// }
// if (cur->next == pos)
// {
// cur->next = cur->next->next;
// free(pos);
// pos = NULL;
// return;
// }
// else
// {
// cur = cur->next;
// }
//}
if (pos == *pphead)
{
//头删
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = cur->next->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}
void SLTDestroy(SLNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
SLNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}SList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SLNDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode //链表定义
{
struct SListNode* next;
SLNDatatype val;
}SLNode;
// 动态申请一个节点
SLNode* CreateNode(SLNDatatype x);
// 单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SLNode** pplist, SLNDatatype x);
//打印单链表
void SListPrint(SLNode** phead);
// 单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SLNode** pplist, SLNDatatype x);
// 单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SLNode** pplist);
// 单链表头删
void SListPopFront(SLNode** pplist);
// 单链表查找
SLNode* SListFind(SLNode* plist, SLNDatatype x);
// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SListInsertAfter(SLNode* pos, SLNDatatype x);
// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SLNode* pos);
// 在pos的前面插入
void SLTInsert(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos, SLNDatatype x);
// 删除pos位置
void SLTErase(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos);
//销毁单链表
void SLTDestroy(SLNode** pphead);以上就是我对单链表的理解和功能实现介绍,身为初学者,作者能力有限,文中不对的地方,需要改进的地方,还望各位指点,感激不尽!!!