*本文是博主对Java各种实验的再整理与详解,除了代码部分和解析部分,一些题目还增加了拓展部分(⭐)。拓展部分不是实验报告中原有的内容,而是博主本人自己的补充,以方便大家额外学习、参考。
(解析部分还没加,过几天补)
目录
一、实验目的
二、实验内容
1、字符串加密
2、模拟用户登录
3、统计字符个数
4、字符串缓冲区练习
(1)使用StringBuffer类对键盘输入的字符串进行反转。
(2)使用String和StringBuffer类分别对数组进行字符串拼接,使其变成一个字符串。
5、生成验证码
6、春节倒计时
7、二月天
8、正则表达式。(选做)
三、实验总结
一、实验目的
1、掌握String、StringBuffer和StringBuilder类的使用;
2、掌握System和Runtime类的使用;
3、掌握Math和Random类的使用;
4、掌握日期时间类的使用;
5、掌握包装类的使用;
6、了解正则表达式的使用。
二、实验内容
1、字符串加密
键盘输入一个原始字符串作为明文,然后使用加密方法加密,再对加密字符串进行解密。样例如下图,加密方法自定,完成其功能并测试。

源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class S5_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("明文:");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String x = in.nextLine();
System.out.println("***************************");
System.out.println("加密方法:每个字符的ASCII码加1");
System.out.println("***************************");
System.out.print("密文:");
char[] a = x.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] += 1;
System.out.print(a[i]);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("***************************");
System.out.print("解密:");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] -= 1;
System.out.print(a[i]);
}
}
}列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

2、模拟用户登录
编写一个程序,模拟用户登录。程序要求如下:
(1)用户名和密码正确(不区分大小写),提示“登录成功”,并打开Windows的计算器程序;
(2)用户名或密码不正确,提示“用户名或密码错误”;
(3)总共有3次登录机会,超过3次,则提示“登录失败,无法再继续登录”。
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class S5_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 定义正确的用户名和密码(不区分大小写)
String correctUsername = "admin";
String correctPassword = "password";
// 设置最大登录次数
int maxLoginAttempts = 3;
int remainingLoginAttempts = maxLoginAttempts;
// 循环进行用户登录
while (remainingLoginAttempts > 0) {
// 用户输入用户名和密码
System.out.print("请输入用户名:");
String username = scanner.nextLine().toLowerCase(); // 将用户名转换为小写进行不区分大小写比较
System.out.print("请输入密码:");
String password = scanner.nextLine();
// 验证用户名和密码
if (username.equals(correctUsername) && password.equals(correctPassword)) {
System.out.println("登录成功!正在打开Windows的计算器程序...");
// 在这里可以添加打开计算器程序的代码
break; // 登录成功,跳出循环
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误。剩余登录次数:" + (--remainingLoginAttempts));
if (remainingLoginAttempts > 0) {
System.out.println("请重新输入。\n");
} else {
System.out.println("登录失败,无法再继续登录。");
}
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
输入错误的情况:

输入正确的情况:

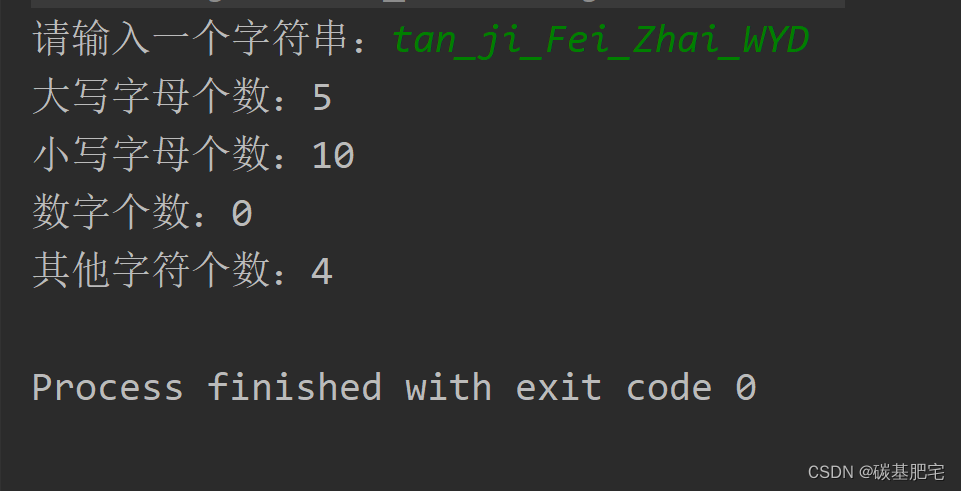
3、统计字符个数
从键盘输入一个字符串,分别统计该字符串中所有大写字母、小写字母、数字、其它字符的个数,并分类输出这些字符和统计结果。(提示:不考虑字符内容,例如:Hello123World,大写2个,小写8个,数字3个。)
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class S5_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 从键盘输入字符串
System.out.print("请输入一个字符串:");
String inputString = scanner.nextLine();
// 统计字符个数
int uppercaseCount = 0;
int lowercaseCount = 0;
int digitCount = 0;
int otherCount = 0;
// 遍历字符串中的每个字符
for (char ch : inputString.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(ch)) {
uppercaseCount++;
} else if (Character.isLowerCase(ch)) {
lowercaseCount++;
} else if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
digitCount++;
} else {
otherCount++;
}
}
// 输出统计结果
System.out.println("大写字母个数:" + uppercaseCount);
System.out.println("小写字母个数:" + lowercaseCount);
System.out.println("数字个数:" + digitCount);
System.out.println("其他字符个数:" + otherCount);
scanner.close();
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
4、字符串缓冲区练习
(1)使用StringBuffer类对键盘输入的字符串进行反转。
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class S5_4_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 从键盘输入字符串
System.out.print("请输入一个字符串:");
String inputString = scanner.nextLine();
// 使用StringBuffer进行字符串反转
StringBuffer reversedStringBuffer = new StringBuffer(inputString);
reversedStringBuffer.reverse();
// 输出反转后的字符串
System.out.println("反转后的字符串:" + reversedStringBuffer.toString());
scanner.close();
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图: 
(2)使用String和StringBuffer类分别对数组进行字符串拼接,使其变成一个字符串。
源代码:
public class S5_4_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用String类进行数组字符串拼接
String[] stringArray = {"Hello", ", ", "world", "!"};
String concatenatedString = concatenateWithString(stringArray);
System.out.println("使用String类拼接的字符串:" + concatenatedString);
// 使用StringBuffer类进行数组字符串拼接
StringBuffer stringBuffer = concatenateWithStringBuffer(stringArray);
System.out.println("使用StringBuffer类拼接的字符串:" + stringBuffer.toString());
}
// 使用String类进行数组字符串拼接
public static String concatenateWithString(String[] array) {
String result = "";
for (String str : array) {
result += str;
}
return result;
}
// 使用StringBuffer类进行数组字符串拼接
public static StringBuffer concatenateWithStringBuffer(String[] array) {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
for (String str : array) {
result.append(str);
}
return result;
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

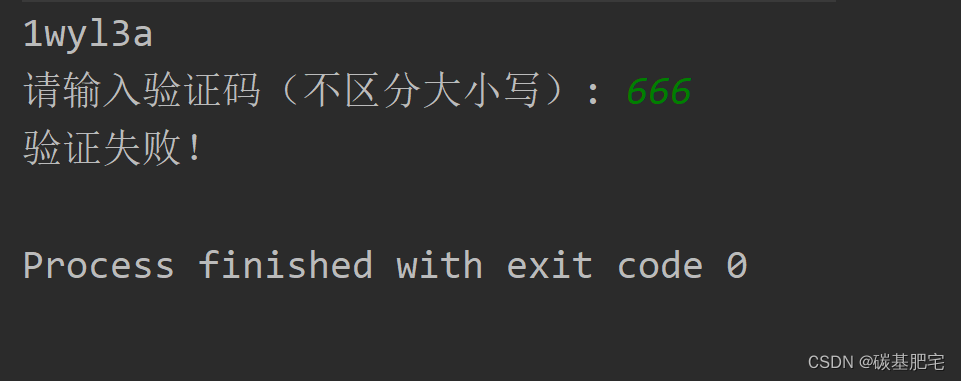
5、生成验证码
使用Random类创建一个6位的验证码,其中包含数字、字母的组合,并通过键盘输入该验证码,验证通过(不区分大小写)时提示“恭喜验证成功!”,否则提示“验证失败!”。
源代码:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class S5_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 生成验证码
String verificationCode = generateVerificationCode();
System.out.println(verificationCode);
// 提示用户输入验证码
System.out.print("请输入验证码(不区分大小写): ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String userInput = scanner.nextLine();
// 验证输入的验证码
if (verifyVerificationCode(userInput, verificationCode)) {
System.out.println("恭喜验证成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("验证失败!");
}
scanner.close();
}
// 生成6位验证码
private static String generateVerificationCode() {
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
// 随机选择数字或字母
int choice = random.nextInt(2);
if (choice == 0) {
// 生成数字
code.append(random.nextInt(10));
} else {
// 生成字母
char randomChar = (char) ('A' + random.nextInt(26));
// 随机选择字母是大写还是小写
if (random.nextBoolean()) {
randomChar = Character.toLowerCase(randomChar);
}
code.append(randomChar);
}
}
return code.toString();
}
// 验证输入的验证码是否匹配
private static boolean verifyVerificationCode(String userInput, String verificationCode) {
return userInput.equalsIgnoreCase(verificationCode);
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

6、春节倒计时
根据所学知识,计算明年(兔年2023年)春节的倒计时天数并输出:“距离兔年春节还有***天”。
源代码:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class S5_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("春节倒计时");
System.out.println("距离兔年春节还有");
LocalDateTime newYear = LocalDateTime.of(2023, 1, 21, 0, 0, 0);
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(newYear.getDayOfYear() + (newYear.getYear() - now.getYear()) * 365 - now.getDayOfYear() - 1 + "天");
System.out.print(newYear.getHour() - now.getHour() + 23 + ":");
System.out.print(newYear.getMinute() - now.getMinute() + 59 + ":");
System.out.print(newYear.getSecond() - now.getSecond() + 59);
System.out.println();
}
}列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

7、二月天
二月是一个有趣的月份,平年的二月有28天,闰年的二月有29天。编写一个程序,从键盘输入年份,根据输入的年份计算这一年的二月有多少天。
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class S5_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 提示用户输入年份
System.out.print("请输入年份: ");
int year = scanner.nextInt();
// 判断是否为闰年,并计算二月的天数
int daysInFebruary = isLeapYear(year) ? 29 : 28;
// 输出结果
System.out.println(year + "年的二月有 " + daysInFebruary + " 天。");
scanner.close();
}
// 判断是否为闰年的方法
private static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
// 闰年的条件:年份能被4整除但不能被100整除,或者能被400整除
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0);
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:

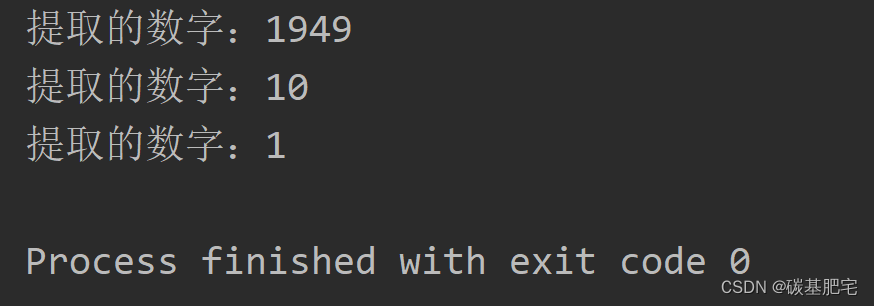
8、正则表达式。(选做)
“中华人民共和国成立于1949年10月1日”,利用正则表达式提取出其中的数字。
源代码:
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class S5_8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String inputString = "中华人民共和国成立于1949年10月1日";
// 定义正则表达式匹配数字
String regex = "\\d+";
// 编译正则表达式
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
// 创建Matcher对象
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(inputString);
// 提取数字并输出
while (matcher.find()) {
String number = matcher.group();
System.out.println("提取的数字:" + number);
}
}
}
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
三、实验总结
1、通过本实验,我理解了String、StringBuffer和StringBuilder类的使用以及String、StringBuffer和StringBuilder的异同:
- 相同点:它们的底层都是通过char数组实现。
- 不同点:①String对象一旦创建其值就不能修改的,如果要修改,将重新开辟内存空间来存储修改之后的对象,而StringBuffer和StringBuilder对象的值可以被修改的;②如果需要对字符串进行频繁的修改,不要使用String,因为会造成内存空间的浪费。
2、掌握了System和Runtime类的使用,用System类中的方法打开系统中的某些程序。
3、掌握了Math和Random类的使用,掌握了如何通过Random类或Math类中的Random()方法生成随机数。
4、掌握了日期时间类的使用。学会了如何编程求出某一时间距离当前时间还差多少时间。
5、对正则表达式有了一个初步的了解。