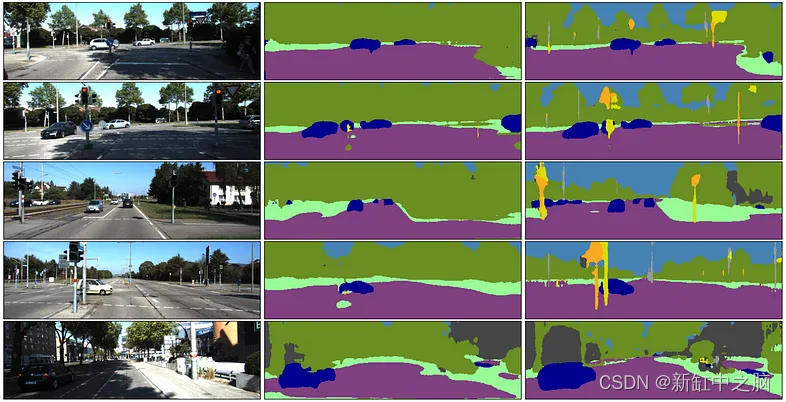
问题描述
| 工件 | A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 工件编号 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 加工时间 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 5 |
| 到达时间 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 交货期 | 10 | 15 | 30 | 24 | 14 | 13 | 20 |
目标函数
最小化交货期总延时时间
运算结果
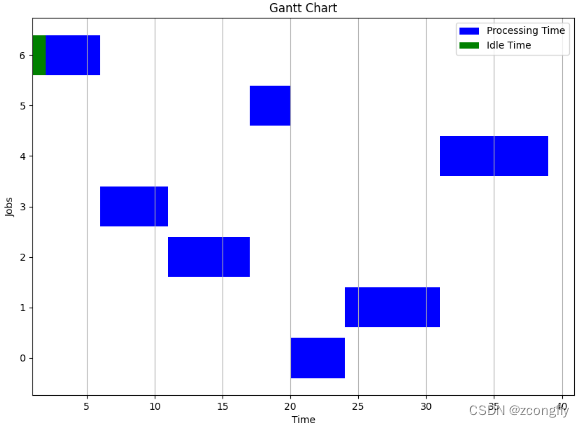
最佳调度顺序: [6, 3, 2, 5, 0, 1, 4]
最小交货期延时时间: 47
python代码
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义遗传算法参数
POP_SIZE = 100 # 种群大小
MAX_GEN = 50 # 最大迭代次数
CROSSOVER_RATE = 0.7 # 交叉概率
MUTATION_RATE = 0.2 # 变异概率
# 随机生成初始种群
def gen_init_pop(pop_size):
population = []
for _ in range(pop_size):
random.shuffle(job)
population.append(list(job))
return population
# 计算染色体的适应度(makespan) 以最小化交货期延时为目标函数,这里计算的是交货期总延时时间
def fitness(job):
n = len(job)
accu_pro_times = [0] * n # 累计加工时间
accu_pro_times[0] = pro_times[job[0]] + arr_times[job[0]]
for i in range(1, n):
accu_pro_times[i] = pro_times[job[i]] + accu_pro_times[i - 1] if arr_times[job[i]] <= accu_pro_times[
i - 1] else arr_times[job[i]] + pro_times[job[i]]
delay_time = sum([max(accu_pro_times[i] - deadlines[i], 0) for i in range(n)])
return delay_time
# 选择父代,这里选择POP_SIZE/2个作为父代
def selection(pop):
fitness_values = [1 / fitness(job) for job in pop] # 以最小化交货期总延时为目标函数,这里把最小化问题转变为最大化问题
total_fitness = sum(fitness_values)
prob = [fitness_value / total_fitness for fitness_value in fitness_values] # 轮盘赌,这里是每个适应度值被选中的概率
# 按概率分布prob从区间[0,len(pop))中随机抽取size个元素,不允许重复抽取,即轮盘赌选择
selected_indices = np.random.choice(len(pop), size=POP_SIZE // 2, p=prob, replace=False)
return [pop[i] for i in selected_indices]
# 交叉操作 这里是单点交叉
def crossover(job_p1, job_p2):
cross_point = random.randint(1, len(job_p1) - 1)
job_c1 = job_p1[:cross_point] + [gene for gene in job_p2 if gene not in job_p1[:cross_point]]
job_c2 = job_p2[:cross_point] + [gene for gene in job_p1 if gene not in job_p2[:cross_point]]
return job_c1, job_c2
# 变异操作
def mutation(job):
index1, index2 = random.sample(range(len(job)), 2)
job[index1], job[index2] = job[index2], job[index1]
return job
# 主遗传算法循环
def GA():
pop = gen_init_pop(POP_SIZE)
for _ in range(MAX_GEN):
pop = selection(pop) # 选择
new_population = []
while len(new_population) < POP_SIZE:
parent1, parent2 = random.sample(pop, 2) # 不重复抽样2个
if random.random() < CROSSOVER_RATE:
child1, child2 = crossover(parent1, parent2) # 交叉
new_population.extend([child1, child2])
else:
new_population.extend([parent1, parent2])
pop = [mutation(job) if random.random() < MUTATION_RATE else job for job in new_population]
best_job = min(pop, key=lambda x: fitness(x)) # 获得最佳个体
best_makespan = fitness(best_job) # 获得最佳个体的适应度值
# "makespan" 是指完成整个生产作业或生产订单所需的总时间,通常以单位时间(例如小时或分钟)来衡量。
return best_job, best_makespan
def plot_gantt(job, pro_times, arr_times):
# 计算每个工件的开始时间和结束时间
start_time = [arr_times[0]] # 第一个工件的开始时间为0
end_time = [start_time[0] + pro_times[0]]
for i in range(1, len(job)):
start_time.append(max(end_time[i - 1], arr_times[i]))
end_time.append(start_time[i] + pro_times[i])
# # 绘制甘特图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.barh(job, pro_times, left=start_time, color='b', label='Processing Time') # 加工时间
plt.barh(job, [st - ed for st, ed in zip(start_time, [0] + end_time[:-1])], left=start_time,
color='g', label='Idle Time') # 空闲时间
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Jobs')
plt.title('Gantt Chart')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(axis='x')
# 显示甘特图
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 定义单机调度问题的工件和加工时间
job = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] # 工件
pro_times = [4, 7, 6, 5, 8, 3, 5] # 加工时间
arr_times = [3, 2, 4, 5, 3, 2, 1] # 到达时间
deadlines = [10, 15, 30, 24, 14, 13, 20] # 交货期
best_job, best_makespan = GA()
best_pro_times = [pro_times[best_job[i]] for i in range(len(best_job))]
best_arr_times = [arr_times[best_job[i]] for i in range(len(best_job))]
print("最佳调度顺序:", best_job)
print("最小交货期延时时间:", best_makespan)
plot_gantt(best_job, best_pro_times, best_arr_times)



![[JavaWeb]——Spring事务管理和@Transactional注解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/609c0a4e8af54078864b4946e3a664f7.png)
![[python 刷题] 1248 Count Number of Nice Subarrays](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/46c00aed5e5c45d7b77dd2c79816e577.jpeg#pic_center)