文章目录
- 一、express的了解
- 1.定义
- 2.作用
- 3.使用express的前提条件
- (1)如果是新文件夹需要薪资package.json文件,如果有就忽略
- (2)安装第三方依赖包
- (3)在使用的地方导入express
- 二、express的基本使用
- 三、express关于路由的基本使用
- 1.什么是路由
- 2.路由的使用
- 3.路由使用示例
- 4、express中的get参数
- (1)query参数
- (2)params参数
- (3)示例代码
- 5、express中的post参数
- 五、express托管静态资源
- 1.了解
- 2.基本使用
- 3:注意点
一、express的了解
express官方中文文档:https://www.expressjs.com.cn/starter/basic-routing.html
1.定义
官网说明:Express 是一个保持最小规模的灵活的 Node.js Web 应用程序开发框架,为 Web 和移动应用程序提供一组强大的功能。
简单理解:一个npm上的第三方包,提供了快捷创建Web服务器的便捷方法。
2.作用
相比于http内置模块创建web服务器而言,Express能极大的提高开发效率。
3.使用express的前提条件
(1)如果是新文件夹需要薪资package.json文件,如果有就忽略
npm init // 生成package.json文件
(2)安装第三方依赖包
npm i express // 安装第三方依赖包
(3)在使用的地方导入express
const express = require('express')
二、express的基本使用
// 1:导入包
const express = require('express')
// 创建服务器的对象
const app = express();
// 3:创建请求路径
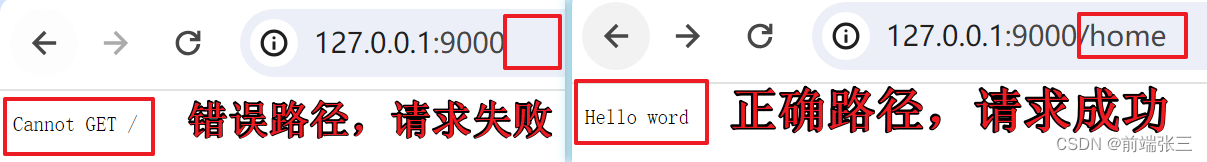
app.get('/home', (req, res) => {
res.end('Hello word')
})
// 4:启动服务
app.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('express服务器创建成功');
})
三、express关于路由的基本使用
1.什么是路由
路由确定了应用程序如何响应客户端对特定端点的请求
2.路由的使用
method 是方法(get、post、all)
path 是请求的路径
callback 回调函数
app.method(path, callback)
3.路由使用示例
需要注意的发送 post 方法表单和ajax,这样才会有效果。
// 1:导入包
const express = require('express')
// 创建服务器的对象
const app = express();
// 3:创建请求路径
// 3.1 get路由——匹配空路径
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.end('home')
})
// 3.2 get路由——匹配home路径
app.get('/home', (req, res) => {
res.end('Hello word')
})
// 3.3 post路由——匹配login
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
res.end('login')
})
// 3.4 匹配所有方法(get、post)
app.all('/test', (req, res) => {
res.end('test')
})
// 3.5 匹配所有方法(get、post)
app.all('*', (req, res) => {
res.end('404 found')
})
// 4:启动服务
app.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('express服务器创建成功');
})

4、express中的get参数
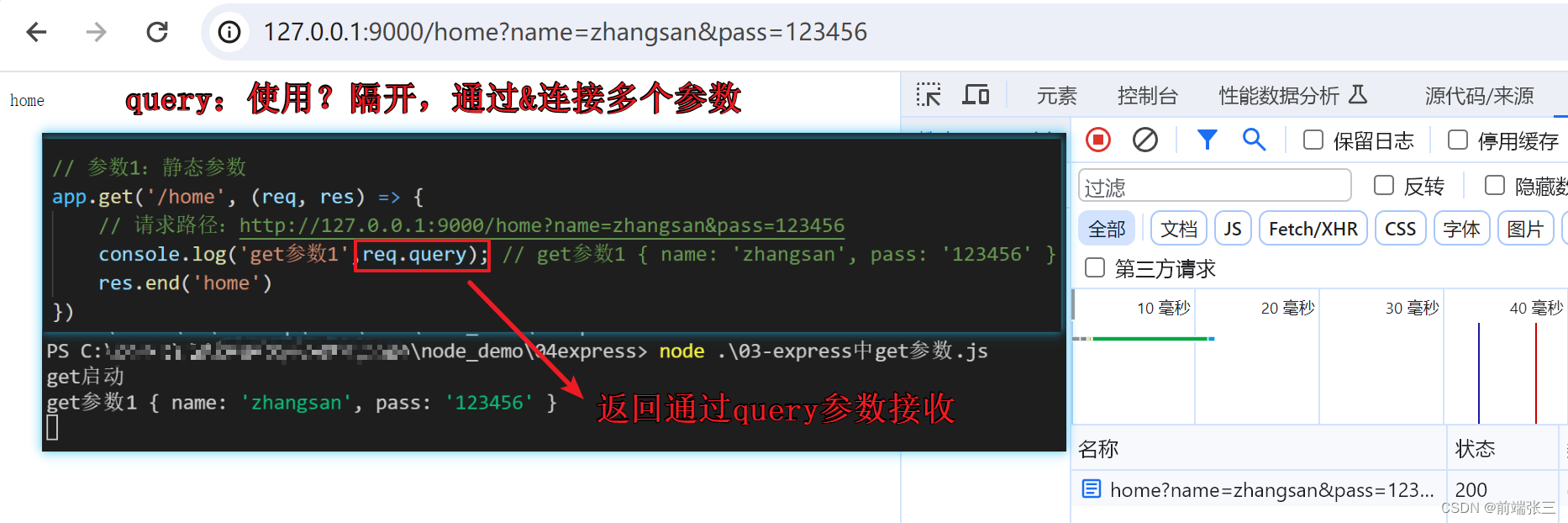
(1)query参数
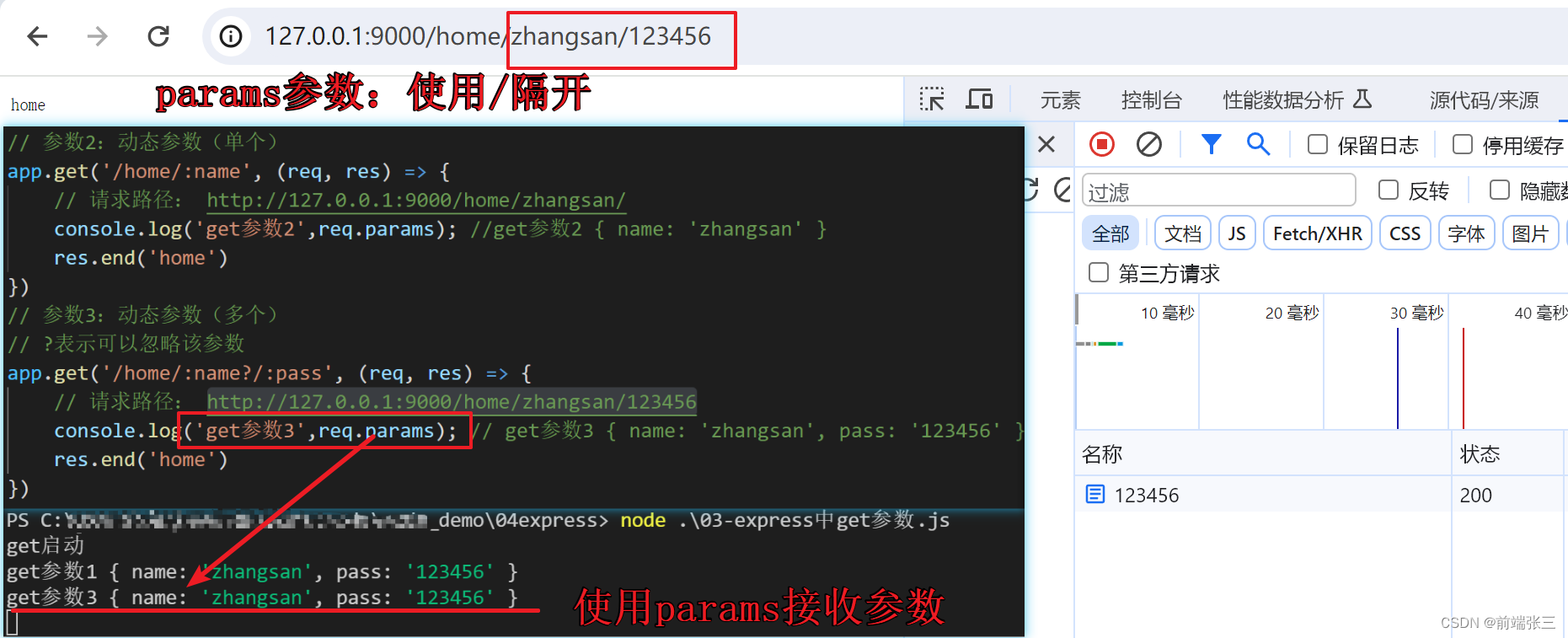
(2)params参数
参数中的 ? 代表 可传可不传
(3)示例代码
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
// 参数1:静态参数
app.get('/home', (req, res) => {
// 请求路径:http://127.0.0.1:9000/home?name=zhangsan&pass=123456
console.log('get参数1',req.query); // get参数1 { name: 'zhangsan', pass: '123456' }
res.end('home')
})
// 参数2:动态参数(单个)
app.get('/home/:name', (req, res) => {
// 请求路径: http://127.0.0.1:9000/home/zhangsan/
console.log('get参数2',req.params); //get参数2 { name: 'zhangsan' }
res.end('home')
})
// 参数3:动态参数(多个)
// ?表示可以忽略该参数
app.get('/home/:name?/:pass', (req, res) => {
// 请求路径: http://127.0.0.1:9000/home/zhangsan/123456
console.log('get参数3',req.params); // get参数3 { name: 'zhangsan', pass: '123456' }
res.end('home')
})
app.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('get启动')
})
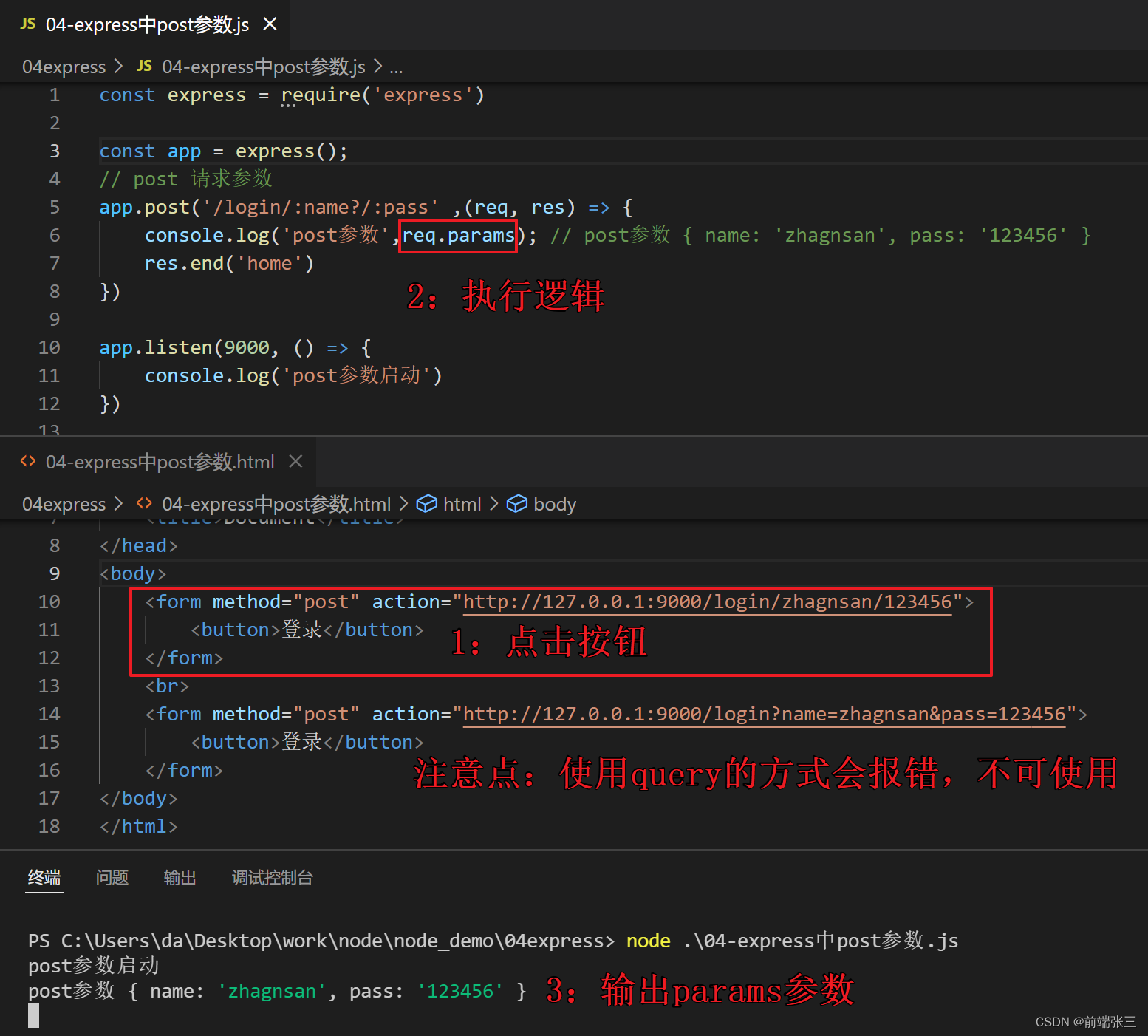
5、express中的post参数
// node 中使用post参数的逻辑
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
// post 请求参数
app.post('/login/:name?/:pass' ,(req, res) => {
console.log('post参数',req.params); // post参数 { name: 'zhagnsan', pass: '123456' }
res.end('home')
})
app.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('post参数启动')
})
五、express托管静态资源
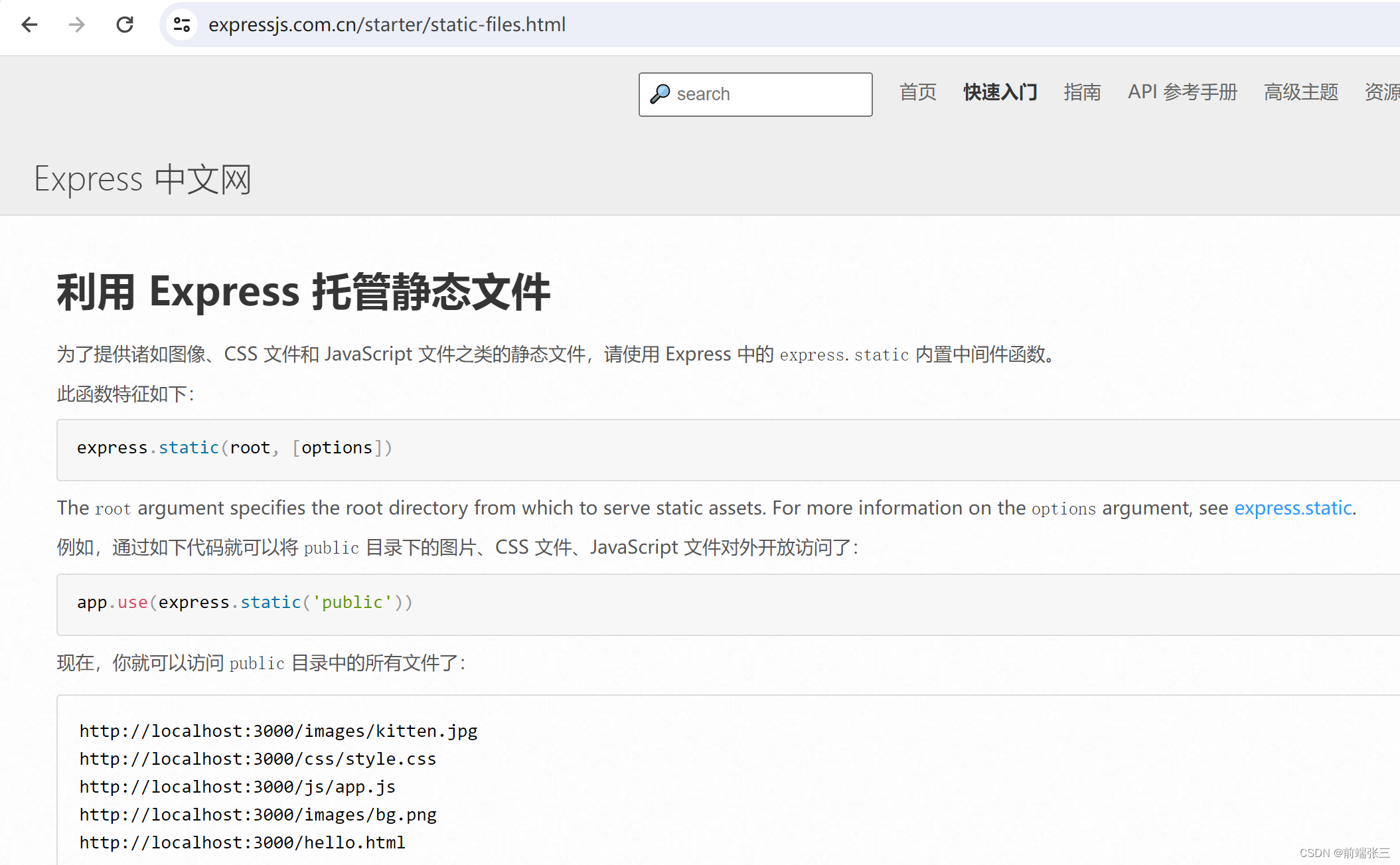
1.了解
express.static(root, [options])
app.use(express.static(‘文件路径’))
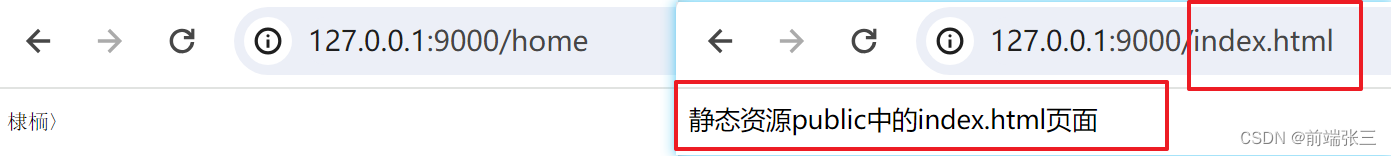
2.基本使用
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
// 以前:获取url路径、拼接url路径,读取文件,写入文件......(现在一行即可)
app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'))
app.get('/home', (req, res) => {
res.end('首页')
})
app.listen(9000, () => {
console.log('服务器启动');
})
3:注意点
如果要使用多个静态资源目录,请多次调用 express.static 中间件函数
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(express.static('files'))