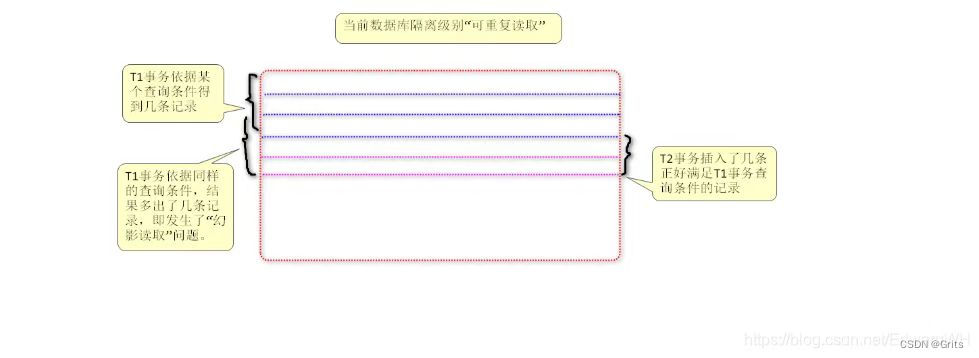
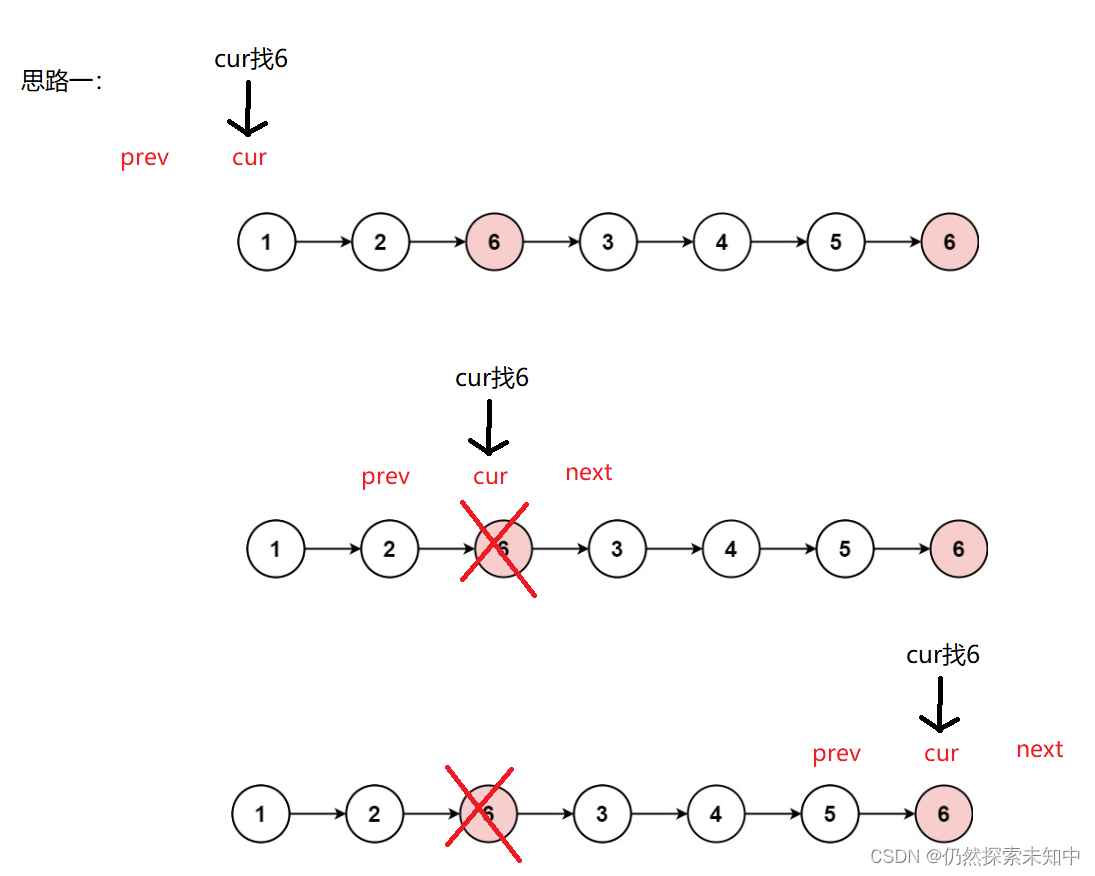
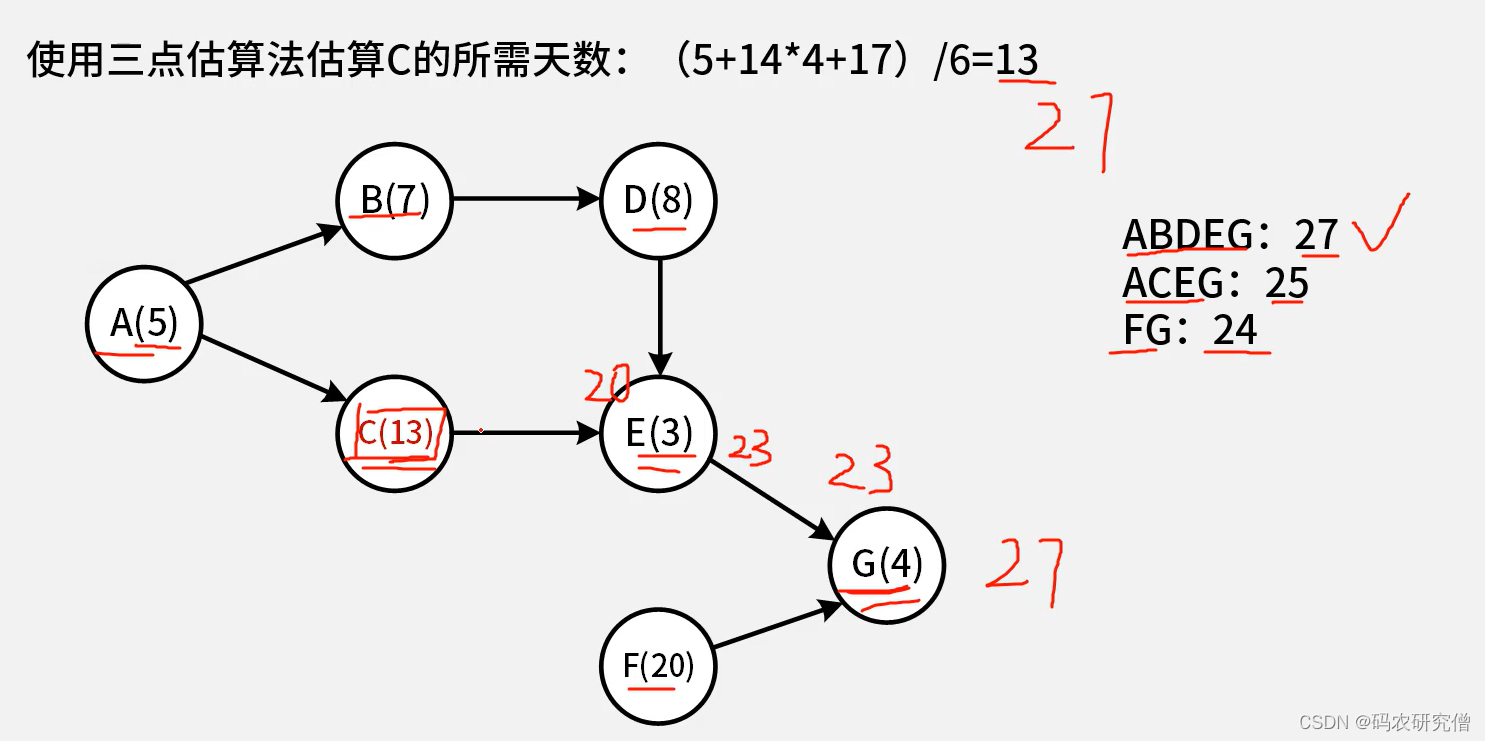
1 lc24《两两交换链表中的节点》
1.1 描述
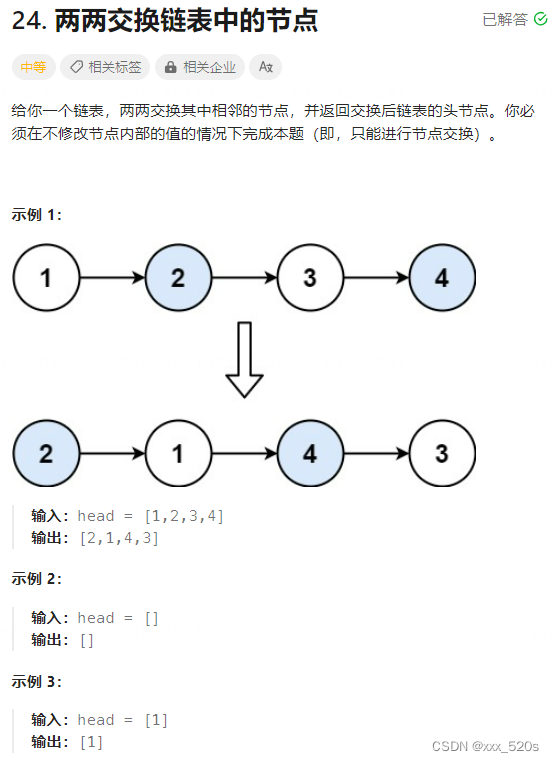
1.2 题解
1.2.1 递归解法
下面的三行注释要理解透彻,
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return head;
// 具体的两两交换过程
ListNode next=head.next;
ListNode nextNext=head.next.next;
head.next=nextNext;
next.next=head;
//将交换后新的尾节点指向下一批节点交换后新的头
head.next=swapPairs(nextNext);
// 返回交换后新的头节点
return next;
}
1.2.2 非递归解法
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy=new ListNode();
dummy.next=head;
ListNode cur=dummy;
while(cur.next!=null&&cur.next.next!=null){
ListNode l=cur.next;
ListNode r=cur.next.next;
//swap
cur.next=r;
l.next=r.next;
r.next=l;
cur=l;
}
return dummy.next;
}
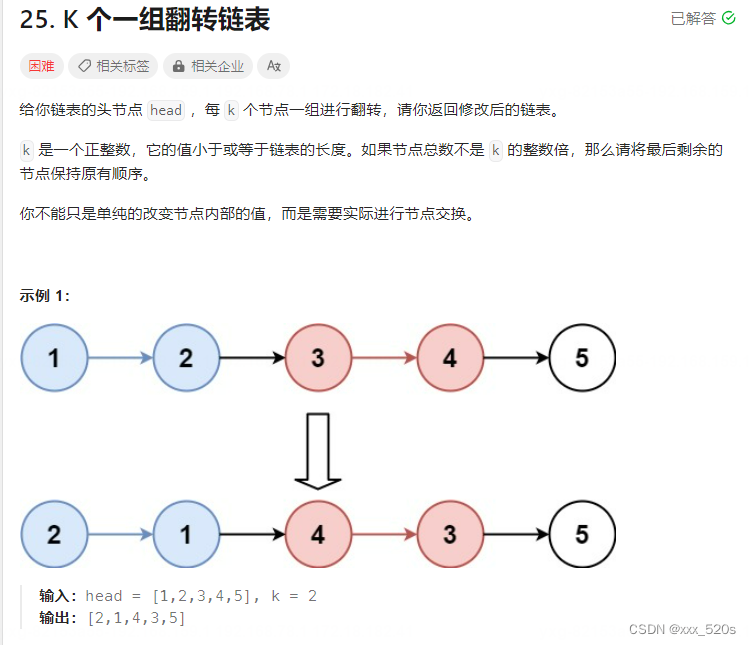
2 lc25. K 个一组翻转链表
2.1 题目描述
2.2 递归写法
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head==null)return head;
ListNode a=head;
ListNode b=head;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
if(b==null)return head;
b=b.next;
}
//
ListNode[]newLink=reverse(a,b);
newLink[1].next=reverseKGroup(b,k);
return newLink[0];
}
ListNode[]reverse(ListNode a,ListNode b){
ListNode pre=null,cur=a;
while(cur!=b){
ListNode next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
//新头,新尾
return new ListNode[]{pre,a};
}