模型实战(1)之YOLOv5 实现目标检测+训练自己的数据集
写一个小总结吧,关于yolov5使用可以参考我的两外两篇博文:
1.YOLOV5算法一之Windows10下yolov5安装测试并训练自己的数据集
2.YOLOV5算法二之数据集转换及自动划分训练集与测试集
3.YOLOV5算法三之各结构文件的功能作用及介绍
4.深度网络模型训练评价指标之yolov5训练结果分析
本文将实现从头训练yolov5并基于python进行封装,以便用于实际应用,可以直接复用的训练模型直接点此下载:https://gitcode.net/openmodel/yolov5,关于具体细节将在文章中做出说明 。
1.本地环境部署
- 克隆代码到本地
git clone https://gitcode.net/openmodel/yolov5.git # clone
cd yolov5
#创建环境
conda create -n yolov5-seg python=3.8
#激活
conda activate yolov5-seg
# 安装 torch 1.8.2+cu11.1
pip install torch==1.8.2 torchvision==0.9.2 torchaudio===0.8.2 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/lts/1.8/cu111
#其他版本:torch+cuda10.2
pip install torch==1.8.1+cu102 torchvision==0.9.1+cu102 torchaudio===0.8.1 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
# 修改requirements.txt,将其中的torch和torchvision注释掉
pip install -r requirements.txt
- 通过labelImg对数据集进行标注,标签格式
.xml,然后再mytrain路径下将label通过xml2txt.py转为yolo需要的.txt格式:
- 若要进行数据集划分:可通过下边demo设置测试集和验证集的占比实现
"""
time:20220729
writer:yohn
function:将数据集分为训练集、测试集和验证集,在此就将测试与验证归为一个了
"""
import os
import shutil
train_p=".\\train"
val_p=".\\val"
imgs_p="images"
labels_p="labels"
#创建训练集
if not os.path.exists(train_p):#指定要创建的目录
os.mkdir(train_p)
tp1=os.path.join(train_p,imgs_p)
tp2=os.path.join(train_p,labels_p)
print(tp1,tp2)
if not os.path.exists(tp1):#指定要创建的目录
os.mkdir(tp1)
if not os.path.exists(tp2): # 指定要创建的目录
os.mkdir(tp2)
#创建测试集文件夹
if not os.path.exists(val_p):#指定要创建的目录
os.mkdir(val_p)
vp1=os.path.join(val_p,imgs_p)
vp2=os.path.join(val_p,labels_p)
print(vp1,vp2)
if not os.path.exists(vp1):#指定要创建的目录
os.mkdir(vp1)
if not os.path.exists(vp2): # 指定要创建的目录
os.mkdir(vp2)
#数据集路径
path1=".\\images"
path2=".\\labels"
#划分数据集,设置数据集数量占比
proportion_ = 0.95 #训练集占比
for root,dirs,files in os.walk(path1,topdown=True):
#print(files) #此处是将所有文件名字一次性取出
nums=0
nums_T=int(len(files)*proportion_)
print("开始数据集划分...")
for file in files:
name = file.split('.')[0]
if(nums <= nums_T):
jpg_1 = os.path.join(path1,file)
jpg_2 = os.path.join(train_p,imgs_p,file)
txt_1 = os.path.join(path2, name + '.txt')
txt_2 = os.path.join(train_p, labels_p, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(jpg_1,jpg_2)
shutil.copyfile(txt_1,txt_2)
nums+=1
else:
jpg_1 = os.path.join(path1, file)
jpg_2 = os.path.join(val_p, imgs_p, file)
txt_1 = os.path.join(path2, name + '.txt')
txt_2 = os.path.join(val_p, labels_p, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(jpg_1, jpg_2)
shutil.copyfile(txt_1, txt_2)
nums+=1
print(nums)
print("数据集划分完成: 总数量:",len(files)," 训练集数量:",nums_T," 测试集数量:",len(files)-nums_T)
- 然后将处理好的数据集和标签统一在下方路径下进行替换:
./data下更改路径:
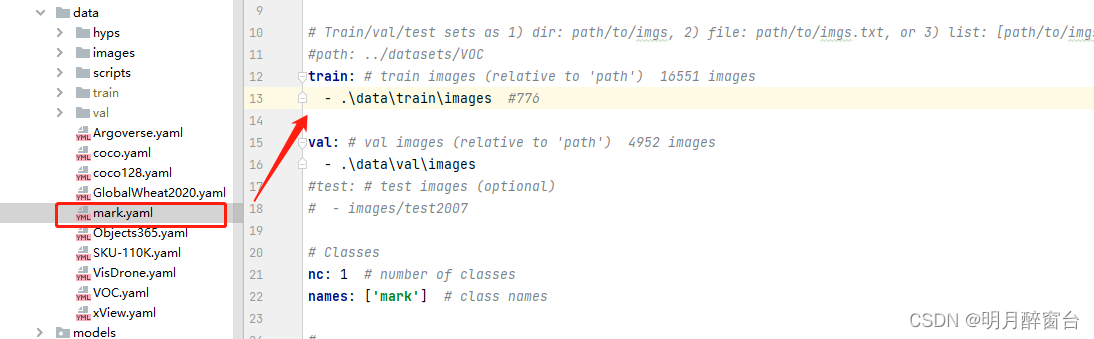
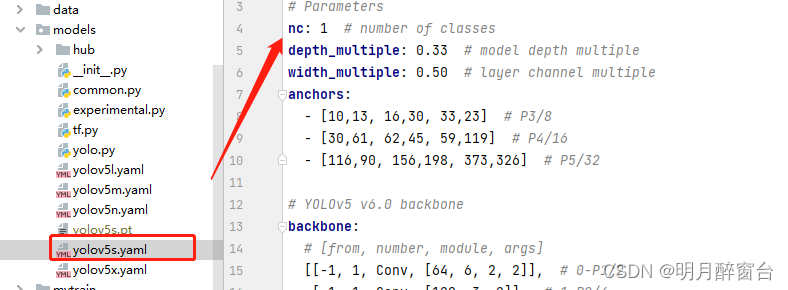
./model下修改想要选择的模型配置
- 修改
train.py:
- 执行训练即可,训练后的结果将在
./runs中保存
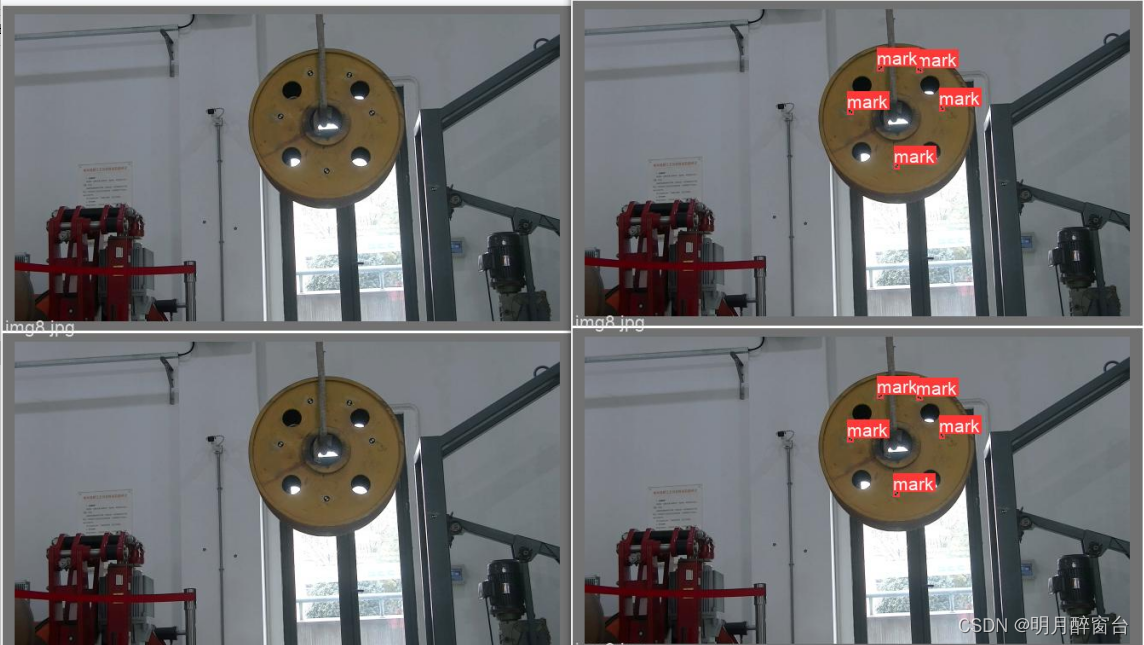
检测结果:
2.推理、部署
- 进行推理预测,即在
detect.py中修改训练好的权重路径即可,或者通过命令行导入参数
python detect.py --source 0 # webcam
img.jpg # image
vid.mp4 # video
path/ # directory
path/*.jpg # glob
'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc' # YouTube
'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' # RTSP, RTMP, HTTP stream
pytorch.hub部署
import torch
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s') # or yolov5n - yolov5x6, custom
# Images
img = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg' # or file, Path, PIL, OpenCV, numpy, list
# Inference
results = model(img)
# Results
results.print() # or .show(), .save(), .crop(), .pandas(), etc.
- 导出onnx、tensorRT模型
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include torchscript onnx
💡 ProTip: Add --half to export models at FP16 half precision for smaller file sizes
output:
export: data=data/coco128.yaml, weights=['yolov5s.pt'], imgsz=[640, 640], batch_size=1, device=cpu, half=False, inplace=False, train=False, keras=False, optimize=False, int8=False, dynamic=False, simplify=False, opset=12, verbose=False, workspace=4, nms=False, agnostic_nms=False, topk_per_class=100, topk_all=100, iou_thres=0.45, conf_thres=0.25, include=['torchscript', 'onnx']
YOLOv5 🚀 v6.2-104-ge3e5122 Python-3.7.13 torch-1.12.1+cu113 CPU
Downloading https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.2/yolov5s.pt to yolov5s.pt...
100% 14.1M/14.1M [00:00<00:00, 274MB/s]
Fusing layers...
YOLOv5s summary: 213 layers, 7225885 parameters, 0 gradients
PyTorch: starting from yolov5s.pt with output shape (1, 25200, 85) (14.1 MB)
TorchScript: starting export with torch 1.12.1+cu113...
TorchScript: export success ✅ 1.7s, saved as yolov5s.torchscript (28.1 MB)
ONNX: starting export with onnx 1.12.0...
ONNX: export success ✅ 2.3s, saved as yolov5s.onnx (28.0 MB)
Export complete (5.5s)
Results saved to /content/yolov5
Detect: python detect.py --weights yolov5s.onnx
Validate: python val.py --weights yolov5s.onnx
PyTorch Hub: model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', 'yolov5s.onnx')
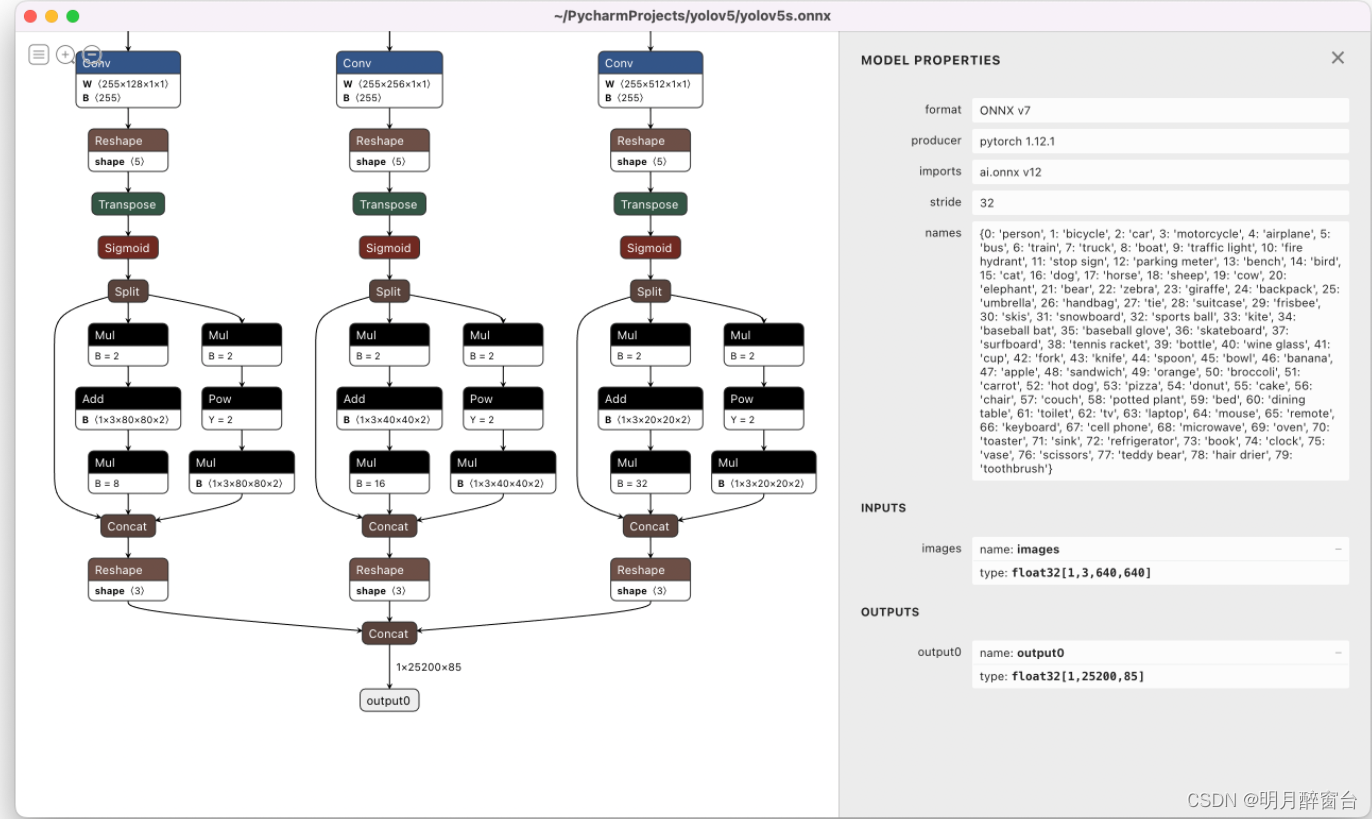
Visualize: https://netron.app/
Netron Viewer is recommended for visualizing exported models:
3.检测接口封装
- 将检测接口进行封装,以便外侧过程调用
"""
time:20220618
writer:yohn
tel:15542286857
"""
import random
from utils.augmentations import letterbox
"""
该文件将yolov5封装成一个接口以便可以被测试过程调用
"""
# Copyright (c) 2022 guluC
# 导入需要的库
import os
import sys
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import cv2
import torch
# 初始化目录
FILE = Path(__file__).resolve()
ROOT = FILE.parents[0] # 定义YOLOv5的根目录
if str(ROOT) not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(str(ROOT)) # 将YOLOv5的根目录添加到环境变量中(程序结束后删除)
ROOT = Path(os.path.relpath(ROOT, Path.cwd())) # relative
from models.common import DetectMultiBackend
from utils.dataloaders import IMG_FORMATS, VID_FORMATS, LoadImages, LoadStreams
from utils.general import (LOGGER, check_file, check_img_size, check_imshow, check_requirements, colorstr, cv2,
increment_path, non_max_suppression, print_args, scale_coords, strip_optimizer, xyxy2xywh)
from utils.plots import Annotator, colors, save_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, time_sync
#定义一个类存放意向检测区域,意向检测区域通过读取图像
# class detect_ROI:
# def __int__(self):
# self.ROI_fall=cv2.imread("SetROI\\mask.png")
#定义一个结构体存放检测结果
class GResult:
def __int__(self):
self.detections={}
self.colors=[]
#self.dst=np.zeros((640,640,3),np.unit8)
def plot_one_box(x, img, label=None,conf=0, color=None, line_thickness=None):
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[0]+x[2]), int(x[1]+x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label+" "+str(conf), 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(img, label+" "+str(conf), (c1[0], c1[1]), 0, tl/3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
weights = ROOT /'weights/best1101.pt' # 权重文件地址 .pt文件
source = ROOT / 'data/images' # 测试数据文件(图片或视频)的保存路径
gresult=GResult()#初始化一个检测结果类
imgsz = (640, 640) # 输入图片的大小 默认640(pixels)
conf_thres = 0.25 # object置信度阈值 默认0.25 用在nms中
iou_thres = 0.45 # 做nms的iou阈值 默认0.45 用在nms中
max_det = 1000 # 每张图片最多的目标数量 用在nms中
device = '0' # 设置代码执行的设备 cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu
classes = None # 在nms中是否是只保留某些特定的类 默认是None 就是所有类只要满足条件都可以保留 --class 0, or --class 0 2 3
agnostic_nms = False # 进行nms是否也除去不同类别之间的框 默认False
augment = False # 预测是否也要采用数据增强 TTA 默认False
visualize = False # 特征图可视化 默认FALSE
half = False # 是否使用半精度 Float16 推理 可以缩短推理时间 但是默认是False
dnn = False # 使用OpenCV DNN进行ONNX推理
# 获取设备
device = select_device(device)
# 载入模型
model = DetectMultiBackend(weights, device=device, dnn=dnn)
stride, names, pt, jit, onnx, engine = model.stride, model.names, model.pt, model.jit, model.onnx, model.engine
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # 检查图片尺寸
# Half
# 使用半精度 Float16 推理
half &= (pt or jit or onnx or engine) and device.type != 'cpu' # FP16 supported on limited backends with CUDA
if pt or jit:
model.model.half() if half else model.model.float()
classnames=model.names
print("label:")
# for i in classnames:
# print(i)
#设置随机颜色绘制标签
colors= [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(len(classnames))]
def detect(img):
# Dataloader
# 载入数据保存路径
#dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt)
# Run inference
# 开始预测
model.warmup(imgsz=(1 , 3, *imgsz)) # warmup
dt, seen = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0
# 对图片进行处理
im0 = img
# Padded resize
im = letterbox(im0, imgsz, stride, auto=pt)[0]
# Convert
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im)
t1 = time_sync()
im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)
im = im.half() if half else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
t2 = time_sync()
dt[0] += t2 - t1
# Inference
# 预测
pred = model(im, augment=augment, visualize=visualize)
t3 = time_sync()
dt[1] += t3 - t2
# NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
dt[2] += time_sync() - t3
# 用于存放结果
detections = []
# Process predictions
#print("目标数 = ",pred[0].shape[0])
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # per image 每张图片
seen += 1
# im0 = im0s.copy()
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Write results
# 写入结果
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4))).view(-1).tolist()
xywh = [round(x) for x in xywh]
xywh = [xywh[0] - xywh[2] // 2, xywh[1] - xywh[3] // 2, xywh[2],
xywh[3]] # 检测到目标位置,格式:(left,top,w,h)
cls = names[int(cls)]
# conf = float(conf)
conf = format(conf,'.2f')
detections.append({'class': cls, 'conf': conf, 'position': xywh})
col=colors[classnames.index(cls)]
plot_one_box(xywh,im0,cls,conf,col)
# # 输出结果
# t=0
# for i in detections:
# print(str(t),i)
# t=t+1
# cv2.imshow("result",im0)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# 推测的时间
#LOGGER.info(f'({t3 - t2:.3f}s)')
gresult.detections=detections
gresult.colors=colors
gresult.dst=im0
return detections
#return gresult
# #自测demo
# path = "F:\\Deeplearning\\yolov5-master\\data\\val\\images\\garb01_801.jpg"
# img = cv2.imread(path)
# # 传入一张图片
# detect(img)