目录
使用BFS求解单源路径问题
BFS重要性质
无权图的最短路径问题
使用BFS求解单源路径问题
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class SingleSourcePath {
private Graph G;
private int s;//在SingleSourcePath中传入的源
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
public SingleSourcePath(Graph G, int s){
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];//图有多少个顶点就开多少空间
for(int i = 0; i < pre.length; i ++)
pre[i] = -1;
bfs(s);//从s到其他连通分量是不可达的
}
private void bfs(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
pre[s] = s;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int v = queue.remove();
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w);
visited[w] = true;
pre[w] = v;//w的上一个顶点是v
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){
G.validateVertex(t);//看用户传入的t是否合法
return visited[t];//若t被遍历到了,说明t和s属于同一个连通分量,从s肯定有条路径到达t
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;//若从s无法到达t则返回一个空的ArrayList,说明没有路径能从s到t
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);//把ArrayList所有元素颠倒出来成为正序
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");//用户自己传入的图
SingleSourcePath sspath = new SingleSourcePath(g, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path(6));
}
}BFS重要性质
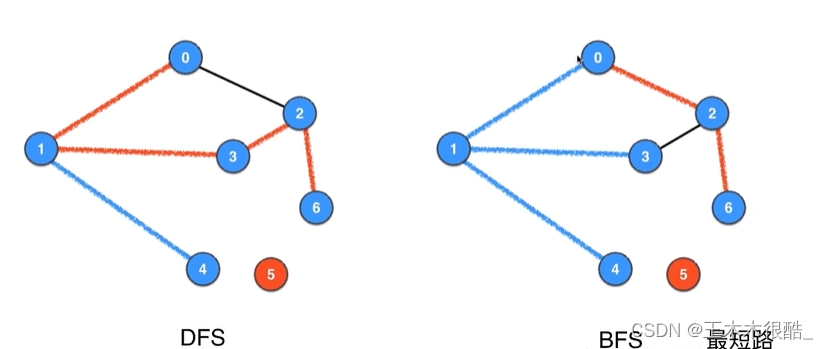
BFS求解的路径不是一般路,而是最短路,而且要注意BFS求最短路径必须是无权图! 广度优先遍历先遍历离源顶点近的,先遍历的顶点的距离小于等于后遍历的顶点离源顶点的距离。其实这个和树的广度优先遍历的顺序是一模一样的。
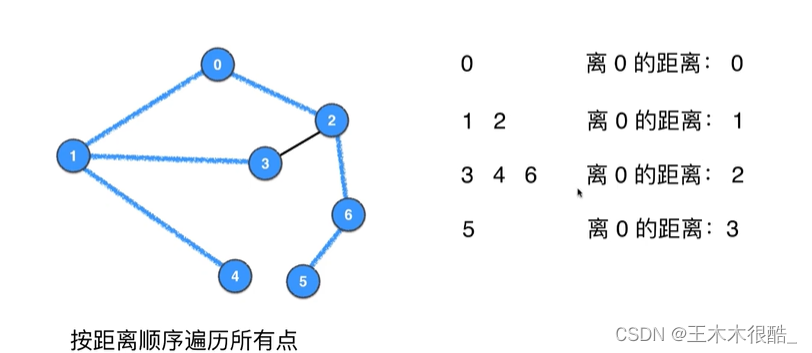
无权图的最短路径问题
用一个dis数组来记录距离。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
// Unweighted Single Source Shortest Path
public class USSSPath {
private Graph G;
private int s;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
private int[] dis;
public USSSPath(Graph G, int s){
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];
dis = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++) {
pre[i] = -1;
dis[i] = -1;
}
bfs(s);
for(int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++)
System.out.print(dis[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
private void bfs(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
pre[s] = s;
dis[s] = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int v = queue.remove();
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w);
visited[w] = true;
pre[w] = v;
dis[w] = dis[v] + 1;
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){
G.validateVertex(t);
return visited[t];
}
public int dis(int t){
G.validateVertex(t);
return dis[t];//返回从源点到某个目标顶点的长度
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
USSSPath ussspath = new USSSPath(g, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + ussspath.path(6));
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + ussspath.dis(6));
}
}





![【蓝桥每日一题]-二分类型(保姆级教程 篇2) #砍树 #木材加工](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/22a827a570e144c3a650a623d3b70b53.png)