57岛屿数量

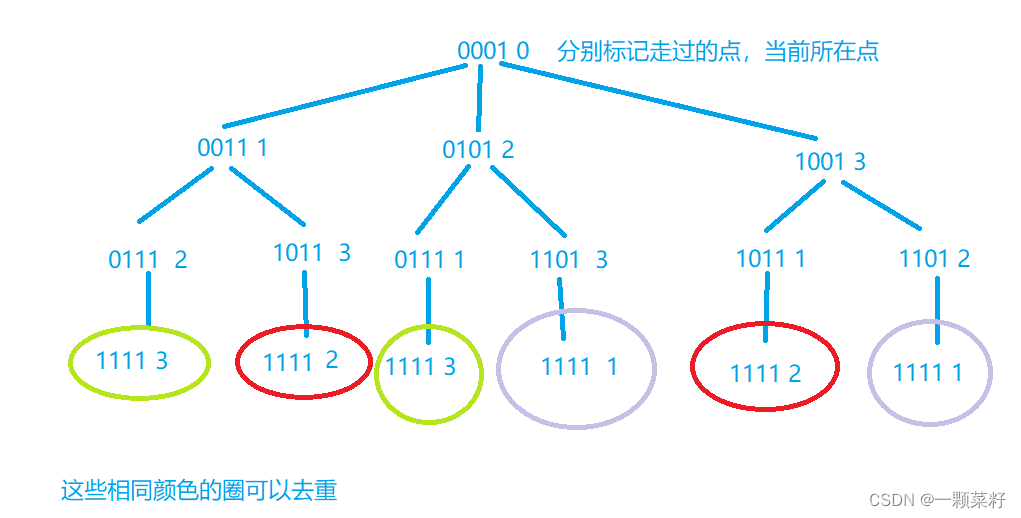
矩阵中多处聚集着1,要想统计1聚集的堆数而不重复统计,那我们可以考虑每次找到一堆相邻的1,就将其全部改成0,而将所有相邻的1改成0的步骤又可以使用深度优先搜索(dfs):当我们遇到矩阵的某个元素为1时,首先将其置为了0,然后查看与它相邻的上下左右四个方向,如果这四个方向任意相邻元素为1,则进入该元素,进入该元素之后我们发现又回到了刚刚的子问题,又是把这一片相邻区域的1全部置为0,因此可以用递归实现。
终止条件: 进入某个元素修改其值为0后,遍历四个方向发现周围都没有1,那就不用继续递归,返回即可,或者递归到矩阵边界也同样可以结束。
返回值: 每一级的子问题就是把修改后的矩阵返回,因为其是函数引用,也不用管。
本级任务: 对于每一级任务就是将该位置的元素置为0,然后查询与之相邻的四个方向,看看能不能进入子问题。
时间复杂度:O(nm),其中m、n为矩阵的长和宽,需要遍历整个矩阵,每次dfs搜索需要经过每个值为1的元素,但是最坏情况下也只是将整个矩阵变成0,因此相当于最坏遍历矩阵2次
空间复杂度:O(nm),最坏情况下整个矩阵都是1,递归栈深度为mn
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 判断岛屿数量
* @param grid char字符型二维数组
* @return int整型
*/
public int solve (char[][] grid) {
// write code here
int m=grid.length;
if(m==0) return 0;
int n=grid[0].length;
if(n==0) return 0;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
count++;
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
return count;
}
public void dfs(char[][]grid,int i,int j){
//把所到地方的1全改成0
grid[i][j]='0';
//记得判断边界
if(i>0&&grid[i-1][j]=='1'){
dfs(grid,i-1,j);
}
if(j>0&&grid[i][j-1]=='1'){
dfs(grid,i,j-1);
}
if(i<grid.length-1&&grid[i+1][j]=='1'){
dfs(grid,i+1,j);
}
if(j<grid[0].length-1&&grid[i][j+1]=='1'){
dfs(grid,i,j+1);
}
}
}
58字符串的排列
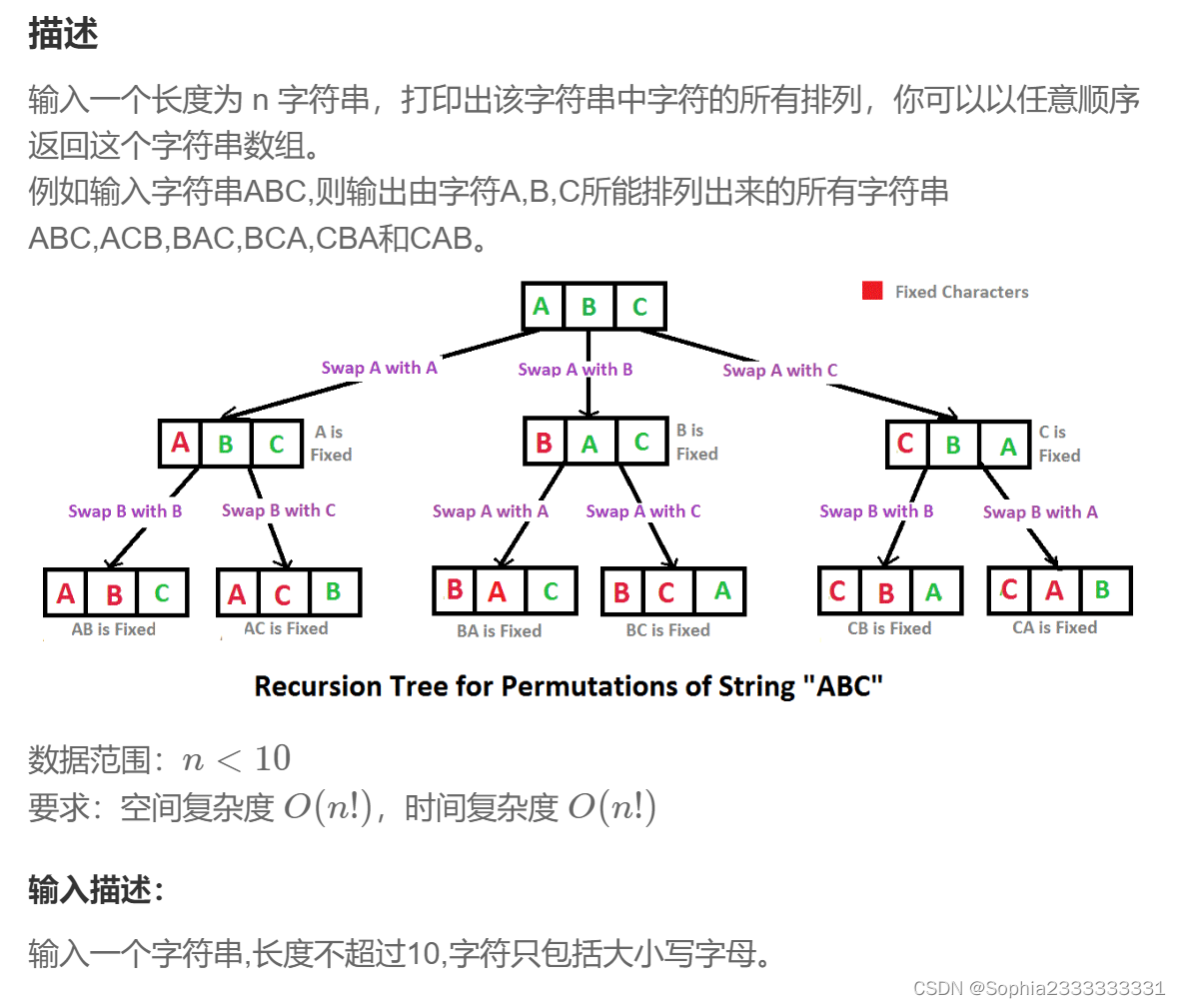
一开始就写完了,但是最后一个测试案例一直超时,最后发现是我在dfs中判断contain的方式,本来就是n*n!,contian还要遍历一遍,还要再乘n,复杂度过高。
解决:1.用set,如下代码,全部结束完毕再遍历一遍set,没增加时间复杂度
2. 首先对输入数组排序之后,
再
if(i > 0 && str[i - 1] == str[i] && !vis[i - 1])
//当前的元素str[i]与同一层的前一个元素str[i-1]相同且str[i-1]已经用过了
continue;
这种做法时间最少
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
StringBuilder list = new StringBuilder();
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
int[] vis = new int[str.length()];//0表示没被访问过
if(str.length()==0){
String st = "";
res.add(st);
return res;
}
dfs(str,vis,0);
for(Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();it.hasNext();){
res.add(it.next());
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(String str, int[] vis, int index){
String s = list.toString();
if(index==str.length()){
// if(!res.contains(s)){
// res.add(s);//还是复制
// }
set.add(s);
// res.add(s);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
if(vis[i]==1) continue;
vis[i]=1;
list.append(Character.toString(str.charAt(i)));
dfs(str,vis,index+1);
vis[i]=0;
list.deleteCharAt(list.length()-1);
}
}
}
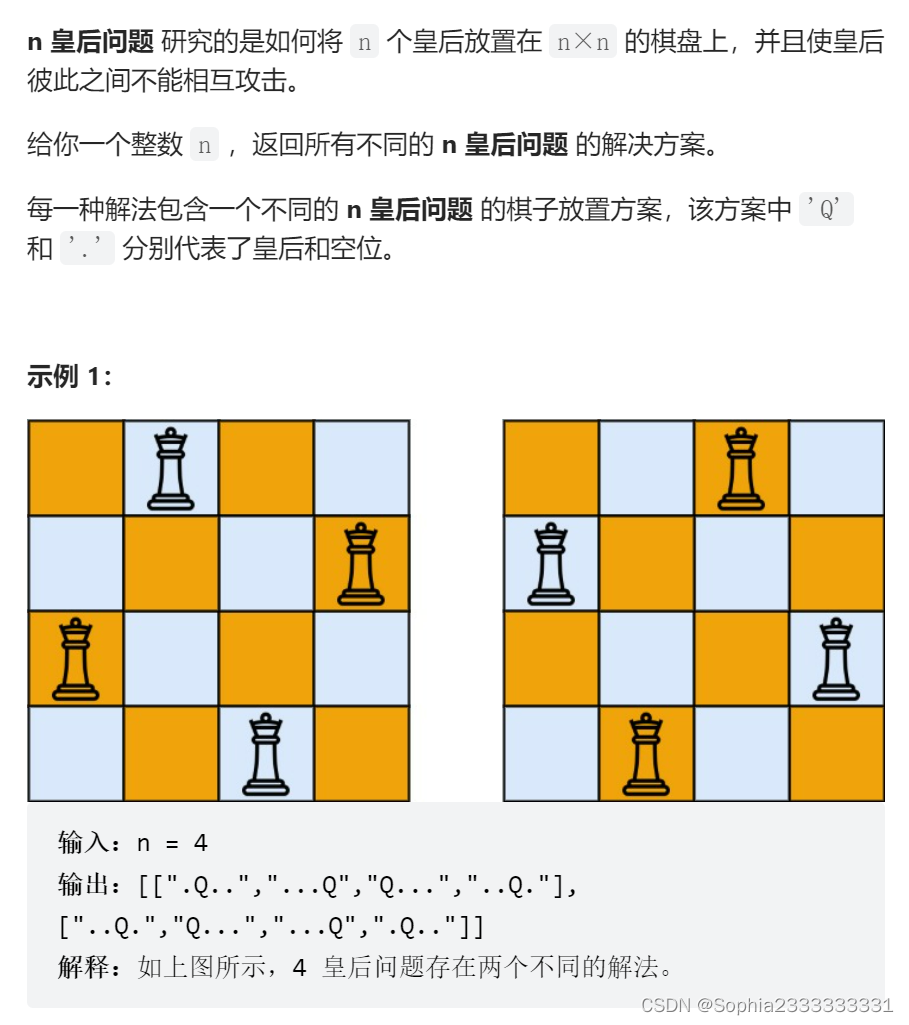
59 N皇后问题

N皇后是回溯的经典题
看过去的第一反应是用一个n*n的数组存是否访问过,然后在判断是否合法的时候都要遍历这个二维数组,有点麻烦,更简洁一点的是用一个一维数组去存,index表示行,存的值表示列,比如pos[i]=j表示i行j列访问过。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param n int整型 the n
* @return int整型
*/
int[] pos = new int[9];//index为行,元素值为列
int count;
public int Nqueen (int n) {
// write code here
Arrays.fill(pos,-1);//初始都为-1
dfs(n,0);
return count;
}
public void dfs(int n,int index){//第index行
if(index==n){
count++;
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(isValid(index,i)){
pos[index]=i;
dfs(n,index+1);
// pos[index]=-1; 有没有没关系,因为本来就是一行一个,返回上一个index,这行资源就释放了
}
}
}
public Boolean isValid(int row,int col){
//遍历已经存过的前面的行
//注意对角线的写法
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
if(row==i||pos[i]==col||Math.abs(row-i)==Math.abs(pos[i]-col)) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n∗n!),isValid函数每次检查复杂度为O(n),递归过程相当于对长度为n的数组求全排列,复杂度为O(n!)
空间复杂度:O(n),辅助数组和栈空间最大为O(n)
但是题目要求空间复杂度O(1),题解中没有发现O(1)的做法
输出数组
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
int count=0;
int[] pos = new int[9];
//注意 new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>()报错
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
Arrays.fill(pos,-1);
dfs(n,0);
return (List<List<String>>)res;
}
public void dfs(int n,int index){
if(index==n){
ArrayList<String> solu = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder();
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(pos[i]==j) temp.append("Q");
else temp.append(".");
}
solu.add(new String(temp));
}
res.add(solu);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(isValid(index,i)){
pos[index]=i;
dfs(n,index+1);
}
}
}
public Boolean isValid(int row,int col){
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
if(i==row||pos[i]==col||Math.abs(i-row)==Math.abs(pos[i]-col)) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
60 括号生成

可以先把n转换为((()))字符串,剩下的做法就和之前的没有什么区别,做完之后这样会有一个问题:没有考虑到括号的特性:可能先出现右括号再出现左括号,于是用两个数组来记录左括号和右括号剩余的个数,当两个个数相等的时候,先放入左括号
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param n int整型
* @return string字符串ArrayList
*/
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
int[] vis = new int[20];
public ArrayList<String> generateParenthesis (int n) {
// write code here
if(n==0) return res;
int[] count = new int[2];
count[0]=n;
count[1]=n;
StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
str.append("(");
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
str.append(")");
}
dfs(str,temp,0,count);
return res;
}
public void dfs(StringBuilder str, StringBuilder temp,int index,int[] count){
if(index==str.length()){
res.add(new String(temp));
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
if(vis[i]==1) continue;
if(i>0&&str.charAt(i)==str.charAt(i-1)&&vis[i-1]==1) continue;
if(count[0]==count[1]&&str.charAt(i)==')') continue;
vis[i]=1;
if(str.charAt(i)=='(') count[0]--;
else count[1]--;
temp.append(Character.toString(str.charAt(i)));
dfs(str,temp,index+1,count);
temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length()-1);
vis[i]=0;
if(str.charAt(i)=='(') count[0]++;
else count[1]++;
}
}
}

61 矩阵最长递增路径



和岛屿数量差不多。用一个数组存到该位置位置最长的递增个数
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
* 递增路径的最大长度
* @param matrix int整型二维数组 描述矩阵的每个数
* @return int整型
*/
public int solve (int[][] matrix) {
// write code here
int[][] count=new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length];
for (int[] temp: count){
//注意fill只能填充一维数组
Arrays.fill(temp, 1);
}
for(int i=0;i<count.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<count[0].length;j++){
dfs(matrix,i,j,count);
}
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<count.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<count[0].length;j++){
if(count[i][j]>max) max = count[i][j];
}
}
return max;
}
public void dfs(int[][] matrix, int i,int j,int[][] count){
if(i>0&&matrix[i-1][j]>matrix[i][j]){
count[i-1][j] = Math.max(count[i][j]+1,count[i-1][j]);
dfs(matrix,i-1,j,count);
}
if(j>0&&matrix[i][j-1]>matrix[i][j]){
count[i][j-1] = Math.max(count[i][j]+1,count[i][j-1]);
dfs(matrix,i,j-1,count);
}
if(i<matrix.length-1&&matrix[i+1][j]>matrix[i][j]){
count[i+1][j] = Math.max(count[i][j]+1,count[i+1][j]);
dfs(matrix,i+1,j,count);
}
if(j<matrix[0].length-1&&matrix[i][j+1]>matrix[i][j]){
count[i][j+1] = Math.max(count[i][j]+1,count[i][j+1]);
dfs(matrix,i,j+1,count);
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(mn),m、n分别为矩阵的两边,遍历整个矩阵以每个点作为起点,然后递归相当于遍历填充dp矩阵
空间复杂度:O(mn),辅助矩阵的空间是一个二维数组
二维数组填充
int[][] count=new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length];
for (int[] temp: count){
Arrays.fill(temp, 1);//给一维的每个元素填充1
}