数据库高级 II
如何保证二叉排序树中的元素是可比较大小的
-
让元素所属的类实现接口Comparable
-
比较器:
Comparable: 内比较器,类实现该接口后,需要重写其中的抽象方法,在类的内部定义比较规则. 观察String对象之间的比较 练习:创建Student类型,其中的属性有:id 学号,name 姓名, age 年龄 1. 将多个Student保存到集合中(乱序),对集合中的所有student数据根据学号进行升序排列 Collections.sort(list) 对集合排序的机制是什么? sort方法内部会自动调用集合中元素的compareTo方法 2. 改变比较规则,要求按照学生的age降序排列 -- 不能改compareTo方法中的代码 3. 改变比较规则,要求按照学生的name升序排列 Comparator:外比较器 比较规则定义在类的外部 通常用于:不改变原有比较规则,要使用新的/临时的比较规则,此时就可以在类的外部实现该接口,定义新的比较规则. Collections.sort(list,Comparator)
定义二叉排序树
public class BinarySearchTree<E extends Comparable<E>> {
//根节点
private Node root;
//定义内部类表示节点
private class Node{
private E ele; //节点中保存的元素对象
private Node left; //左子树指向的节点
private Node right; //右子树指向的节点
//定义有参构造方法,用于创建节点
Node(E ele){
this.ele = ele;
}
}
添加元素
思路:
1. 判断root是否为null
-为null,则将元素封装成节点,称为root,返回true
-不为null,和root进行比较,比较的目的是将元素尝试添加为root的left/right子树
- 和root相等,添加失败,返回false,结束
- 大于>root,尝试添加为root的right;判断right是否为null,
- 为null,则让新元素封装成节点,称为right,添加成功,返回true
- 不为null,继续和right的节点进行比较,尝试将元素添加为right的left/right子树
- 小于,同理
遍历二叉排序树中元素
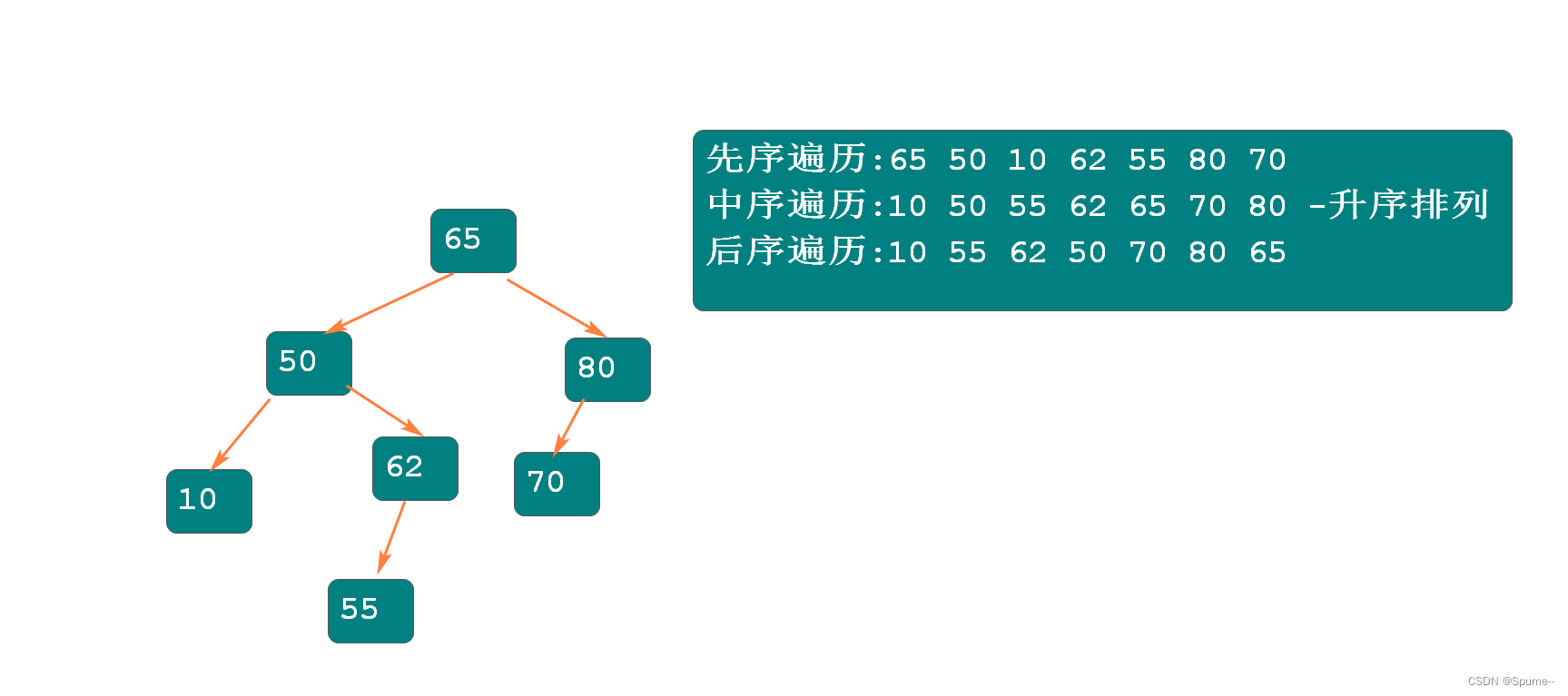
二叉树的遍历:
先序遍历: 根 左 右
中序遍历: 左 根 右 -- 得到升序排列的结果
后序遍历: 左 右 根
重写toString
目的:实现输出引用,将二叉排序树中的元素遍历,并以以下格式返回:
若树中没有节点,此时返回[];若树不为空,则返回[1,2,3,45,78]
1. 定义方法完成中序遍历,要求改方法返回遍历后元素拼接成的字符串
2. 重写toString方法,其中调用中序遍历的方法,用于获取所有元素
1. 判断root是否为null,为null,则返回"[]"
- 不为null,调用中序遍历的方法,得到元素遍历结果
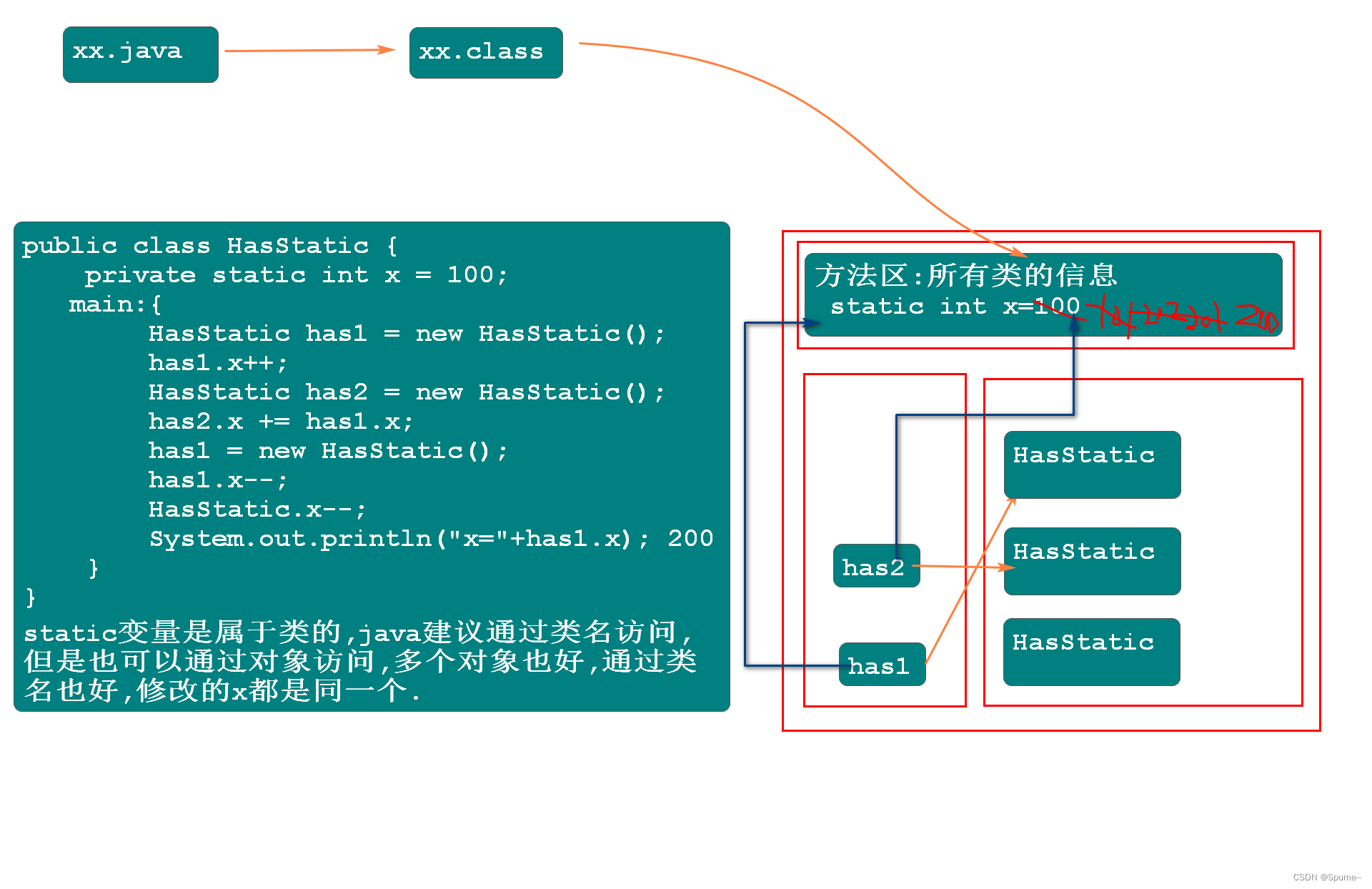
注意点:非static成员变量是属于对象的,会随着对象的重新创建而重新初始化
查询元素的节点
判断root是否为null
- 为null,则树中没有节点,返回null
- 不为null,以root节点为基准,判断root是否为要找的目标节点
- 判断e是否和root的ele相等 -- compareTo,
- 若相等,说明root为要找的节点,返回当前节点,结束
- 若e>ele,则到节点的right去查找目标节点
- 若right为null,说明目标元素不存在于树中,返回null
- 若right不为null,判断right指向的节点是否为要找的目标节点,重复上述过程
- 若e<ele,同理
删除元素
1. 删除叶子节点:让其父节点指向它的引用置为null
2. 删除有一颗子树的节点:让父节点指向它的引用指向删除节点的子节点
3. 删除有两颗子树的节点:可以选择让删除节点的前驱节点或后继节点上来替换该节点.
前驱节点和后继节点:是指升序排列后,删除节点的前一个元素叫做前驱节点;删除节点的后一个元素叫做后继节点
排序: 12,33,45,67,88
题目
-
以下程序的输出结果是什么
非static成员变量是属于对象的,会随着对象的重新创建而重新初始化. public class HasStatic { private int x = 100; public static void main(String[] args) { HasStatic has1 = new HasStatic(); has1.x++; HasStatic has2 = new HasStatic(); has2.x += has1.x; has1 = new HasStatic(); has1.x--; System.out.println("x="+has1.x); //99 System.out.println("x="+has2.x); //201 } }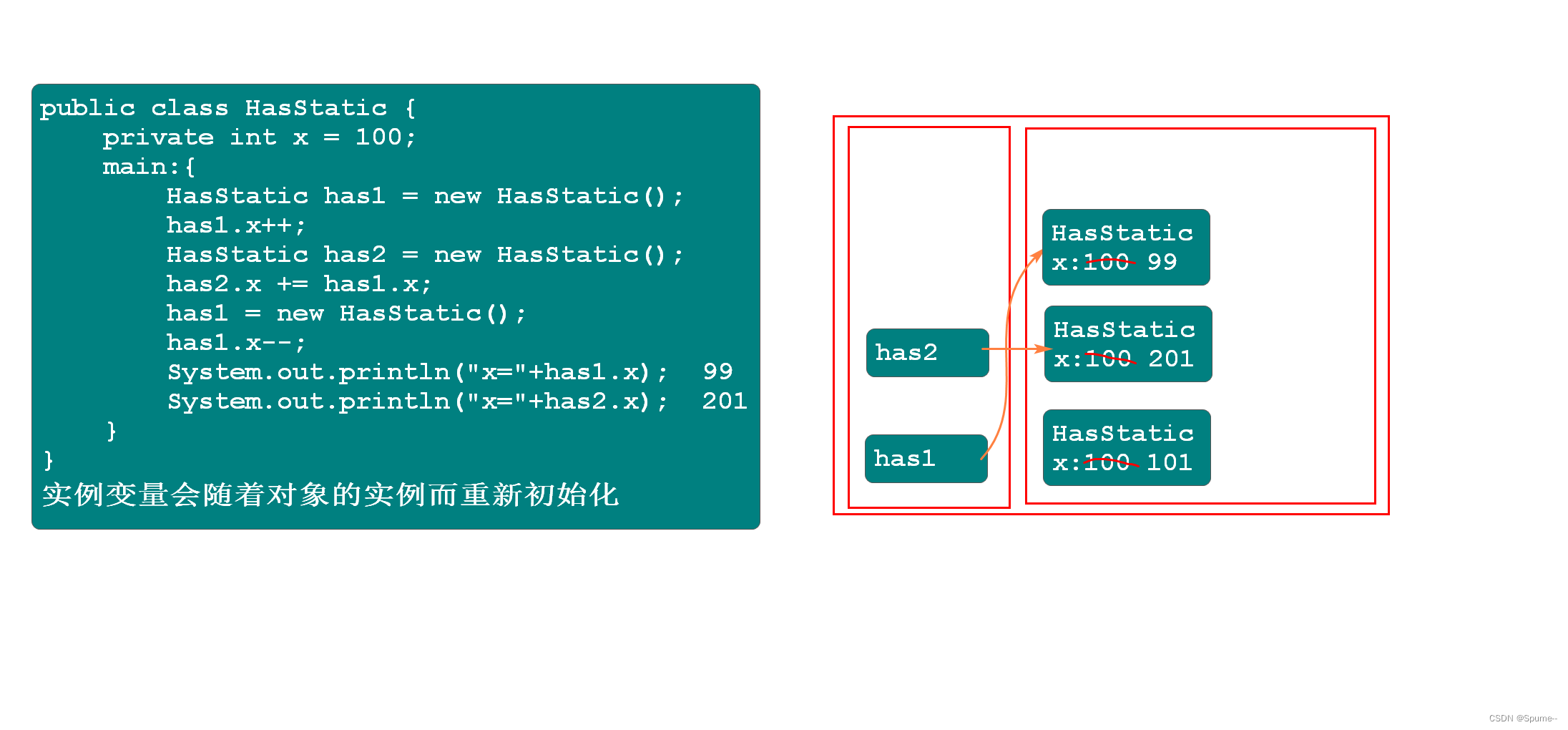
以下程序的输出结果是什么
public class HasStatic {
private static int x = 100;
public static void main(String[] args) {
HasStatic has1 = new HasStatic();
has1.x++;
HasStatic has2 = new HasStatic();
has2.x += has1.x;
has1 = new HasStatic();
has1.x--;
HasStatic.x--;
System.out.println("x="+has1.x); //200
}
}
-
String Str = new String(“ab”+“c”+“d”) 创建了几个String对象
2个 字符串字面量之间的拼接是在什么时候完成的? "ab"+"c"+"d" 是在编译期完成 xx.java中代码为:String Str = new String("ab"+"c"+"d") 经过编译期会产生.class文件 :String str=new String("abcd") 运行期:执行以上代码,创建2个字符串对象 -
String str = new String(“abc”) 创建了几个StringObject
2个 -
选择题
public class Ppvg{ public static void main(String[] args){ Ppvg p = new Ppvg(); int x = p.flition(); System.out.println(x); } public int flition(){ try{ FileInputStream din = new FileInputStream("Ppvg.java"); din.read(); }catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("flytwick"); return 99; }finally{ System.out.println("flition"); } return -1;}} 编译和运行上面的代码,下面对这段程序的描述中正确的是:(C) A. 程序可以正常运行并且输出“flition”和99; B. 程序可以正常运行并且输出“flytwick“,“flition”和-1; C. 程序可以正常运行并且输出“flytwick”,“flition”和99; D. 在编译的时候会产生错误,因为flition方法会要求返回两个值 -
以下程序是否存在问题,若存在,请指出,若没有问题,请给出输出结果
public class Test{ private static Integer b; //null public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; print(a); print(b); b = a; print(b); } private static void print(Integer value){ int add = value+5; //自动拆箱将Integer类型转换为int类型 value.intValue():int System.out.println("add value="+add); } } add value=15 出现空指针异常 -
选择
public static void main(String args[]) { B Thread t = new Thread() { public void run() { pong(); } }; t.run(); //启动线程 t.start() t.run()则不是启动线程,而是普通方法调用 System.out.print("ping"); } static void pong() { System.out.print("pong"); } A pingpong B pongping C pingpong和pongping都有可能 D 都不输出