相关地址
代码:
https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything
在线网站:
https://segment-anything.com/demo
环境配置
建议可以clone下来学习相关代码,安装可以不依赖与这个库
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything.git
1.创建environment.yaml
name: sam
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3.8
- pytorch=1.9.0
- torchvision=0.10.0
- cudatoolkit=11.1
- pip
conda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate raptor
2.安装
pip install git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything.git
3.其他库
pip install opencv-python pycocotools matplotlib onnxruntime onnx
目前安装的版本
Successfully installed coloredlogs-15.0.1 contourpy-1.1.1
cycler-0.12.1 flatbuffers-23.5.26 fonttools-4.43.1 humanfriendly-10.0
importlib-resources-6.1.0 kiwisolver-1.4.5 matplotlib-3.7.3
mpmath-1.3.0 numpy-1.24.4 onnx-1.15.0 onnxruntime-1.16.1
opencv-python-4.8.1.78 packaging-23.2 protobuf-4.24.4
pycocotools-2.0.7 pyparsing-3.1.1 python-dateutil-2.8.2 six-1.16.0
sympy-1.12 zipp-3.17.0
初阶测试
1.下载模型
https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything#model-checkpoints
2.测试代码
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append("..")
from segment_anything import sam_model_registry, SamAutomaticMaskGenerator, SamPredictor
def show_anns(anns):
if len(anns) == 0:
return
sorted_anns = sorted(anns, key=(lambda x: x['area']), reverse=True)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_autoscale_on(False)
img = np.ones((sorted_anns[0]['segmentation'].shape[0], sorted_anns[0]['segmentation'].shape[1], 4))
img[:,:,3] = 0
for ann in sorted_anns:
m = ann['segmentation']
color_mask = np.concatenate([np.random.random(3), [0.35]])
img[m] = color_mask
ax.imshow(img)
sam_checkpoint = "./checkpoints/sam_vit_h_4b8939.pth"
model_type = "vit_h"
device = "cuda"
sam = sam_model_registry[model_type](checkpoint=sam_checkpoint)
sam.to(device=device)
mask_generator = SamAutomaticMaskGenerator(sam)
img_path = '/data/qinl/code/segment-anything/notebooks/images/dog.jpg'
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
masks = mask_generator.generate(image)
'''
Mask generation returns a list over masks, where each mask is a dictionary containing various data about the mask. These keys are:
* `segmentation` : the mask
* `area` : the area of the mask in pixels
* `bbox` : the boundary box of the mask in XYWH format
* `predicted_iou` : the model's own prediction for the quality of the mask
* `point_coords` : the sampled input point that generated this mask
* `stability_score` : an additional measure of mask quality
* `crop_box` : the crop of the image used to generate this mask in XYWH format
'''
print(len(masks))
print(masks[0].keys())
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
plt.imshow(image)
show_anns(masks)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
3.输出
65
dict_keys(['segmentation', 'area', 'bbox', 'predicted_iou', 'point_coords', 'stability_score', 'crop_box'])
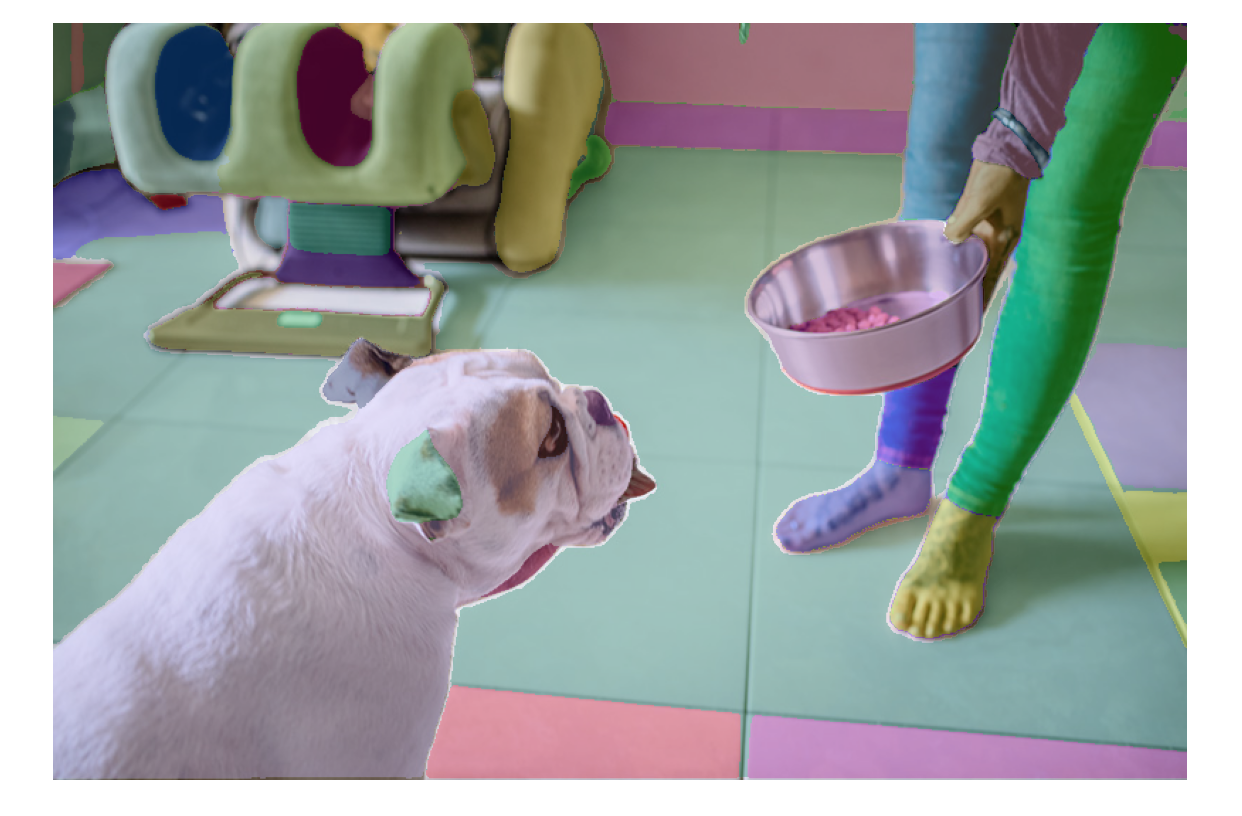

进阶测试
图片预处理部分
其他instruction,都是在这个基础上进行处理
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append("..")
from segment_anything import sam_model_registry, SamPredictor
def show_mask(mask, ax, random_color=False):
if random_color:
color = np.concatenate([np.random.random(3), np.array([0.6])], axis=0)
else:
color = np.array([30/255, 144/255, 255/255, 0.6])
h, w = mask.shape[-2:]
mask_image = mask.reshape(h, w, 1) * color.reshape(1, 1, -1)
ax.imshow(mask_image)
def show_points(coords, labels, ax, marker_size=375):
pos_points = coords[labels==1]
neg_points = coords[labels==0]
ax.scatter(pos_points[:, 0], pos_points[:, 1], color='green', marker='*', s=marker_size, edgecolor='white', linewidth=1.25)
ax.scatter(neg_points[:, 0], neg_points[:, 1], color='red', marker='*', s=marker_size, edgecolor='white', linewidth=1.25)
def show_box(box, ax):
x0, y0 = box[0], box[1]
w, h = box[2] - box[0], box[3] - box[1]
ax.add_patch(plt.Rectangle((x0, y0), w, h, edgecolor='green', facecolor=(0,0,0,0), lw=2))
sam_checkpoint = "./checkpoints/sam_vit_h_4b8939.pth"
model_type = "vit_h"
device = "cuda"
sam = sam_model_registry[model_type](checkpoint=sam_checkpoint)
sam.to(device=device)
predictor = SamPredictor(sam)
img_path = '/data/qinl/code/segment-anything/notebooks/images/truck.jpg'
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 预处理输入图片
predictor.set_image(image)
输入的instruction为point的情况
# 输入为point的情况
input_point = np.array([[500, 375]])
input_label = np.array([1])
# 可以用来显示一下点的位置
# plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
# plt.imshow(image)
# show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
# plt.axis('on')
# plt.show()
masks, scores, logits = predictor.predict(
point_coords=input_point,
point_labels=input_label,
multimask_output=True,
)
print('masks.shape',masks.shape) # (number_of_masks) x H x W
# 输出3个mask,分别有不同的score
for i, (mask, score) in enumerate(zip(masks, scores)):
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.imshow(image)
show_mask(mask, plt.gca())
show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
plt.title(f"Mask {i+1}, Score: {score:.3f}", fontsize=18)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
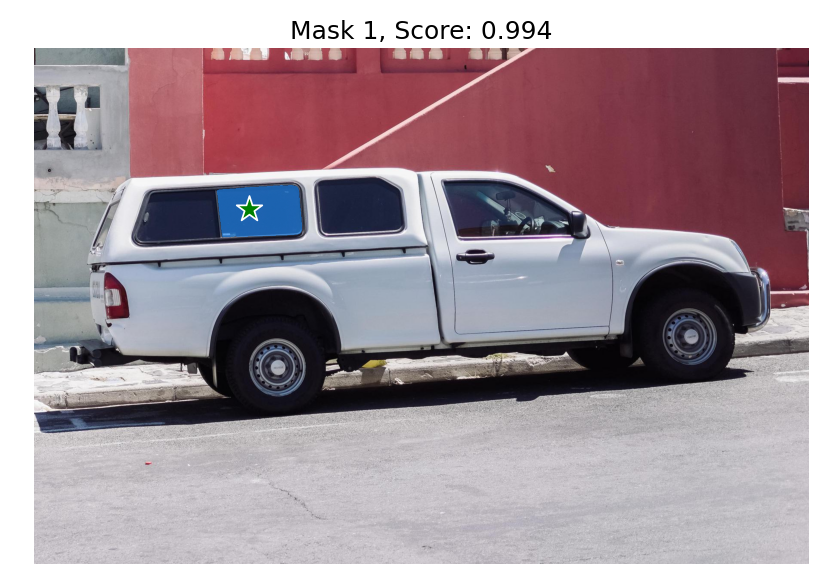
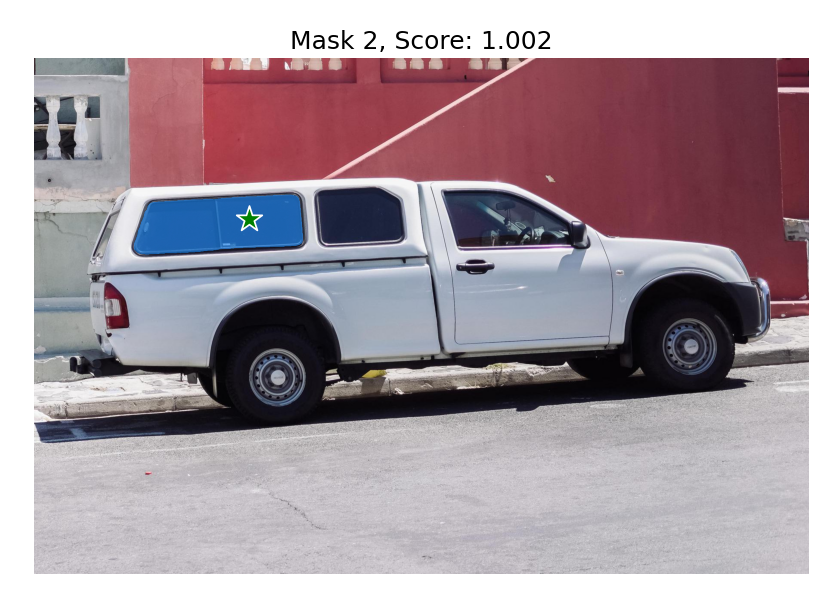
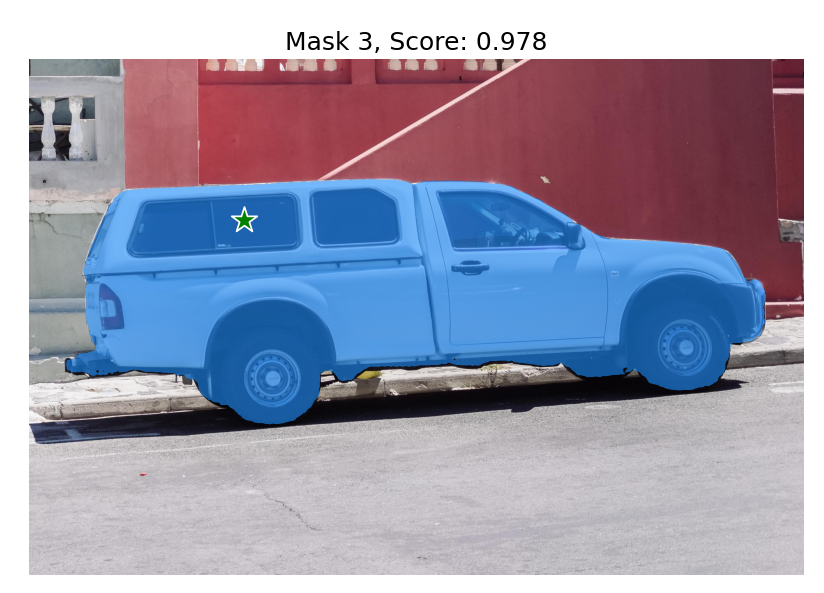



多点输入(都视为前景点)
# 输入为多个point的情况(前景点)
input_point = np.array([[500, 375]])
input_label = np.array([1])
masks, scores, logits = predictor.predict(
point_coords=input_point,
point_labels=input_label,
multimask_output=True,
)
# additional points
input_point = np.array([[500, 375], [1125, 625]])
input_label = np.array([1, 1])
mask_input = logits[np.argmax(scores), :, :] # Choose the model's best mask
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict(
point_coords=input_point,
point_labels=input_label,
mask_input=mask_input[None, :, :],
multimask_output=False,
)
print('masks.shape',masks.shape) # only 1 x H x W
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.imshow(image)
show_mask(masks, plt.gca())
show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
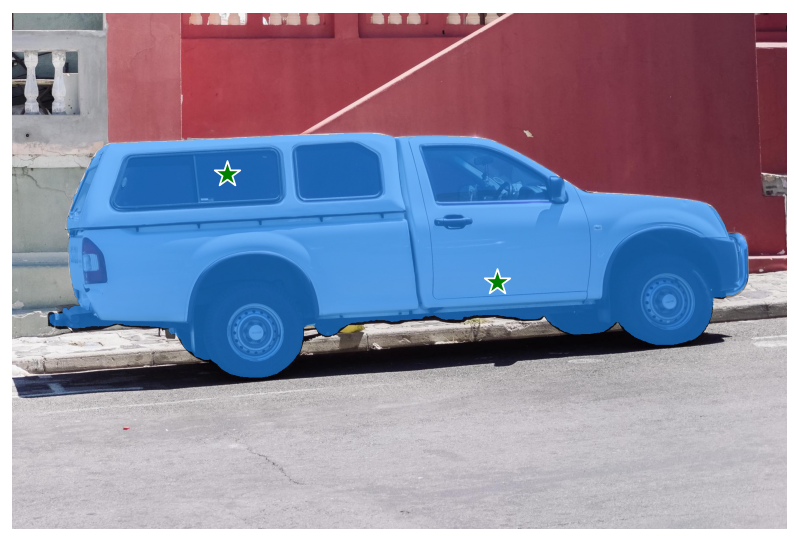

多点输入(前景点加后景点)
决定这个点是前景点还是后景点的就是label,0就是背景的意思
修改标签,得到不一样的结果
# input_point = np.array([[500, 375], [1125, 625]])
# input_label = np.array([1, 1])
input_point = np.array([[500, 375], [1125, 625]])
input_label = np.array([1, 0])
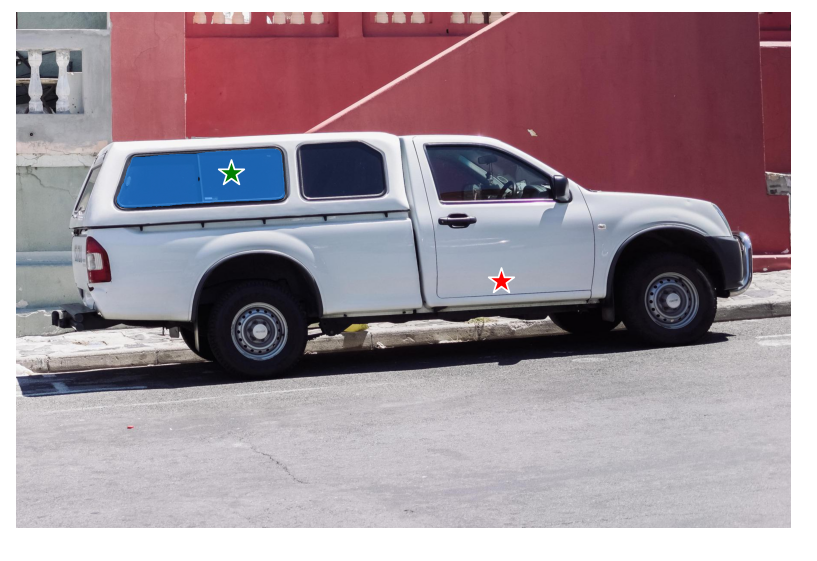

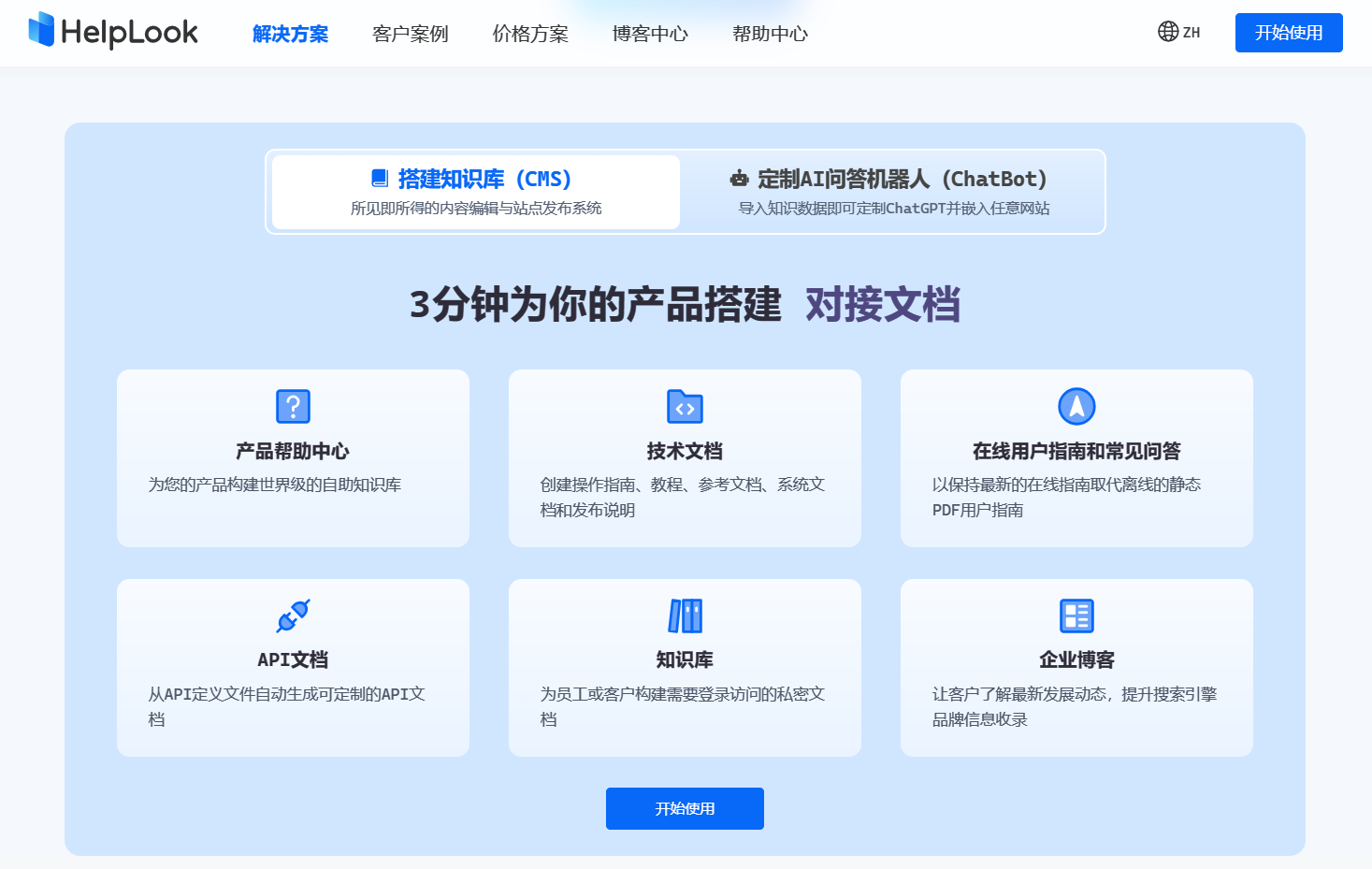
使用box框具体物体
# 输入为additional points
input_box = np.array([425, 600, 700, 875])
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict(
point_coords=None,
point_labels=None,
box=input_box[None, :],
multimask_output=False,
)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(image)
show_mask(masks[0], plt.gca())
show_box(input_box, plt.gca())
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
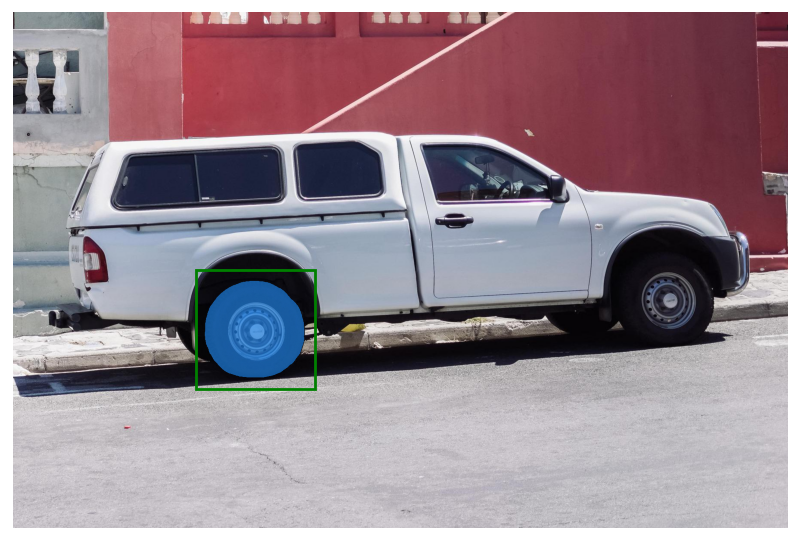
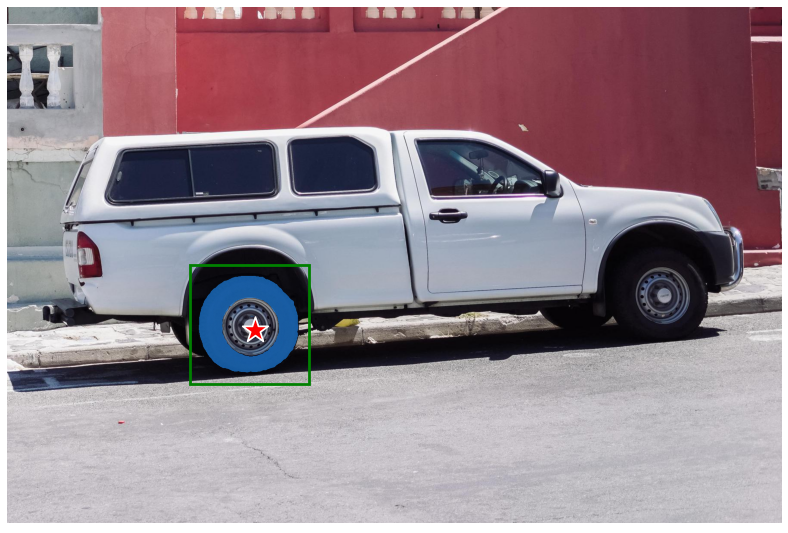
结合points和box
# 输入为point和box
input_box = np.array([425, 600, 700, 875])
input_point = np.array([[575, 750]])
input_label = np.array([0])
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict(
point_coords=input_point,
point_labels=input_label,
box=input_box,
multimask_output=False,
)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(image)
show_mask(masks[0], plt.gca())
show_box(input_box, plt.gca())
show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()

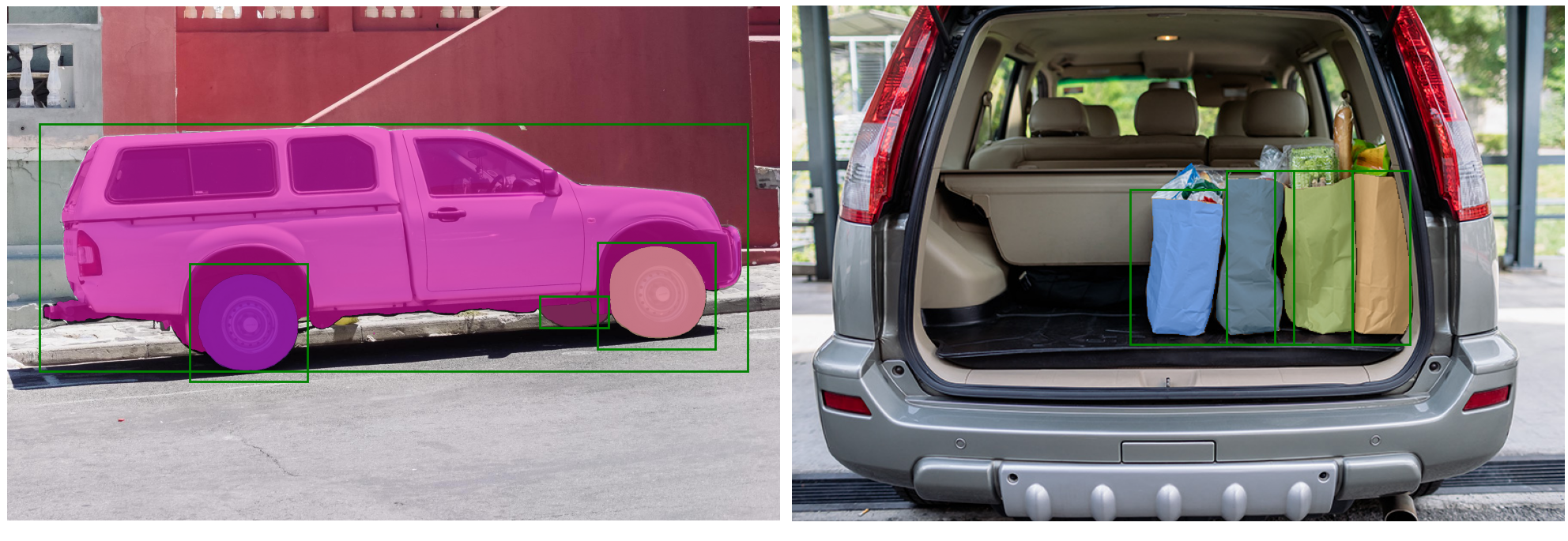
batch prompt inputs
# batch prompt inputs
input_boxes = torch.tensor([
[75, 275, 1725, 850],
[425, 600, 700, 875],
[1375, 550, 1650, 800],
[1240, 675, 1400, 750],
], device=predictor.device)
transformed_boxes = predictor.transform.apply_boxes_torch(input_boxes, image.shape[:2])
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict_torch(
point_coords=None,
point_labels=None,
boxes=transformed_boxes,
multimask_output=False,
)
print(masks.shape) # (batch_size) x (num_predicted_masks_per_input) x H x W
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(image)
for mask in masks:
show_mask(mask.cpu().numpy(), plt.gca(), random_color=True)
for box in input_boxes:
show_box(box.cpu().numpy(), plt.gca())
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
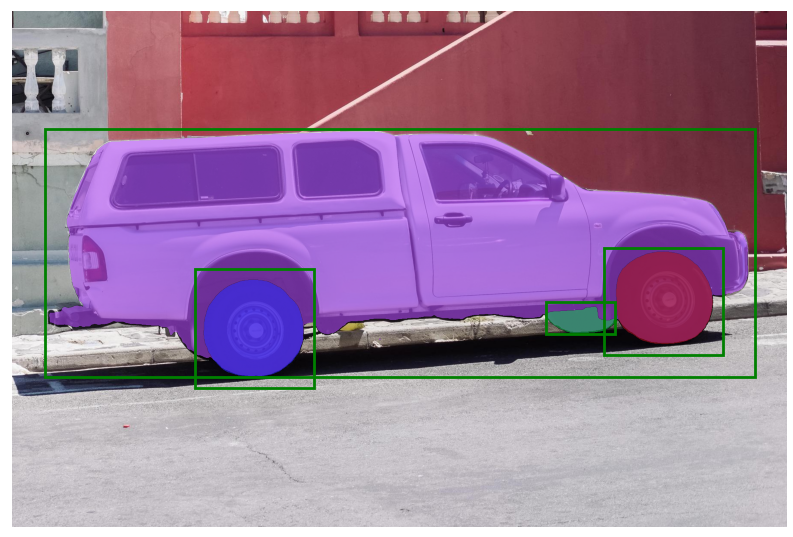
End-to-end batched inference
## End-to-end batched inference
image1 = image # truck.jpg from above
image1_boxes = torch.tensor([
[75, 275, 1725, 850],
[425, 600, 700, 875],
[1375, 550, 1650, 800],
[1240, 675, 1400, 750],
], device=sam.device)
image2 = cv2.imread('./notebooks/images/groceries.jpg')
image2 = cv2.cvtColor(image2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image2_boxes = torch.tensor([
[450, 170, 520, 350],
[350, 190, 450, 350],
[500, 170, 580, 350],
[580, 170, 640, 350],
], device=sam.device)
# Both images and prompts are input as PyTorch tensors that are already transformed to the correct frame.
# Inputs are packaged as a list over images, which each element is a dict that takes the following keys:
# * `image`: The input image as a PyTorch tensor in CHW format.
# * `original_size`: The size of the image before transforming for input to SAM, in (H, W) format.
# * `point_coords`: Batched coordinates of point prompts.
# * `point_labels`: Batched labels of point prompts.
# * `boxes`: Batched input boxes.
# * `mask_inputs`: Batched input masks.
from segment_anything.utils.transforms import ResizeLongestSide
resize_transform = ResizeLongestSide(sam.image_encoder.img_size)
def prepare_image(image, transform, device):
image = transform.apply_image(image)
image = torch.as_tensor(image, device=device.device)
return image.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
batched_input = [
{
'image': prepare_image(image1, resize_transform, sam),
'boxes': resize_transform.apply_boxes_torch(image1_boxes, image1.shape[:2]),
'original_size': image1.shape[:2]
},
{
'image': prepare_image(image2, resize_transform, sam),
'boxes': resize_transform.apply_boxes_torch(image2_boxes, image2.shape[:2]),
'original_size': image2.shape[:2]
}
]
batched_output = sam(batched_input, multimask_output=False)
# The output is a list over results for each input image, where list elements are dictionaries with the following keys:
# * `masks`: A batched torch tensor of predicted binary masks, the size of the original image.
# * `iou_predictions`: The model's prediction of the quality for each mask.
# * `low_res_logits`: Low res logits for each mask, which can be passed back to the model as mask input on a later iteration.
print('batched_output[0].keys()',batched_output[0].keys())
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 20))
ax[0].imshow(image1)
for mask in batched_output[0]['masks']:
show_mask(mask.cpu().numpy(), ax[0], random_color=True)
for box in image1_boxes:
show_box(box.cpu().numpy(), ax[0])
ax[0].axis('off')
ax[1].imshow(image2)
for mask in batched_output[1]['masks']:
show_mask(mask.cpu().numpy(), ax[1], random_color=True)
for box in image2_boxes:
show_box(box.cpu().numpy(), ax[1])
ax[1].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

高阶测试
模型训练(waiting)