目录
一、什么是中断机制
二、三大中断方法
2.1、如何停止中断运行中的线程?
2.1.1、通过volatile实现线程中断停止
2.1.2、通过AtomicBoolean实现线程中断停止
2.1.3、通过interrupt()实现线程中断停止
2.2、interrupted()方法使用
一、什么是中断机制
一个线程不应该由其他线程来强制中断或停止,而是应该线程自己自行停止,自己来决定自己的命运。所以,Thread.stop,Thread.suspend,Thread.resume都已经被废弃了。
在Java中没有办法立即停止一条线程,然而停止线程却显得尤为重要,如取消一个耗时操作。因此,Java提供了一种用于停止线程的协商机制-----中断,也为中断标识协商机制。
中断只是一种协作协商机制,Java没有给中断增加任何语法,中断的过程完全需要程序员自己实现。若要中断一个线程,你需要手动调用该线程的interrupt方法,该方法也仅仅是将线程对象的中断标识设成true,接着你需要自己写代码不断地检测当前线程地标识位,如果为true,表示别的线程请求这条线程中断,此时究竟该做什么需要自己写代码实现。
每个线程对象中都有一个中断标识位,用于表示线程是否被中断;该标识位为true表示中断,为false表示未中断;通过调用线程对象的interrupt方法将该线程的标识位设为true,可以在别的线程中调用,也可以在自己的线程中调用。
二、三大中断方法
public void interrupt():实例方法interrupt()仅仅是设置线程的中断状态为true,发起一个不协商而不会立刻停止线程。
public static boolean interrupted():静态方法,判断线程是否被中断并清除当前中断状态。该方法主要做两件事:1、返回当前线程的中断状态,测试当前线程是否已被中断。2、将当前线程的中断状态清零并重新设为false,清除线程的中断状态。
public boolean isInterrupted():实例方法,判断当前线程是否被中断(通过检查中断标志位)
2.1、如何停止中断运行中的线程?
2.1.1、通过volatile实现线程中断停止
public class InterruptTest {
public static volatile boolean isStop = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
if (isStop){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1....hello");
}
},"t1").start();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() ->{
isStop = true;
},"t2").start();
}
}
2.1.2、通过AtomicBoolean实现线程中断停止
public class InterruptTest {
public static AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean(false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
while (true){
if (atomicBoolean.get()){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1....hello");
}
},"t1").start();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() ->{
atomicBoolean.set(true);
},"t2").start();
}
}
2.1.3、通过interrupt()实现线程中断停止
public class InterruptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "程序停止");
break;
}
System.out.println("t1....hello");
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// new Thread(() ->{
// t1.interrupt();
// },"t2").start();
//也可以自己设置
t1.interrupt();
}
}当对一个线程,调用interrupt()时;
①、如果线程处于正常活动状态,那么会将该线程的中断标志设置为true,仅此而已。被设置中断标志的线程将继续正常运行,不受影响。所以,interrupt()并不能真正的中断线程,需要被调用的线程自己进行配合才行。
public class InterruptTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <=400 ; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("t1线程调用interrupt()后的中断标识02"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}, "t1");
t1.start();
System.out.println("t1线程默认的中断标识为:" + t1.isInterrupted());//false
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t1.interrupt();//true
System.out.println("t1线程默认的中断标识01:"+t1.isInterrupted());
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t1线程默认的中断标识03:"+t1.isInterrupted());//false
}
}
②、如果线程处于被阻塞状态(例如处于sleep,wait,join等状态),在别的线程中调用当前线程对象的interrupt方法,那么线程将立即退出被阻塞状态,并抛出一个InterruptedException异常。
public class InterruptTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true){
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("t1线程的中断标识位:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t1正在工作");
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->t1.interrupt(),"t2").start();
}
}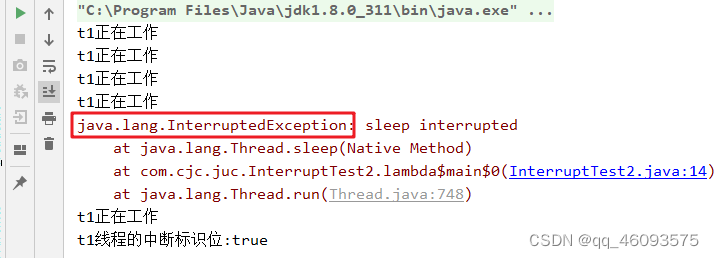
sleep方法抛出InterruptedException后,中断标识也被清空置为false,在catch没有通过调用th。Interrupt()方法再次将中断标识置为true,这就导致无限死循环。
2.2、interrupted()方法使用
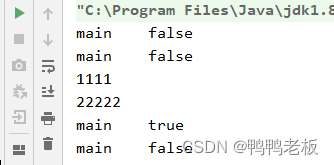
public class InterruptTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("1111");
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("22222");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + Thread.interrupted());
}
}