字符流
FileReader(文件字符输入流)

使用文件字符输入流,有啥好处?
读取中文不会出现乱码问题
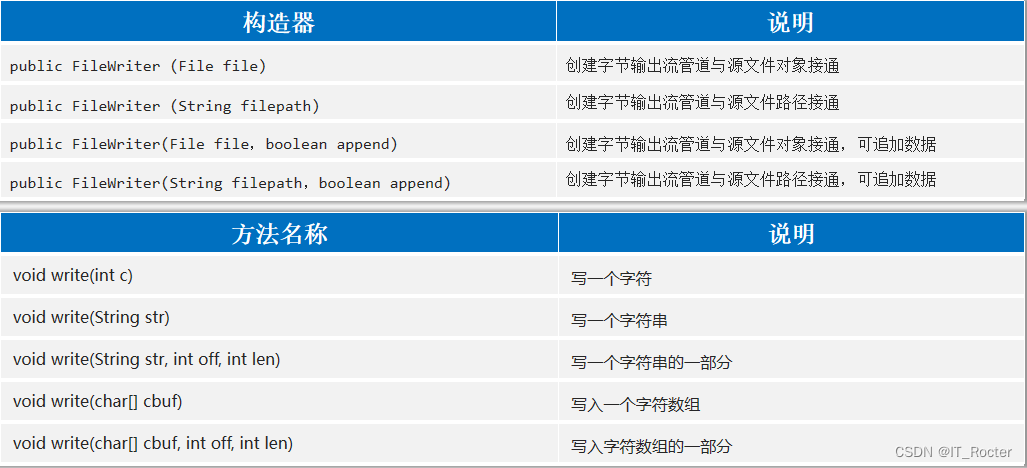
FileWriter(文件字符输出流)
利用字符流将一个文本文件复制到E:盘下,例如:D:/1.txt复制到E:/2.txt
请使用字符流:FileReader和FileWriter实现
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try ( FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:/1.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("E:/2.txt")){
char[] chars = new char[3];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chars)) != -1){
fw.write(chars);
}
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("哈哈哈");
}
}
}字节流、字符流的使用场景小结:
1.字节流适合做一切文件数据的拷贝(音视频,文本);字节流不适合读取中文内容输出。
2.字符流适合做文本文件的操作(读,写)。
缓冲流
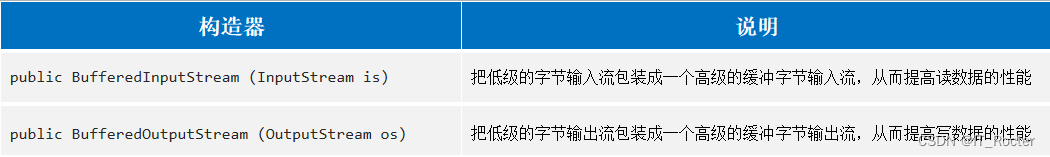
字节缓冲流的作用
1.提高字节流读写数据的性能
2.字节缓冲输入流自带了8KB缓冲池;字节缓冲输出流也自带了8KB缓冲池。
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bi = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("E:\\QQmusic\\MV\\赵雷-少年锦时 (2015湘江音乐节)(高清).mp4"));
BufferedOutputStream bo = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("E:\\QQmusic\\haha\\赵雷-少年锦时 (2015湘江音乐节)(高清).mp4"));
byte[] a = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int len;
while ((len = bi.read(a)) != -1){
bo.write(a,0,len);
}
bi.close();
bo.close();
}
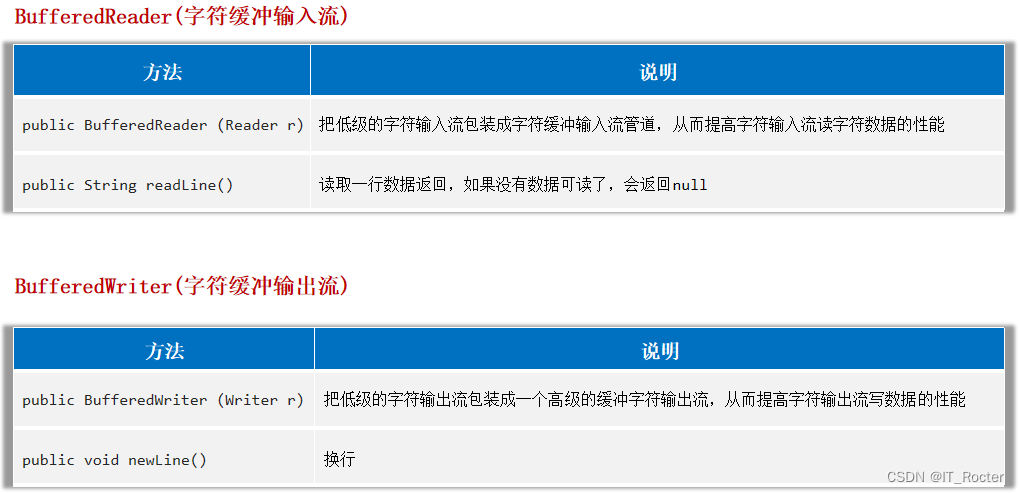
}字符缓冲流
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader( new FileReader("E:/Code191Day/day09/b-3.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:/Code191Day/day09/b-4.txt"));
String a;
while ((a = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(a);
bw.newLine();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
转换流
为了解决不同编码读取出现乱码问题
打印流
打印流可以实现更方便、更高效的打印数据出去,能实现打印啥出去就是啥出去。
数据流
允许把数据和其类型一并写出去。
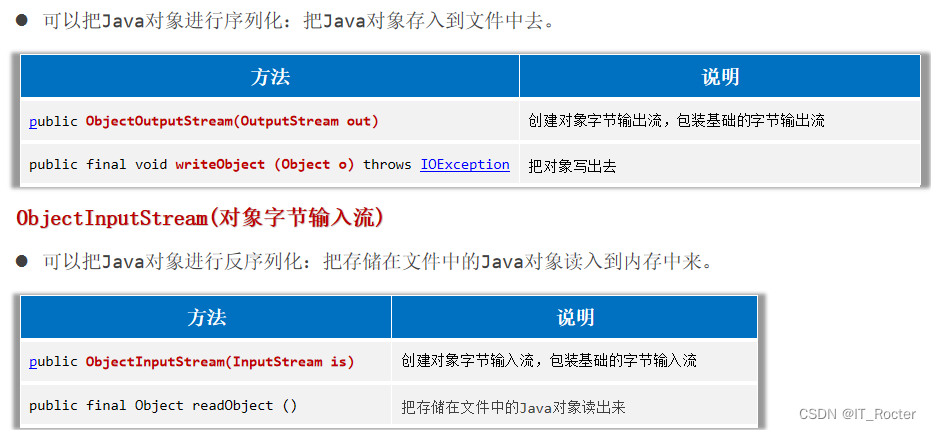
序列化流
ObjectOutputStream(对象字节输出流)
![]()
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//0. 准备一个Student对象
Student student = new Student("张三", 18);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/Code191Day/day09/c-5.txt"));
oos.writeObject(student);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/Code191Day/day09/c-5.txt"));
Student student1 = (Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(student1.getAge());
ois.close();
}
}
//学生类
class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String
toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
如果一次要序列化多个对象咋整?

public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//0. 准备一个Student对象的集合
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("张三", 18));
students.add(new Student("李四", 19));
students.add(new Student("王五", 20));
//1. 序列化(f-1.txt)
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/Code191Day/day09/c-6.txt"));
oos.writeObject(students);
oos.close();
//2. 反序列化(f-1.txt)
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/Code191Day/day09/c-6.txt"));
List<Student> objects = (ArrayList)ois.readObject();
objects.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
ois.close();
}
}
IO框架