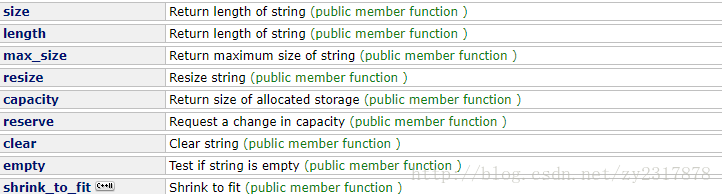
string类与头文件包含:#include <string>
string构造方法:
// string constructor
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string s0 ("Initial string"); //根据已有字符串构造新的string实例
// constructors used in the same order as described above:
std::string s1; //构造一个默认为空的string
std::string s2 (s0); //通过复制一个string构造一个新的string
std::string s3 (s0, 8, 3); //通过复制一个string的一部分来构造一个新的string。8为起始位置,3为偏移量。
std::string s4 ("A character sequence"); //与s0构造方式相同。
std::string s5 ("Another character sequence", 12); //已知字符串,通过截取指定长度来创建一个string
std::string s6a (10, 'x'); //指定string长度,与一个元素,则默认重复该元素创建string
std::string s6b (10, 42); // 42 is the ASCII code for '*' //通过ASCII码来代替s6a中的指定元素。
std::string s7 (s0.begin(), s0.begin()+7); //通过迭代器来指定复制s0的一部分,来创建s7
std::cout << "s1: " << s1 << "\ns2: " << s2 << "\ns3: " << s3;
std::cout << "\ns4: " << s4 << "\ns5: " << s5 << "\ns6a: " << s6a;
std::cout << "\ns6b: " << s6b << "\ns7: " << s7 << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
s1:
s2: Initial string
s3: str
s4: A character sequence
s5: Another char
s6a: xxxxxxxxxx
s6b: **********
s7: Initialstring::operation = :使用 = 运算符也可以创建string。
// string assigning
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str1, str2, str3;
str1 = "Test string: "; // c-string //通过=运算符来给已创建的string“赋值”
str2 = 'x'; // single character
str3 = str1 + str2; // string
//注意这里重载了"+",string类的"+"可以理解为胶水,将两个string类型连接起来了
std::cout << str3 << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
Test string: xstring-Iterators:string也有迭代器,熟练掌握迭代器的使用,有时能避免繁杂的for循环,但代码更有灵活性。
// string::begin/end
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("Test string");
for ( std::string::iterator it=str.begin(); it!=str.end(); ++it)
std::cout << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
Test stringstring-capacity:
// string::size
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("Test string");
std::cout << "The size of str is " << str.size() << " bytes.\n";
return 0;
}
//Output:
//The size of str is 11 bytes
// string::length
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("Test string");
std::cout << "The size of str is " << str.length() << " bytes.\n";
return 0;
}
//Output:
//The size of str is 11 bytes比较一下size与length,其实二者没有任何区别,length是因为沿用C语言的习惯而保留下来的,string类最初只有length,引入STL之后,为了兼容又加入了size,它是作为STL容器的属性存在的,便于符合STL的接口规则,以便用于STL的算法。
string::clear:擦除字符串的内容,成为一个空字符串(长度为0个字符)。
调用方式:
str.clear();string::empty:判断string其中内容是否为空。再判断一个string是否为空时,可以使用该函数,也可以使用size()函数与length()函数来获取string的长度,然后判断长度是否为0。但优先使用empty()函数,因为该函数运行速度更快。
string-element access
.string::operator[]:获取字符串的字符,返回字符串中位置pos处字符的引用。示例代码如下
// string::operator[]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("Test string");
for (int i=0; i<str.length(); ++i)
{
std::cout << str[i];
}
return 0;
}
输出:
Test string.string::at:获取字符串中的字符,返回字符串中位置pos处字符的引用。该函数自动检查pos是否是字符串中字符的有效位置(即pos是否小于字符串长度),如果不是,则会抛出out_of_range异常。示例代码如下
// string::at
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("Test string");
for (unsigned i=0; i<str.length(); ++i)
{
std::cout << str.at(i);
}
return 0;
}
//Output:
//Test stringoperator[]和at()均返回当前字符串中第n个字符的位置,但at函数提供范围检查,当越界时会抛出out_of_range异常,下标运算符[]不提供检查访问。[]访问的速度比at()要快,但不作越界检查.用[]访问之前, 要对下标进行检查( > string::npos && < string::size())
string::back:访问最后一个字符,返回对字符串最后一个字符的引用。这个函数不能在空字符串上调用。
// string::back
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("hello world.");
str.back() = '!';
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
//Output:
//hello world! //将原来的最后一个'.' 变为了'!'。string::front:访问第一个字符,返回对字符串的第一个字符的引用。与成员string :: begin不同,它将一个迭代器返回给这个相同的字符,这个函数返回一个直接引用。这个函数不能在空字符串上调用。
// string::front
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("test string");
str.front() = 'T';
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
//Output:
//Test string //将原来的第一个't'变为了'T'。string-modifiers:
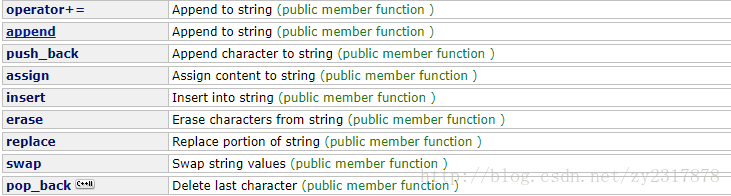
string::operator+=:附加到字符串。通过在当前值的末尾添加其他字符来扩展字符串:
// string::operator+=
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string name ("John");
std::string family ("Smith");
name += " K. "; // c-string
name += family; // string
name += '\n'; // character
std::cout << name;
return 0;
}
//Output:
//John K. Smithstring::append:附加到字符串。通过在当前值的末尾添加其他字符来扩展字符串:
// appending to string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str;
std::string str2="Writing ";
std::string str3="print 10 and then 5 more";
// used in the same order as described above:
str.append(str2); // "Writing "
str.append(str3,6,3); // "10 "
str.append("dots are cool",5); // "dots "
str.append("here: "); // "here: "
str.append(10u,'.'); // ".........."
str.append(str3.begin()+8,str3.end()); // " and then 5 more"
str.append<int>(5,0x2E); // "....."
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}
//Output:
//Writing 10 dots here: .......... and then 5 more.....string::push_ back:追加字符到字符串。将字符c附加到字符串的末尾,将其长度增加1。与vector、set、map等容器的push_ back类似功能。
string::assign:将内容分配给字符串。为字符串分配一个新值,替换其当前内容。
string::insert:插入字符串。在由pos(或p)指示的字符之前的字符串中插入附加字符:
// inserting into a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str="to be question";
std::string str2="the ";
std::string str3="or not to be";
std::string::iterator it;
// used in the same order as described above:
//后面注释中()括号的作用只是帮助显示插入的内容与位置信息。实际string中并没有这对括号
str.insert(6,str2); // to be (the )question
str.insert(6,str3,3,4); // to be (not )the question
str.insert(10,"that is cool",8); // to be not (that is )the question
str.insert(10,"to be "); // to be not (to be )that is the question
str.insert(15,1,':'); // to be not to be(:) that is the question
it = str.insert(str.begin()+5,','); // to be(,) not to be: that is the question
str.insert (str.end(),3,'.'); // to be, not to be: that is the question(...)
str.insert (it+2,str3.begin(),str3.begin()+3); // (or )
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
//Output:
//to be, or not to be: that is the question...
}string::erase:擦除字符串中的字符。擦除部分字符串,减少其长度
// string::erase
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("This is an example sentence.");
std::cout << str << '\n';
//后面注释有两部分,上一行是当前字符串内容,下一行是箭头,表示的意思就是箭头指向内容是处理的内容
// "This is an example sentence."
str.erase (10,8); // ^^^^^^^^
std::cout << str << '\n'; //消除第11到第19之间的字符。即" example",注意,有一个空格符
// "This is an sentence."
str.erase (str.begin()+9); // ^
std::cout << str << '\n'; //消除第10个字符,即begin()后9个字符:'n'
// "This is a sentence."
str.erase (str.begin()+5, str.end()-9); // ^^^^^
std::cout << str << '\n'; //消除begin()后5个字符,end()前9个字符。
// "This sentence."
return 0;
}string::replace:替换字符串的一部分。替换以字符pos开头的字符串部分,并通过新内容跨越len字符(或[i1,i2之间的范围内的字符串部分)):
// replacing in a string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string base="this is a test string.";
std::string str2="n example";
std::string str3="sample phrase";
std::string str4="useful.";
// replace signatures used in the same order as described above:
// Using positions: 0123456789*123456789*12345
std::string str=base; // "this is a test string."
// ^^^^^
str.replace(9,5,str2); // "this is an example string." (1)
// ^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^
str.replace(19,6,str3,7,6); // "this is an example phrase." (2)
// ^^^^^^
str.replace(8,10,"just a"); // "this is just a phrase." (3)
str.replace(8,6,"a shorty",7); // "this is a short phrase." (4)
str.replace(22,1,3,'!'); // "this is a short phrase!!!" (5)
// Using iterators: 0123456789*123456789*
str.replace(str.begin(),str.end()-3,str3); // "sample phrase!!!" (1)
str.replace(str.begin(),str.begin()+6,"replace"); // "replace phrase!!!" (3)
str.replace(str.begin()+8,str.begin()+14,"is coolness",7); // "replace is cool!!!" (4)
str.replace(str.begin()+12,str.end()-4,4,'o'); // "replace is cooool!!!" (5)
str.replace(str.begin()+11,str.end(),str4.begin(),str4.end());// "replace is useful." (6)
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}string::swap:交换字符串值。通过str的内容交换容器的内容,str是另一个字符串对象。 长度可能有所不同。在对这个成员函数的调用之后,这个对象的值是str在调用之前的值,str的值是这个对象在调用之前的值。请注意,非成员函数存在具有相同名称的交换,并使用与此成员函数相似的优化来重载该算法。
// swap strings
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
main ()
{
std::string buyer ("money");
std::string seller ("goods");
std::cout << "Before the swap, buyer has " << buyer;
std::cout << " and seller has " << seller << '\n';
seller.swap (buyer);
std::cout << " After the swap, buyer has " << buyer;
std::cout << " and seller has " << seller << '\n';
return 0;
//Output:
//Before the swap, buyer has money and seller has goods
// After the swap, buyer has goods and seller has money
}string::pop_back:删除最后一个字符。擦除字符串的最后一个字符,有效地将其长度减1:
// string::pop_back
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("hello world!");
str.pop_back();
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
//Output:
//hello world
}string-string operations:
string::c_str:获取C字符串等效。返回一个指向包含以空字符结尾的字符序列(即C字符串)的数组的指针,该字符串表示字符串对象的当前值。该数组包含相同的字符序列,这些字符组成字符串对象的值,并在末尾添加一个附加的终止空字符(’\ 0’)。
.string::copy:从字符串复制字符序列。将字符串对象的当前值的子字符串复制到s指向的数组中。 这个子字符串包含从位置pos开始的len字符。该函数不会在复制内容的末尾添加空字符。
// string::copy
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
char buffer[20];
std::string str ("Test string...");
std::size_t length = str.copy(buffer,6,5);
buffer[length]='\0';
std::cout << "buffer contains: " << buffer << '\n';
return 0;
}
//Output:
//buffer contains: stringstring::find:在字符串中查找内容。在字符串中搜索由其参数指定的序列的第一次出现。当指定pos时,搜索仅包括位置pos处或之后的字符,忽略包括pos之前的字符在内的任何可能的事件。注意,与成员find_first_of不同,只要有一个以上的字符被搜索,仅仅这些字符中的一个匹配是不够的,但是整个序列必须匹配。返回值:第一场比赛的第一个字符的位置。如果没有找到匹配,函数返回string :: npos
// string::find
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
int main ()
{
std::string str ("There are two needles in this haystack with needles.");
std::string str2 ("needle");
// different member versions of find in the same order as above:
std::size_t found = str.find(str2);
if (found!=std::string::npos)
std::cout << "first 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';
found=str.find("needles are small",found+1,6);
if (found!=std::string::npos)
std::cout << "second 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';
found=str.find("haystack");
if (found!=std::string::npos)
std::cout << "'haystack' also found at: " << found << '\n';
found=str.find('.');
if (found!=std::string::npos)
std::cout << "Period found at: " << found << '\n';
// let's replace the first needle:
str.replace(str.find(str2),str2.length(),"preposition");
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
//Output
//first 'needle' found at: 14
//second 'needle' found at: 44
//'haystack' also found at: 30
//Period found at: 51
//There are two prepositions in this haystack with needles
}string::substr:生成子字符串。返回一个新构造的字符串对象,其值初始化为此对象的子字符串的副本。子字符串是从字符位置pos开始的对象的一部分,并且跨越了len字符(或者直到字符串的末尾,以先到者为准)。
// string::substr
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str="We think in generalities, but we live in details.";
// (quoting Alfred N. Whitehead)
std::string str2 = str.substr (3,5); // "think"
std::size_t pos = str.find("live"); // position of "live" in str 返回pos类型size_t
std::string str3 = str.substr (pos); // get from "live" to the end
std::cout << str2 << ' ' << str3 << '\n';
return 0;
//Output:
//think live in details.
}string::compare:比较字符串。将字符串对象(或子字符串)的值与其参数指定的字符序列进行比较。被比较的字符串是字符串对象的值或者 - 如果使用的签名具有pos和len参数 - 在字符位置pos处开始的子字符串,并且跨越len字符。该字符串与比较字符串进行比较,该比较字符串由传递给该函数的其他参数确定。
// comparing apples with apples
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str1 ("green apple");
std::string str2 ("red apple");
if (str1.compare(str2) != 0) //!=0成立
std::cout << str1 << " is not " << str2 << '\n';
if (str1.compare(6,5,"apple") == 0) //==0成立
std::cout << "still, " << str1 << " is an apple\n";
if (str2.compare(str2.size()-5,5,"apple") == 0) //==0成立
std::cout << "and " << str2 << " is also an apple\n";
if (str1.compare(6,5,str2,4,5) == 0) //==0成立
std::cout << "therefore, both are apples\n";
return 0;
}string::find_ first_ of:在字符串中查找字符。在字符串中搜索与其参数中指定的任何字符匹配的第一个字符。当指定pos时,搜索仅包括位置pos或之后的字符,忽略pos之前的任何可能的事件。请注意,对于序列中的一个字符来说,就足够了(不是全部)。 请参阅string :: find以查找与整个序列匹配的函数。
string::find_ first_ not_of:查找字符串中没有字符。在字符串中搜索与其参数中指定的任何字符不匹配的第一个字符。指定pos时,搜索仅包含位置pos或之后的字符,忽略该字符之前的任何可能的事件。
// string::find_first_of
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
#include <cstddef> // std::size_t
int main ()
{
std::string str ("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");
std::size_t found = str.find_first_of("aeiou");
//下面的循环实现了找到str中,”aeiou“中所有字符:'a''e''i''o''u',并将其都替换为'* '
while (found!=std::string::npos)
{
str[found]='*';
found=str.find_first_of("aeiou",found+1);
}
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
//Output:
//Pl**s*, r*pl*c* th* v*w*ls *n th*s s*nt*nc* by *st*r*sks.
}
string::find_ last_of:从结尾查找字符串。在字符串中搜索与其参数中指定的任何字符匹配的最后一个字符。当pos被指定时,搜索只包含位置pos之前或之前的字符,忽略pos之后的任何可能的事件。
// string::find_last_of
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
#include <cstddef> // std::size_t
void SplitFilename (const std::string& str)
{
std::cout << "Splitting: " << str << '\n';
std::size_t found = str.find_last_of("/\\"); //在str中搜索与"/\\"中任一个字符匹配的最后一个字符。
std::cout << " path: " << str.substr(0,found) << '\n'; //pos就是匹配到的位置。0~pos
std::cout << " file: " << str.substr(found+1) << '\n'; //pos~string结束
}
int main ()
{
std::string str1 ("/usr/bin/man");
std::string str2 ("c:\\windows\\winhelp.exe");
SplitFilename (str1);
SplitFilename (str2);
return 0;
\\Output
\\Splitting: /usr/bin/man
\\ path: /usr/bin
\\ file: man
\\Splitting: c:\windows\winhelp.exe
\\ path: c:\windows
\\ file: winhelp.exe
}string::npos
size_ t的最大值。npos是一个静态成员常量值,对于size_ t类型的元素具有最大的可能值。这个值在字符串的成员函数中用作len(或sublen)参数的值时,意思是“直到字符串结尾”。作为返回值,通常用来表示不匹配。这个常量被定义为-1,这是因为size_ t是一个无符号整型,它是这种类型最大的可表示值
operator>> (string)与operator<< (string):示例代码如下:
// extract to string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
main ()
{
std::string name;
std::cout << "Please, enter your name: ";
std::cin >> name;
std::cout << "Hello, " << name << "!\n";
return 0;
}.getline (string):示例代码如下:
// extract to string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string name;
std::cout << "Please, enter your full name: ";
std::getline (std::cin,name);
std::cout << "Hello, " << name << "!\n";
return 0;
}在以往的C++中,比较难转换的,要使用std::stringstream,这个使用起来怎么感觉都有点麻烦,还是喜欢使用itoa()的实现,现在C++11带来新的std::to_string(),就更加方便了,如下:
string to_string (int val);
string to_string (long val);
string to_string (long long val);
string to_string (unsigned val);
string to_string (unsigned long val);
string to_string (unsigned long long val);
string to_string (float val);
string to_string (double val);
string to_string (long double val);
// to_string example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string, std::to_string
int main ()
{
std::string pi = "pi is " + std::to_string(3.1415926);
std::string perfect = std::to_string(1+2+4+7+14) + " is a perfect number";
std::cout << pi << '\n';
std::cout << perfect << '\n';
return 0;
}





![在配置文件“tsconfig.json”中找不到任何输入。指定的 “include“ 路径为“[“**/*“]”,“exclude“ 路径为[]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cb5cad62f254498aa2a401f75176c624.png)