第五届太原理工大学程序设计竞赛新生赛(初赛)题解
时隔半年重做一次,还是有几道不会,,,,,
⭐️A.饿饿饭饭
题目:
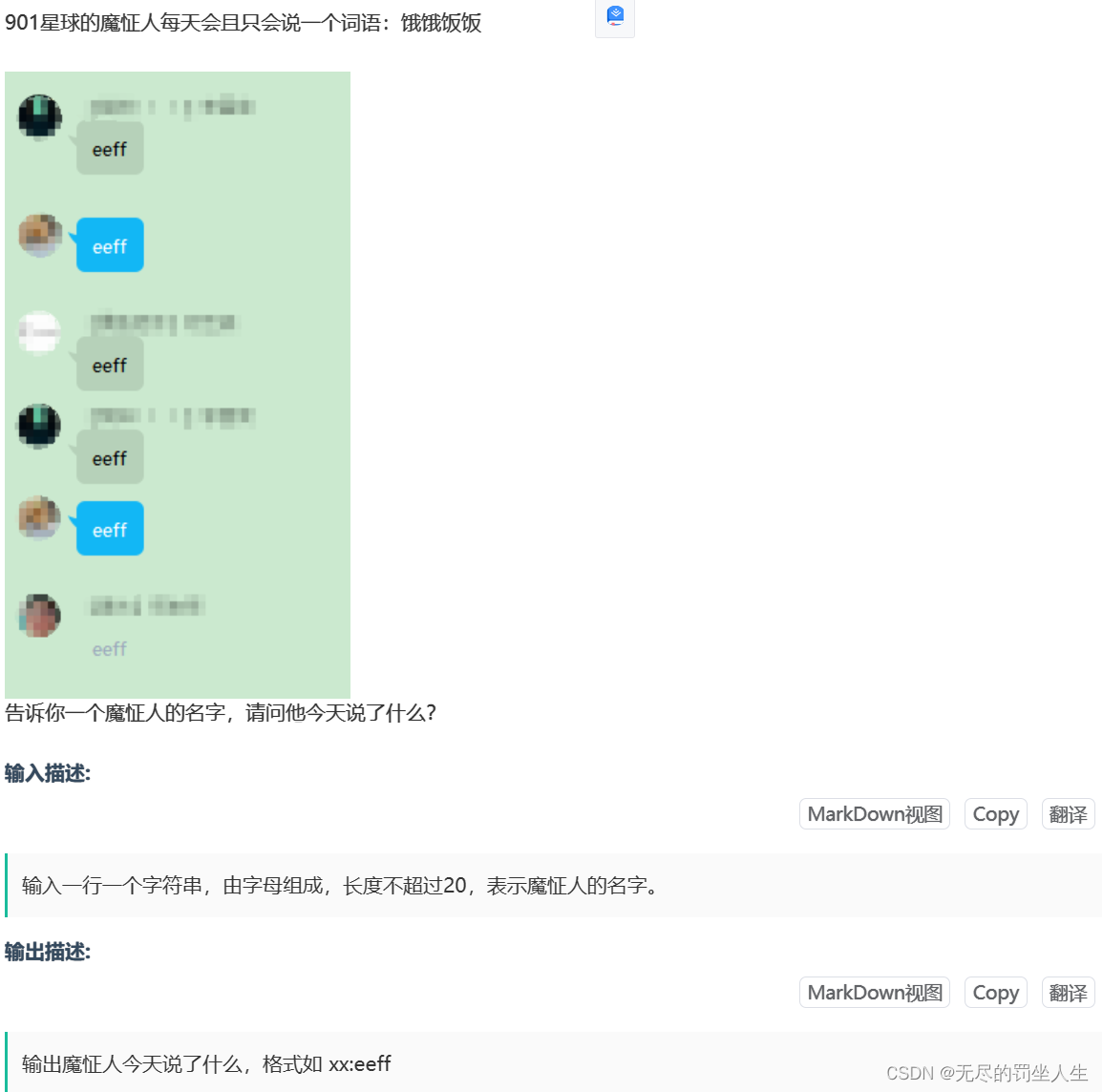
🌟题解:
很简单,签个到输出谁饿了
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; cin>>s;
cout<<s<<":eeff";
}
⭐️B.扣点点
题目:

🌟题解:
hammer喜欢玩扣点点但太菜了理不清牌(doge),让你帮忙按一定顺序整理,典型的排序吧
代码:
1.这种字符串数组排序较为简单
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
string s[N];
int main()
{
int n; cin>>n;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)
{
char j[2];
cin>>j[1]>>j[0];
s[i] += j[0];
s[i] += j[1];
}
sort(s,s+n);
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<s[i][1]<<s[i][0]<<' ';
}
return 0;
}
2.标记法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int cnt[4][10];
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int num;
char s;
cin >> num >> s;
int id;
if (s == 'B') id = 0;
else if (s == 'C') id = 1;
else id = 2;
cnt[id][num]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < cnt[i][j]; ++k) { //可能这里不好理解,就是看k+到比cnt这大就是cnt-反过来也可以写成while(cnt[i][j]--&&cnt>0)
cout << j << (i==0 ? 'B' : i==1 ? 'C' : 'D') << " ";
}
}
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3.自己写个结构体排序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct node{
char x,y;
}a[15];
bool cmp(node q,node p){
if(q.y!=p.y)return q.y<p.y;
else return q.x<p.x;
}
string s;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>s;
a[i].x=s[0];
a[i].y=s[1];
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<a[i].x<<a[i].y<<" ";
}
}
4.利用mulimap性质(某孙神的)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
multimap<char,char>mp;
multimap<char,char>ans;
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
char ch;
char temp;
cin>>temp>>ch;
mp.insert({temp,ch});
}
for(auto it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++){
ans.insert(pair<char,char>(it->second,it->first));
}
for(auto it=ans.begin();it!=ans.end();it++){
cout<<it->second<<it->first<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
⭐️String problem
题目:
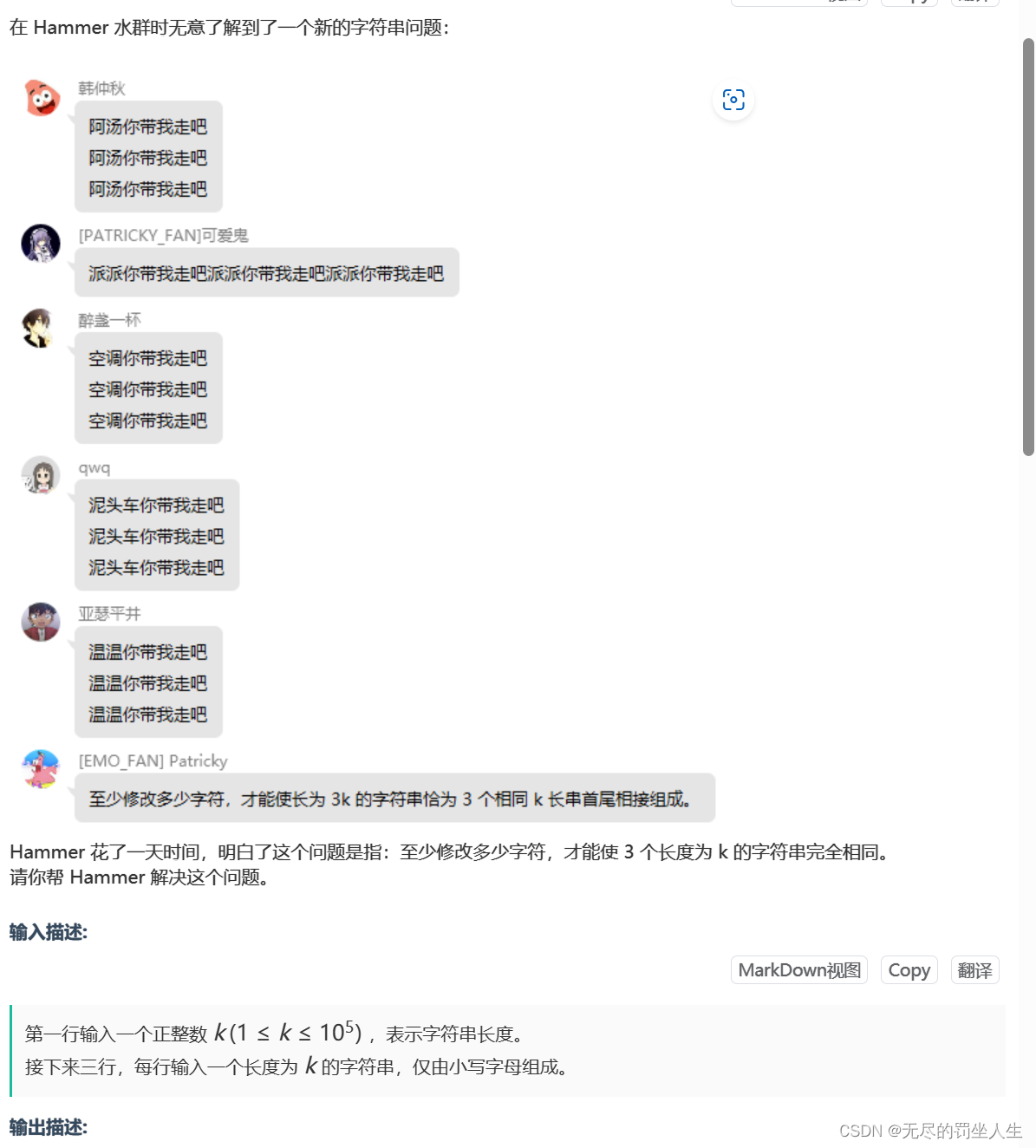
🌟题解:
也很简单的一道,比较三个字符串字符就行,2个一样就改一次,都不一样就改两次,
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
string s1,s2,s3;
int ans;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
cin>>s1>>s2>>s3;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(s1[i]==s2[i] && s1[i]==s3[i]) continue;
else if(s1[i]==s2[i] || s1[i]==s3[i] || s2[i]==s3[i]) ans++;
else ans+=2;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
⭐️D.数豆豆
题目:
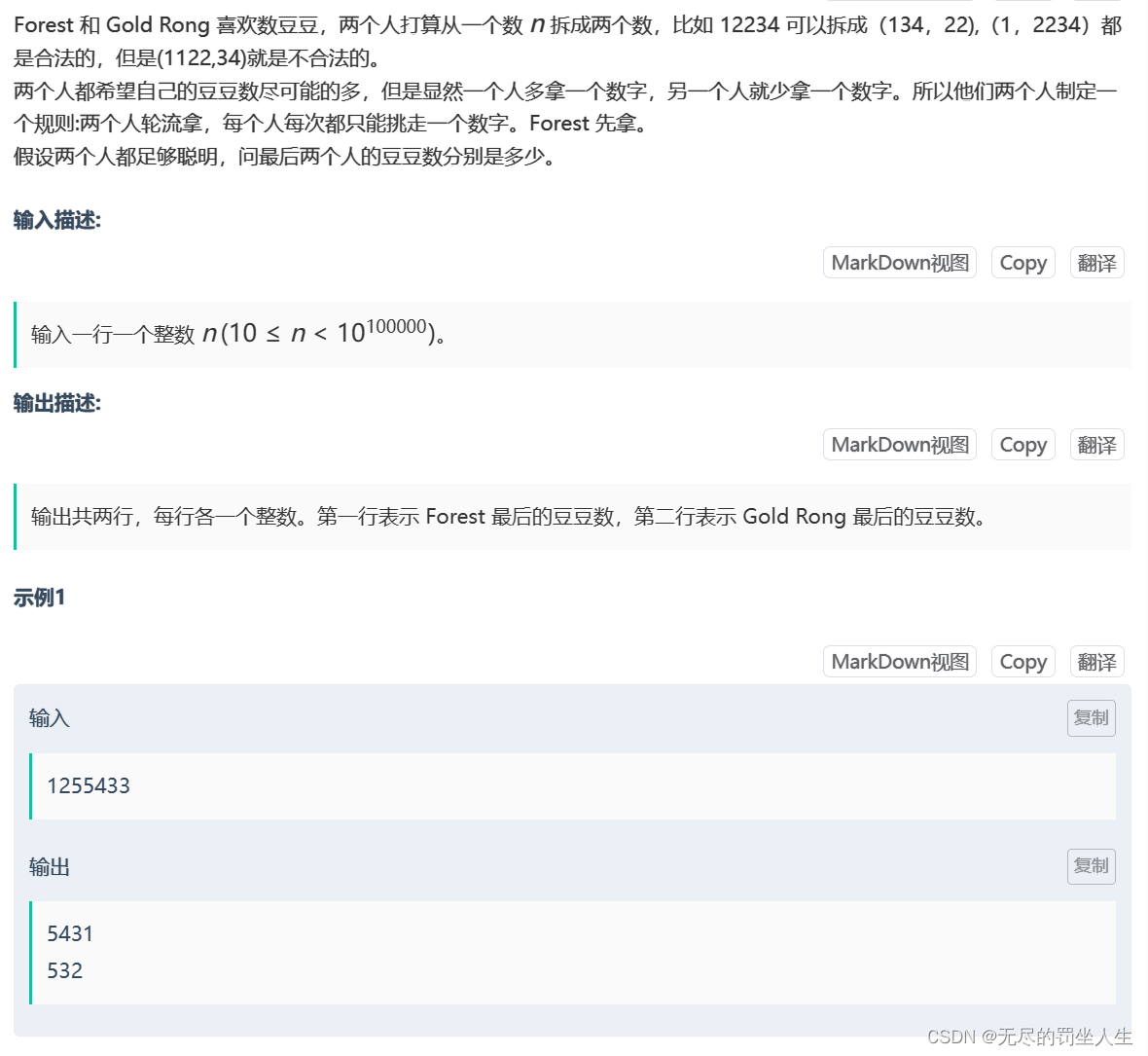
🌟题解:
考察一下思维吧,其实也很简单,就是每次拿大的数字,排下序就好了
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
string s1,s2;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i)
{
if(i%2==0)
s1=s1+s[i];
else
s2=s2+s[i];
}
if(s1[0]=='0') s1="0";
if(s2[0]=='0') s2="0";
cout<<s1<<endl;
cout<<s2<<endl;
return 0;
}
⭐️E.Another string problem
题目:
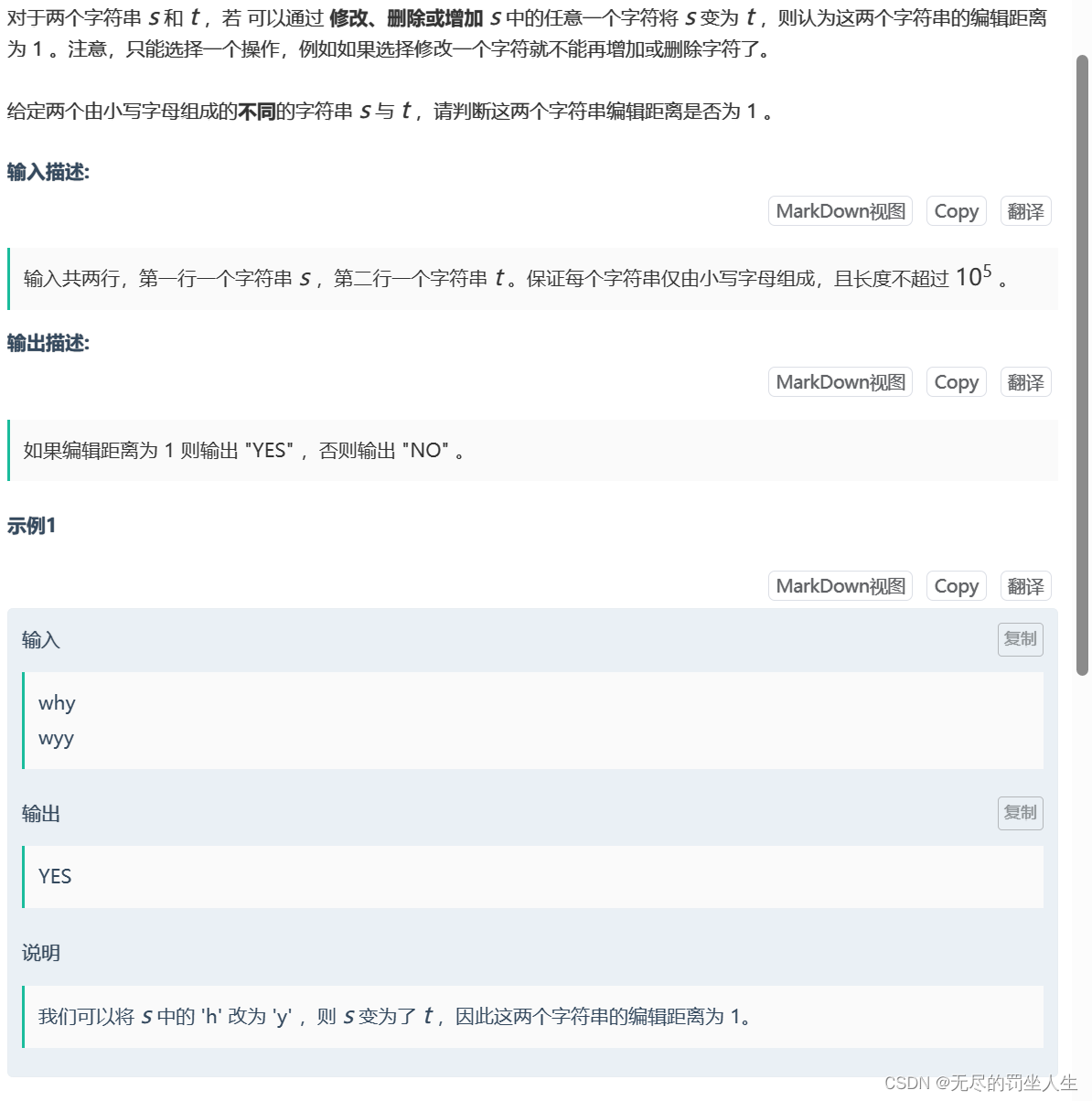
🌟题解:
也是挺简单的,呆梨同学们都可以报名新生赛体验今年12月。就判断下是否两个字符串只有一个字符不一样就行,注意中间缺字符或者多字符也是可以的,那么就有三种情况,字符一样长,不一样长是删除还是增加(差距为1),还有差距大于1了因为只能改一次肯定不行。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s, t;
cin >> s ; cin>>t;
int n = s.size(), m = t.size();
if (abs(n-m) > 1) cout << "NO" << endl;
else if (n == m) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (s[i] != t[i] && ++cnt > 1) {
cout << "NO" << endl; return 0;
}
cout << "YES" << endl;
} else {
int i, j,cnt=0;
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < n && j < m; ++i, ++j) {
if (s[i] != t[j]) {
if (n > m) --j;
else --i;
if (++cnt > 1) {
cout << "NO" << endl; return 0;
}
}
}
if (i < n || j < m) ++cnt;
cout << (cnt == 1 ? "YES" : "NO") << endl;
}
return 0;
}
⭐️F.迷失的Syuggie
题目:
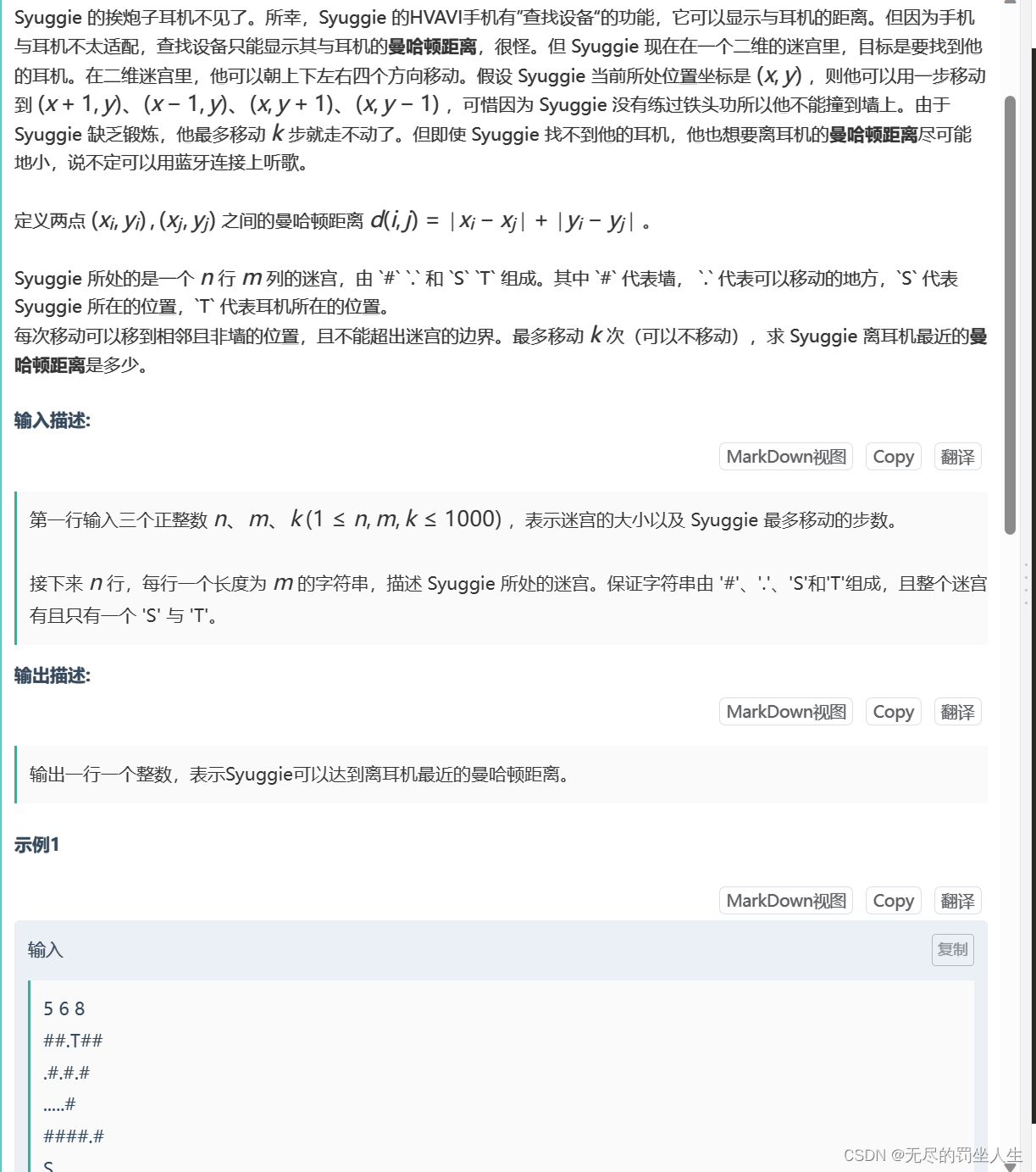
🌟题解:
也是一道典型的bfs题
网格由字符的二维数组"f"表示,其中"#“表示障碍物,”."表示空白格子。算法从起始点(标记为’S’)开始,探索所有可能的路径,直到达到目标点(标记为’T’)或者在给定的步数限制"k"内探索完所有可能的路径。最短路径长度存储在变量"ans"中,每当找到一条更短的路径时,它就会被更新。最后,最短路径长度被打印出来。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=1010;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
struct point {
int x,y,step;
};
queue<point> q;
char f[N][N];
int x[]={-1,0,1,0},y[]={0,1,0,-1};
int n,m,k;
int sx,sy,tx,ty;
int ans=1e6;
int bfs()
{
q.push({sx,sy,0});
f[sx][sy]='#';
while(q.size())
{
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
if(t.step<=k)
{
ans=min(ans,abs(t.x-tx)+abs(t.y-ty));
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int a=t.x+x[i],b=t.y+y[i];
if(a>=1&&a<=n&&b>=1&&b<=m&&f[a][b]!='#')
{
q.push({a,b,t.step+1});
f[a][b]='#';
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
char c;
cin>>c;
if(c=='T')
{
tx=i;
ty=j;
}
else if(c=='S')
{
sx=i;
sy=j;
}
f[i][j]=c;
}
cout<<bfs()<<endl;
return 0;
}
⭐️G.寻找签到题之路
题目:
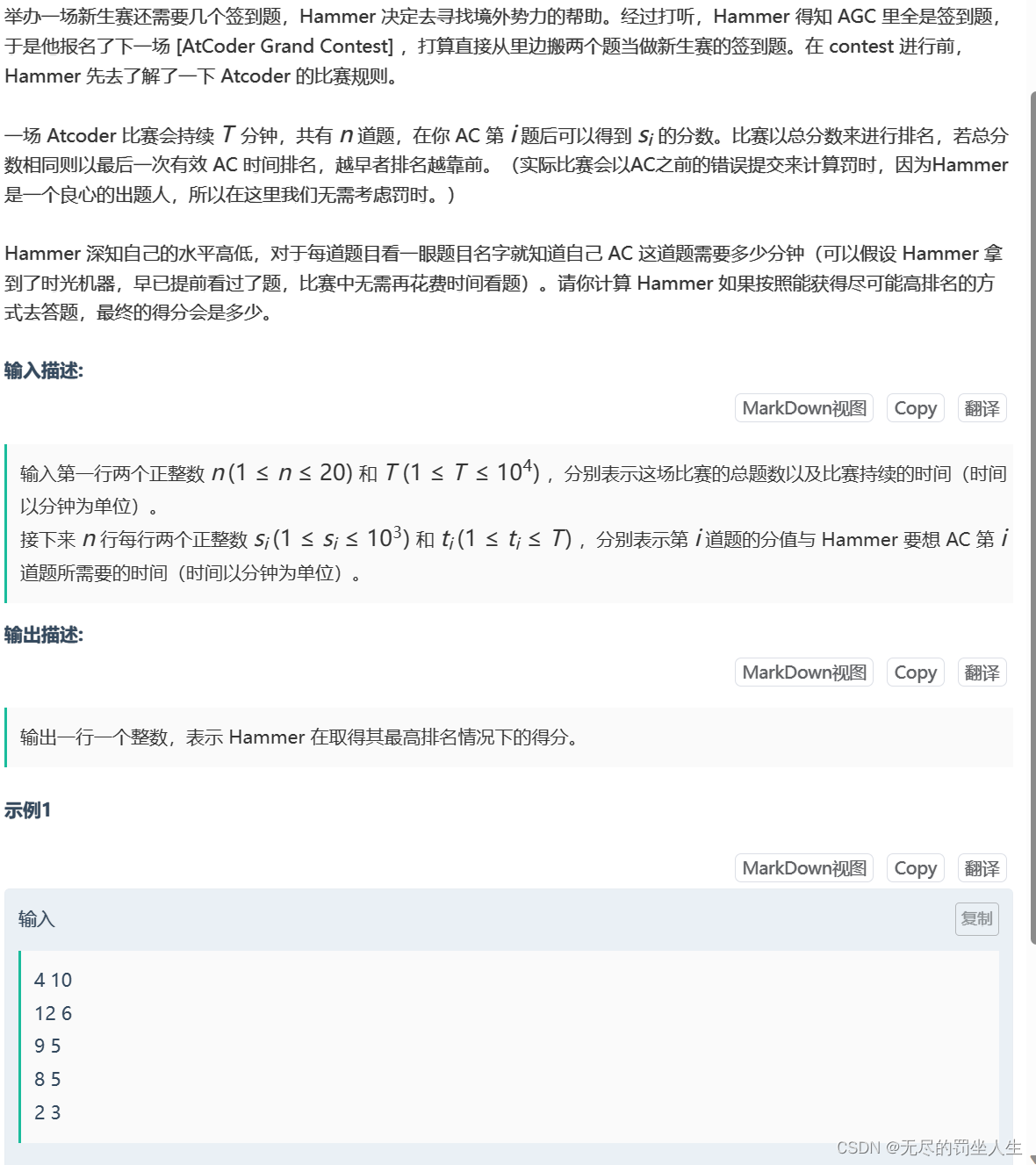
🌟题解:
一眼典型背包dp,直接写就好。。。。就是时间有限要得分最大,每个题目时间也知道。总时间就是背包,每个题目分数就是价值,时间就是重量。不过也有大佬别的做法
代码:
1.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int t[N],s[N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> s[i] >> t[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if(j < t[i])
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
else
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - t[i]] + s[i]);
}
cout << f[n][m] << endl;
return 0;
}//正的
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000005;
int n,m;
int f[N];
int v,w;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>w>>v;
for(int j=m;j>=v;j--)
{
f[j]=max(f[j],f[j-v]+w);
}
}
cout<<f[m]<<endl;
return 0;
}//逆的
2.dfs来自dy
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int t, n;
int s[21], ti[21];
int maxn;
void dfs(int time, int score, int tit) {
if (time <0)return;
if (tit == n){
maxn = max(maxn, score);
return;}
dfs(time,score,tit+1);
dfs(time-ti[tit],score+s[tit],tit+1);
return;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> s[i] >> ti[i];
}
dfs(t, 0, 0);
cout << maxn;
}
⭐️H.子矩阵和
题目:

🌟题解:
就是典型的二维前缀和处理一下查询
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=10010;
ll a[N],b[N],c[N][N],s[N][N];
int main()
{
ll n,m,q;
cin>>n>>m;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
for(ll i=1;i<=m;i++)
cin>>b[i];
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(ll j=1;j<=m;j++)
c[i][j]=a[i]*b[j];
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(ll j=1;j<=m;j++)
s[i][j] = s[i][j - 1] + s[i - 1][j] - s[i - 1][j - 1] + c[i][j];
cin>>q;
while(q--)
{
ll x1,y1,x2,y2;
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
cout<<s[x2][y2] - s[x1 - 1][y2] - s[x2][y1 - 1] + s[x1 - 1][y1 - 1]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
⭐️I.最短区间
题目:
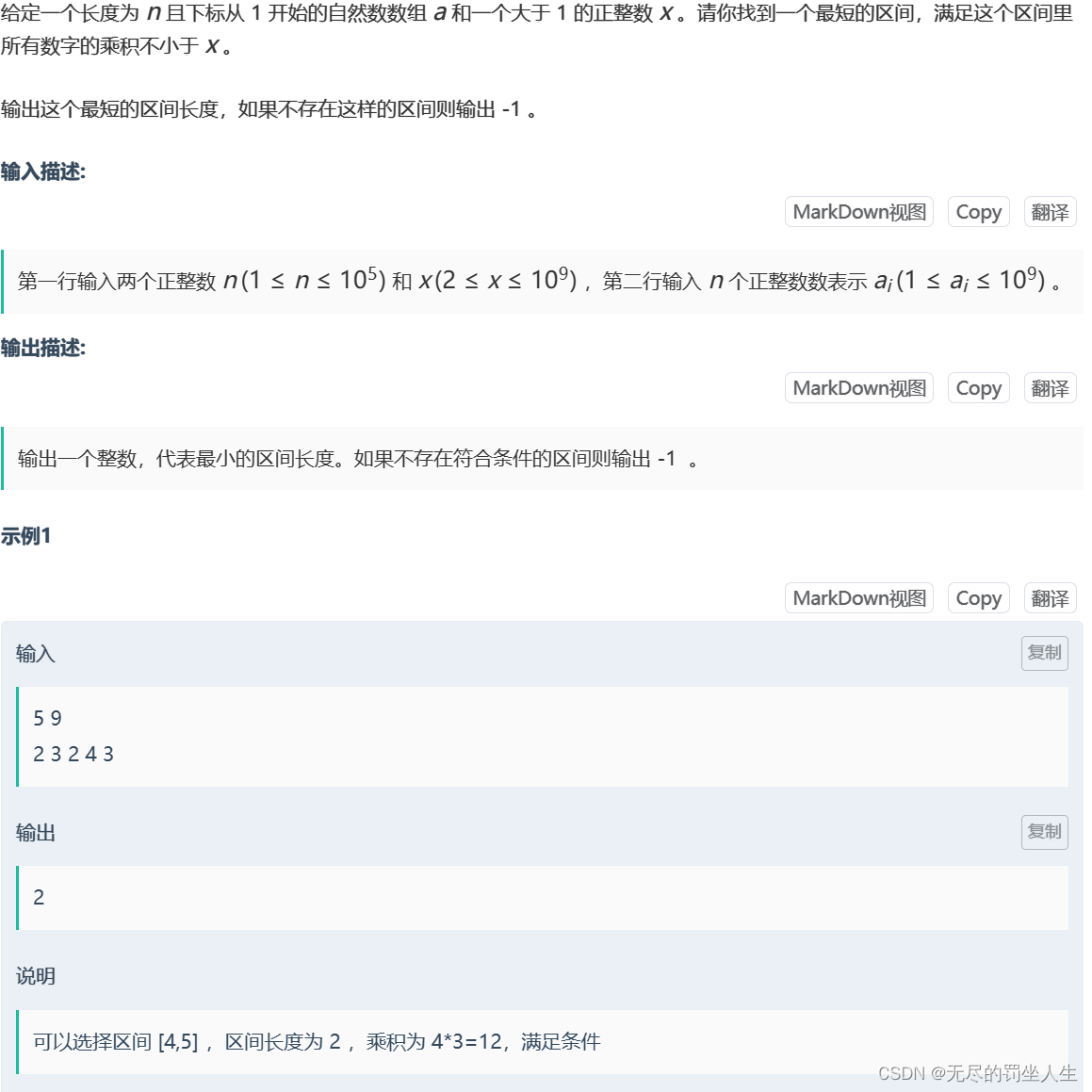
🌟题解:
双指针i,j指一指循环区间根据条件找到最小区间
代码:
1.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
typedef long long ll;
ll n,x;
ll a[N];
ll mul=1,ma;
int ans=N;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>x;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=1,j=1;i<=n;i++)
{
while(mul<x && j<=n)
{
mul*=a[j];j++;
}
if(mul>=x) ans=min(ans,j-i);
mul/=a[i];
}
if(ans>n) ans=-1;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
2.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int a[N];
int main() {
int n, x;
cin >> n >> x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
int left = 1, right = 1, len = 0;
long long prod = a[1];
while (right <= n) {
if (prod >= x) {
if (len == 0 || right - left + 1 < len)
len = right - left + 1;
prod /= a[left];
left++;
if (left > right) {
right++;
if (right <= n)
prod *= a[right];
}
} else {
right++;
if (right <= n)
prod *= a[right];
}
}
if (len == 0)
cout << "-1" << endl;
else
cout << len << endl;
return 0;
}
⭐️J.点球大战
题目:
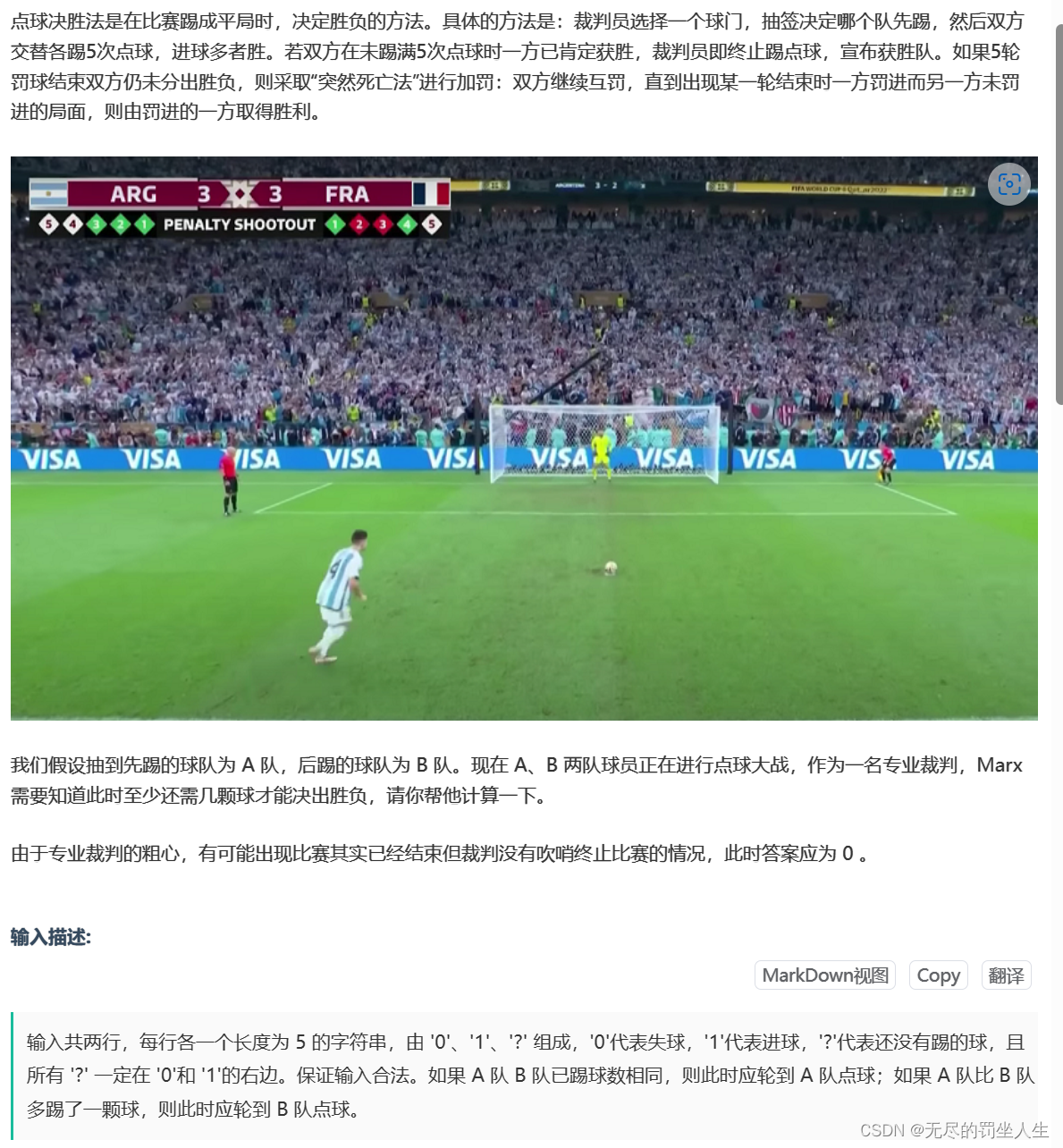
🌟题解:
代码:
⭐️K.冠军预言
题目:
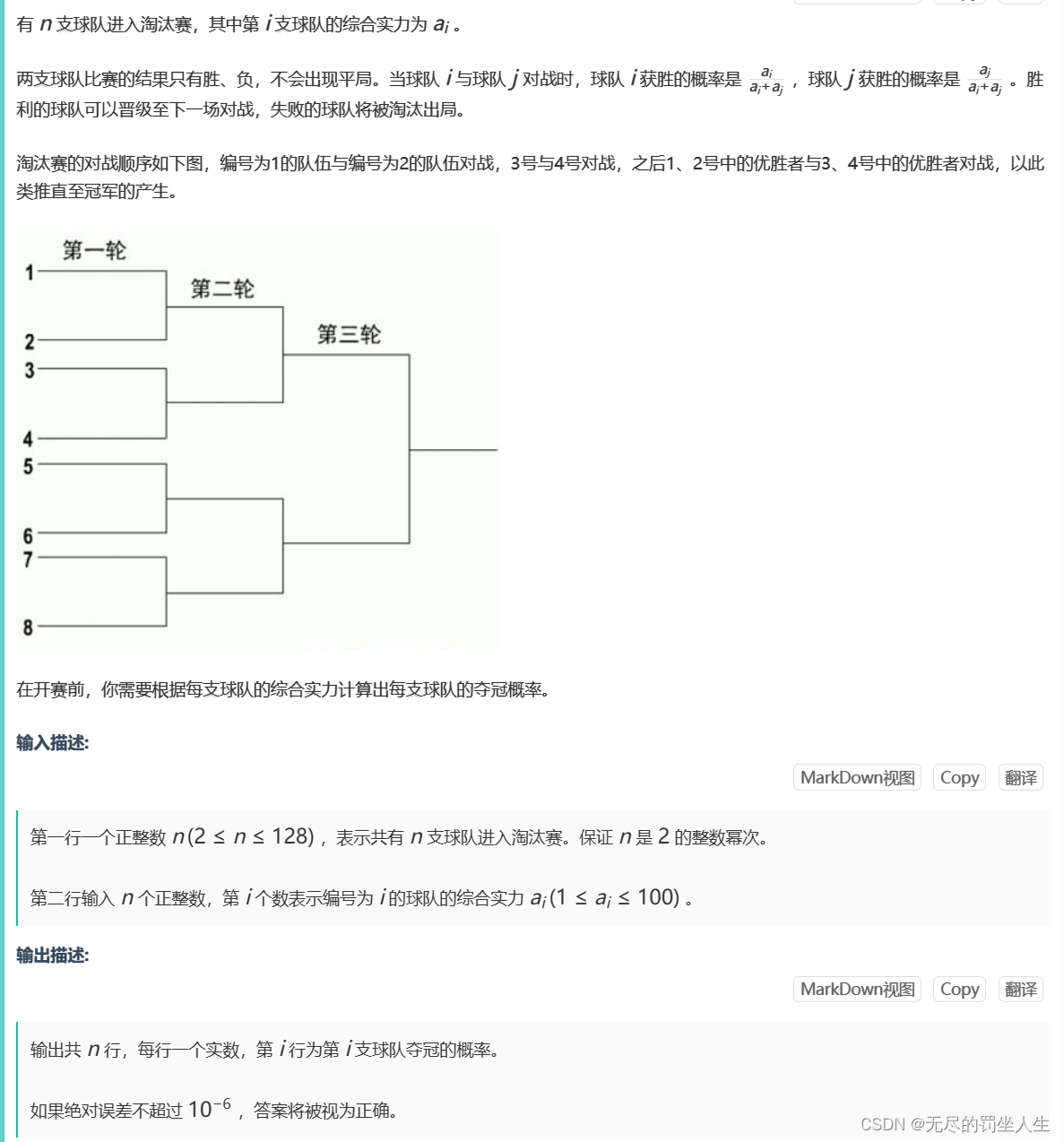
🌟题解:
代码:
⭐️L.an interesting problem
题目:



🌟题解:
很复杂的一道题但是思维很简单,代码量很多
代码:
⭐️M.选数异或
题目:
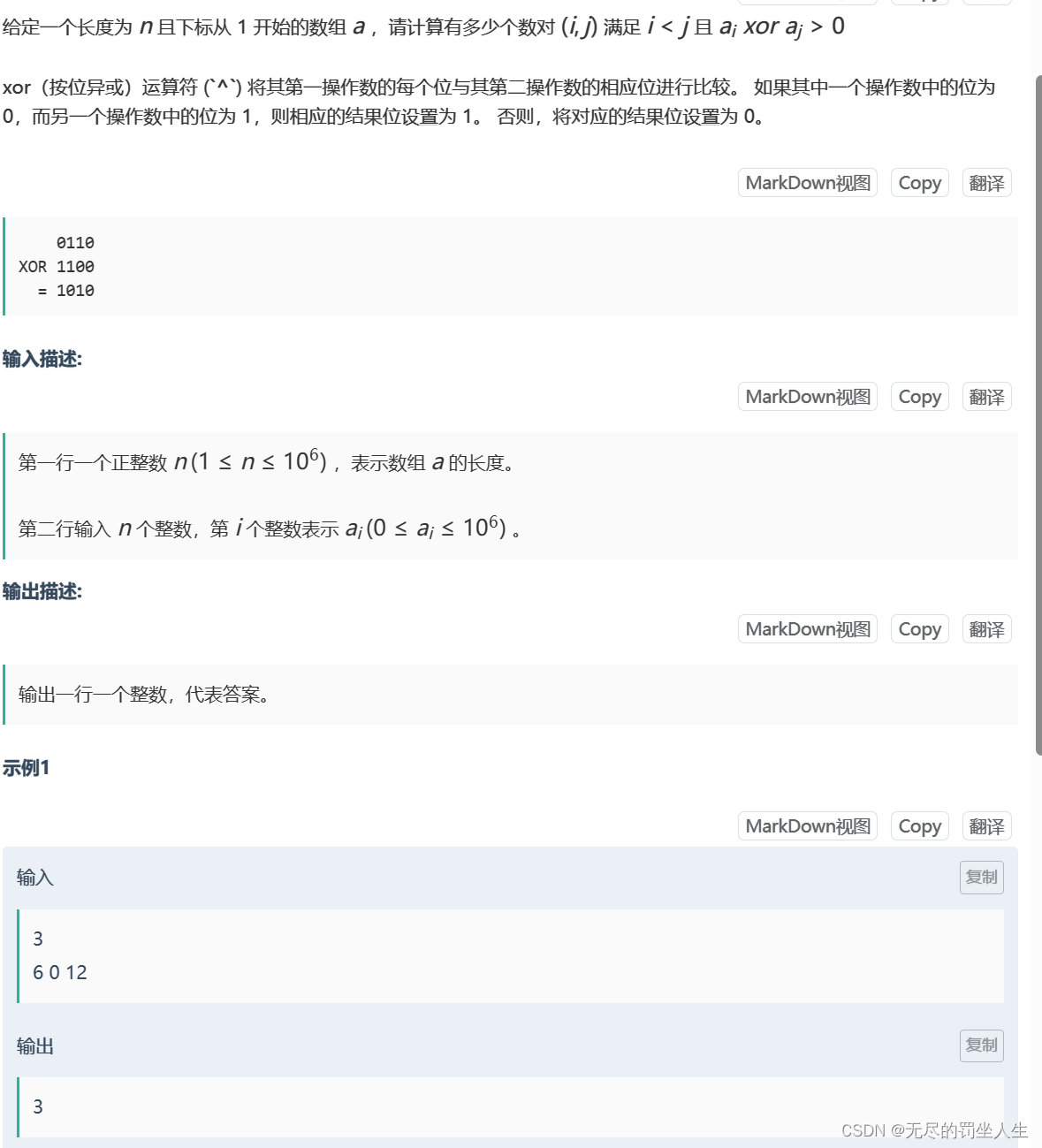
🌟题解:
我们可以用一个桶来记录每个数出现的次数,然后从前往后遍历数列,对于每个数 x,我们可以计算出在它之前出现的比它大的数的个数,就是(i-1-cnt[x]),其中 i 是当前遍历到的位置,cnt[x] 是 x* 出现的次数。这个式子的意思是,在 x 之前,一共有 i−1 个数,其中有 cnt[x] 个数等于 x,所以比 x大的数的个数就是 i−1−cnt[x]。
最后的答案就是所有的逆序对个数之和。时间复杂度 O*(*n)。
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
typedef long long ll;
ll n,cnt[N],x,ans;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>x;
ans+=(i-1-cnt[x]);
cnt[x]++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}

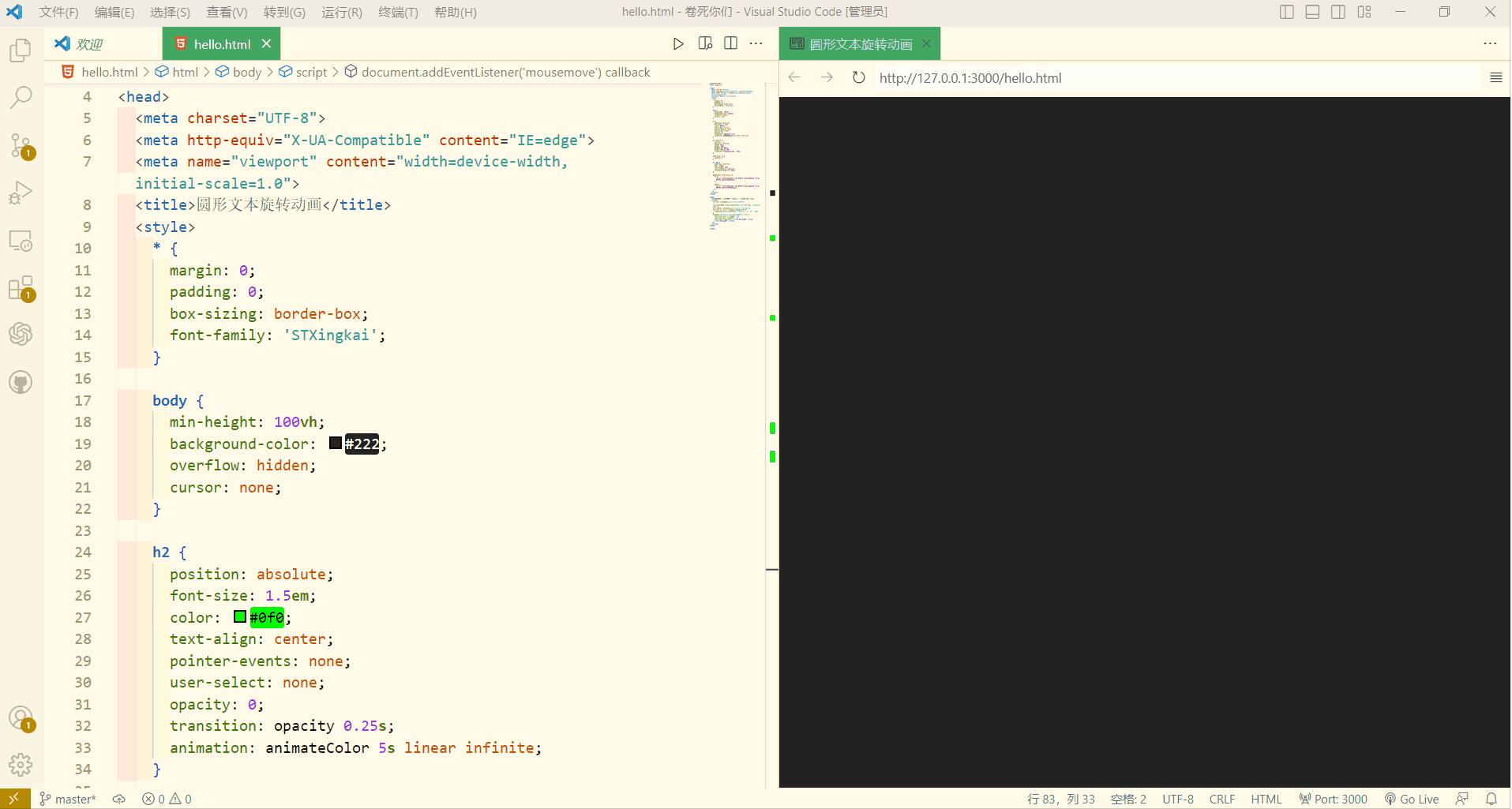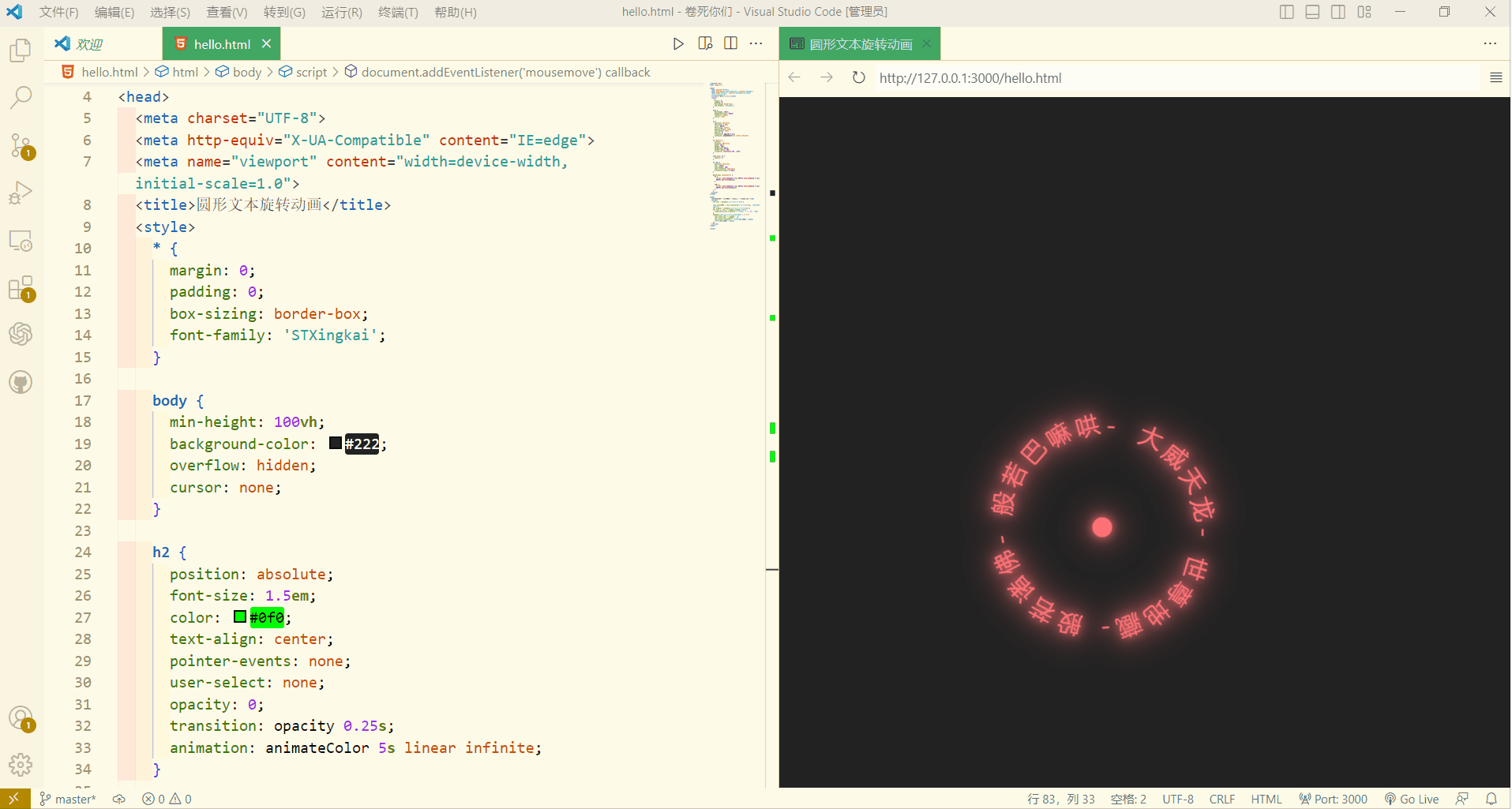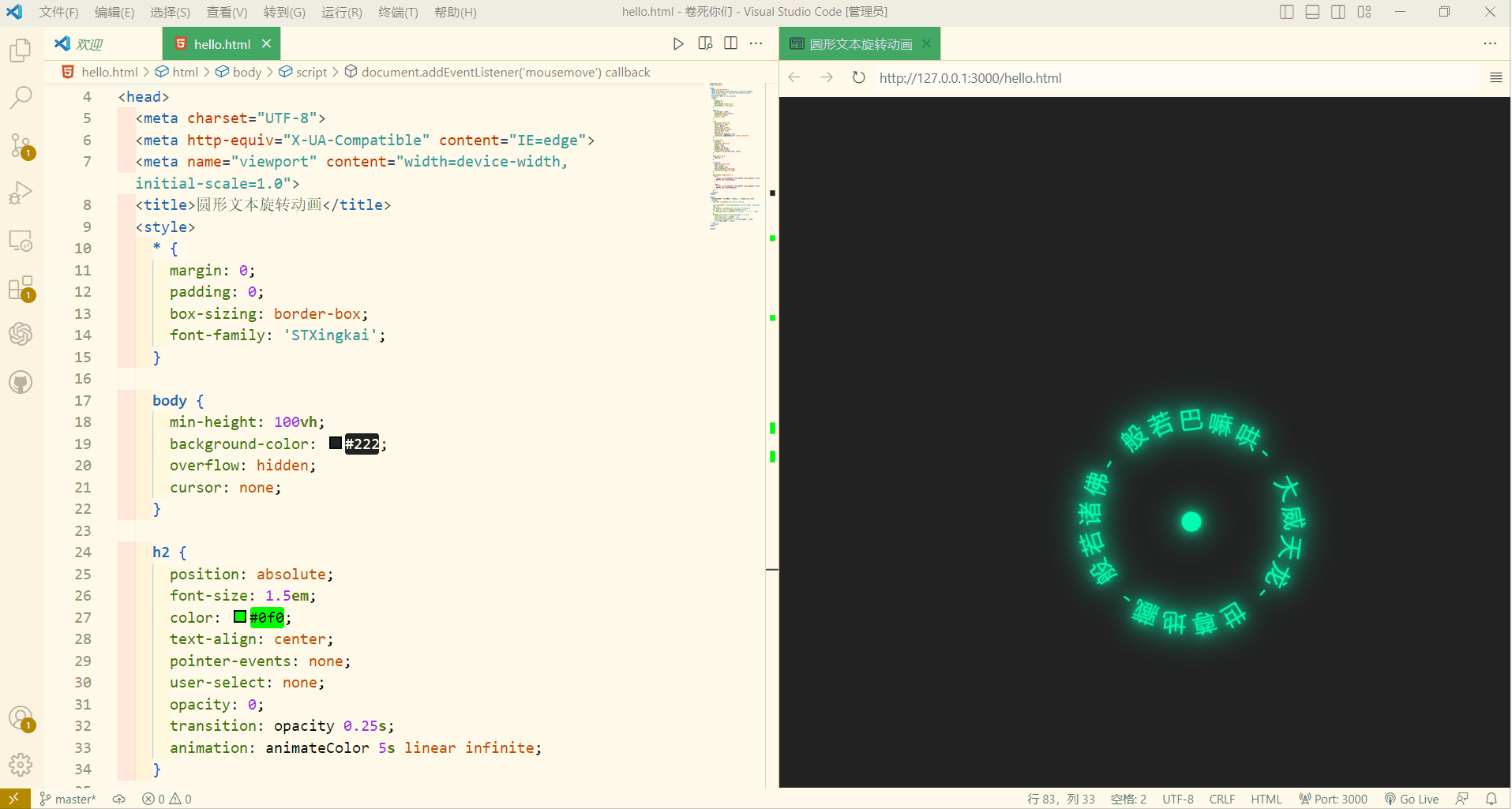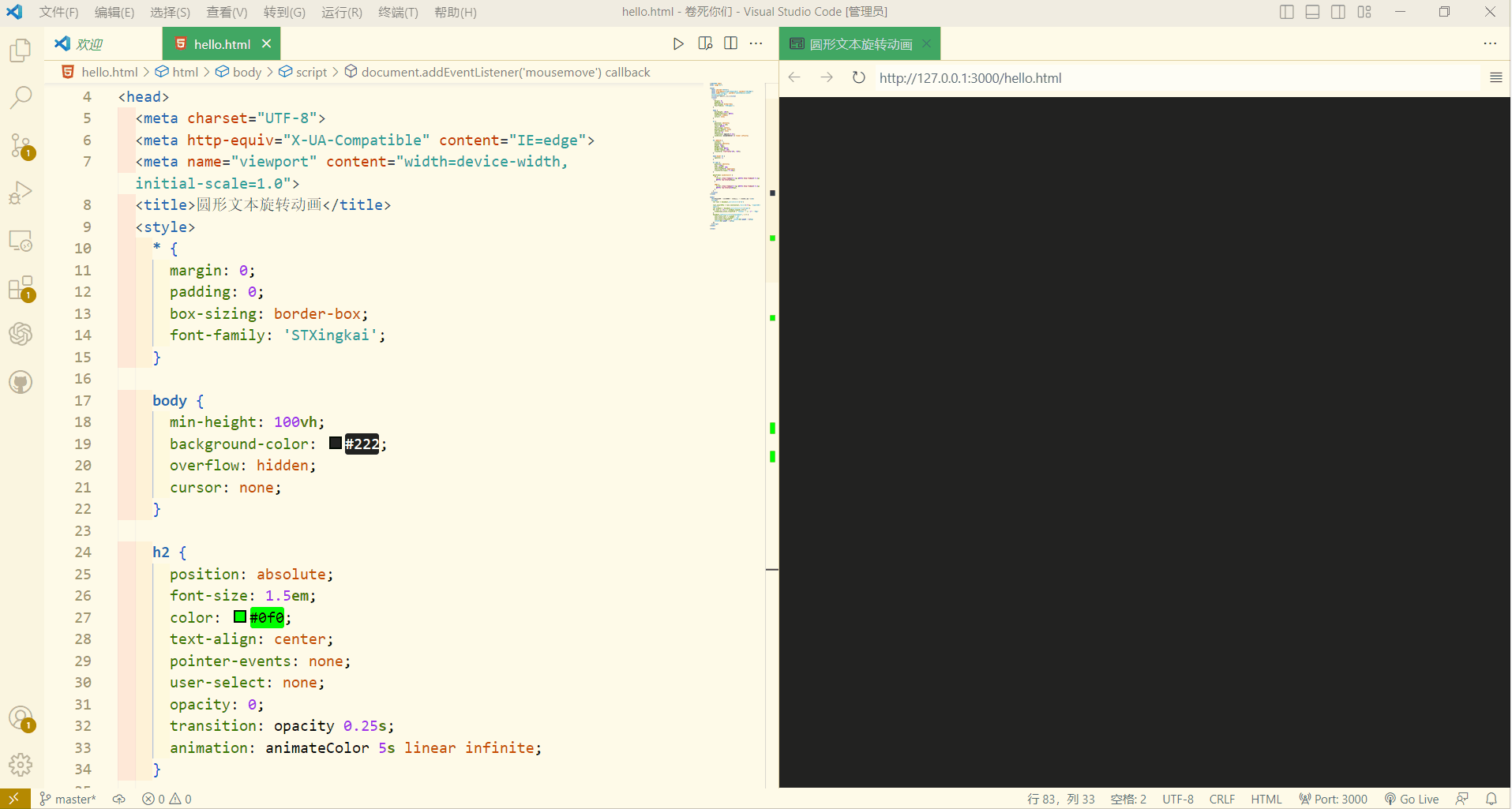


![[java进阶]——异常详解,try catch捕获异常,抛出异常](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b9d2f15be56d42f1b41b2f31d5a7b570.png)