OR62 倒置字符串
链接:倒置字符串
题目:
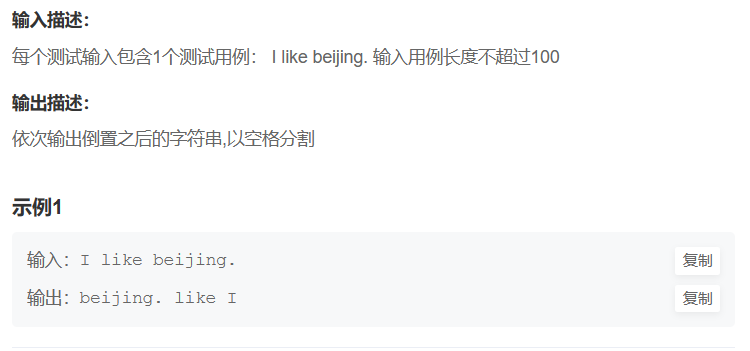
将一句话的单词进行倒置,标点不倒置。比如 I like beijing. 经过函数后变为:beijing. like I
题目分析:
我们先有一个整体的思路,然后用代码去实现:
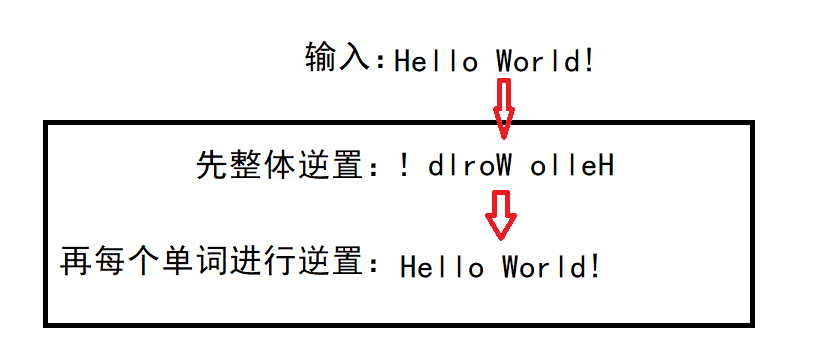
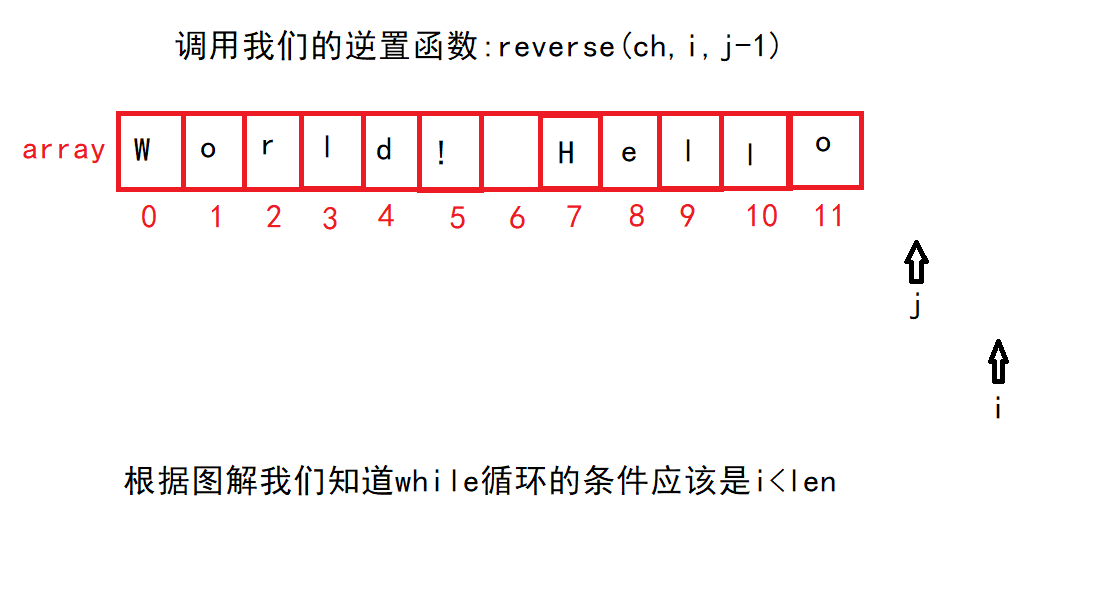
可是这里具体怎么逆置?---->
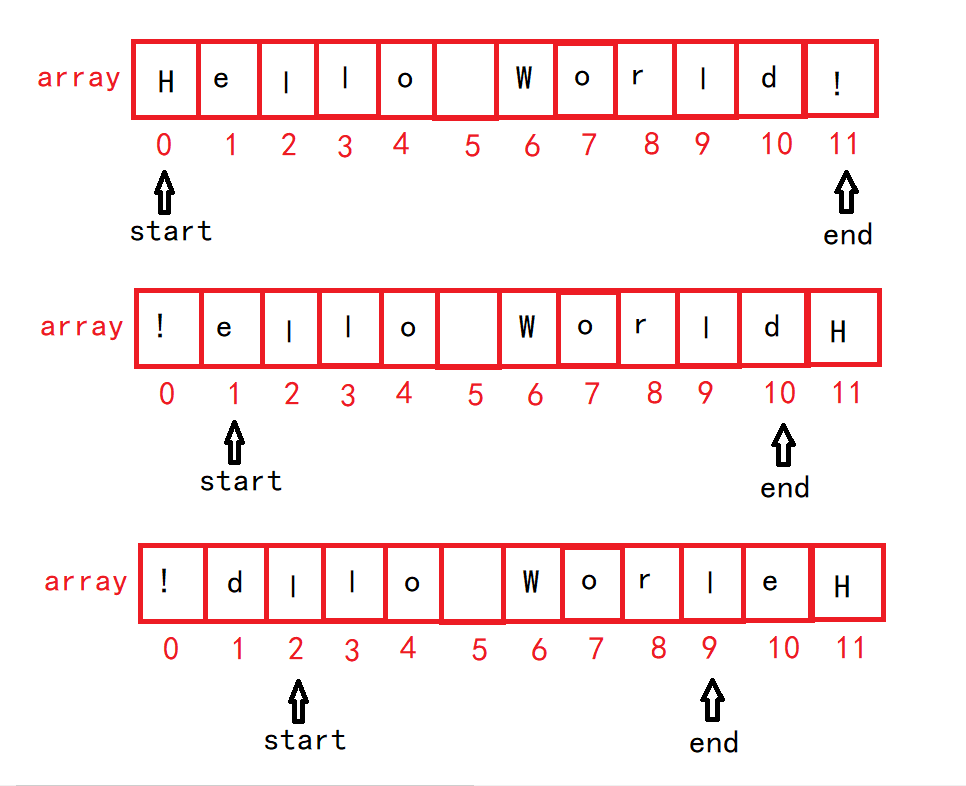
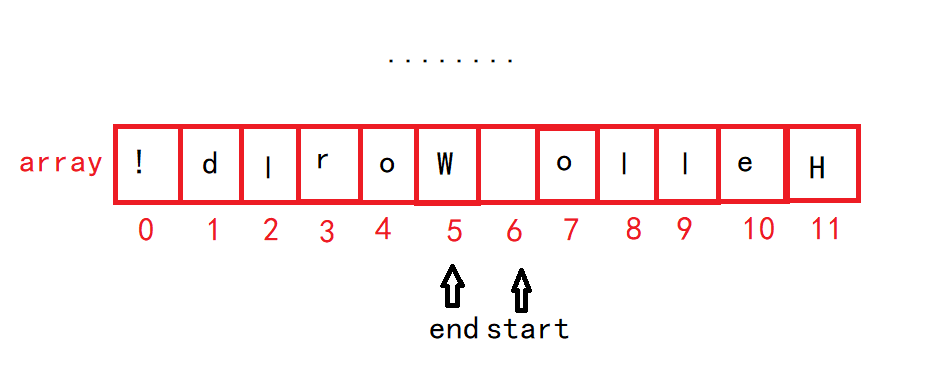
通过这个逆置函数我们对整体进行逆置,然后再对每个单词进行逆置—>

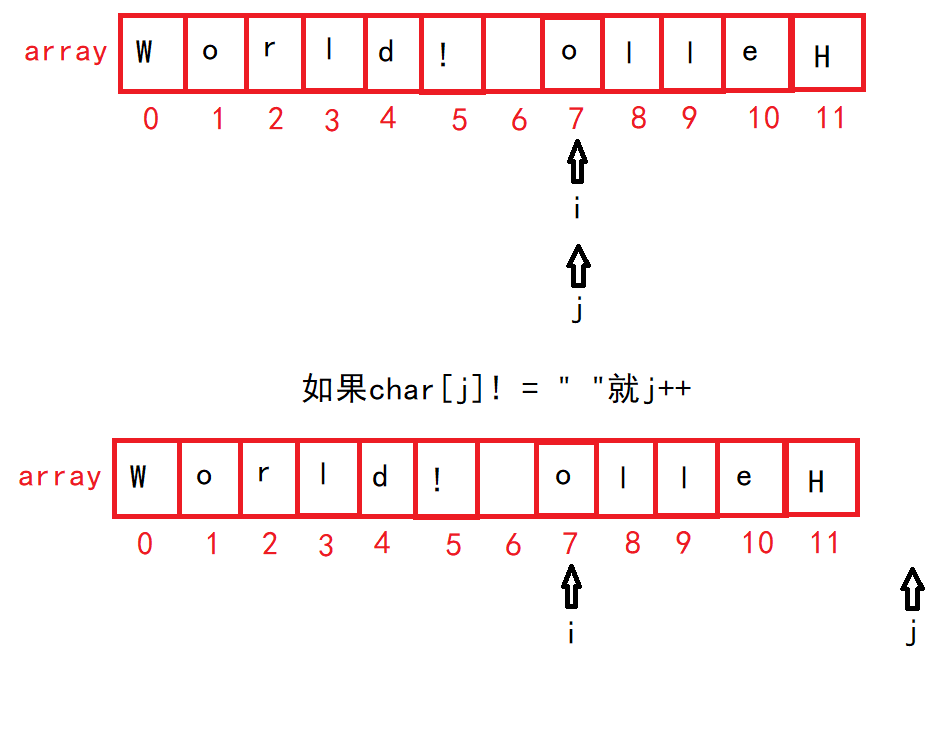
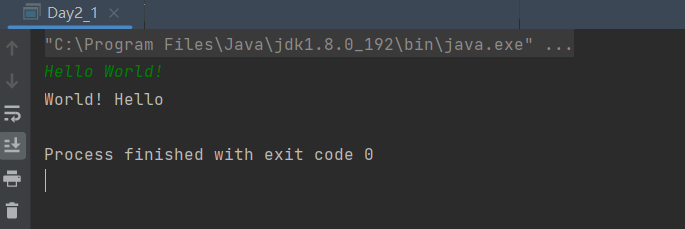
代码实现:
package Day2;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Day2_1 {
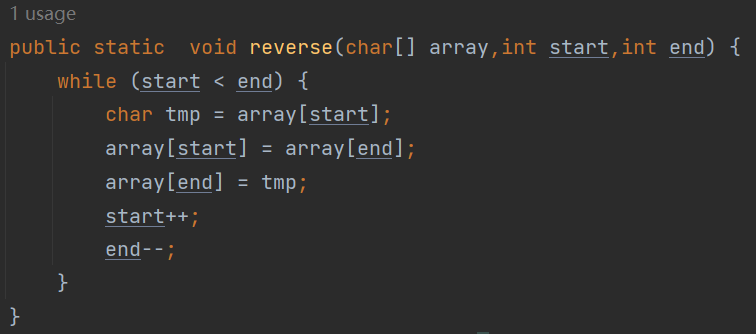
public static void reverse(char[] array,int start,int end) {
while (start < end) {
char tmp = array[start];
array[start] = array[end];
array[end] = tmp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = scanner.nextLine();
//字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
int len = ch.length;
reverse(ch,0,len-1);
int i = 0;
while (i < len) {
int j = i;
while (j < len && ch[j] != ' ') {
j++;
}
if(j < len) {
reverse(ch,i,j-1);
i = j + 1;
}else {
reverse(ch,i,j-1);
i = j;
}
}
String outstr = new String(ch);
System.out.println(ch);
}
}
排序子序列
链接:排序子序列
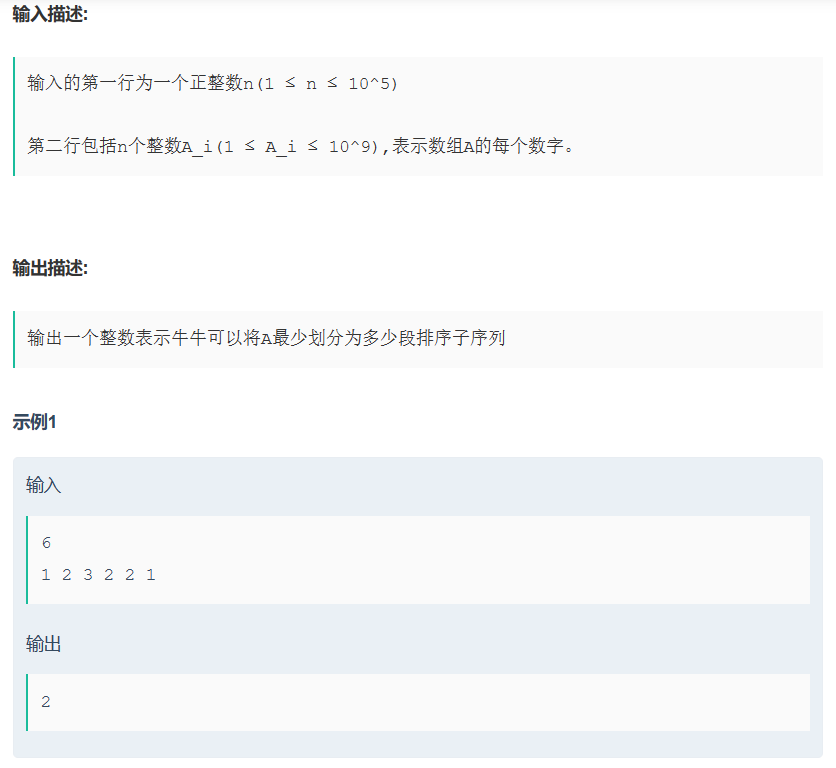
题目:
牛牛定义排序子序列为一个数组中一段连续的子序列,并且这段子序列是非递增或者非递减排序的。牛牛有一个长度为n的整数数组A,他现在有一个任务是把数组A分为若干段排序子序列,牛牛想知道他最少可以把这个数组分为几段排序子序列.
如样例所示,牛牛可以把数组A划分为[1,2,3]和[2,2,1]两个排序子序列,至少需要划分为2个排序子序列,所以输出2
题目分析:

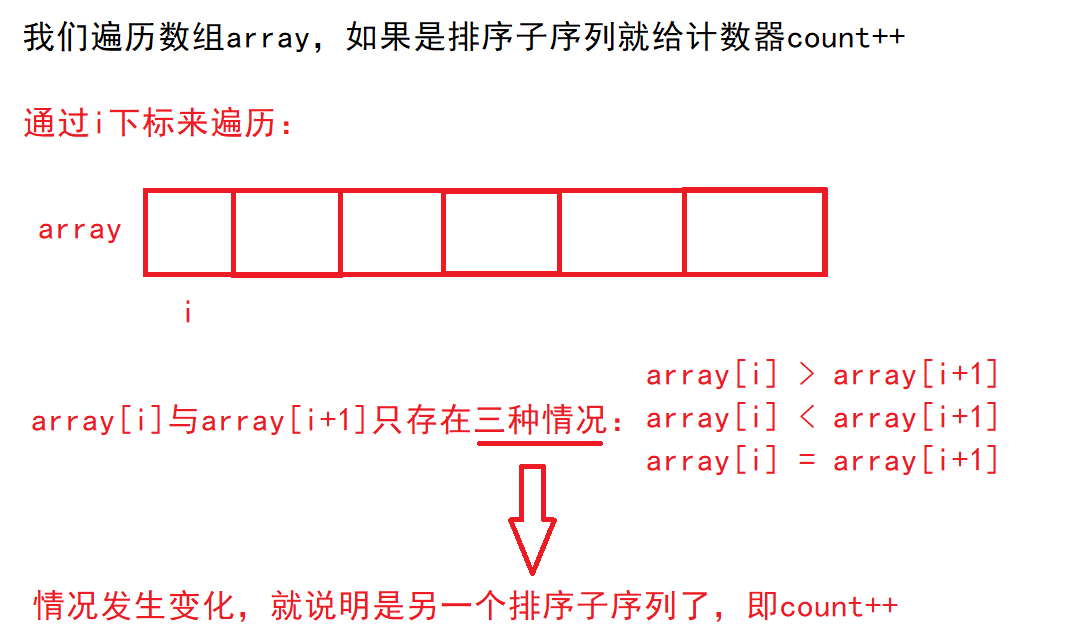
代码如下:
package Day2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Day2_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
array[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int i = 0;
int count = 0;
while (i < n) {
if(array[i] < array[i+1]) {
while (array[i] < array[i+1]) {
i++;
}
count++;
}else if (array[i] == array[i+1]) {
i++;
}else {
while (array[i] > array[i+1]) {
i++;
}
count++;
i++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
乍一看没有问题,但运行后发现存在数组指针越界!!

如果我们把条件改为(i < n && array[i] > array[i+1])可以吗?

正确的解决方案是:int[] array = new int[n + 1];加上i < n的同时给数组多一块空间!!!

代码实现:
package Day2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Day2_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
array[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int i = 0;
int count = 0;
while (i < n) {
if(array[i] < array[i+1]) {
while (array[i] < array[i+1]) {
i++;
}
count++;
}else if (array[i] == array[i+1]) {
i++;
}else {
while (i < n && array[i] > array[i+1]) {
i++;
}
count++;
i++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}