文章目录
- 第9讲 后端1
- 9.1.2 线性系统和 KF
- 9.1.4 扩展卡尔曼滤波器 EKF 不足
- 9.2 BA 与 图优化
- 9.2.1 投影模型和 BA 代价函数
- 9.2.2 BA 的求解
- 9.2.3 稀疏性 和 边缘化
- 9.2.4 鲁棒核函数
- 9.3 实践: Ceres BA 【Code】
- 本讲 CMakeLists.txt
- 9.4 实践:g2o 求解 BA 【Code】
- 习题
第9讲 后端1
滤波器 EKF
前端视觉里程计: 短时间内的轨迹和地图。
后端优化: 长时间内的最优轨迹和地图
9.1 概述
9.1.1 状态估计的概率解释
渐进的(Incremental): 当前的状态 只由 过去的时刻决定,甚至只由前一个决定。
批量的(Batch):不仅使用过去的信息更新自己的状态,也会用未来的信息来更新。


SfM: Structure from Motion.

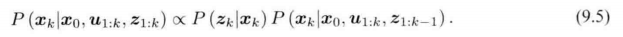
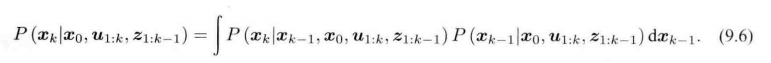
马尔可夫性:
k
k
k 时刻状态仅与
k
−
1
k-1
k−1 时刻状态 有关。 【扩展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)】
考虑
k
k
k 时刻状态 与 之前所有状态 的关系。 【非线性优化】
- 视觉 SLAM 主流
9.1.2 线性系统和 KF

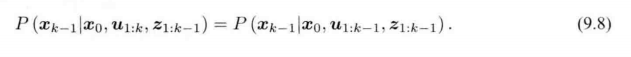






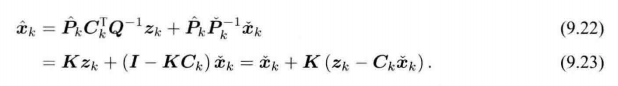
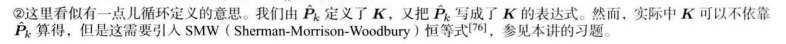
经典卡尔曼滤波:从概率角度出发的最大后验概率估计方式。
在线性高斯系统中,卡尔曼滤波器 构成了 该系统中的最大后验概率估计。
卡尔曼滤波器构成了线性系统的最优无偏估计。

9.1.3 非线性系统 和 EKF
把卡尔曼滤波器 的结果 扩展到 非线性系统中, 扩展卡尔曼滤波器。



9.1.4 扩展卡尔曼滤波器 EKF 不足





同等计算量的情况下, 非线性优化能取得更好的效果。
精度和鲁棒性更好。
9.2 BA 与 图优化
视觉三维重建
Bundle Adjustment (BA):从视觉图像中提炼出最优的3D模型和相机参数(内参和外差)。
考虑从任意特征点 发射出来的几束光线(bundles of light rays), 它们会在几个相机的成像平面上变成像素或是检测到的特征点,如果我们调整(adjustment) 各相机姿态和各自特征点的空间位置,使得这些光纤最终收束到 相机的光心,称为BA
其它译法: 光束法平差、捆集调整
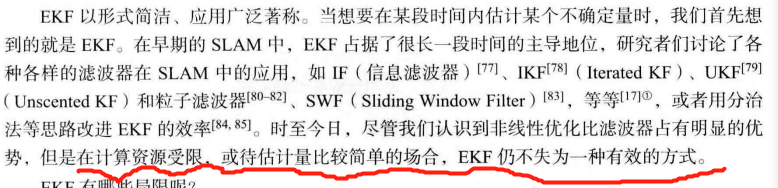
9.2.1 投影模型和 BA 代价函数



9.2.2 BA 的求解

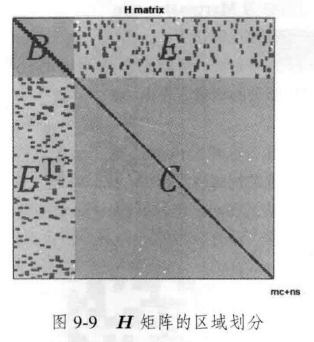
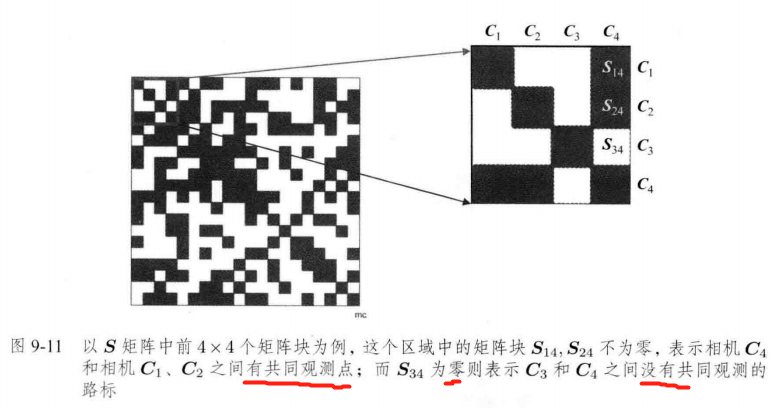
9.2.3 稀疏性 和 边缘化
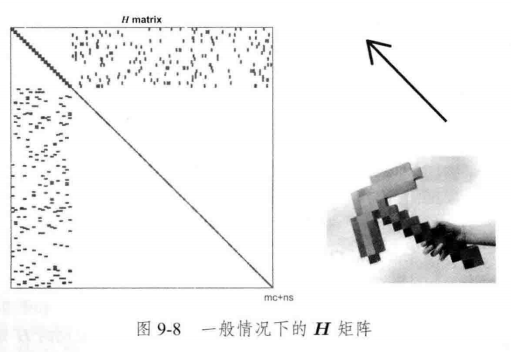
Schur消元 Marginalization(边缘化)
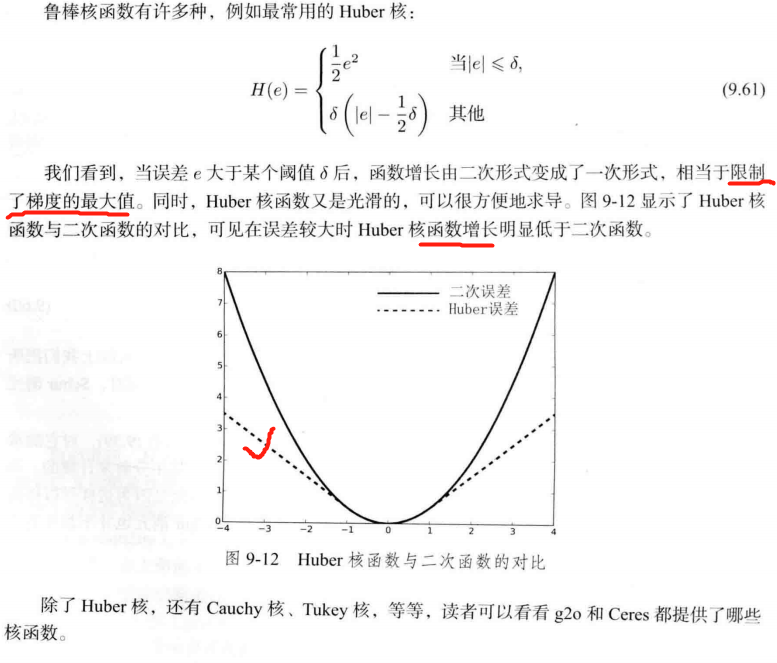
9.2.4 鲁棒核函数



1、构造 BA 问题
2、设置 Schur 消元
3、调用 稠密或稀疏 矩阵求解器对变量进行优化
9.3 实践: Ceres BA 【Code】

定义 投影误差模型



sudo apt-get install meshlab
本讲 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
project(bundle_adjustment)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-O3 -std=c++14")
LIST(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
Find_Package(G2O REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Ceres REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Sophus REQUIRED)
Find_Package(CSparse REQUIRED)
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_csparse_extension g2o_stuff g2o_core cxsparse)
include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR} ${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR} ${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR})
add_library(bal_common common.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_ceres bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_ceres ${CERES_LIBRARIES} bal_common)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_g2o bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_g2o
${G2O_LIBS}
g2o_solver_csparse g2o_csparse_extension
${Sophus_LIBRARIES}
bal_common)
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./bundle_adjustment_ceres ../problem-16-22106-pre.txt
byzanz-record -x 72 -y 64 -w 1848 -h 893 -d 20 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif
byzanz-record -x 72 -y 64 -w 1848 -h 893 -d 30 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif

bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include "common.h"
#include "SnavelyReprojectionError.h"
using namespace std;
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_ceres bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]);
bal_problem.Normalize();
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply");
SolveBA(bal_problem);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply");
return 0;
}
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// Observations is 2 * num_observations long array observations
// [u_1, u_2, ... u_n], where each u_i is two dimensional, the x
// and y position of the observation.
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
ceres::Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function;
// Each Residual block takes a point and a camera as input
// and outputs a 2 dimensional Residual
cost_function = SnavelyReprojectionError::Create(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]);
// If enabled use Huber's loss function.
ceres::LossFunction *loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(1.0);
// Each observation corresponds to a pair of a camera and a point
// which are identified by camera_index()[i] and point_index()[i]
// respectively.
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * bal_problem.camera_index()[i];
double *point = points + point_block_size * bal_problem.point_index()[i];
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, camera, point);
}
// show some information here ...
std::cout << "bal problem file loaded..." << std::endl;
std::cout << "bal problem have " << bal_problem.num_cameras() << " cameras and "
<< bal_problem.num_points() << " points. " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Forming " << bal_problem.num_observations() << " observations. " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Solving ceres BA ... " << endl;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::LinearSolverType::SPARSE_SCHUR;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
std::cout << summary.FullReport() << "\n";
}
9.4 实践:g2o 求解 BA 【Code】

报错:
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch9/bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp:10:10: fatal error: sophus/se3.hpp: No such file or directory
10 | #include "sophus/se3.hpp"
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~

SO3d 去掉 d 。 共3个
报错2:
/usr/local/include/g2o/stuff/tuple_tools.h:41:46: error: ‘tuple_size_v’ is not a member of ‘std’; did you mean ‘tuple_size’?
41 | f, t, i, std::make_index_sequence<std::tuple_size_v<std::decay_t<T>>>());
改动3:
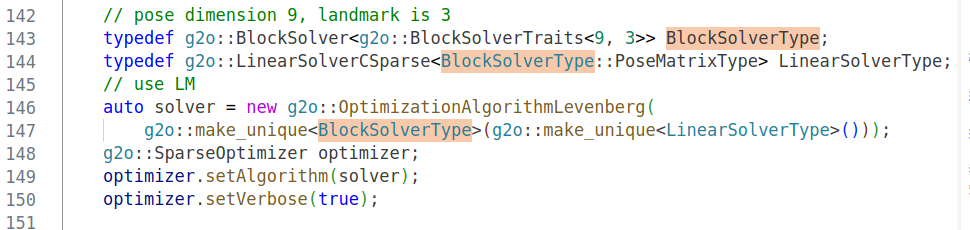
第143-147行 更换成下述代码
std::unique_ptr<g2o::BlockSolverX::LinearSolverType> linearSolver (new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<g2o::BlockSolverX::PoseMatrixType>());
std::unique_ptr<g2o::BlockSolverX> solver_ptr (new g2o::BlockSolverX(std::move(linearSolver)));
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(std::move(solver_ptr));
其它问题: 链接库的问题, 看 CMakeLists.txt
cd build
cmake ..
make
./bundle_adjustment_g2o ../problem-16-22106-pre.txt
byzanz-record -x 72 -y 64 -w 1848 -h 893 -d 30 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif
byzanz-record -x 72 -y 64 -w 1848 -h 893 -d 20 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif

bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "common.h"
#include "sophus/se3.h"
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
/// 姿态和内参的结构
struct PoseAndIntrinsics {
PoseAndIntrinsics() {}
/// set from given data address
explicit PoseAndIntrinsics(double *data_addr) {
rotation = SO3::exp(Vector3d(data_addr[0], data_addr[1], data_addr[2]));
translation = Vector3d(data_addr[3], data_addr[4], data_addr[5]);
focal = data_addr[6];
k1 = data_addr[7];
k2 = data_addr[8];
}
/// 将估计值放入内存
void set_to(double *data_addr) {
auto r = rotation.log();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i] = r[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i + 3] = translation[i];
data_addr[6] = focal;
data_addr[7] = k1;
data_addr[8] = k2;
}
SO3 rotation;
Vector3d translation = Vector3d::Zero();
double focal = 0;
double k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
};
/// 位姿加相机内参的顶点,9维,前三维为so3,接下去为t, f, k1, k2
class VertexPoseAndIntrinsics : public g2o::BaseVertex<9, PoseAndIntrinsics> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics() {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = PoseAndIntrinsics();
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate.rotation = SO3::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2])) * _estimate.rotation;
_estimate.translation += Vector3d(update[3], update[4], update[5]);
_estimate.focal += update[6];
_estimate.k1 += update[7];
_estimate.k2 += update[8];
}
/// 根据估计值投影一个点
Vector2d project(const Vector3d &point) {
Vector3d pc = _estimate.rotation * point + _estimate.translation;
pc = -pc / pc[2];
double r2 = pc.squaredNorm();
double distortion = 1.0 + r2 * (_estimate.k1 + _estimate.k2 * r2);
return Vector2d(_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[0],
_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[1]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
class VertexPoint : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Vector3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoint() {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate += Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
class EdgeProjection :
public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2d, VertexPoseAndIntrinsics, VertexPoint> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
virtual void computeError() override {
auto v0 = (VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *) _vertices[0];
auto v1 = (VertexPoint *) _vertices[1];
auto proj = v0->project(v1->estimate());
_error = proj - _measurement;
}
// use numeric derivatives
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_g2o bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]);
bal_problem.Normalize();
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply");
SolveBA(bal_problem);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply");
return 0;
}
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// pose dimension 9, landmark is 3
/*typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<9, 3>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
// use LM
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));*/
std::unique_ptr<g2o::BlockSolverX::LinearSolverType> linearSolver (new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<g2o::BlockSolverX::PoseMatrixType>());
std::unique_ptr<g2o::BlockSolverX> solver_ptr (new g2o::BlockSolverX(std::move(linearSolver)));
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(std::move(solver_ptr));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
/// build g2o problem
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
// vertex
vector<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *> vertex_pose_intrinsics;
vector<VertexPoint *> vertex_points;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *v = new VertexPoseAndIntrinsics();
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
v->setId(i);
v->setEstimate(PoseAndIntrinsics(camera));
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_pose_intrinsics.push_back(v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
VertexPoint *v = new VertexPoint();
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
v->setId(i + bal_problem.num_cameras());
v->setEstimate(Vector3d(point[0], point[1], point[2]));
// g2o在BA中需要手动设置待Marg的顶点
v->setMarginalized(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
// edge
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection;
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose_intrinsics[bal_problem.camera_index()[i]]);
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_points[bal_problem.point_index()[i]]);
edge->setMeasurement(Vector2d(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]));
edge->setInformation(Matrix2d::Identity());
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(40);
// set to bal problem
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_pose_intrinsics[i];
auto estimate = vertex->estimate();
estimate.set_to(camera);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_points[i];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) point[k] = vertex->estimate()[k];
}
}


习题