文章目录
- 12.2 单目稠密 重建
- 12.2.2 极线搜索 && 块匹配
- 12.2.3 高斯分布的深度滤波器
- 12.3 单目稠密重建 【Code】
- 待改进
- 12.3.4 图像间的变换
- 12.4 RGB-D 稠密建图
- 12.4.1 点云地图 【Code】
- 查询OpenCV版本 opencv_version
- 12.4.2 从点云 重建 网格 【Code】
- 查看PCL 版本 aptitude show libpcl-dev
- 12.4.3 八叉树地图(Octomap) 【灵活压缩、随时更新】
- 12.4.4 八叉树地图 【建模大场景】 【Code】
- 习题
- √ 题1
- √ 题2
- 题3
- 题4
- 题5
- 题6
单目SLAM 稠密 深度估计
单目 稠密 重建
RGB-D 重建 的地图形式
估计 相机运动轨迹 + 特征点空间位置
机器人SLAM:定位、导航、避障和交互
SLAM: 同时定位 与 建图
经典 SLAM 地图(路标点的集合)
视觉里程计、BA: 建模了路标点的位置
扫地机: 全局定位,导航,路径规划
增强现实设备: 将虚拟物叠加在现实物体之中, 处理虚拟物体与真实物体之间的遮挡关系。
定位(空间位姿信息): 把地图保存下来,这样只需对地图进行一次建模, 而不是每次启动机器人都重新做一次完整的SLAM
导航、避障:需要 稠密地图。哪些地方可通过
重建 三维视频通话、网上购物 纹理稠密
交互 语义地图
稀疏路标地图 只建模感兴趣部分 定位
稠密地图 建模 所有看到过的部分 导航避障
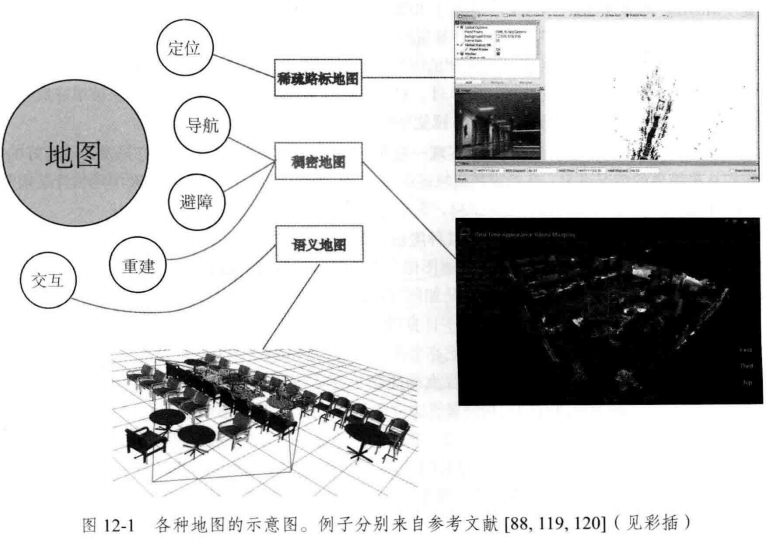
视觉SLAM 如何建 稠密地图
12.2 单目稠密 重建
获取像素点间距离的方法:
1、单目相机 三角化 计算像素之间的距离
2、双目相机, 利用左右目的视差 计算像素的距离
3、RGB-D相机 直接 获取 像素距离。
立体视觉(Stereo Vision)
移动单目相机 (移动视角的立体视觉(Moving View Stereo,MVS))
使用单目和双目 获取深度 费力不讨好。 计算量巨大、不可靠
场景: 室外,大场景
RGB-D: 量程、应用范围、光照限制。
极线搜索 块匹配
深度滤波技术 :多次使用 三角测量法 让深度估计收敛。
12.2.2 极线搜索 && 块匹配
单个像素的亮度 没有区分性 ——> 比较 像素块。
计算两个小块之间的差异:

去均值 的 NCC
不断 对不同图像 进行极线 搜索时, 估计的深度分布将如何变化。
12.2.3 高斯分布的深度滤波器
均匀-高斯混合分布的滤波器


12.3 单目稠密重建 【Code】


mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./dense_mapping /home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch12/semi_dense_mono/dataset/test_data
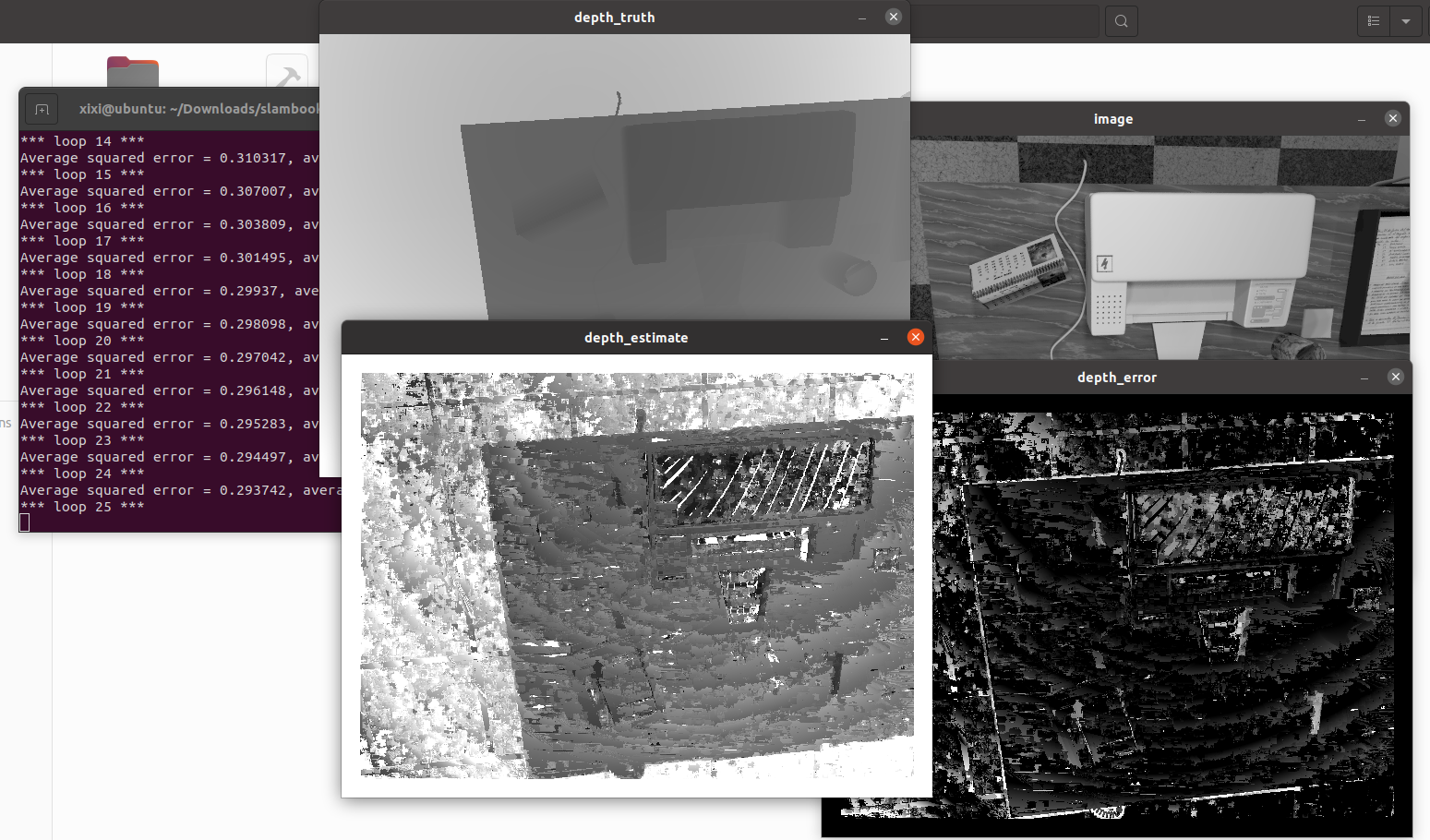


dense_mapping.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
// for sophus
#include <sophus/se3.h>
using Sophus::SE3; // 该文件里的全部 SE3d 都要 去掉 d
// for eigen
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
using namespace Eigen;
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
/**********************************************
* 本程序演示了单目相机在已知轨迹下的稠密深度估计
* 使用极线搜索 + NCC 匹配的方式,与书本的 12.2 节对应
* 请注意本程序并不完美,你完全可以改进它——我其实在故意暴露一些问题(这是借口)。
***********************************************/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// parameters
const int boarder = 20; // 边缘宽度
const int width = 640; // 图像宽度
const int height = 480; // 图像高度
const double fx = 481.2f; // 相机内参
const double fy = -480.0f;
const double cx = 319.5f;
const double cy = 239.5f;
const int ncc_window_size = 3; // NCC 取的窗口半宽度
const int ncc_area = (2 * ncc_window_size + 1) * (2 * ncc_window_size + 1); // NCC窗口面积
const double min_cov = 0.1; // 收敛判定:最小方差
const double max_cov = 10; // 发散判定:最大方差
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 重要的函数
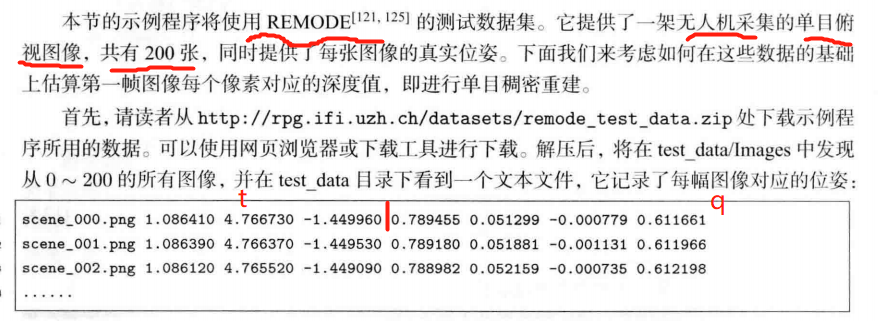
/// 从 REMODE 数据集读取数据
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string &path,
vector<string> &color_image_files,
vector<SE3> &poses,
cv::Mat &ref_depth
);
/**
* 根据新的图像更新深度估计
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param T_C_R 参考图像到当前图像的位姿
* @param depth 深度
* @param depth_cov 深度方差
* @return 是否成功
*/
void update(
const Mat &ref,
const Mat &curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
Mat &depth,
Mat &depth_cov2
);
/**
* 极线搜索
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param T_C_R 位姿
* @param pt_ref 参考图像中点的位置
* @param depth_mu 深度均值
* @param depth_cov 深度方差
* @param pt_curr 当前点
* @param epipolar_direction 极线方向
* @return 是否成功
*/
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat &ref,
const Mat &curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const double &depth_mu,
const double &depth_cov,
Vector2d &pt_curr,
Vector2d &epipolar_direction
);
/**
* 更新深度滤波器
* @param pt_ref 参考图像点
* @param pt_curr 当前图像点
* @param T_C_R 位姿
* @param epipolar_direction 极线方向
* @param depth 深度均值
* @param depth_cov2 深度方向
* @return 是否成功
*/
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const Vector2d &pt_curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
const Vector2d &epipolar_direction,
Mat &depth,
Mat &depth_cov2
);
/**
* 计算 NCC 评分
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param pt_ref 参考点
* @param pt_curr 当前点
* @return NCC评分
*/
double NCC(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &pt_ref, const Vector2d &pt_curr);
// 双线性灰度插值
inline double getBilinearInterpolatedValue(const Mat &img, const Vector2d &pt) {
uchar *d = &img.data[int(pt(1, 0)) * img.step + int(pt(0, 0))];
double xx = pt(0, 0) - floor(pt(0, 0));
double yy = pt(1, 0) - floor(pt(1, 0));
return ((1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * double(d[0]) +
xx * (1 - yy) * double(d[1]) +
(1 - xx) * yy * double(d[img.step]) +
xx * yy * double(d[img.step + 1])) / 255.0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 一些小工具
// 显示估计的深度图
void plotDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate);
// 像素到相机坐标系
inline Vector3d px2cam(const Vector2d px) {
return Vector3d(
(px(0, 0) - cx) / fx,
(px(1, 0) - cy) / fy,
1
);
}
// 相机坐标系到像素
inline Vector2d cam2px(const Vector3d p_cam) {
return Vector2d(
p_cam(0, 0) * fx / p_cam(2, 0) + cx,
p_cam(1, 0) * fy / p_cam(2, 0) + cy
);
}
// 检测一个点是否在图像边框内
inline bool inside(const Vector2d &pt) {
return pt(0, 0) >= boarder && pt(1, 0) >= boarder
&& pt(0, 0) + boarder < width && pt(1, 0) + boarder <= height;
}
// 显示极线匹配
void showEpipolarMatch(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_curr);
// 显示极线
void showEpipolarLine(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_min_curr,
const Vector2d &px_max_curr);
/// 评测深度估计
void evaludateDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate);
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "Usage: dense_mapping path_to_test_dataset" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 从数据集读取数据
vector<string> color_image_files;
vector<SE3> poses_TWC;
Mat ref_depth;
bool ret = readDatasetFiles(argv[1], color_image_files, poses_TWC, ref_depth);
if (ret == false) {
cout << "Reading image files failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "read total " << color_image_files.size() << " files." << endl;
// 第一张图
Mat ref = imread(color_image_files[0], 0); // gray-scale image
SE3 pose_ref_TWC = poses_TWC[0];
double init_depth = 3.0; // 深度初始值
double init_cov2 = 3.0; // 方差初始值
Mat depth(height, width, CV_64F, init_depth); // 深度图
Mat depth_cov2(height, width, CV_64F, init_cov2); // 深度图方差
for (int index = 1; index < color_image_files.size(); index++) {
cout << "*** loop " << index << " ***" << endl;
Mat curr = imread(color_image_files[index], 0);
if (curr.data == nullptr) continue;
SE3 pose_curr_TWC = poses_TWC[index];
SE3 pose_T_C_R = pose_curr_TWC.inverse() * pose_ref_TWC; // 坐标转换关系: T_C_W * T_W_R = T_C_R
update(ref, curr, pose_T_C_R, depth, depth_cov2);
evaludateDepth(ref_depth, depth);
plotDepth(ref_depth, depth);
imshow("image", curr);
waitKey(1);
}
cout << "estimation returns, saving depth map ..." << endl;
imwrite("depth.png", depth);
cout << "done." << endl;
return 0;
}
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string &path,
vector<string> &color_image_files,
std::vector<SE3> &poses,
cv::Mat &ref_depth) {
ifstream fin(path + "/first_200_frames_traj_over_table_input_sequence.txt");
if (!fin) return false;
while (!fin.eof()) {
// 数据格式:图像文件名 tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw ,注意是 TWC 而非 TCW
string image;
fin >> image;
double data[7];
for (double &d:data) fin >> d;
color_image_files.push_back(path + string("/images/") + image);
poses.push_back(
SE3(Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]))
);
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
fin.close();
// load reference depth
fin.open(path + "/depthmaps/scene_000.depth");
ref_depth = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_64F);
if (!fin) return false;
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
double depth = 0;
fin >> depth;
ref_depth.ptr<double>(y)[x] = depth / 100.0;
}
return true;
}
// 对整个深度图进行更新
void update(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const SE3 &T_C_R, Mat &depth, Mat &depth_cov2) {
for (int x = boarder; x < width - boarder; x++)
for (int y = boarder; y < height - boarder; y++){
// 遍历每个像素
if (depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x] > max_cov) // 深度已收敛或发散
continue;
// 在极线上搜索 (x,y) 的匹配
Vector2d pt_curr;
Vector2d epipolar_direction;
bool ret = epipolarSearch(
ref,
curr,
T_C_R,
Vector2d(x, y),
depth.ptr<double>(y)[x],
sqrt(depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x]),
pt_curr,
epipolar_direction
);
if (ret == false) // 匹配失败
continue;
// 取消该注释以显示匹配
// showEpipolarMatch(ref, curr, Vector2d(x, y), pt_curr);
// 匹配成功,更新深度图
updateDepthFilter(Vector2d(x, y), pt_curr, T_C_R, epipolar_direction, depth, depth_cov2);
}
}
// 极线搜索
// 方法见书 12.2 12.3 两节
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R, const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const double &depth_mu, const double &depth_cov,
Vector2d &pt_curr, Vector2d &epipolar_direction) {
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam(pt_ref);
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d P_ref = f_ref * depth_mu; // 参考帧的 P 向量
Vector2d px_mean_curr = cam2px(T_C_R * P_ref); // 按深度均值投影的像素
double d_min = depth_mu - 3 * depth_cov, d_max = depth_mu + 3 * depth_cov;
if (d_min < 0.1) d_min = 0.1;
Vector2d px_min_curr = cam2px(T_C_R * (f_ref * d_min)); // 按最小深度投影的像素
Vector2d px_max_curr = cam2px(T_C_R * (f_ref * d_max)); // 按最大深度投影的像素
Vector2d epipolar_line = px_max_curr - px_min_curr; // 极线(线段形式)
epipolar_direction = epipolar_line; // 极线方向
epipolar_direction.normalize();
double half_length = 0.5 * epipolar_line.norm(); // 极线线段的半长度
if (half_length > 100) half_length = 100; // 我们不希望搜索太多东西
// 取消此句注释以显示极线(线段)
// showEpipolarLine( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_min_curr, px_max_curr );
// 在极线上搜索,以深度均值点为中心,左右各取半长度
double best_ncc = -1.0;
Vector2d best_px_curr;
for (double l = -half_length; l <= half_length; l += 0.7) { // l+=sqrt(2)
Vector2d px_curr = px_mean_curr + l * epipolar_direction; // 待匹配点
if (!inside(px_curr))
continue;
// 计算待匹配点与参考帧的 NCC
double ncc = NCC(ref, curr, pt_ref, px_curr);
if (ncc > best_ncc) {
best_ncc = ncc;
best_px_curr = px_curr;
}
}
if (best_ncc < 0.85f) // 只相信 NCC 很高的匹配
return false;
pt_curr = best_px_curr;
return true;
}
double NCC(
const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr,
const Vector2d &pt_ref, const Vector2d &pt_curr) {
// 零均值-归一化互相关
// 先算均值
double mean_ref = 0, mean_curr = 0;
vector<double> values_ref, values_curr; // 参考帧和当前帧的均值
for (int x = -ncc_window_size; x <= ncc_window_size; x++)
for (int y = -ncc_window_size; y <= ncc_window_size; y++) {
double value_ref = double(ref.ptr<uchar>(int(y + pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(x + pt_ref(0, 0))]) / 255.0;
mean_ref += value_ref;
double value_curr = getBilinearInterpolatedValue(curr, pt_curr + Vector2d(x, y));
mean_curr += value_curr;
values_ref.push_back(value_ref);
values_curr.push_back(value_curr);
}
mean_ref /= ncc_area;
mean_curr /= ncc_area;
// 计算 Zero mean NCC
double numerator = 0, demoniator1 = 0, demoniator2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < values_ref.size(); i++) {
double n = (values_ref[i] - mean_ref) * (values_curr[i] - mean_curr);
numerator += n;
demoniator1 += (values_ref[i] - mean_ref) * (values_ref[i] - mean_ref);
demoniator2 += (values_curr[i] - mean_curr) * (values_curr[i] - mean_curr);
}
return numerator / sqrt(demoniator1 * demoniator2 + 1e-10); // 防止分母出现零
}
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const Vector2d &pt_curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
const Vector2d &epipolar_direction,
Mat &depth,
Mat &depth_cov2) {
// 不知道这段还有没有人看
// 用三角化计算深度
SE3 T_R_C = T_C_R.inverse();
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam(pt_ref);
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d f_curr = px2cam(pt_curr);
f_curr.normalize();
// 方程
// d_ref * f_ref = d_cur * ( R_RC * f_cur ) + t_RC
// f2 = R_RC * f_cur
// 转化成下面这个矩阵方程组
// => [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f2 ] [d_ref] [f_ref^T t]
// [ f_2^T f_ref, -f2^T f2 ] [d_cur] = [f2^T t ]
Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation();
Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.so3() * f_curr;
Vector2d b = Vector2d(t.dot(f_ref), t.dot(f2));
Matrix2d A;
A(0, 0) = f_ref.dot(f_ref);
A(0, 1) = -f_ref.dot(f2);
A(1, 0) = -A(0, 1);
A(1, 1) = -f2.dot(f2);
Vector2d ans = A.inverse() * b;
Vector3d xm = ans[0] * f_ref; // ref 侧的结果
Vector3d xn = t + ans[1] * f2; // cur 结果
Vector3d p_esti = (xm + xn) / 2.0; // P的位置,取两者的平均
double depth_estimation = p_esti.norm(); // 深度值
// 计算不确定性(以一个像素为误差)
Vector3d p = f_ref * depth_estimation;
Vector3d a = p - t;
double t_norm = t.norm();
double a_norm = a.norm();
double alpha = acos(f_ref.dot(t) / t_norm);
double beta = acos(-a.dot(t) / (a_norm * t_norm));
Vector3d f_curr_prime = px2cam(pt_curr + epipolar_direction);
f_curr_prime.normalize();
double beta_prime = acos(f_curr_prime.dot(-t) / t_norm);
double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime;
double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma);
double d_cov = p_prime - depth_estimation;
double d_cov2 = d_cov * d_cov;
// 高斯融合
double mu = depth.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))];
double sigma2 = depth_cov2.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))];
double mu_fuse = (d_cov2 * mu + sigma2 * depth_estimation) / (sigma2 + d_cov2);
double sigma_fuse2 = (sigma2 * d_cov2) / (sigma2 + d_cov2);
depth.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))] = mu_fuse;
depth_cov2.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))] = sigma_fuse2;
return true;
}
// 后面这些太简单我就不注释了(其实是因为懒)
void plotDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate) {
imshow("depth_truth", depth_truth * 0.4);
imshow("depth_estimate", depth_estimate * 0.4);
imshow("depth_error", depth_truth - depth_estimate);
waitKey(1);
}
void evaludateDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate) {
double ave_depth_error = 0; // 平均误差
double ave_depth_error_sq = 0; // 平方误差
int cnt_depth_data = 0;
for (int y = boarder; y < depth_truth.rows - boarder; y++)
for (int x = boarder; x < depth_truth.cols - boarder; x++) {
double error = depth_truth.ptr<double>(y)[x] - depth_estimate.ptr<double>(y)[x];
ave_depth_error += error;
ave_depth_error_sq += error * error;
cnt_depth_data++;
}
ave_depth_error /= cnt_depth_data;
ave_depth_error_sq /= cnt_depth_data;
cout << "Average squared error = " << ave_depth_error_sq << ", average error: " << ave_depth_error << endl;
}
void showEpipolarMatch(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_curr) {
Mat ref_show, curr_show;
cv::cvtColor(ref, ref_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(curr, curr_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::circle(ref_show, cv::Point2f(px_ref(0, 0), px_ref(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 250), 2);
cv::circle(curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_curr(0, 0), px_curr(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 250), 2);
imshow("ref", ref_show);
imshow("curr", curr_show);
waitKey(1);
}
void showEpipolarLine(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_min_curr,
const Vector2d &px_max_curr) {
Mat ref_show, curr_show;
cv::cvtColor(ref, ref_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(curr, curr_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::circle(ref_show, cv::Point2f(px_ref(0, 0), px_ref(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
cv::circle(curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_min_curr(0, 0), px_min_curr(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
cv::circle(curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_max_curr(0, 0), px_max_curr(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
cv::line(curr_show, Point2f(px_min_curr(0, 0), px_min_curr(1, 0)), Point2f(px_max_curr(0, 0), px_max_curr(1, 0)),
Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
imshow("ref", ref_show);
imshow("curr", curr_show);
waitKey(1);
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(dense_monocular)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++17 -march=native -O3")
############### dependencies ######################
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV 4.8.0 REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Sophus
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
set(THIRD_PARTY_LIBS
${OpenCV_LIBS}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(dense_mapping dense_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(dense_mapping ${THIRD_PARTY_LIBS})
待改进
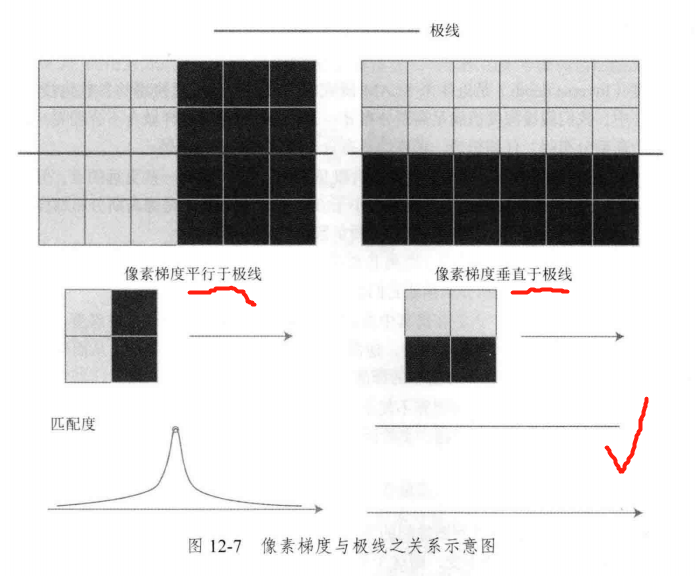
12.3.2 像素梯度
块匹配的正确与否 依赖于 图像块是否具有区分度。
立体视觉的重建质量 依赖 环境纹理。
——————————
12.3.3 逆深度(深度的倒数), 认为符合高斯分布。
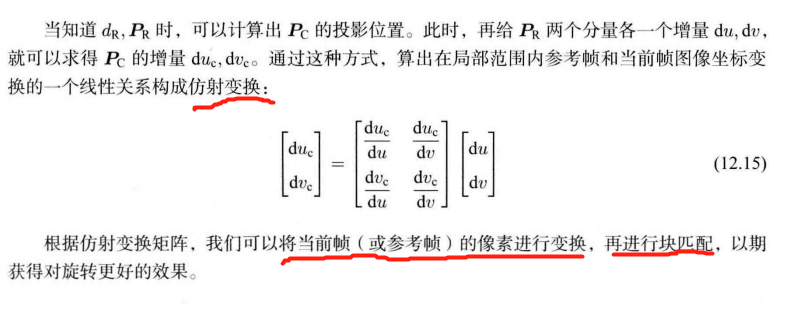
12.3.4 图像间的变换

GPU 并行化 提高效率
极线搜索
其它改进:
1、给深度估计 加上 空间正则项
2、考虑错误匹配的情形: 均匀-高斯混合分布下的深度滤波器(显式地将内点与外点进行区别并进行概率建模)
————————
12.4 RGB-D 稠密建图
深度数据与纹理无关
根据估算的相机位姿,将RGB-D数据转化为点云,然后进行拼接。
12.4.1 点云地图 【Code】
点云: 一组离散的点表示的地图。
外点去除滤波器 体素网格的降采样滤波器(Voxel grid filter)
安装点云库
sudo apt-get install libpcl-dev pcl-tools

与第5讲的变化:
1、生成每帧点云时,去掉深度值无效的点。Kinect 的量程限制
2、利用统计滤波器去除孤立点。计算附近N个点距离的平均值,去除距离均值过大的点。
3、体素网格滤波器进行降采样。
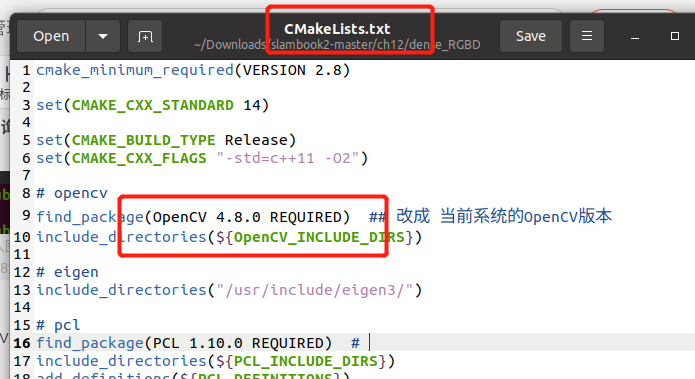
要在CMakeLists.txt文件里加这一句,使得 支持C++14标准。 可能是最新版本的PCL 要求支持C++14标准。
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
查询OpenCV版本 opencv_version
增加OpenCV的版本
所有.cpp中的文件路径都要改成..多回一级
pointcloud_mapping.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <boost/format.hpp> // for formating strings
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
vector<cv::Mat> colorImgs, depthImgs; // 彩色图和深度图
vector<Eigen::Isometry3d> poses; // 相机位姿
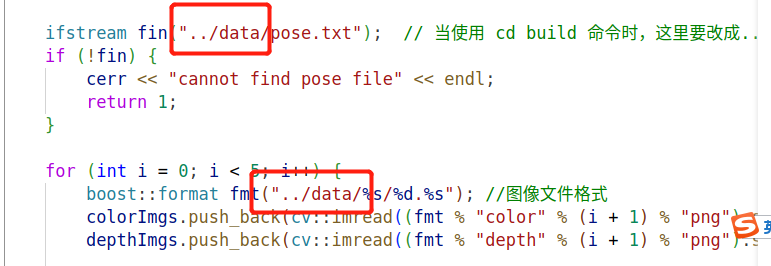
ifstream fin("../data/pose.txt"); // 当使用 cd build 命令时,这里要改成..
if (!fin) {
cerr << "cannot find pose file" << endl;
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
boost::format fmt("../data/%s/%d.%s"); //图像文件格式
colorImgs.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "color" % (i + 1) % "png").str()));
depthImgs.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "depth" % (i + 1) % "png").str(), -1)); // 使用-1读取原始图像
double data[7] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
fin >> data[i];
}
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
Eigen::Isometry3d T(q);
T.pretranslate(Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]));
poses.push_back(T);
}
// 计算点云并拼接
// 相机内参
double cx = 319.5;
double cy = 239.5;
double fx = 481.2;
double fy = -480.0;
double depthScale = 5000.0;
cout << "正在将图像转换为点云..." << endl;
// 定义点云使用的格式:这里用的是XYZRGB
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGB PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud;
// 新建一个点云
PointCloud::Ptr pointCloud(new PointCloud);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
PointCloud::Ptr current(new PointCloud);
cout << "转换图像中: " << i + 1 << endl;
cv::Mat color = colorImgs[i];
cv::Mat depth = depthImgs[i];
Eigen::Isometry3d T = poses[i];
for (int v = 0; v < color.rows; v++)
for (int u = 0; u < color.cols; u++) {
unsigned int d = depth.ptr<unsigned short>(v)[u]; // 深度值
if (d == 0) continue; // 为0表示没有测量到
Eigen::Vector3d point;
point[2] = double(d) / depthScale;
point[0] = (u - cx) * point[2] / fx;
point[1] = (v - cy) * point[2] / fy;
Eigen::Vector3d pointWorld = T * point;
PointT p;
p.x = pointWorld[0];
p.y = pointWorld[1];
p.z = pointWorld[2];
p.b = color.data[v * color.step + u * color.channels()];
p.g = color.data[v * color.step + u * color.channels() + 1];
p.r = color.data[v * color.step + u * color.channels() + 2];
current->points.push_back(p);
}
// depth filter and statistical removal
PointCloud::Ptr tmp(new PointCloud);
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT> statistical_filter;
statistical_filter.setMeanK(50);
statistical_filter.setStddevMulThresh(1.0);
statistical_filter.setInputCloud(current);
statistical_filter.filter(*tmp);
(*pointCloud) += *tmp;
}
pointCloud->is_dense = false;
cout << "点云共有" << pointCloud->size() << "个点." << endl;
// voxel filter
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> voxel_filter;
double resolution = 0.03;
voxel_filter.setLeafSize(resolution, resolution, resolution); // resolution
PointCloud::Ptr tmp(new PointCloud);
voxel_filter.setInputCloud(pointCloud);
voxel_filter.filter(*tmp);
tmp->swap(*pointCloud);
cout << "滤波之后,点云共有" << pointCloud->size() << "个点." << endl;
pcl::io::savePCDFileBinary("map.pcd", *pointCloud);
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O2")
# opencv
find_package(OpenCV 4.8.0 REQUIRED) ## 改成 当前系统的OpenCV版本
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3/")
# pcl
find_package(PCL 1.10.0 REQUIRED) #
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
# octomap
find_package(octomap REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OCTOMAP_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(pointcloud_mapping pointcloud_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pointcloud_mapping ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(octomap_mapping octomap_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(octomap_mapping ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} ${OCTOMAP_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(surfel_mapping surfel_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(surfel_mapping ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
mkdir build && cd build ## 需要将.cpp中数据的路径 多加一个.
cmake ..
make
./pointcloud_mapping
pcl_viewer map.pcd
体素滤波之后的点云:

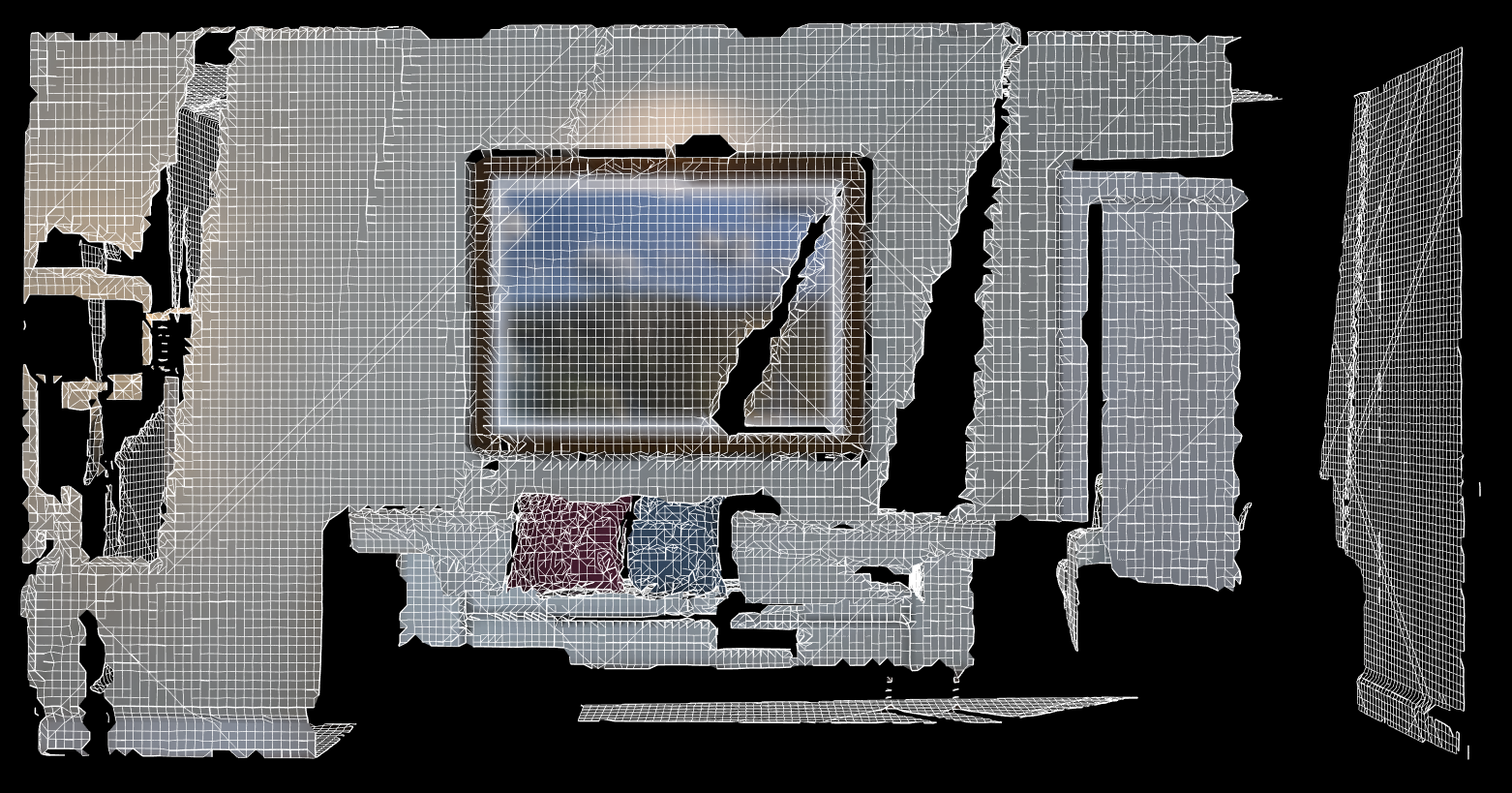
12.4.2 从点云 重建 网格 【Code】
./surfel_mapping map.pcd
点云转换成 网格地图(栅格地图)。

surfel_mapping.cpp
//
// Created by gaoxiang on 19-4-25.
//
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/surface/surfel_smoothing.h>
#include <pcl/surface/mls.h>
#include <pcl/surface/gp3.h>
#include <pcl/surface/impl/mls.hpp>
// typedefs
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGB PointT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr PointCloudPtr;
typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBNormal SurfelT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<SurfelT> SurfelCloud;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<SurfelT>::Ptr SurfelCloudPtr;
SurfelCloudPtr reconstructSurface(
const PointCloudPtr &input, float radius, int polynomial_order) {
pcl::MovingLeastSquares<PointT, SurfelT> mls;
pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<PointT>);
mls.setSearchMethod(tree);
mls.setSearchRadius(radius);
mls.setComputeNormals(true);
mls.setSqrGaussParam(radius * radius);
mls.setPolynomialFit(polynomial_order > 1);
mls.setPolynomialOrder(polynomial_order);
mls.setInputCloud(input);
SurfelCloudPtr output(new SurfelCloud);
mls.process(*output);
return (output);
}
pcl::PolygonMeshPtr triangulateMesh(const SurfelCloudPtr &surfels) {
// Create search tree*
pcl::search::KdTree<SurfelT>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<SurfelT>);
tree->setInputCloud(surfels);
// Initialize objects
pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation<SurfelT> gp3;
pcl::PolygonMeshPtr triangles(new pcl::PolygonMesh);
// Set the maximum distance between connected points (maximum edge length)
gp3.setSearchRadius(0.05);
// Set typical values for the parameters
gp3.setMu(2.5);
gp3.setMaximumNearestNeighbors(100);
gp3.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI / 4); // 45 degrees
gp3.setMinimumAngle(M_PI / 18); // 10 degrees
gp3.setMaximumAngle(2 * M_PI / 3); // 120 degrees
gp3.setNormalConsistency(true);
// Get result
gp3.setInputCloud(surfels);
gp3.setSearchMethod(tree);
gp3.reconstruct(*triangles);
return triangles;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// Load the points
PointCloudPtr cloud(new PointCloud);
if (argc == 0 || pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[1], *cloud)) {
cout << "failed to load point cloud!";
return 1;
}
cout << "point cloud loaded, points: " << cloud->points.size() << endl;
// Compute surface elements
cout << "computing normals ... " << endl;
double mls_radius = 0.05, polynomial_order = 2;
auto surfels = reconstructSurface(cloud, mls_radius, polynomial_order);
// Compute a greedy surface triangulation
cout << "computing mesh ... " << endl;
pcl::PolygonMeshPtr mesh = triangulateMesh(surfels);
cout << "display mesh ... " << endl;
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer vis;
vis.addPolylineFromPolygonMesh(*mesh, "mesh frame");
vis.addPolygonMesh(*mesh, "mesh");
vis.resetCamera();
vis.spin();
}
重建算法: Moving Least Square 、 Greedy Projection
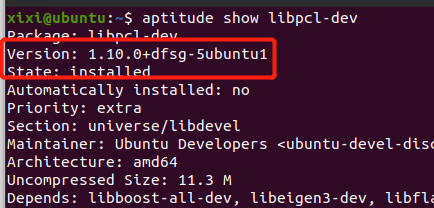
查看PCL 版本 aptitude show libpcl-dev
aptitude show libpcl-dev
可参考链接
12.4.3 八叉树地图(Octomap) 【灵活压缩、随时更新】
点云地图 不足:
1、占内存,提供了很多不必要的细节
2、无法处理运动物体。 只有 “添加点”,点消失时 不会 被移除。
八叉树 比 点云 节省大量的存储空间
- 当某个方块的所有子结点都被占据或都不被占据时,就没必要展开。
12.4.4 八叉树地图 【建模大场景】 【Code】
安装 octomap库
sudo apt-get install liboctomap-dev octovis
./octomap_mapping
octovis octomap.bt
动图截取:
byzanz-record -x 72 -y 64 -w 1848 -h 893 -d 10 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif

octomap_mapping.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <octomap/octomap.h> // for octomap
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <boost/format.hpp> // for formating strings
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
vector<cv::Mat> colorImgs, depthImgs; // 彩色图和深度图
vector<Eigen::Isometry3d> poses; // 相机位姿
ifstream fin("../data/pose.txt");
if (!fin) {
cerr << "cannot find pose file" << endl;
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
boost::format fmt("../data/%s/%d.%s"); //图像文件格式
colorImgs.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "color" % (i + 1) % "png").str()));
depthImgs.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % "depth" % (i + 1) % "png").str(), -1)); // 使用-1读取原始图像
double data[7] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
fin >> data[i];
}
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
Eigen::Isometry3d T(q);
T.pretranslate(Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]));
poses.push_back(T);
}
// 计算点云并拼接
// 相机内参
double cx = 319.5;
double cy = 239.5;
double fx = 481.2;
double fy = -480.0;
double depthScale = 5000.0;
cout << "正在将图像转换为 Octomap ..." << endl;
// octomap tree
octomap::OcTree tree(0.01); // 参数为分辨率
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << "转换图像中: " << i + 1 << endl;
cv::Mat color = colorImgs[i];
cv::Mat depth = depthImgs[i];
Eigen::Isometry3d T = poses[i];
octomap::Pointcloud cloud; // the point cloud in octomap
for (int v = 0; v < color.rows; v++)
for (int u = 0; u < color.cols; u++) {
unsigned int d = depth.ptr<unsigned short>(v)[u]; // 深度值
if (d == 0) continue; // 为0表示没有测量到
Eigen::Vector3d point;
point[2] = double(d) / depthScale;
point[0] = (u - cx) * point[2] / fx;
point[1] = (v - cy) * point[2] / fy;
Eigen::Vector3d pointWorld = T * point;
// 将世界坐标系的点放入点云
cloud.push_back(pointWorld[0], pointWorld[1], pointWorld[2]);
}
// 将点云存入八叉树地图,给定原点,这样可以计算投射线
tree.insertPointCloud(cloud, octomap::point3d(T(0, 3), T(1, 3), T(2, 3)));
}
// 更新中间节点的占据信息并写入磁盘
tree.updateInnerOccupancy();
cout << "saving octomap ... " << endl;
tree.writeBinary("octomap.bt");
return 0;
}
——————————
12.5 TSDF 地图 和 Fusion系列
TSDF(Truncated Signed Distance Function,截断符号距离函数)
实时三维重建: 重建准确地图
定位算法 可以满足实时性需求,地图加工可在关键帧处进行处理,无需实时。
SLAM 轻量级、小型化
实时三维重建 大规模、大型动态场景。

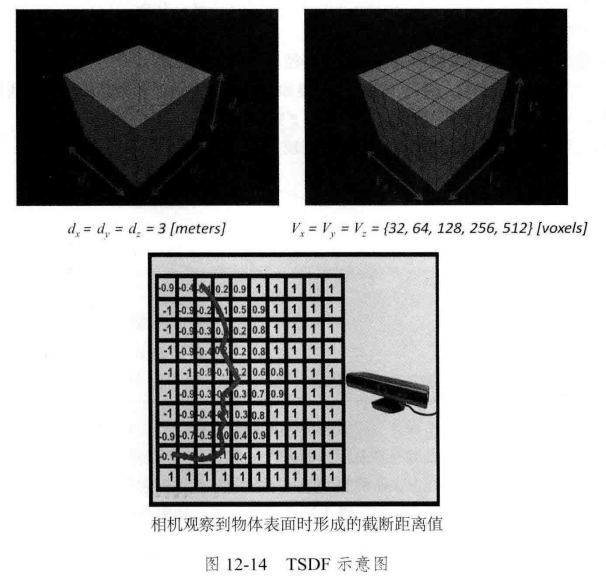
——————————
12.6 小结
度量地图
RGB-D 构建稠密地图 更容易、更稳定一些
习题

√ 题1


#*********************************解题1开始
设某个像素点的深度
d
d
d 服从高斯分布
P
(
d
)
=
N
(
μ
,
σ
2
)
P(d) = N(\mu, σ^2)
P(d)=N(μ,σ2)
增加新数据后,重新观测到的深度分布符合高斯分布 P ( d o b s ) = N ( μ o b s , σ o b s 2 ) P(d_{obs}) = N(\mu_{obs}, σ_{obs}^2) P(dobs)=N(μobs,σobs2)
信息融合后的深度为这两个高斯分布的乘积,即
P
(
d
f
u
s
e
)
=
N
(
μ
,
σ
2
)
⋅
N
(
μ
o
b
s
,
σ
o
b
s
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
(
x
−
μ
)
2
σ
2
)
⋅
1
2
π
σ
o
b
s
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
(
x
−
μ
o
b
s
)
2
σ
o
b
s
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
σ
o
b
s
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
(
x
−
μ
)
2
σ
2
−
1
2
(
x
−
μ
o
b
s
)
2
σ
o
b
s
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
σ
o
b
s
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
σ
o
b
s
2
⋅
(
x
−
μ
)
2
+
σ
2
⋅
(
x
−
μ
o
b
s
)
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
σ
o
b
s
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
(
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
⋅
x
2
−
2
(
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
)
⋅
x
+
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
2
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
σ
o
b
s
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
x
2
−
2
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
⋅
x
+
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
2
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
σ
o
b
s
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
(
x
−
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
⋅
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
2
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
−
(
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
=
1
2
π
σ
σ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
(
x
−
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
⋅
e
x
p
(
−
1
2
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
2
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
−
(
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
2
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
)
2
π
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
\begin{align*}P(d_{fuse}) &= N(\mu, σ^2) ·N(\mu_{obs}, σ_{obs}^2) \\ & = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{\sigma^2}) · \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu_{obs})^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2}) \\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{\sigma^2}-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\mu_{obs})^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2·(x-\mu)^2+\sigma^2·(x-\mu_{obs})^2}{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2)·x^2-2(\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs})·x+\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{x^2-2\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}·x+\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})\\ &= \frac{1}{2\pi\sigma\sigma_{obs}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})·exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}-(\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})\\ &= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\frac{\sigma\sigma_{obs}}{\sqrt{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}}}exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{(x-\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})·\frac{exp(-\frac{1}{2}\frac{\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu^2+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}-(\frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2})^2}{\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}})}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sqrt{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}}\\ \end{align*}
P(dfuse)=N(μ,σ2)⋅N(μobs,σobs2)=2πσ1exp(−21σ2(x−μ)2)⋅2πσobs1exp(−21σobs2(x−μobs)2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σ2(x−μ)2−21σobs2(x−μobs)2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σ2σobs2σobs2⋅(x−μ)2+σ2⋅(x−μobs)2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σ2σobs2(σobs2+σ2)⋅x2−2(σobs2μ+σ2μobs)⋅x+σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2x2−2σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs⋅x+σobs2+σ2σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2)=2πσσobs1exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2(x−σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)⋅exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2σobs2+σ2σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2−(σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)=2πσobs2+σ2σσobs1exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2(x−σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)⋅2πσobs2+σ2exp(−21σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2σobs2+σ2σobs2μ2+σ2μobs2−(σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs)2)
显然,前面部分符合高斯分布
N
(
μ
f
u
s
e
,
σ
f
u
s
e
2
)
N(\mu_{fuse}, σ_{fuse}^2)
N(μfuse,σfuse2),其中
μ
f
u
s
e
=
σ
o
b
s
2
μ
+
σ
2
μ
o
b
s
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
,
,
,
σ
f
u
s
e
2
=
σ
2
σ
o
b
s
2
σ
o
b
s
2
+
σ
2
\mu_{fuse} = \frac{\sigma_{obs}^2\mu+\sigma^2\mu_{obs}}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}, ,, σ_{fuse}^2=\frac{\sigma^2\sigma_{obs}^2}{\sigma_{obs}^2+\sigma^2}
μfuse=σobs2+σ2σobs2μ+σ2μobs,,,σfuse2=σobs2+σ2σ2σobs2
后面部分为 常数,不影响其高斯分布类型
关于这个常数的补充说明如下,供参考
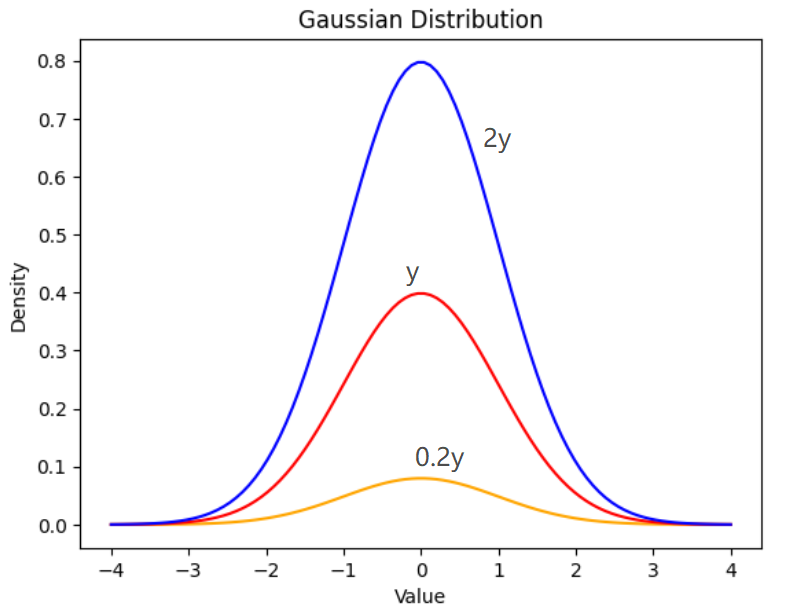
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 绘制高斯分布曲线
x = np.linspace(-4, 4, 100)
y = gaussian.pdf(x)
plt.plot(x, 0.2*y, 'orange')
plt.plot(x, y, 'r')
plt.plot(x, 2*y, 'b')
plt.xlabel('Value')
plt.ylabel('Density')
plt.title('Gaussian Distribution')
plt.show()
正态分布的数学期望值或期望值
μ
μ
μ 等于位置参数,决定了分布的位置;其方差
σ
2
\sigma ^{2}
σ2 等于尺度参数,决定了分布的幅度。
#*********************************解题1结束
√ 题2
半稠密深度估计,先把梯度明显的地方筛选出来。


数据集下载链接: https://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch/datasets/remode_test_data.zip
在 update 函数部分添加梯度比较和筛选代码。

#*********************************解题2开始
建 空白文件
touch CMakeLists.txt
touch semi_dense_mapping.cpp
复制相应的代码
报错:
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch12/dense_mono/dense_mapping.cpp:12:15: error: ‘Sophus::SE3d’ has not been declared
12 | using Sophus::SE3d;
解决办法链接
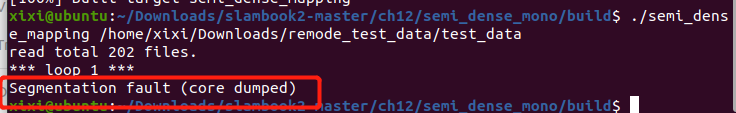
报错原因:没将 update函数的类型改为 void
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./semi_dense_mapping /home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch12/semi_dense_mono/dataset/test_data
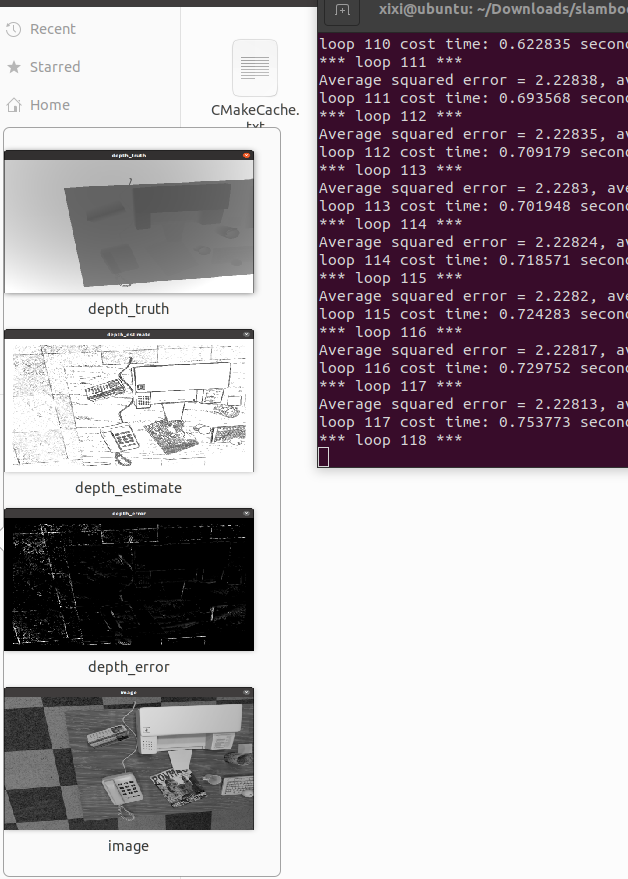
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(semi_dense_monocular)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -march=native -O3")
############### dependencies ######################
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV 4 REQUIRED) ## OpenCV是4.8.0 .cpp文件需要修改
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Sophus
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
set(THIRD_PARTY_LIBS
${OpenCV_LIBS}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(semi_dense_mapping semi_dense_mapping.cpp)
target_link_libraries(semi_dense_mapping ${THIRD_PARTY_LIBS})
semi_dense_mapping.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
// for sophus
#include <sophus/se3.h> // 修改
using Sophus::SE3; // 修改 本代码里的 SE3d 的 d 都要去掉
// for eigen
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
using namespace Eigen;
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
/**********************************************
* 本程序演示了单目相机在已知轨迹下的稠密深度估计
* 使用极线搜索 + NCC 匹配的方式,与书本的 12.2 节对应
* 请注意本程序并不完美,你完全可以改进它——我其实在故意暴露一些问题(这是借口)。
***********************************************/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// parameters
const int boarder = 20; // 边缘宽度
const int width = 640; // 图像宽度
const int height = 480; // 图像高度
const double fx = 481.2f; // 相机内参
const double fy = -480.0f;
const double cx = 319.5f;
const double cy = 239.5f;
const int ncc_window_size = 3; // NCC 取的窗口半宽度
const int ncc_area = (2 * ncc_window_size + 1) * (2 * ncc_window_size + 1); // NCC窗口面积
const double min_cov = 0.1; // 收敛判定:最小方差
const double max_cov = 10; // 发散判定:最大方差
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 重要的函数
/// 从 REMODE 数据集读取数据
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string &path,
vector<string> &color_image_files,
vector<SE3> &poses,
cv::Mat &ref_depth
);
/**
* 根据新的图像更新深度估计
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param T_C_R 参考图像到当前图像的位姿
* @param depth 深度
* @param depth_cov 深度方差
* @return 是否成功
*/
void update(
const Mat &ref,
const Mat &curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
Mat &depth,
Mat &depth_cov2
);
/**
* 极线搜索
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param T_C_R 位姿
* @param pt_ref 参考图像中点的位置
* @param depth_mu 深度均值
* @param depth_cov 深度方差
* @param pt_curr 当前点
* @param epipolar_direction 极线方向
* @return 是否成功
*/
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat &ref,
const Mat &curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const double &depth_mu,
const double &depth_cov,
Vector2d &pt_curr,
Vector2d &epipolar_direction
);
/**
* 更新深度滤波器
* @param pt_ref 参考图像点
* @param pt_curr 当前图像点
* @param T_C_R 位姿
* @param epipolar_direction 极线方向
* @param depth 深度均值
* @param depth_cov2 深度方向
* @return 是否成功
*/
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const Vector2d &pt_curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
const Vector2d &epipolar_direction,
Mat &depth,
Mat &depth_cov2
);
/**
* 计算 NCC 评分
* @param ref 参考图像
* @param curr 当前图像
* @param pt_ref 参考点
* @param pt_curr 当前点
* @return NCC评分
*/
double NCC(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &pt_ref, const Vector2d &pt_curr);
// 双线性灰度插值
inline double getBilinearInterpolatedValue(const Mat &img, const Vector2d &pt) {
uchar *d = &img.data[int(pt(1, 0)) * img.step + int(pt(0, 0))];
double xx = pt(0, 0) - floor(pt(0, 0));
double yy = pt(1, 0) - floor(pt(1, 0));
return ((1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * double(d[0]) +
xx * (1 - yy) * double(d[1]) +
(1 - xx) * yy * double(d[img.step]) +
xx * yy * double(d[img.step + 1])) / 255.0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 一些小工具
// 显示估计的深度图
void plotDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate);
// 像素到相机坐标系
inline Vector3d px2cam(const Vector2d px) {
return Vector3d(
(px(0, 0) - cx) / fx,
(px(1, 0) - cy) / fy,
1
);
}
// 相机坐标系到像素
inline Vector2d cam2px(const Vector3d p_cam) {
return Vector2d(
p_cam(0, 0) * fx / p_cam(2, 0) + cx,
p_cam(1, 0) * fy / p_cam(2, 0) + cy
);
}
// 检测一个点是否在图像边框内
inline bool inside(const Vector2d &pt) {
return pt(0, 0) >= boarder && pt(1, 0) >= boarder
&& pt(0, 0) + boarder < width && pt(1, 0) + boarder <= height;
}
// 显示极线匹配
void showEpipolarMatch(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_curr);
// 显示极线
void showEpipolarLine(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_min_curr,
const Vector2d &px_max_curr);
/// 评测深度估计
void evaludateDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate);
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "Usage: dense_mapping path_to_test_dataset" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 从数据集读取数据
vector<string> color_image_files;
vector<SE3> poses_TWC;
Mat ref_depth;
bool ret = readDatasetFiles(argv[1], color_image_files, poses_TWC, ref_depth);
if (ret == false) {
cout << "Reading image files failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "read total " << color_image_files.size() << " files." << endl;
// 第一张图
Mat ref = imread(color_image_files[0], 0); // gray-scale image
SE3 pose_ref_TWC = poses_TWC[0];
double init_depth = 3.0; // 深度初始值
double init_cov2 = 3.0; // 方差初始值
Mat depth(height, width, CV_64F, init_depth); // 深度图
Mat depth_cov2(height, width, CV_64F, init_cov2); // 深度图方差
for (int index = 1; index < color_image_files.size(); index++) {
cout << "*** loop " << index << " ***" << endl;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
Mat curr = imread(color_image_files[index], 0);
if (curr.data == nullptr) continue;
SE3 pose_curr_TWC = poses_TWC[index];
SE3 pose_T_C_R = pose_curr_TWC.inverse() * pose_ref_TWC; // 坐标转换关系: T_C_W * T_W_R = T_C_R
update(ref, curr, pose_T_C_R, depth, depth_cov2);
evaludateDepth(ref_depth, depth);
plotDepth(ref_depth, depth);
imshow("image", curr);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "loop " << index << " cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
waitKey(1);
}
cout << "estimation returns, saving depth map ..." << endl;
imwrite("depth.png", depth);
cout << "done." << endl;
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string &path,
vector<string> &color_image_files,
std::vector<SE3> &poses,
cv::Mat &ref_depth) {
ifstream fin(path + "/first_200_frames_traj_over_table_input_sequence.txt");
if (!fin) return false;
while (!fin.eof()) {
// 数据格式:图像文件名 tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw ,注意是 TWC 而非 TCW
string image;
fin >> image;
double data[7];
for (double &d:data) fin >> d;
color_image_files.push_back(path + string("/images/") + image);
poses.push_back(
SE3(Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]))
);
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
fin.close();
// load reference depth
fin.open(path + "/depthmaps/scene_000.depth");
ref_depth = cv::Mat(height, width, CV_64F);
if (!fin) return false;
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
double depth = 0;
fin >> depth;
ref_depth.ptr<double>(y)[x] = depth / 100.0;
}
return true;
}
// 对整个深度图进行更新
void update(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const SE3 &T_C_R, Mat &depth, Mat &depth_cov2) {
for (int x = boarder; x < width - boarder; x++)
for (int y = boarder; y < height - boarder; y++) {
// 挑选梯度较高的点进行极线搜索
// 先对原始图像进行处理,通过相邻两个像素之间的差分来近似当前像素的梯度值
Vector2d gradient(ref.ptr<uchar>(y)[x + 1] - ref.ptr<uchar>(y)[x - 1],
ref.ptr<uchar>(y + 1)[x] - ref.ptr<uchar>(y - 1)[x]);
// 通过norm函数评估梯度的大小,这里阈值设置为25,若小于25,证明梯度不明显,此时不考虑该点
if (gradient.norm() < 25)
continue;
// 下面是原来的程序
// 遍历每个像素
if (depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x] > max_cov) // 深度已收敛或发散
continue;
// 在极线上搜索 (x,y) 的匹配
Vector2d pt_curr;
Vector2d epipolar_direction;
bool ret = epipolarSearch(
ref,
curr,
T_C_R,
Vector2d(x, y),
depth.ptr<double>(y)[x],
sqrt(depth_cov2.ptr<double>(y)[x]),
pt_curr,
epipolar_direction
);
if (ret == false) // 匹配失败
continue;
// 取消该注释以显示匹配
// showEpipolarMatch(ref, curr, Vector2d(x, y), pt_curr);
// 匹配成功,更新深度图
updateDepthFilter(Vector2d(x, y), pt_curr, T_C_R, epipolar_direction, depth, depth_cov2);
}
}
// 极线搜索
// 方法见书 12.2 12.3 两节
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R, const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const double &depth_mu, const double &depth_cov,
Vector2d &pt_curr, Vector2d &epipolar_direction) {
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam(pt_ref);
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d P_ref = f_ref * depth_mu; // 参考帧的 P 向量
Vector2d px_mean_curr = cam2px(T_C_R * P_ref); // 按深度均值投影的像素
double d_min = depth_mu - 3 * depth_cov, d_max = depth_mu + 3 * depth_cov;
if (d_min < 0.1) d_min = 0.1;
Vector2d px_min_curr = cam2px(T_C_R * (f_ref * d_min)); // 按最小深度投影的像素
Vector2d px_max_curr = cam2px(T_C_R * (f_ref * d_max)); // 按最大深度投影的像素
Vector2d epipolar_line = px_max_curr - px_min_curr; // 极线(线段形式)
epipolar_direction = epipolar_line; // 极线方向
epipolar_direction.normalize();
double half_length = 0.5 * epipolar_line.norm(); // 极线线段的半长度
if (half_length > 100) half_length = 100; // 我们不希望搜索太多东西
// 取消此句注释以显示极线(线段)
// showEpipolarLine( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_min_curr, px_max_curr );
// 在极线上搜索,以深度均值点为中心,左右各取半长度
double best_ncc = -1.0;
Vector2d best_px_curr;
for (double l = -half_length; l <= half_length; l += 0.7) { // l+=sqrt(2)
Vector2d px_curr = px_mean_curr + l * epipolar_direction; // 待匹配点
if (!inside(px_curr))
continue;
// 计算待匹配点与参考帧的 NCC
double ncc = NCC(ref, curr, pt_ref, px_curr);
if (ncc > best_ncc) {
best_ncc = ncc;
best_px_curr = px_curr;
}
}
if (best_ncc < 0.85f) // 只相信 NCC 很高的匹配
return false;
pt_curr = best_px_curr;
return true;
}
double NCC(
const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr,
const Vector2d &pt_ref, const Vector2d &pt_curr) {
// 零均值-归一化互相关
// 先算均值
double mean_ref = 0, mean_curr = 0;
vector<double> values_ref, values_curr; // 参考帧和当前帧的均值
for (int x = -ncc_window_size; x <= ncc_window_size; x++)
for (int y = -ncc_window_size; y <= ncc_window_size; y++) {
double value_ref = double(ref.ptr<uchar>(int(y + pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(x + pt_ref(0, 0))]) / 255.0;
mean_ref += value_ref;
double value_curr = getBilinearInterpolatedValue(curr, pt_curr + Vector2d(x, y));
mean_curr += value_curr;
values_ref.push_back(value_ref);
values_curr.push_back(value_curr);
}
mean_ref /= ncc_area;
mean_curr /= ncc_area;
// 计算 Zero mean NCC
double numerator = 0, demoniator1 = 0, demoniator2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < values_ref.size(); i++) {
double n = (values_ref[i] - mean_ref) * (values_curr[i] - mean_curr);
numerator += n;
demoniator1 += (values_ref[i] - mean_ref) * (values_ref[i] - mean_ref);
demoniator2 += (values_curr[i] - mean_curr) * (values_curr[i] - mean_curr);
}
return numerator / sqrt(demoniator1 * demoniator2 + 1e-10); // 防止分母出现零
}
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d &pt_ref,
const Vector2d &pt_curr,
const SE3 &T_C_R,
const Vector2d &epipolar_direction,
Mat &depth,
Mat &depth_cov2) {
// 不知道这段还有没有人看
// 用三角化计算深度
SE3 T_R_C = T_C_R.inverse();
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam(pt_ref);
f_ref.normalize();
Vector3d f_curr = px2cam(pt_curr);
f_curr.normalize();
// 方程
// d_ref * f_ref = d_cur * ( R_RC * f_cur ) + t_RC
// f2 = R_RC * f_cur
// 转化成下面这个矩阵方程组
// => [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f2 ] [d_ref] [f_ref^T t]
// [ f_2^T f_ref, -f2^T f2 ] [d_cur] = [f2^T t ]
Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation();
Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.so3() * f_curr;
Vector2d b = Vector2d(t.dot(f_ref), t.dot(f2));
Matrix2d A;
A(0, 0) = f_ref.dot(f_ref);
A(0, 1) = -f_ref.dot(f2);
A(1, 0) = -A(0, 1);
A(1, 1) = -f2.dot(f2);
Vector2d ans = A.inverse() * b;
Vector3d xm = ans[0] * f_ref; // ref 侧的结果
Vector3d xn = t + ans[1] * f2; // cur 结果
Vector3d p_esti = (xm + xn) / 2.0; // P的位置,取两者的平均
double depth_estimation = p_esti.norm(); // 深度值
// 计算不确定性(以一个像素为误差)
Vector3d p = f_ref * depth_estimation;
Vector3d a = p - t;
double t_norm = t.norm();
double a_norm = a.norm();
double alpha = acos(f_ref.dot(t) / t_norm);
double beta = acos(-a.dot(t) / (a_norm * t_norm));
Vector3d f_curr_prime = px2cam(pt_curr + epipolar_direction);
f_curr_prime.normalize();
double beta_prime = acos(f_curr_prime.dot(-t) / t_norm);
double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime;
double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma);
double d_cov = p_prime - depth_estimation;
double d_cov2 = d_cov * d_cov;
// 高斯融合
double mu = depth.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))];
double sigma2 = depth_cov2.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))];
double mu_fuse = (d_cov2 * mu + sigma2 * depth_estimation) / (sigma2 + d_cov2);
double sigma_fuse2 = (sigma2 * d_cov2) / (sigma2 + d_cov2);
depth.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))] = mu_fuse;
depth_cov2.ptr<double>(int(pt_ref(1, 0)))[int(pt_ref(0, 0))] = sigma_fuse2;
return true;
}
// 后面这些太简单我就不注释了(其实是因为懒)
void plotDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate) {
imshow("depth_truth", depth_truth * 0.4);
imshow("depth_estimate", depth_estimate * 0.4);
imshow("depth_error", depth_truth - depth_estimate);
waitKey(1);
}
void evaludateDepth(const Mat &depth_truth, const Mat &depth_estimate) {
double ave_depth_error = 0; // 平均误差
double ave_depth_error_sq = 0; // 平方误差
int cnt_depth_data = 0;
for (int y = boarder; y < depth_truth.rows - boarder; y++)
for (int x = boarder; x < depth_truth.cols - boarder; x++) {
double error = depth_truth.ptr<double>(y)[x] - depth_estimate.ptr<double>(y)[x];
ave_depth_error += error;
ave_depth_error_sq += error * error;
cnt_depth_data++;
}
ave_depth_error /= cnt_depth_data;
ave_depth_error_sq /= cnt_depth_data;
cout << "Average squared error = " << ave_depth_error_sq << ", average error: " << ave_depth_error << endl;
}
void showEpipolarMatch(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_curr) {
Mat ref_show, curr_show;
cv::cvtColor(ref, ref_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(curr, curr_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::circle(ref_show, cv::Point2f(px_ref(0, 0), px_ref(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 250), 2);
cv::circle(curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_curr(0, 0), px_curr(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 250), 2);
imshow("ref", ref_show);
imshow("curr", curr_show);
waitKey(1);
}
void showEpipolarLine(const Mat &ref, const Mat &curr, const Vector2d &px_ref, const Vector2d &px_min_curr,
const Vector2d &px_max_curr) {
Mat ref_show, curr_show;
cv::cvtColor(ref, ref_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(curr, curr_show, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
cv::circle(ref_show, cv::Point2f(px_ref(0, 0), px_ref(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
cv::circle(curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_min_curr(0, 0), px_min_curr(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
cv::circle(curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_max_curr(0, 0), px_max_curr(1, 0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
cv::line(curr_show, Point2f(px_min_curr(0, 0), px_min_curr(1, 0)), Point2f(px_max_curr(0, 0), px_max_curr(1, 0)),
Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
imshow("ref", ref_show);
imshow("curr", curr_show);
waitKey(1);
}
#*********************************解题2结束
题3
3、单目稠密重建从正深度 改成 逆深度,并添加仿射变换。
仿射变换用于 块匹配前,进一步考虑了相机发生运动的情形(当前帧和参考帧之间发行运动了),以期可以取得更好的 匹配效果。
实际的深度分布: 尾部稍长,负数区域为0 逆深度


ORB_SLAM2
题4
4、论证如何在八叉树中进行导航和路径规划
navigation based on octomap
导航:如何从地图中A点到B点。
- 如何在地图中地位自己(localization)
- 如何从 A 到 B 规划一条路径(planning), path planning 有global和local之分,同时都需要。global path planning有dijkstra,A* ,D*等算法。local path planning 有自适应动态窗法等。
Autonomous Navigation in Unknown Environments with Sparse Bayesian Kernel-based Occupancy Mapping
OctoMap:An Efficient Probabilistic 3D Mapping Framework Based on Octrees
找到了别的树
FAST-LIO2: Fast Direct LiDAR-inertial Odometry
题5
5、TSDF是如何进行位姿估计和更新的。
论文链接: KinectFusion: Real-Time Dense Surface Mapping and Tracking
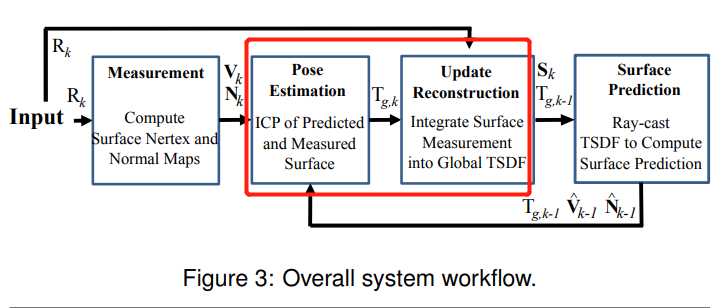

题6
6、均匀-高斯混合滤波器的原理与实现
待做:
- 用数据集 跑源码
在12.2.3 节讨论了。P311
SVO源码链接
PDF链接:https://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch/docs/ICRA14_Forster.pdf
SVO 全称 Semi-direct monocular Visual Odometry(半直接视觉里程计)
点云 深度 概率模型是 高斯+均匀分布
瑞士苏黎世大学 机器人与感知小组http://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch。
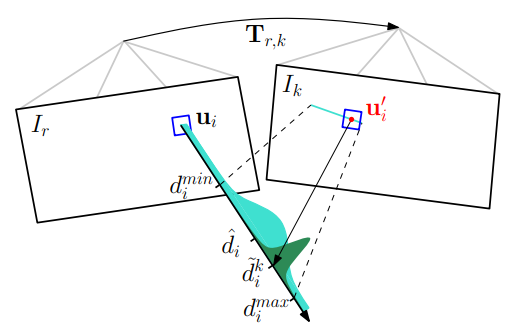

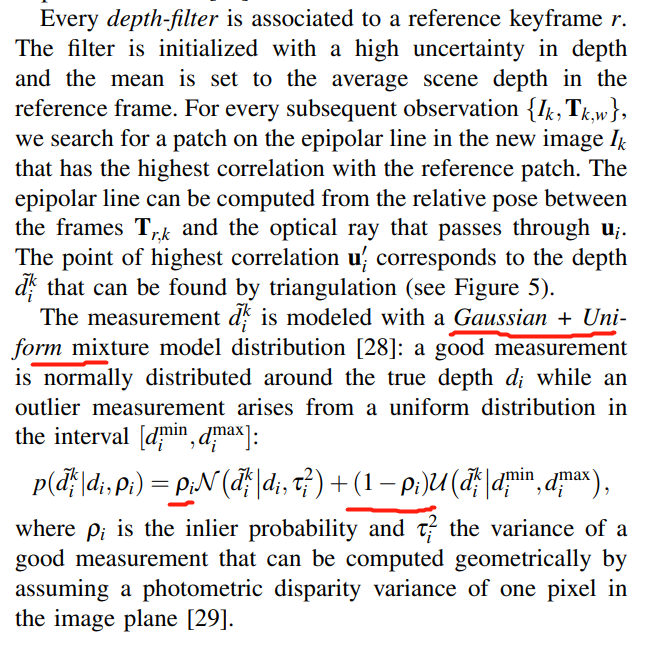
https://github.com/uzh-rpg/rpg_svo/blob/master/svo/src/depth_filter.cpp
其它:
SVO的深度滤波器使用的概率模型是《Video-based, Real-Time Multi View Stereo》中的深度概率模型,不同的是SVO中的使用的逆深度估计。
Video-based, Real-Time Multi View Stereo》pdf链接