1、二叉树基本操作
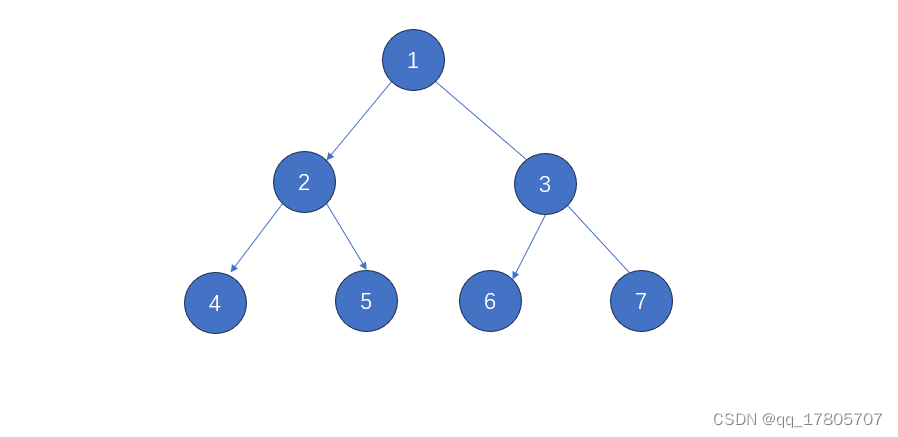
二叉树的定义就不在这里多说了,下面这个图就是一个简单的二叉树:
 二叉树的三种遍历方式:
二叉树的三种遍历方式:
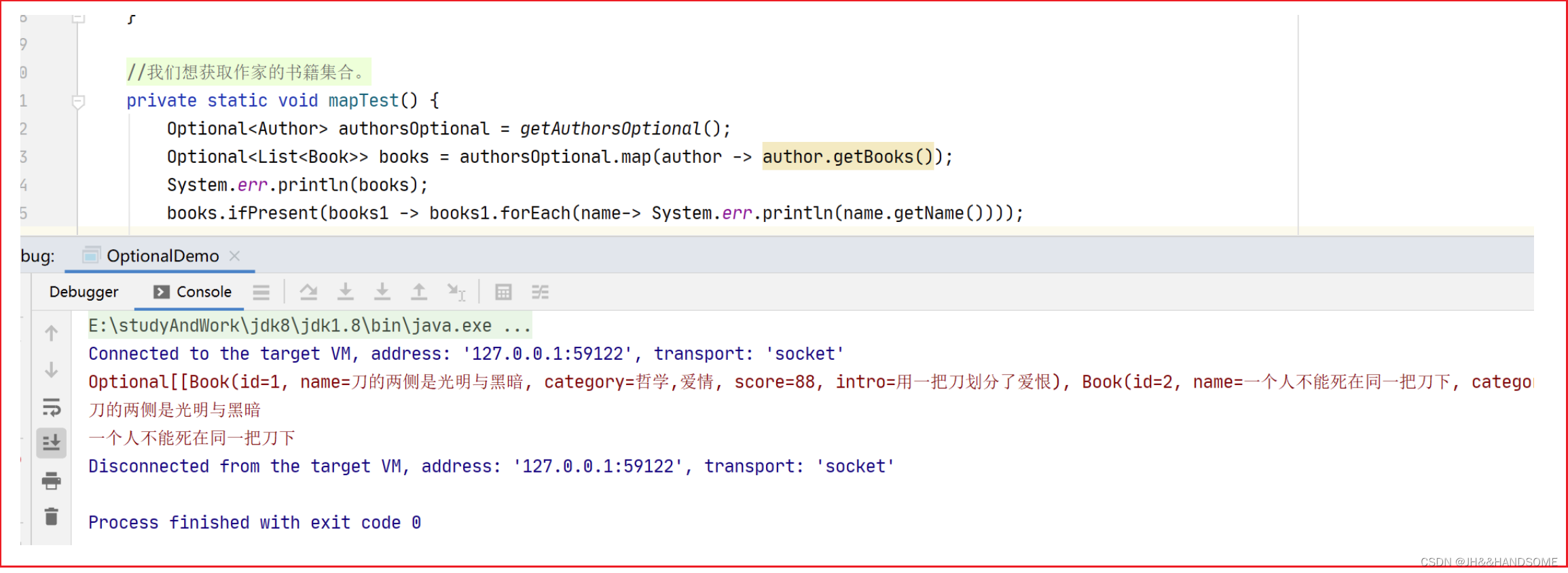
前序遍历:头左右,也就是先头后左再右:1245367
public static void prePrint(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
System.err.print(root.val);
prePrint(root.left);
prePrint(root.right);
}
}中序遍历:左头右,也就是先左后头再右:4251637
public static void midPrint(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
midPrint(root.left);
System.err.print(root.val);
midPrint(root.right);
}
}后序遍历:左头右,也就是先左后右再头:4526731
public static void posPrint(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
posPrint(root.left);
posPrint(root.right);
System.err.print(root.val);
}
}测试代码:
class BinaryTreeNode {
int val;
BinaryTreeNode left;
BinaryTreeNode right;
public BinaryTreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public BinaryTreeNode(int val, BinaryTreeNode left, BinaryTreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
} public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTreeNode one = new BinaryTreeNode(1,
new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),
new BinaryTreeNode(3, new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null)));
prePrint(one);
System.err.println();
midPrint(one);
System.err.println();
posPrint(one);
}那么我们可以看出来,不论是哪种遍历方式,其在处理左右子节点的时候,逻辑都是一样的,都是要递归处理,不同的只是头结点的输出时机,那么可以优化成下面的代码:
public static void print(BinaryTreeNode root, int type) {
switch (type) {
case 1:
if (root != null) {
System.err.print(root.val);
print(root.left, 1);
print(root.right, 1);
}
break;
case 2:
if (root != null) {
print(root.left, 2);
System.err.print(root.val);
print(root.right, 2);
}
break;
case 3:
if (root != null) {
print(root.left, 3);
print(root.right, 3);
System.err.print(root.val);
}
break;
}
}2、两棵树是否结构一样
如下面的图中,只有左上角和右上角两棵树的结构是一样的,才算符合条件:

Java实现判断两棵树是否一样:
public static boolean isSameTree(BinaryTreeNode node1, BinaryTreeNode node2) {
if (node1 == null ^ node2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {
return true;
}
return node1.val == node2.val && isSameTree(node1.left, node2.left) && isSameTree(node1.right, node2.right);
}
@Test
public void testSame() {
BinaryTreeNode one = new BinaryTreeNode(1,
new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),
new BinaryTreeNode(3, new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null)));
BinaryTreeNode two = new BinaryTreeNode(1,
new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),
new BinaryTreeNode(3, new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null)));
System.err.println(isSameTree(one, two));
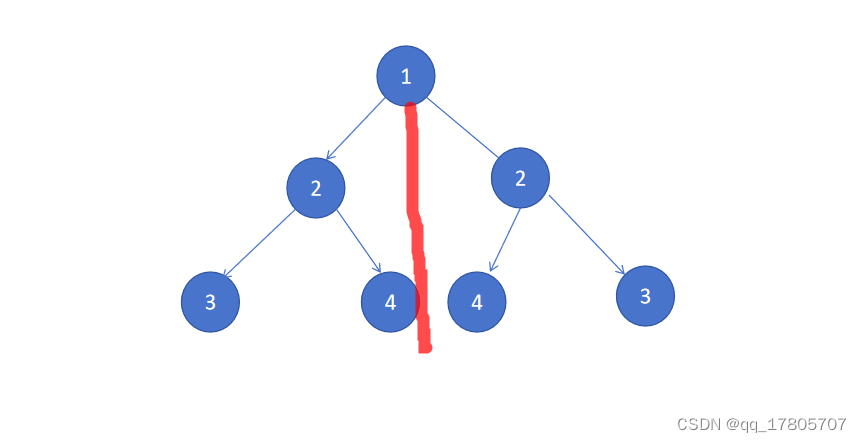
}3、镜面树
镜面树有两种情况:
- 两棵树互为镜面:按照红线对折,可以重叠

- 单棵树两边互为镜面:
 代码实现:
代码实现: public static boolean isMirror(BinaryTreeNode node1, BinaryTreeNode node2) { if (node1 == null ^ node2 == null) { return false; } if (node1 == null && node2 == null) { return true; } return node1.val == node2.val && isMirror(node1.left, node2.right) && isMirror(node1.right, node2.left); } @Test public void testMirror() { BinaryTreeNode one = new BinaryTreeNode(1, new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)), new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null))); BinaryTreeNode two = new BinaryTreeNode(1, new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)), new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null))); System.err.println(isMirror(one, two)); }
4、树的最大深度
二叉树的最大深度其实就是左子树和右子树的最大深度加一,代码实现如下:
public static int maxDepth(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
@Test
public void testMaxDepth() {
BinaryTreeNode two = new BinaryTreeNode(1,
new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),
new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null)));
System.err.println(maxDepth(two));
}




![2023年全球及中国多肽CDMO市场发展概述分析:CDMO头部企业将拓展至多肽领域[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/95111679129fb081eefe42f531fbd70c.png)