这里写目录标题
- 基于深度优先搜索的无向图遍历
- 算法流程图
- Python实现
- Java实现
- 基于深度优先搜索的有向图遍历
- Python实现
基于深度优先搜索的无向图遍历
使用深度优先搜索遍历无向图,将无向图用邻接表存储:
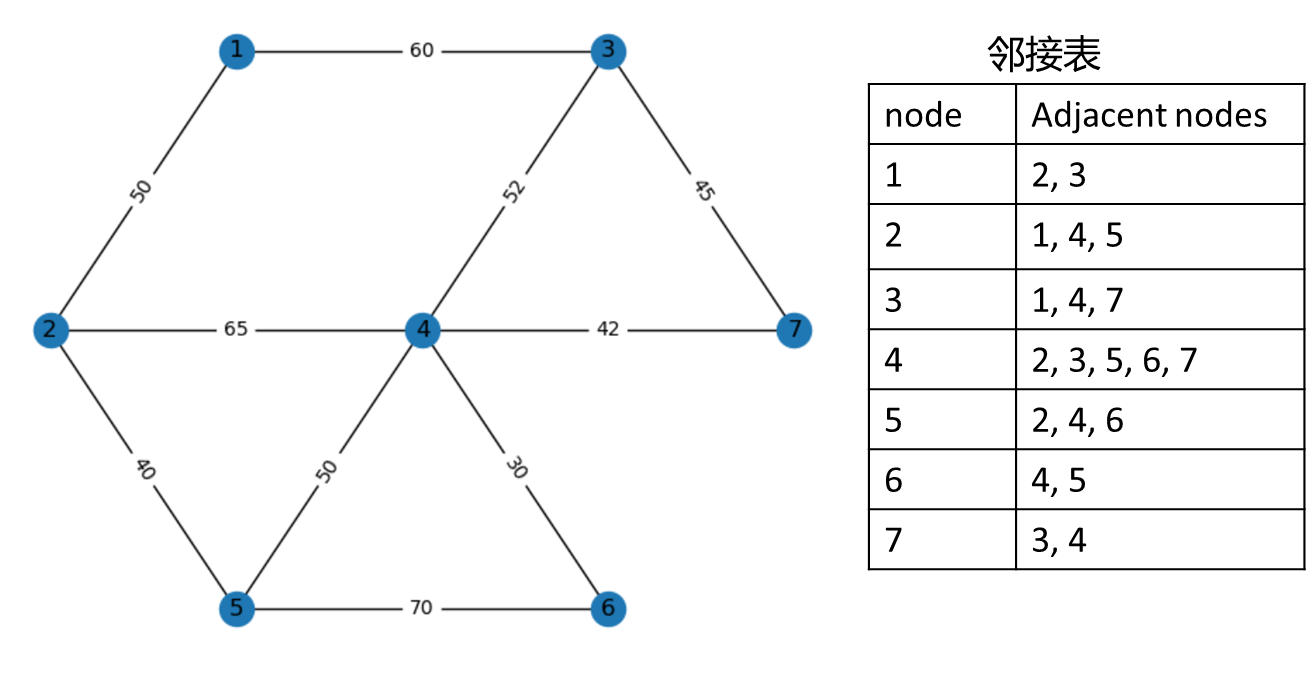
算法流程图
- 初始化起点 source,当前节点v为起点,终点 target,路径path为空,路径集合 paths 为空
- 将当前节点v添加到 path 中
- 判断当前节点v是否为终点,是转step4,否转step5
- 保存 path 至 paths 中,转step7
- 获取当前节点的所有邻接点,用集合N表示
- 遍历N,若 N_i 不在 path 中,令v=N_i ,转step2;若N_i 在path 中,i +=1。
- 删除 path 中最后一个节点,令v=path中最后一个节点,转step5
- 以上步骤遍历了所有每一个点的邻接点,算法结束,输出起点到终点的所有路径paths
Python实现
from typing import List
def dfs(adjacent_list, source, target):
"""
:param adjacent_list: 邻接表
:param source: 起点
:param target: 终点
:return: 起点-终点的所有路径
"""
def dfs_helper(adjacent_list, source, current_node, target):
path.append(current_node) # 压栈
if current_node == target:
paths.append(path.copy())
else:
neighbors = adjacent_list[current_node]
for neighbor in neighbors:
if neighbor not in path:
dfs_helper(adjacent_list, source, neighbor, target)
path.pop() # 弹栈
paths = []
path = []
dfs_helper(adjacent_list, source, source, target)
return paths
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 邻接表
adjacent_list = {
1: [2, 3],
2: [1, 4, 5],
3: [1, 4, 7],
4: [2, 3, 5, 6, 7],
5: [2, 4, 6],
6: [4, 5],
7: [3, 4]
}
# 深搜
paths: List[List] = dfs(adjacent_list, 1, 6)
[print(path) for path in paths]
Java实现
package org.example;
import java.util.*;
public class DepthFirstSearch {
// List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
void dfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> adjacent_list, int source, int current_node, int target) {
path.push(current_node);
if (current_node == target) {
paths.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
} else {
List<Integer> neighbors = adjacent_list.get(current_node);
for (Integer neighbor : neighbors) {
if (!path.contains(neighbor)) {
dfs(adjacent_list, source, neighbor, target);
}
}
path.pop();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> adjacent_list = new HashMap<>();
adjacent_list.put(1, Arrays.asList(2, 3));
adjacent_list.put(2, Arrays.asList(1, 4, 5));
adjacent_list.put(3, Arrays.asList(1, 4, 7));
adjacent_list.put(4, Arrays.asList(2, 3, 5, 6, 7));
adjacent_list.put(5, Arrays.asList(2, 4, 6));
adjacent_list.put(6, Arrays.asList(4, 5));
adjacent_list.put(7, Arrays.asList(3, 4));
System.out.println(adjacent_list);
DepthFirstSearch dfs = new DepthFirstSearch();
dfs.dfs(adjacent_list, 1, 1, 6);
for (List<Integer> path : dfs.paths) {
System.out.println(path);
}
}
}
基于深度优先搜索的有向图遍历
和无向图遍历一样,建立邻接矩阵即可。
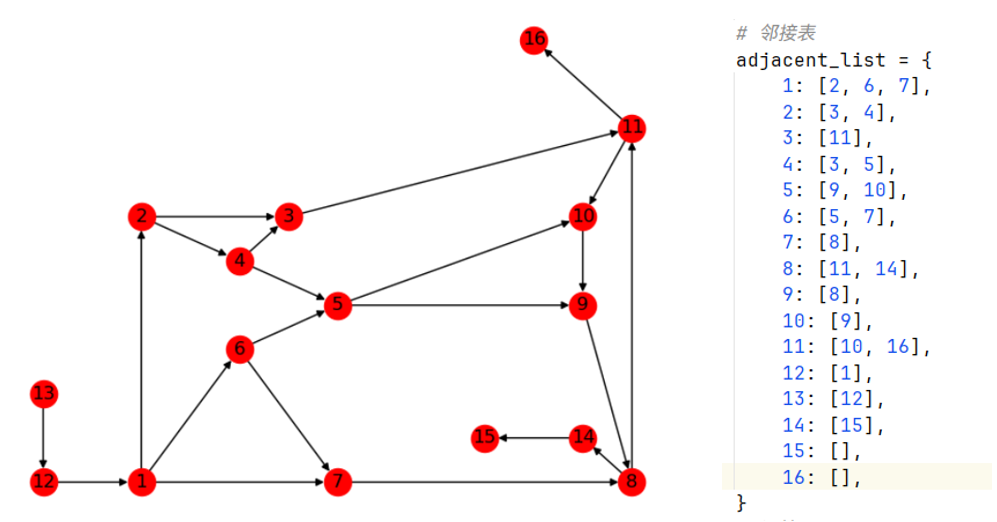
Python实现
from typing import List, Tuple, Any, Dict
import networkx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from typing import List
def paint_topological_graph(nodes,
edges: List[Tuple],
coordinates: Dict[Any, Tuple] = None,
directed=False
):
print(nodes)
print(edges)
print(coordinates)
graph = networkx.DiGraph() if directed else networkx.Graph() # 全连通 有向图
graph.add_nodes_from(nodes)
graph.add_edges_from(edges)
networkx.draw(graph, pos=coordinates, with_labels=True, node_color='red', )
plt.show()
print(networkx.has_path(graph, 1, 12))
return graph
def dfs(adjacent_list, source, target):
"""
:param adjacent_list: 邻接表
:param source: 起点
:param target: 终点
:return: 起点-终点的所有路径
"""
def dfs_helper(adjacent_list, source, current_node, target):
path.append(current_node)
if current_node == target:
paths.append(path.copy())
path.pop()
else:
neighbors = adjacent_list[current_node]
for neighbor in neighbors:
if neighbor not in path:
dfs_helper(adjacent_list, source, neighbor, target)
path.pop()
paths = []
path = []
dfs_helper(adjacent_list, source, source, target)
return paths
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 点坐标
node_coord = {
1: (1, 0), 2: (1, 3), 3: (2.5, 3), 4: (2, 2.5), 5: (3, 2), 6: (2, 1.5), 7: (3, 0), 8: (6, 0), 9: (5.5, 2),
10: (5.5, 3), 11: (6, 4), 12: (0, 0), 13: (0, 1), 14: (5.5, 0.5), 15: (4.5, 0.5), 16: (5, 5),
}
edges = [
(13, 12), (1, 2), (2, 4), (2, 3), (4, 3), (4, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (6, 7), (6, 5), (7, 8), (5, 9), (5, 10),
(3, 11), (11, 10), (9, 8), (10, 9), (8, 11), (14, 15), (8, 14), (12, 1), (11, 16),
]
# 画图
paint_topological_graph(nodes=np.arange(1, 17, 1),
edges=edges,
directed=True,
coordinates=node_coord
)
# 邻接表
adjacent_list = {
1: [2, 6, 7],
2: [3, 4],
3: [11],
4: [3, 5],
5: [9, 10],
6: [5, 7],
7: [8],
8: [11, 14],
9: [8],
10: [9],
11: [10, 16],
12: [1],
13: [12],
14: [15],
15: [],
16: [],
}
# 深搜
paths: List[List] = dfs(adjacent_list, 1, 11)
[print(path) for path in paths]