本文分享 MonoDLE 的模型训练、模型推理、可视化3D检测结果。
模型原理,参考我这篇博客:【论文解读】单目3D目标检测 MonoDLE(CVPR2021)_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
源码地址:https://github.com/xinzhuma/monodle

目录
一、环境搭建
二、准备数据集
三、训练模型
四、模型推理
4.1 使用刚才训练的权重推理
4.2 使用预训练权重推理
五、可视化3D检测结果
一、环境搭建
1.1 需要用到Conda来搭建环境,首先创建一个MonoCon环境;
conda create --name MonoDLE python=3.8
conda activate MonoDLE
1.2 下载代码到本地;
git clone https://github.com/xinzhuma/monodle
cd monocon-pytorch-main
1.3 安装pytorch和对应CUDA,这里以为示例;
conda install pytorch==1.12.0 torchvision==0.13.0 torchaudio==0.12.0 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
其他版本安装,或使用pip安装的,参考pytorch官网:Previous PyTorch Versions | PyTorch
1.4 安装MonoCon的依赖库;
cd monodle-main
pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
在 pip 命令中使用 -i 参数来指定清华镜像地址,加速安装。
二、准备数据集
官网链接:The KITTI Vision Benchmark Suite
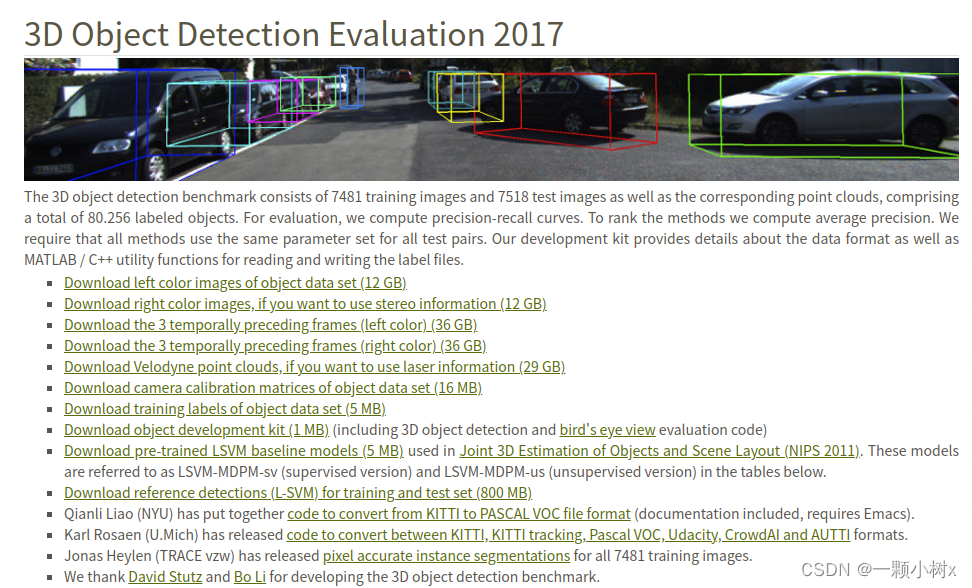
需要下载的文件:
- Download left color images of object data set (12 GB) 这是图片,包括训练集和测试集
- Download camera calibration matrices of object data set (16 MB) 这是相机的标定相关的文件
- Download training labels of object data set (5 MB) 这是图片训练集对应的标签
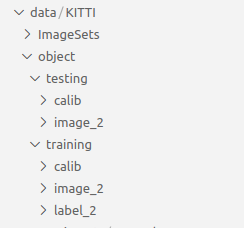
下载后的文件放在dataset目录中,存放的目录结构:
data/KITTI/object
│
├── training
│ ├── calib
│ │ ├── 000000.txt
│ │ ├── 000001.txt
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── image_2
│ │ ├── 000000.png
│ │ ├── 000001.png
│ │ └── ...
│ └── label_2
│ ├── 000000.txt
│ ├── 000001.txt
│ └── ...
│
└── testing
├── calib
└── image_2
存放好数据集后,目录结构如下所示:
三、训练模型
训练模型的配置在experiments/example/kitti_example.yaml:
-
batch_size: 16 ,可以根据显存大小调整,默认是16
-
writelist: ['Car'] , 这里是训练那些类别;默认只有Car一种;如果是3种类别:writelist: ['Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist']
-
数据增强,random_flip、random_crop、scale、shif
-
max_epoch: 140,最大训练轮数
-
gpu_ids: 0,1,使用那些GPU训练;如果只有一张显卡:gpu_ids: 0,0
-
save_frequency: 5=10,间隔多少轮,保存模型权重,默认是10轮保存一次
示例代码如下
random_seed: 444
dataset:
type: &dataset_type 'KITTI'
batch_size: 8 # 16
use_3d_center: True
class_merging: False
use_dontcare: False
bbox2d_type: 'anno' # 'proj' or 'anno'
meanshape: False # use predefined anchor or not
writelist: ['Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist']
random_flip: 0.5
random_crop: 0.5
scale: 0.4
shift: 0.1
model:
type: 'centernet3d'
backbone: 'dla34'
neck: 'DLAUp'
num_class: 3
optimizer:
type: 'adam'
lr: 0.00125
weight_decay: 0.00001
lr_scheduler:
warmup: True # 5 epoches, cosine warmup, init_lir=0.00001 in default
decay_rate: 0.1
decay_list: [90, 120]
trainer:
max_epoch: 140
gpu_ids: 0,0 # 0,1
save_frequency: 5 # checkpoint save interval (in epoch) 10
# resume_model: 'checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_70.pth'
tester:
type: *dataset_type
mode: single # 'single' or 'all'
checkpoint: '../../checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_5.pth' # for 'single' mode
checkpoints_dir: '../../checkpoints' # for 'all' model
threshold: 0.2 # confidence filter然后执行命令 ,开始训练。
cd experiments/example
python ../../tools/train_val.py --config kitti_example.yaml训练会打印一些信息
(MonoDLE) root@8677bec7ab74:/guopu/monodle-main/experiments/example# python ../../tools/train_val.py --config kitti_example.yaml
2023-10-15 13:14:09,144 INFO ################### Training ##################
2023-10-15 13:14:09,146 INFO Batch Size: 8
2023-10-15 13:14:09,146 INFO Learning Rate: 0.001250epochs: 8%|█████████▌ | 11/140 [1:23:27<16:47:33, 468.63s/it]
.......
训练中会有模型的验证结果,和保存模型权重
权重:experiments/example/checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_5.pth
experiments/example/checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_10.pth
experiments/example/checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_15.pth
......
experiments/example/checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_140.pth
日志信息:experiments/example/train.log.20231015_144054
四、模型推理
4.1 使用刚才训练的权重推理
首先修改配置文件experiments/example/kitti_example.yaml
tester:
type: *dataset_type
mode: single # 'single' or 'all'
checkpoint: './checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_50.pth' # for 'single' mode
checkpoints_dir: '../../checkpoints' # for 'all' model
threshold: 0.2 # confidence filter
然后执行命令,模型推理示例:
python ../../tools/train_val.py --config kitti_example.yaml --e4.2 使用预训练权重推理
首先下载预训练权重:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jaGdvu_XFn5woX0eJ5I2R6wIcBLVMJV6/view
下载好的权重名称为:checkpoint_epoch_140.pth,新建一个文件夹monocon-pytorch-main/checkpoints/,存放权重
然后修改配置文件experiments/example/kitti_example.yaml
tester:
type: *dataset_type
mode: single # 'single' or 'all'
checkpoint: '../../checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_140.pth' # for 'single' mode
checkpoints_dir: '../../checkpoints' # for 'all' model
threshold: 0.2 # confidence filter
最后执行命令,模型推理示例:
python ../../tools/train_val.py --config kitti_example.yaml --e会打印信息:
(MonoDLE) root@8677bec7ab74:/guopu/monodle-main/experiments/example# python ../../tools/train_val.py --config kitti_example.yaml --e
2023-10-15 14:12:24,658 INFO ################### Evaluation Only ##################
2023-10-15 14:12:24,658 INFO ==> Loading from checkpoint '../../checkpoints/checkpoint_epoch_140.pth'
2023-10-15 14:12:27,092 INFO ==> Done
Evaluation Progress: 100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 472/472 [03:26<00:00, 2.29it/s]
2023-10-15 14:15:54,147 INFO ==> Saving ...
2023-10-15 14:15:54,649 INFO ==> Loading detections and GTs...
2023-10-15 14:15:55,746 INFO ==> Evaluating (official) ........
2023-10-15 14:16:25,506 INFO Car AP@0.70, 0.70, 0.70:
bbox AP:90.1217, 88.3670, 79.8853
bev AP:31.2712, 24.7619, 23.4836
3d AP:23.7493, 20.7087, 17.9959
aos AP:89.09, 87.18, 78.04
Car AP_R40@0.70, 0.70, 0.70:
bbox AP:95.9642, 91.8784, 84.7531
bev AP:25.8910, 20.8330, 18.1531
3d AP:18.2593, 14.5657, 12.9989
aos AP:94.80, 90.55, 82.54
Car AP@0.70, 0.50, 0.50:
bbox AP:90.1217, 88.3670, 79.8853
bev AP:61.6387, 50.2435, 44.7139
3d AP:57.7730, 44.3736, 42.4333
aos AP:89.09, 87.18, 78.04
Car AP_R40@0.70, 0.50, 0.50:
bbox AP:95.9642, 91.8784, 84.7531
bev AP:61.4324, 47.3653, 41.9808
3d AP:56.0393, 42.8401, 38.6675
aos AP:94.80, 90.55, 82.54
.....
推理完成后,结果存放在experiments/example/outputs/data
五、可视化3D检测结果
由于开源代码,没有可视化推理结果,首先观察 experiments/example/outputs/data 目录的txt文件,以为000002.txt例
Car 0.0 0 1.28 661.70 192.01 701.36 225.01 1.54 1.61 3.64 2.93 2.22 30.01 1.38 0.05
其实生成的结果,和kitii标签格式是一致的。
然后准备kitti的val集 相机标定参数,和图片。这里新建一个vis目录,用于可视化3D检测结果。
在vis目录包括:
dataset 存放相机标定数据、图片、推理结果
save_3d_output 存放可视化图片
kitti_3d_vis.py 可视化运行此代码
kitti_util.py 依赖代码
主代码 kitti_3d_vis.py
# kitti_3d_vis.py
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import sys
import cv2
import random
import os.path
import shutil
from PIL import Image
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'mayavi'))
from kitti_util import *
def visualization():
import mayavi.mlab as mlab
dataset = kitti_object(r'./dataset/')
path = r'./dataset/testing/label_2/'
Save_Path = r'./save_3d_output/'
files = os.listdir(path)
for file in files:
name = file.split('.')[0]
save_path = Save_Path + name + '.png'
data_idx = int(name)
# Load data from dataset
objects = dataset.get_label_objects(data_idx)
img = dataset.get_image(data_idx)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
calib = dataset.get_calibration(data_idx)
print(' ------------ save image with 3D bounding box ------- ')
print('name:', name)
show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, save_path, True)
if __name__=='__main__':
visualization()依赖代码 kitti_util.py
# kitti_util.py
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = os.path.dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'mayavi'))
class kitti_object(object):
def __init__(self, root_dir, split='testing'):
self.root_dir = root_dir
self.split = split
self.split_dir = os.path.join(root_dir, split)
if split == 'training':
self.num_samples = 7481
elif split == 'testing':
self.num_samples = 7518
else:
print('Unknown split: %s' % (split))
exit(-1)
self.image_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'image_2')
self.calib_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'calib')
self.label_dir = os.path.join(self.split_dir, 'label_2')
def __len__(self):
return self.num_samples
def get_image(self, idx):
assert(idx<self.num_samples)
img_filename = os.path.join(self.image_dir, '%06d.png'%(idx))
return load_image(img_filename)
def get_calibration(self, idx):
assert(idx<self.num_samples)
calib_filename = os.path.join(self.calib_dir, '%06d.txt'%(idx))
return Calibration(calib_filename)
def get_label_objects(self, idx):
# assert(idx<self.num_samples and self.split=='training')
label_filename = os.path.join(self.label_dir, '%06d.txt'%(idx))
return read_label(label_filename)
def show_image_with_boxes(img, objects, calib, save_path, show3d=True):
''' Show image with 2D bounding boxes '''
img1 = np.copy(img) # for 2d bbox
img2 = np.copy(img) # for 3d bbox
for obj in objects:
if obj.type=='DontCare':continue
cv2.rectangle(img1, (int(obj.xmin),int(obj.ymin)), (int(obj.xmax),int(obj.ymax)), (0,255,0), 2) # 画2D框
box3d_pts_2d, box3d_pts_3d = compute_box_3d(obj, calib.P) # 获取3D框-图像(8*2)、3D框-相机坐标系(8*3)
img2 = draw_projected_box3d(img2, box3d_pts_2d) # 在图像上画3D框
if show3d:
Image.fromarray(img2).save(save_path) # 保存带有3D框的图像
# Image.fromarray(img2).show()
else:
Image.fromarray(img1).save(save_path) # 保存带有2D框的图像
# Image.fromarray(img1).show()
class Object3d(object):
''' 3d object label '''
def __init__(self, label_file_line):
data = label_file_line.split(' ')
data[1:] = [float(x) for x in data[1:]]
# extract label, truncation, occlusion
self.type = data[0] # 'Car', 'Pedestrian', ...
self.truncation = data[1] # truncated pixel ratio [0..1]
self.occlusion = int(data[2]) # 0=visible, 1=partly occluded, 2=fully occluded, 3=unknown
self.alpha = data[3] # object observation angle [-pi..pi]
# extract 2d bounding box in 0-based coordinates
self.xmin = data[4] # left
self.ymin = data[5] # top
self.xmax = data[6] # right
self.ymax = data[7] # bottom
self.box2d = np.array([self.xmin,self.ymin,self.xmax,self.ymax])
# extract 3d bounding box information
self.h = data[8] # box height
self.w = data[9] # box width
self.l = data[10] # box length (in meters)
self.t = (data[11],data[12],data[13]) # location (x,y,z) in camera coord.
self.ry = data[14] # yaw angle (around Y-axis in camera coordinates) [-pi..pi]
def print_object(self):
print('Type, truncation, occlusion, alpha: %s, %d, %d, %f' % \
(self.type, self.truncation, self.occlusion, self.alpha))
print('2d bbox (x0,y0,x1,y1): %f, %f, %f, %f' % \
(self.xmin, self.ymin, self.xmax, self.ymax))
print('3d bbox h,w,l: %f, %f, %f' % \
(self.h, self.w, self.l))
print('3d bbox location, ry: (%f, %f, %f), %f' % \
(self.t[0],self.t[1],self.t[2],self.ry))
class Calibration(object):
''' Calibration matrices and utils
3d XYZ in <label>.txt are in rect camera coord.
2d box xy are in image2 coord
Points in <lidar>.bin are in Velodyne coord.
y_image2 = P^2_rect * x_rect
y_image2 = P^2_rect * R0_rect * Tr_velo_to_cam * x_velo
x_ref = Tr_velo_to_cam * x_velo
x_rect = R0_rect * x_ref
P^2_rect = [f^2_u, 0, c^2_u, -f^2_u b^2_x;
0, f^2_v, c^2_v, -f^2_v b^2_y;
0, 0, 1, 0]
= K * [1|t]
image2 coord:
----> x-axis (u)
|
|
v y-axis (v)
velodyne coord:
front x, left y, up z
rect/ref camera coord:
right x, down y, front z
Ref (KITTI paper): http://www.cvlibs.net/publications/Geiger2013IJRR.pdf
TODO(rqi): do matrix multiplication only once for each projection.
'''
def __init__(self, calib_filepath, from_video=False):
if from_video:
calibs = self.read_calib_from_video(calib_filepath)
else:
calibs = self.read_calib_file(calib_filepath)
# Projection matrix from rect camera coord to image2 coord
self.P = calibs['P2']
self.P = np.reshape(self.P, [3,4])
# Rigid transform from Velodyne coord to reference camera coord
self.V2C = calibs['Tr_velo_to_cam']
self.V2C = np.reshape(self.V2C, [3,4])
self.C2V = inverse_rigid_trans(self.V2C)
# Rotation from reference camera coord to rect camera coord
self.R0 = calibs['R0_rect']
self.R0 = np.reshape(self.R0,[3,3])
# Camera intrinsics and extrinsics
self.c_u = self.P[0,2]
self.c_v = self.P[1,2]
self.f_u = self.P[0,0]
self.f_v = self.P[1,1]
self.b_x = self.P[0,3]/(-self.f_u) # relative
self.b_y = self.P[1,3]/(-self.f_v)
def read_calib_file(self, filepath):
''' Read in a calibration file and parse into a dictionary.'''
data = {}
with open(filepath, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
line = line.rstrip()
if len(line)==0: continue
key, value = line.split(':', 1)
# The only non-float values in these files are dates, which
# we don't care about anyway
try:
data[key] = np.array([float(x) for x in value.split()])
except ValueError:
pass
return data
def read_calib_from_video(self, calib_root_dir):
''' Read calibration for camera 2 from video calib files.
there are calib_cam_to_cam and calib_velo_to_cam under the calib_root_dir
'''
data = {}
cam2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_cam_to_cam.txt'))
velo2cam = self.read_calib_file(os.path.join(calib_root_dir, 'calib_velo_to_cam.txt'))
Tr_velo_to_cam = np.zeros((3,4))
Tr_velo_to_cam[0:3,0:3] = np.reshape(velo2cam['R'], [3,3])
Tr_velo_to_cam[:,3] = velo2cam['T']
data['Tr_velo_to_cam'] = np.reshape(Tr_velo_to_cam, [12])
data['R0_rect'] = cam2cam['R_rect_00']
data['P2'] = cam2cam['P_rect_02']
return data
def cart2hom(self, pts_3d):
''' Input: nx3 points in Cartesian
Oupput: nx4 points in Homogeneous by pending 1
'''
n = pts_3d.shape[0]
pts_3d_hom = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1))))
return pts_3d_hom
# ===========================
# ------- 3d to 3d ----------
# ===========================
def project_velo_to_ref(self, pts_3d_velo):
pts_3d_velo = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_velo) # nx4
return np.dot(pts_3d_velo, np.transpose(self.V2C))
def project_ref_to_velo(self, pts_3d_ref):
pts_3d_ref = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_ref) # nx4
return np.dot(pts_3d_ref, np.transpose(self.C2V))
def project_rect_to_ref(self, pts_3d_rect):
''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''
return np.transpose(np.dot(np.linalg.inv(self.R0), np.transpose(pts_3d_rect)))
def project_ref_to_rect(self, pts_3d_ref):
''' Input and Output are nx3 points '''
return np.transpose(np.dot(self.R0, np.transpose(pts_3d_ref)))
def project_rect_to_velo(self, pts_3d_rect):
''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.
Output: nx3 points in velodyne coord.
'''
pts_3d_ref = self.project_rect_to_ref(pts_3d_rect)
return self.project_ref_to_velo(pts_3d_ref)
def project_velo_to_rect(self, pts_3d_velo):
pts_3d_ref = self.project_velo_to_ref(pts_3d_velo)
return self.project_ref_to_rect(pts_3d_ref)
def corners3d_to_img_boxes(self, corners3d):
"""
:param corners3d: (N, 8, 3) corners in rect coordinate
:return: boxes: (None, 4) [x1, y1, x2, y2] in rgb coordinate
:return: boxes_corner: (None, 8) [xi, yi] in rgb coordinate
"""
sample_num = corners3d.shape[0]
corners3d_hom = np.concatenate((corners3d, np.ones((sample_num, 8, 1))), axis=2) # (N, 8, 4)
img_pts = np.matmul(corners3d_hom, self.P.T) # (N, 8, 3)
x, y = img_pts[:, :, 0] / img_pts[:, :, 2], img_pts[:, :, 1] / img_pts[:, :, 2]
x1, y1 = np.min(x, axis=1), np.min(y, axis=1)
x2, y2 = np.max(x, axis=1), np.max(y, axis=1)
boxes = np.concatenate((x1.reshape(-1, 1), y1.reshape(-1, 1), x2.reshape(-1, 1), y2.reshape(-1, 1)), axis=1)
boxes_corner = np.concatenate((x.reshape(-1, 8, 1), y.reshape(-1, 8, 1)), axis=2)
return boxes, boxes_corner
# ===========================
# ------- 3d to 2d ----------
# ===========================
def project_rect_to_image(self, pts_3d_rect):
''' Input: nx3 points in rect camera coord.
Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.
'''
pts_3d_rect = self.cart2hom(pts_3d_rect)
pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_rect, np.transpose(self.P)) # nx3
pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2]
pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2]
return pts_2d[:,0:2]
def project_velo_to_image(self, pts_3d_velo):
''' Input: nx3 points in velodyne coord.
Output: nx2 points in image2 coord.
'''
pts_3d_rect = self.project_velo_to_rect(pts_3d_velo)
return self.project_rect_to_image(pts_3d_rect)
# ===========================
# ------- 2d to 3d ----------
# ===========================
def project_image_to_rect(self, uv_depth):
''' Input: nx3 first two channels are uv, 3rd channel
is depth in rect camera coord.
Output: nx3 points in rect camera coord.
'''
n = uv_depth.shape[0]
x = ((uv_depth[:,0]-self.c_u)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_u + self.b_x
y = ((uv_depth[:,1]-self.c_v)*uv_depth[:,2])/self.f_v + self.b_y
pts_3d_rect = np.zeros((n,3))
pts_3d_rect[:,0] = x
pts_3d_rect[:,1] = y
pts_3d_rect[:,2] = uv_depth[:,2]
return pts_3d_rect
def project_image_to_velo(self, uv_depth):
pts_3d_rect = self.project_image_to_rect(uv_depth)
return self.project_rect_to_velo(pts_3d_rect)
def rotx(t):
''' 3D Rotation about the x-axis. '''
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, c, -s],
[0, s, c]])
def roty(t):
''' Rotation about the y-axis. '''
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[c, 0, s],
[0, 1, 0],
[-s, 0, c]])
def rotz(t):
''' Rotation about the z-axis. '''
c = np.cos(t)
s = np.sin(t)
return np.array([[c, -s, 0],
[s, c, 0],
[0, 0, 1]])
def transform_from_rot_trans(R, t):
''' Transforation matrix from rotation matrix and translation vector. '''
R = R.reshape(3, 3)
t = t.reshape(3, 1)
return np.vstack((np.hstack([R, t]), [0, 0, 0, 1]))
def inverse_rigid_trans(Tr):
''' Inverse a rigid body transform matrix (3x4 as [R|t])
[R'|-R't; 0|1]
'''
inv_Tr = np.zeros_like(Tr) # 3x4
inv_Tr[0:3,0:3] = np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3])
inv_Tr[0:3,3] = np.dot(-np.transpose(Tr[0:3,0:3]), Tr[0:3,3])
return inv_Tr
def read_label(label_filename):
lines = [line.rstrip() for line in open(label_filename)]
objects = [Object3d(line) for line in lines]
return objects
def load_image(img_filename):
return cv2.imread(img_filename)
def load_velo_scan(velo_filename):
scan = np.fromfile(velo_filename, dtype=np.float32)
scan = scan.reshape((-1, 4))
return scan
def project_to_image(pts_3d, P):
'''
将3D坐标点投影到图像平面上,生成2D坐
pts_3d是一个nx3的矩阵,包含了待投影的3D坐标点(每行一个点),P是相机的投影矩阵,通常是一个3x4的矩阵。
函数返回一个nx2的矩阵,包含了投影到图像平面上的2D坐标点。
'''
''' Project 3d points to image plane.
Usage: pts_2d = projectToImage(pts_3d, P)
input: pts_3d: nx3 matrix
P: 3x4 projection matrix
output: pts_2d: nx2 matrix
P(3x4) dot pts_3d_extended(4xn) = projected_pts_2d(3xn)
=> normalize projected_pts_2d(2xn)
<=> pts_3d_extended(nx4) dot P'(4x3) = projected_pts_2d(nx3)
=> normalize projected_pts_2d(nx2)
'''
n = pts_3d.shape[0] # 获取3D点的数量
pts_3d_extend = np.hstack((pts_3d, np.ones((n,1)))) # 将每个3D点的坐标扩展为齐次坐标形式(4D),通过在每个点的末尾添加1,创建了一个nx4的矩阵。
# print(('pts_3d_extend shape: ', pts_3d_extend.shape))
pts_2d = np.dot(pts_3d_extend, np.transpose(P)) # 将扩展的3D坐标点矩阵与投影矩阵P相乘,得到一个nx3的矩阵,其中每一行包含了3D点在图像平面上的投影坐标。每个点的坐标表示为[x, y, z]。
pts_2d[:,0] /= pts_2d[:,2] # 将投影坐标中的x坐标除以z坐标,从而获得2D图像上的x坐标。
pts_2d[:,1] /= pts_2d[:,2] # 将投影坐标中的y坐标除以z坐标,从而获得2D图像上的y坐标。
return pts_2d[:,0:2] # 返回一个nx2的矩阵,其中包含了每个3D点在2D图像上的坐标。
def compute_box_3d(obj, P):
'''
计算对象的3D边界框在图像平面上的投影
输入: obj代表一个物体标签信息, P代表相机的投影矩阵-内参。
输出: 返回两个值, corners_3d表示3D边界框在 相机坐标系 的8个角点的坐标-3D坐标。
corners_2d表示3D边界框在 图像上 的8个角点的坐标-2D坐标。
'''
# compute rotational matrix around yaw axis
# 计算一个绕Y轴旋转的旋转矩阵R,用于将3D坐标从世界坐标系转换到相机坐标系。obj.ry是对象的偏航角
R = roty(obj.ry)
# 3d bounding box dimensions
# 物体实际的长、宽、高
l = obj.l;
w = obj.w;
h = obj.h;
# 3d bounding box corners
# 存储了3D边界框的8个角点相对于对象中心的坐标。这些坐标定义了3D边界框的形状。
x_corners = [l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2,l/2,l/2,-l/2,-l/2];
y_corners = [0,0,0,0,-h,-h,-h,-h];
z_corners = [w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2,w/2,-w/2,-w/2,w/2];
# rotate and translate 3d bounding box
# 1、将3D边界框的角点坐标从对象坐标系转换到相机坐标系。它使用了旋转矩阵R
corners_3d = np.dot(R, np.vstack([x_corners,y_corners,z_corners]))
# 3D边界框的坐标进行平移
corners_3d[0,:] = corners_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0];
corners_3d[1,:] = corners_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1];
corners_3d[2,:] = corners_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2];
# 2、检查对象是否在相机前方,因为只有在相机前方的对象才会被绘制。
# 如果对象的Z坐标(深度)小于0.1,就意味着对象在相机后方,那么corners_2d将被设置为None,函数将返回None。
if np.any(corners_3d[2,:]<0.1):
corners_2d = None
return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)
# project the 3d bounding box into the image plane
# 3、将相机坐标系下的3D边界框的角点,投影到图像平面上,得到它们在图像上的2D坐标。
corners_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(corners_3d), P);
return corners_2d, np.transpose(corners_3d)
def compute_orientation_3d(obj, P):
''' Takes an object and a projection matrix (P) and projects the 3d
object orientation vector into the image plane.
Returns:
orientation_2d: (2,2) array in left image coord.
orientation_3d: (2,3) array in in rect camera coord.
'''
# compute rotational matrix around yaw axis
R = roty(obj.ry)
# orientation in object coordinate system
orientation_3d = np.array([[0.0, obj.l],[0,0],[0,0]])
# rotate and translate in camera coordinate system, project in image
orientation_3d = np.dot(R, orientation_3d)
orientation_3d[0,:] = orientation_3d[0,:] + obj.t[0]
orientation_3d[1,:] = orientation_3d[1,:] + obj.t[1]
orientation_3d[2,:] = orientation_3d[2,:] + obj.t[2]
# vector behind image plane?
if np.any(orientation_3d[2,:]<0.1):
orientation_2d = None
return orientation_2d, np.transpose(orientation_3d)
# project orientation into the image plane
orientation_2d = project_to_image(np.transpose(orientation_3d), P);
return orientation_2d, np.transpose(orientation_3d)
def draw_projected_box3d(image, qs, color=(0,60,255), thickness=2):
'''
qs: 包含8个3D边界框角点坐标的数组, 形状为(8, 2)。图像坐标下的3D框, 8个顶点坐标。
'''
''' Draw 3d bounding box in image
qs: (8,2) array of vertices for the 3d box in following order:
1 -------- 0
/| /|
2 -------- 3 .
| | | |
. 5 -------- 4
|/ |/
6 -------- 7
'''
qs = qs.astype(np.int32) # 将输入的顶点坐标转换为整数类型,以便在图像上绘制。
# 这个循环迭代4次,每次处理一个边界框的一条边。
for k in range(0,4):
# Ref: http://docs.enthought.com/mayavi/mayavi/auto/mlab_helper_functions.html
# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的前四条边。
i,j=k,(k+1)%4
cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)
# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制边界框的后四条边,与前四条边平行
i,j=k+4,(k+1)%4 + 4
cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)
# 定义了要绘制的边的起始点和结束点的索引。在这个循环中,它用于绘制连接前四条边和后四条边的边界框的边。
i,j=k,k+4
cv2.line(image, (qs[i,0],qs[i,1]), (qs[j,0],qs[j,1]), color, thickness)
return image
运行后会在save_3d_output中保存可视化的图像。
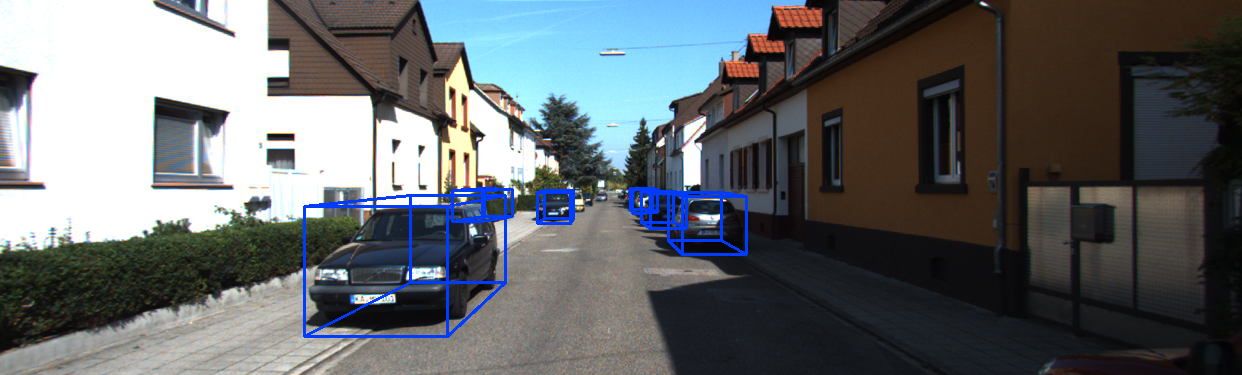
模型推理结果可视化效果:
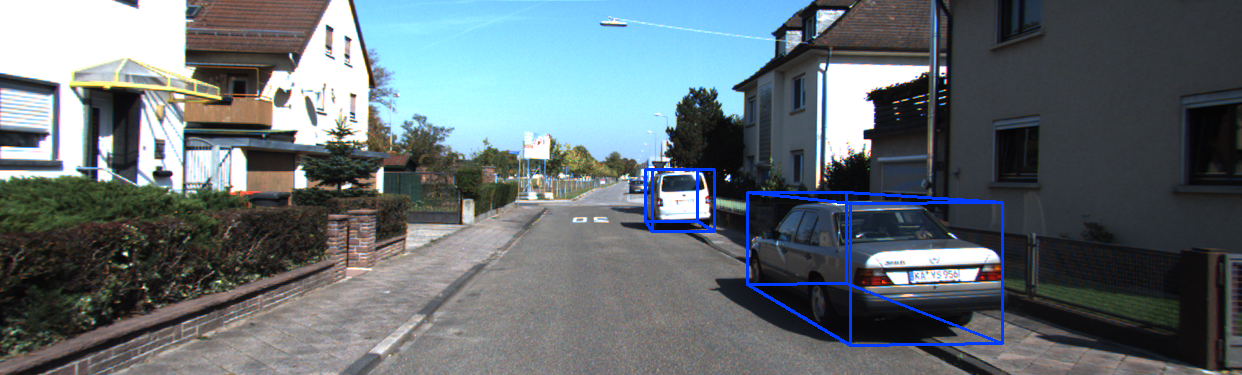

分享完成~
【数据集】单目3D目标检测:
3D目标检测数据集 KITTI(标签格式解析、3D框可视化、点云转图像、BEV鸟瞰图)_kitti标签_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
3D目标检测数据集 DAIR-V2X-V_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
【论文解读】单目3D目标检测:
【论文解读】SMOKE 单目相机 3D目标检测(CVPR2020)_相机smoke-CSDN博客
【论文解读】单目3D目标检测 MonoDLE(CVPR2021)_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
【论文解读】单目3D目标检测 MonoCon(AAAI2022)_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
【实践应用】
单目3D目标检测——SMOKE 环境搭建|模型训练_一颗小树x的博客-CSDN博客
单目3D目标检测——SMOKE 模型推理 | 可视化结果-CSDN博客
单目3D目标检测——MonoCon 模型训练 | 模型推理-CSDN博客
后面计划分享,实时性的单目3D目标检测:MonoFlex、MonoEF、MonoDistillI、GUPNet、DEVIANT等