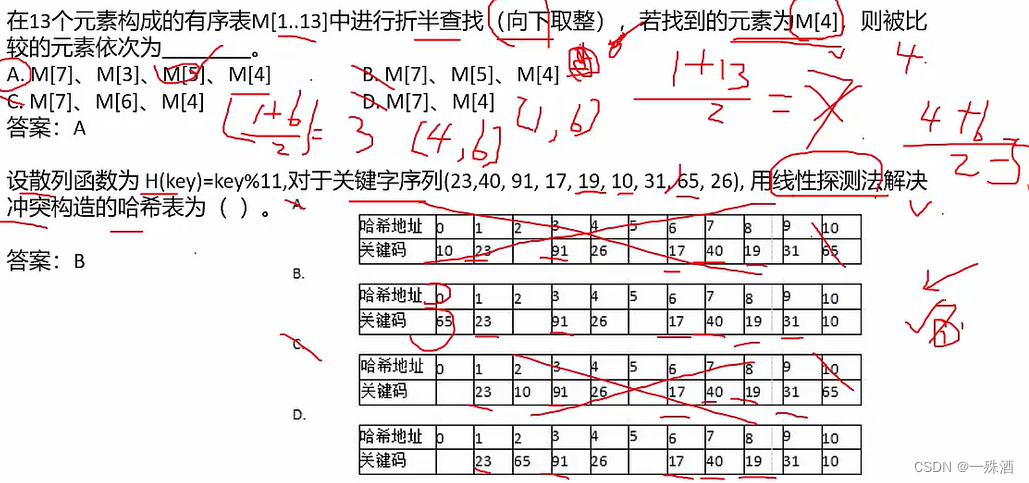
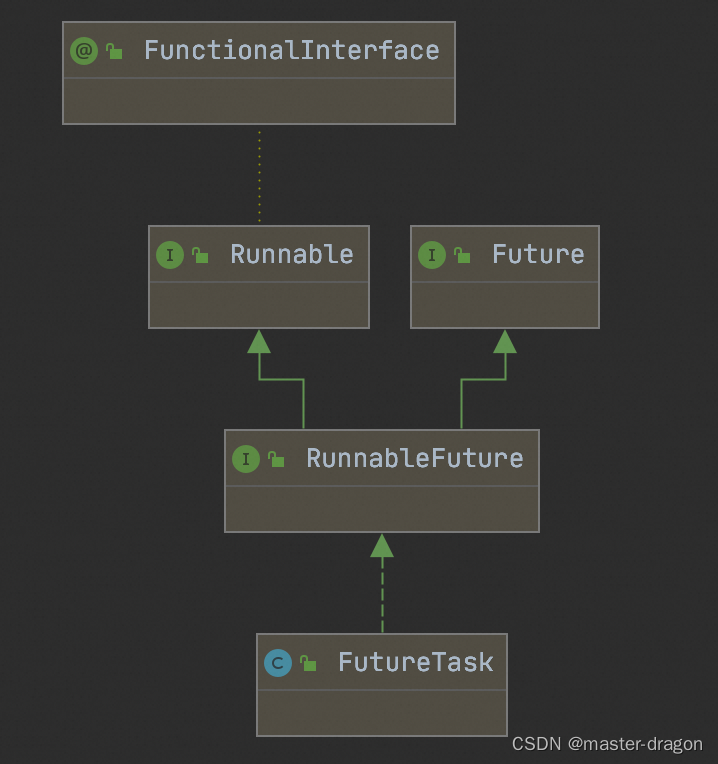
FutureTask类图如下
java.util.concurrent.FutureTask#run run方法执行逻辑如下
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!RUNNER.compareAndSet(this, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
state说明:
- NEW:新任务的初始状态;
- COMPLETING:当任务被设置结果时,处于COMPLETING状态,是一个中间状态;
- NORMAL:表示任务正常结束;
- EXCEPTIONAL:表示任务因异常而结束;
- CANCELLED:任务还未执行完成之前就调用了cancel方法,任务处于CANCELLED;
- INTERRUPTING:当任务调用cancel(true)中断程序时,任务处于INTERRUPTING状态,是一个中间状态;
- INTERRUPTED:任务调用cancel(true)中断程序时会调用interrupt()方法中断线程运行,任务状态由INTERRUPTING转变为INTERRUPTED;
代码逻辑说明:
- 如果不是新建状态或者已经在运行中,则直接返回
- 否则执行如下:
- 取FutureTask内部的Callable,不是空且是新建状态就去执行
- 执行成功失败记录
- 成功,记录结果,状态最后为:NORMAL
- 失败,记录异常, 状态最后为:EXCEPTIONAL
- 最后会并完成任务,会执行
java.util.concurrent.FutureTask#finishCompletion(最后内部的Callable会设置为null)
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (WAITERS.weakCompareAndSet(this, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
唤醒下一个线程,并从等待队列中移除掉。
get超时方法
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
/**
* Awaits completion or aborts on interrupt or timeout.
*
* @param timed true if use timed waits
* @param nanos time to wait, if timed
* @return state upon completion or at timeout
*/
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
// The code below is very delicate, to achieve these goals:
// - call nanoTime exactly once for each call to park
// - if nanos <= 0L, return promptly without allocation or nanoTime
// - if nanos == Long.MIN_VALUE, don't underflow
// - if nanos == Long.MAX_VALUE, and nanoTime is non-monotonic
// and we suffer a spurious wakeup, we will do no worse than
// to park-spin for a while
long startTime = 0L; // Special value 0L means not yet parked
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING)
// We may have already promised (via isDone) that we are done
// so never return empty-handed or throw InterruptedException
Thread.yield();
else if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
else if (q == null) {
if (timed && nanos <= 0L)
return s;
q = new WaitNode();
}
else if (!queued)
queued = WAITERS.weakCompareAndSet(this, q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
final long parkNanos;
if (startTime == 0L) { // first time
startTime = System.nanoTime();
if (startTime == 0L)
startTime = 1L;
parkNanos = nanos;
} else {
long elapsed = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
if (elapsed >= nanos) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
parkNanos = nanos - elapsed;
}
// nanoTime may be slow; recheck before parking
if (state < COMPLETING)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, parkNanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
- 判断如果是运行中,特定时间内就while(true)不断判断完成或异常; 中间有个细节( Thread.yield() : 自己在运行,尝试让出CPU )
- 超时仍运行(即特定时间判断完后线程还是运行中)则抛出TimeoutException; 否则返回对应结果
返回结果
/**
* Returns result or throws exception for completed task.
*
* @param s completed state value
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask1 = new FutureTask(()->{
try{
System.out.println("task Run....");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
}catch (Exception e){
}
System.out.println("task finish....");
return 1;
});
System.out.println(futureTask1);
executorService.submit(futureTask1);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
futureTask1.cancel(false);
System.out.println(futureTask1.toString());
Integer a = null;
try {
a = futureTask1.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(futureTask1);
}