文章目录
- 1.可变参数模板的介绍
- 1.1C语言中的可变参数
- 1.2C++98/C++11的类模板和函数模板
- 1.3可变参数的函数模板
- 1.4展开参数包
- 递归展开
- 初始化列表展开
- 2.可变参数模板的应用

1.可变参数模板的介绍
1.1C语言中的可变参数

1.2C++98/C++11的类模板和函数模板
- C++98/03,类模版和函数模版中只能含固定数量的模版参数
- C++11的可变参数模板能够让您创建可以接受可变参数的函数模板和类模板
1.3可变参数的函数模板
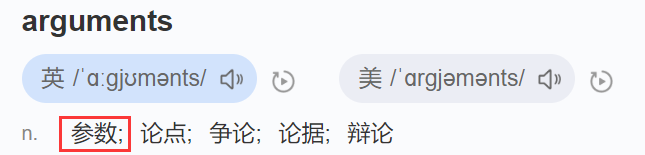

void ShowList(Args... args)
{
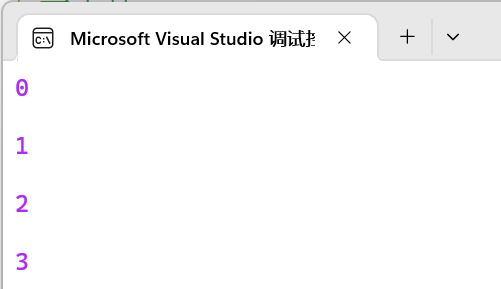
//sizeof可以计算参数包中有几个参数
cout << sizeof...(args) << endl;
/*不支持
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof...(args); ++i)
{
cout << args[i] << " ";
}
*/
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
string str("I am A!");
ShowList();
ShowList(65);
ShowList(65, 'A');
ShowList(65, 'A', str);
return 0;
}
1.4展开参数包
我们无法直接获取参数包args中的每个参数,只能通过展开参数包的方式来获取参数包中的每个参数
递归展开
//当参数包个数为0时 最后一次函数调用需要有无参函数
void ShowList()
{
cout << endl;
}
//参数包含参数个数 >= 0
template <class T, class ...Args>
void ShowList(const T& single, Args... args)
{
cout << "ShowList(" << single << ", " << "参数包 含" << sizeof...(args) << "个参数)" << endl;
ShowList(args...);
}
int main()
{
string s("3");
ShowList(1, '2', s);
ShowList(1, '2', s, 4, '5', 6);
return 0;
}

初始化列表展开
template<class T>
int Display(const T& single)
{
cout << single << " ";
return 0;
}
template <class ...Args>
void ShowList(Args... args)
{
int a[] = { Display(args)... };
//int a[] = { Display(arg1), Display(arg2), Display(arg3)...};
cout << "当前参数包共" << sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) << "个参数" << endl;
}
int main()
{
string s("3");
ShowList(1, '2', s);
ShowList(1, '2', s, 4, '5', 6);
return 0;
}

2.可变参数模板的应用

class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
cout << "Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)" << endl;
}
Date(const Date& d)
:_year(d._year)
, _month(d._month)
, _day(d._day)
{
cout << "Date(const Date& d)" << endl;
}
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
cout << "Date& operator=(const Date& d))" << endl;
return *this;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// template <class... Args>
// iterator emplace(const_iterator pos, Args&&... args);
// template <class... Args>
// void emplace_back(Args&&... args);
int main()
{
/// emplace的优势1
//没有区别
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.emplace_back(2);
//emplace_back的优势 此情况更高效
vector<pair<string, int>> v2;
v2.push_back(make_pair("A", 65));
v2.emplace_back(make_pair("A", 65));
v2.emplace_back("A", 65);
/// emplace的优势2
cout << "-------------- push_back --------------" << endl << endl;
list<Date> lt1;
lt1.push_back(Date(2022, 11, 16));
cout << endl;
cout << "------------- emplace_back -----------" << endl << endl;
lt1.emplace_back(2022, 11, 16);
return 0;
}