1,简述
GPIO 资源是相对来说较为简单,而且比较通用(比如 LED 灯),而 Linux 的 GPIO 驱动属于 Linux Driver 中较为容易上手的部分,但是简单归简单,在 Linux 系统中,要使用 GPIO 资源,还是需要了解一些内容。
Linux Kernel 中对 GPIO 资源进行了抽象,抽象出一个叫做 Gpiolib 的东东,这个东东作为 GPIO 资源的管理核心存在:
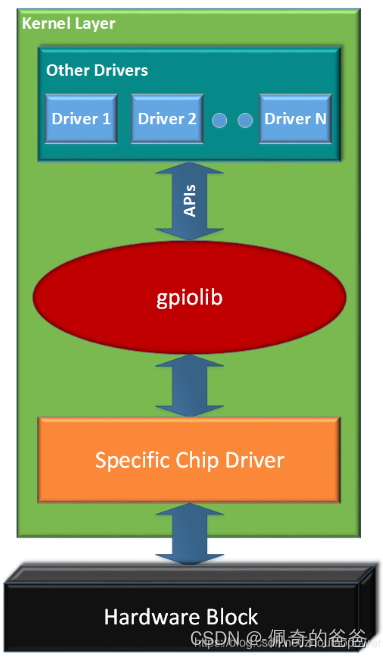
中间层是 Gpiolib,用于管理系统中的 GPIO。Gpiolib 汇总了 GPIO 的通用操作,根据 GPIO 的特性,Gpiolib 对上(其他 Drivers)提供的一套统一通用的操作 GPIO 的软件接口,屏蔽了不同芯片的具体实现。对下,Gpiolib 提供了针对不同芯片操作的一套 framework,针对不同芯片,只需要实现 Specific Chip Driver ,然后使用 Gpiolib 提供的注册函数,将其挂接到 Gpiolib 上,这样就完成了这一套东西。
对于其他驱动来说,比如 LED 灯驱动,就需要用到通用的 Gpiolib 的函数来进行 I/O 口的操作。
2,Gpiolib相关数据结构分析
先分析数据结构,Gpiolib 其实就是围绕几个数据结构在做文章,数据结构以及抽象层次清楚了,代码自然很快。
数据结构主要定义在 include/linux/gpio/driver.h 和 /drivers/gpio/gpiolib.h 中
首先看一个数据结构,叫 struct gpio_chip (include/linux/gpio/driver.h):
struct gpio_chip {
const char *label;
struct gpio_device *gpiodev;
struct device *parent;
struct module *owner;
int (*request)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
void (*free)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*get_direction)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*direction_input)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*direction_output)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset, int value);
int (*get)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
int (*get_multiple)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned long *mask,
unsigned long *bits);
void (*set)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset, int value);
void (*set_multiple)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned long *mask,
unsigned long *bits);
int (*set_config)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset,
unsigned long config);
int (*to_irq)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned int offset);
void (*dbg_show)(struct seq_file *s,
struct gpio_chip *gc);
int (*init_valid_mask)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
unsigned long *valid_mask,
unsigned int ngpios);
int (*add_pin_ranges)(struct gpio_chip *gc);
int base;
u16 ngpio;
const char *const *names;
bool can_sleep;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GPIO_GENERIC)
unsigned long (*read_reg)(void __iomem *reg);
void (*write_reg)(void __iomem *reg, unsigned long data);
bool be_bits;
void __iomem *reg_dat;
void __iomem *reg_set;
void __iomem *reg_clr;
void __iomem *reg_dir_out;
void __iomem *reg_dir_in;
bool bgpio_dir_unreadable;
int bgpio_bits;
spinlock_t bgpio_lock;
unsigned long bgpio_data;
unsigned long bgpio_dir;
#endif /* CONFIG_GPIO_GENERIC */
#ifdef CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP
/*
* With CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP we get an irqchip inside the gpiolib
* to handle IRQs for most practical cases.
*/
/**
* @irq:
*
* Integrates interrupt chip functionality with the GPIO chip. Can be
* used to handle IRQs for most practical cases.
*/
struct gpio_irq_chip irq;
#endif /* CONFIG_GPIOLIB_IRQCHIP */
/**
* @valid_mask:
*
* If not %NULL holds bitmask of GPIOs which are valid to be used
* from the chip.
*/
unsigned long *valid_mask;
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_GPIO)
/*
* If CONFIG_OF is enabled, then all GPIO controllers described in the
* device tree automatically may have an OF translation
*/
/**
* @of_node:
*
* Pointer to a device tree node representing this GPIO controller.
*/
struct device_node *of_node;
/**
* @of_gpio_n_cells:
*
* Number of cells used to form the GPIO specifier.
*/
unsigned int of_gpio_n_cells;
/**
* @of_xlate:
*
* Callback to translate a device tree GPIO specifier into a chip-
* relative GPIO number and flags.
*/
int (*of_xlate)(struct gpio_chip *gc,
const struct of_phandle_args *gpiospec, u32 *flags);
#endif /* CONFIG_OF_GPIO */
ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);
ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);
};
gpio_chip 这个数据结构一看,很多函数指针结构,明眼人秒懂,此结构是为了抽象 GPIO 的所有操作,同时适配不同芯片的一个 common 的结构,所以,这个结构是要开出去给其他芯片进行特定的操作赋值的,比如你是 Qcom 的芯片,那么你需要实现你的这些 gpio_chip 的内容。
2.1 gpio_chip 结构
一般的,在一个芯片中,针对所有的 I/O 口都会有配置,默认状态有些是 I/O 口全部默认 GPIO 输入(稳当)。一般芯片会提供管脚复用的功能(后期的 Linux 版本中,使用 pin control 来抽象),要使用 GPIO ,则首先需要配置他为 GPIO 功能,而不是其他的复用功能。
而针对 GPIO 呢,有一些通用的特性,比如设置 GPIO 的方向,读 GPIO 的电平(输入的时候),写 GPIO 的电平(输出的时候),GPIO 作为外部中断输入,等等。
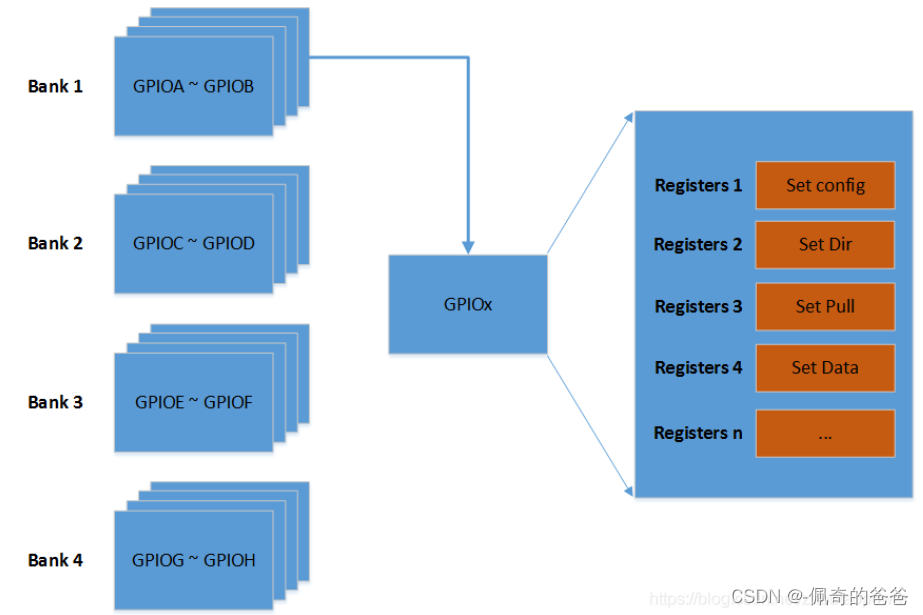
gpio_chip 的抽象,其实是对 GPIO 一组 Bank 的抽象,通常在硬件上,一个芯片对 IO 口来说,分为了很多个 Bank,每个 Bank 分为了 N 组 GPIO。
比如:1 个 SoC 将 I/O 分为了 4 个 Bank:
Bank 1:GPIOA ~ GPIOB
Bank 2:GPIOC ~ GPIOD
Bank 3:GPIOE ~ GPIOF
Bank 4:GPIOG ~ GPIOH然鹅,每个 Bank 都有 N 组寄存器来表示 GPIO 的操作,比如:
Bank 1 中,针对 GPIO A:
GPIOA_CFG 来表示对 GPIO A 的配置
GPIOA_PULL 来表示对 GPIO A 的上下拉的配置
GPIOA_DIR 来表示对 GPIO A 配置成为输入或者输出
GPIOA_DATA 来表示 GPIO A 设置为输出的时候设置为高低或者输入的时候读高低当然,Bank 1 中 针对 GPIO B,也是一样的操作:
GPIOB_CFG 来表示对 GPIO B 的配置
GPIOB_PULL 来表示对 GPIO B 的上下拉的配置
GPIOB_DIR 来表示对 GPIO B 配置成为输入或者输出
GPIOB_DATA 来表示 GPIO B 设置为输出的时候设置为高低或者输入的时候读高低上面说的是一个 Bank 的情况,那么芯片有好几个 Bank,所以它们都是类似的,这里不在赘述。
所以整体结构是如下所示(这里只是打个比方,有的芯片 Bank 很多,寄存器也很多):
Linux Driver Gpiolib 对他们的抽象,使用 gpio_chip 对应了一组 Bank 描述,比如 Bank ·1,用一个 gpio_chip 来抽象:
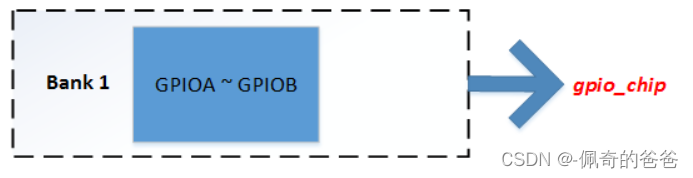
那么多个 Bank ,就用指针,或者数组来表示咯。当然这里可能说得有点不准确,gpio_chip 只是抽象了一组 Bank 的统一的接口而已。
那么对于一颗芯片底层来说,需要根据芯片手册 Datasheet,来实现这些结构的接口。
2.2 gpio_desc结构
既然系统分为多个 Bank,每个 Bank 又由几组组成,那么每个 GPIO 实体就由一个 gpio_desc 来描述:
struct gpio_desc {
struct gpio_device *gdev;
unsigned long flags;
/* flag symbols are bit numbers */
#define FLAG_REQUESTED 0
#define FLAG_IS_OUT 1
#define FLAG_EXPORT 2 /* protected by sysfs_lock */
#define FLAG_SYSFS 3 /* exported via /sys/class/gpio/control */
#define FLAG_ACTIVE_LOW 6 /* value has active low */
#define FLAG_OPEN_DRAIN 7 /* Gpio is open drain type */
#define FLAG_OPEN_SOURCE 8 /* Gpio is open source type */
#define FLAG_USED_AS_IRQ 9 /* GPIO is connected to an IRQ */
#define FLAG_IRQ_IS_ENABLED 10 /* GPIO is connected to an enabled IRQ */
#define FLAG_IS_HOGGED 11 /* GPIO is hogged */
#define FLAG_TRANSITORY 12 /* GPIO may lose value in sleep or reset */
#define FLAG_PULL_UP 13 /* GPIO has pull up enabled */
#define FLAG_PULL_DOWN 14 /* GPIO has pull down enabled */
#define FLAG_BIAS_DISABLE 15 /* GPIO has pull disabled */
#define FLAG_EDGE_RISING 16 /* GPIO CDEV detects rising edge events */
#define FLAG_EDGE_FALLING 17 /* GPIO CDEV detects falling edge events */
/* Connection label */
const char *label;
/* Name of the GPIO */
const char *name;
#ifdef CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC
struct device_node *hog;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GPIO_CDEV
/* debounce period in microseconds */
unsigned int debounce_period_us;
#endif
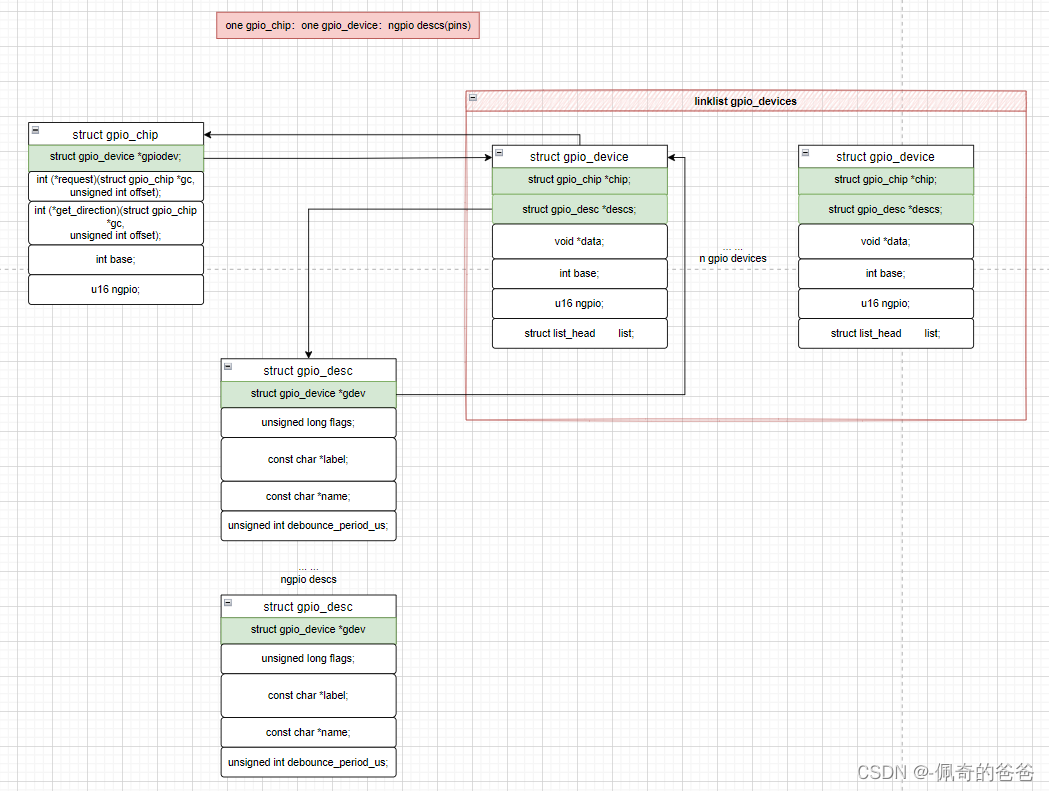
};这个结构比较简单,可以看到,他包含了一个 gpio_device 的结构和 flag,以及 lable 和 name;
gdev 指针指向了这个 gpio_desc 所属的 gpio_device(马上描述),flag 代表了这个 GPIO 的属性状态;

看起来 gpio_chip 和 gpio_desc 应该是包含关系,但是 Kernel 中并没有直接将其两个结构联系上,而是通过另外一个结构将其联系在一起,这个结构就是 gpio_device。
2.3 gpio_device结构
gpio_device 应该算是大内总管了(最新的内核有,Linux 3 版本的内核没有这个),如果说 gpio_chip 是对一个 Bank 的 GPIO 的硬件的具体抽象的话,那么 gpio_device 就是软件层面上对一个 Bank 的 GPIO 进行管理的单元,它的数据结构是:
struct gpio_device {
int id;
struct device dev;
struct cdev chrdev;
struct device *mockdev;
struct module *owner;
struct gpio_chip *chip;
struct gpio_desc *descs;
int base;
u16 ngpio;
const char *label;
void *data;
struct list_head list;
struct blocking_notifier_head notifier;
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRL
/*
* If CONFIG_PINCTRL is enabled, then gpio controllers can optionally
* describe the actual pin range which they serve in an SoC. This
* information would be used by pinctrl subsystem to configure
* corresponding pins for gpio usage.
*/
struct list_head pin_ranges;
#endif
};在这个 gpio_device 结构中,包含了 gpio_chip(对接芯片的操作集),gpio_desc(一些 GPIO 的描述);这个结构贯穿了整个 Gpiolib,因为 gpio_device 代表的是一个 Bank,一般的 GPIO 有多个 Bank,所以 Kernel 中,对这 gpio_device 的组织是由一个 gpio_devices 的链表构成(此处是多个 device,所以后面加了 s),在 gpiolib.c:
LIST_HEAD(gpio_devices);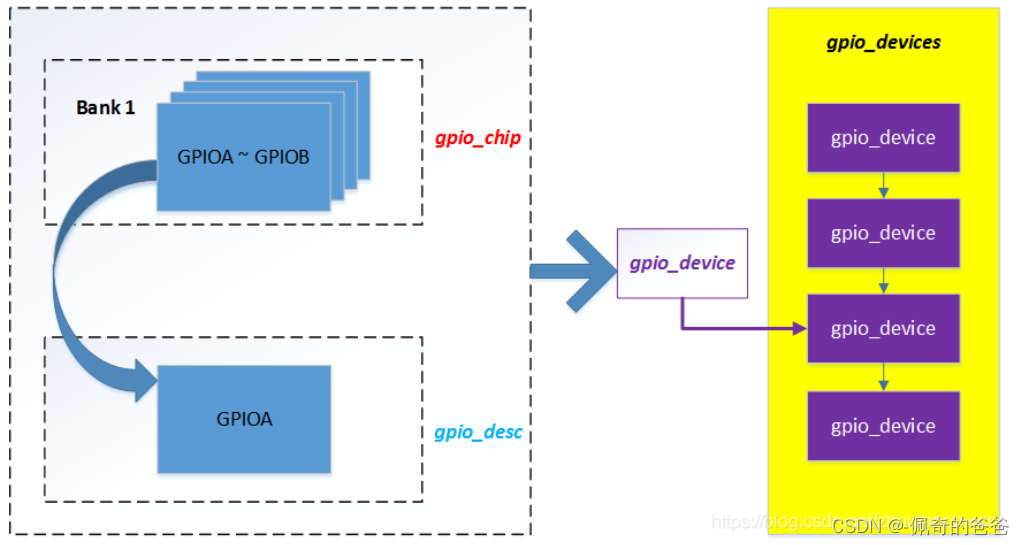
2.4 gpio_chip/gpio_desc/gpio_device 结构体之间的关系
3,Gpiolib对接芯片底层
先聊聊 Gpiolib 是怎么对接到底层实际的驱动的。在前面的 2.1 部分讲过,底层需要对接的,其实对接的部分只有那些通用的操作,其实也就是 gpio_chip 这个玩意,所以,对接底层的部分,主要关心的是这个结构体,并且对这个结构体进行赋值的过程。
在底层对接到 Gpiolib 的时候,主要是对 gpio_chip 进行实现,然后调用 gpiochip_add 的接口,向 Gpiolib 注册你的 GPIO 。
实现的过程,主要是根据芯片手册,实现对应的 GPIO 的操作,也就是说,把寄存器操作编程成为函数,对接到这个 gpio_chip 结构体上。
3.1 gpio_chip具体芯片操作函数的填充 - 一个gpio controller驱动gpio-pl061.c
代码路径:drivers/gpio/gpio-pl061.c
寄存器手册:http://access.ee.ntu.edu.tw/course/SOC%E5%AF%A6%E9%A9%97%E6%95%99%E6%9D%90/Version%203/Lab05_External%20IO%20Control/Doc/Ref/ddi0190_gpio_trm.pdf
pl061是通过AMBA总线连接在SOC上的片上gpio controller,arm架构的芯片经过授权之后可以直接使用。
部分寄存器描述:

suspend/resume操作:
#ifdef CONFIG_PM
//suspend函数中保存当前所有gpio pin寄存器状态
static int pl061_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
struct pl061 *pl061 = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
int offset;
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_data = 0;
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_dir = readb(pl061->base + GPIODIR);
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_is = readb(pl061->base + GPIOIS);
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_ibe = readb(pl061->base + GPIOIBE);
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_iev = readb(pl061->base + GPIOIEV);
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_ie = readb(pl061->base + GPIOIE);
for (offset = 0; offset < PL061_GPIO_NR; offset++) {
if (pl061->csave_regs.gpio_dir & (BIT(offset)))
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_data |=
pl061_get_value(&pl061->gc, offset) << offset;
}
return 0;
}
//resume函数中将gpio pin的寄存器状态恢复
static int pl061_resume(struct device *dev)
{
struct pl061 *pl061 = dev_get_drvdata(dev);
int offset;
for (offset = 0; offset < PL061_GPIO_NR; offset++) {
if (pl061->csave_regs.gpio_dir & (BIT(offset)))
pl061_direction_output(&pl061->gc, offset,
pl061->csave_regs.gpio_data &
(BIT(offset)));
else
pl061_direction_input(&pl061->gc, offset);
}
writeb(pl061->csave_regs.gpio_is, pl061->base + GPIOIS);
writeb(pl061->csave_regs.gpio_ibe, pl061->base + GPIOIBE);
writeb(pl061->csave_regs.gpio_iev, pl061->base + GPIOIEV);
writeb(pl061->csave_regs.gpio_ie, pl061->base + GPIOIE);
return 0;
}probe函数流程:
static int pl061_probe(struct amba_device *adev, const struct amba_id *id)
{
struct device *dev = &adev->dev;
struct pl061 *pl061;
struct gpio_irq_chip *girq;
int ret, irq;
pl061 = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(*pl061), GFP_KERNEL);
if (pl061 == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
pl061->base = devm_ioremap_resource(dev, &adev->res);
if (IS_ERR(pl061->base))
return PTR_ERR(pl061->base);
//填充gpio_chip中的回调函数
raw_spin_lock_init(&pl061->lock);
pl061->gc.request = gpiochip_generic_request;
pl061->gc.free = gpiochip_generic_free;
pl061->gc.base = -1;
pl061->gc.get_direction = pl061_get_direction;
pl061->gc.direction_input = pl061_direction_input;
pl061->gc.direction_output = pl061_direction_output;
pl061->gc.get = pl061_get_value;
pl061->gc.set = pl061_set_value;
pl061->gc.ngpio = PL061_GPIO_NR; //8
pl061->gc.label = dev_name(dev);
pl061->gc.parent = dev;
pl061->gc.owner = THIS_MODULE;
/*
* irq_chip support
*/
pl061->irq_chip.name = dev_name(dev);
pl061->irq_chip.irq_ack = pl061_irq_ack;
pl061->irq_chip.irq_mask = pl061_irq_mask;
pl061->irq_chip.irq_unmask = pl061_irq_unmask;
pl061->irq_chip.irq_set_type = pl061_irq_type;
pl061->irq_chip.irq_set_wake = pl061_irq_set_wake;
writeb(0, pl061->base + GPIOIE); /* disable irqs */
irq = adev->irq[0];
if (!irq)
dev_warn(&adev->dev, "IRQ support disabled\n");
pl061->parent_irq = irq;
girq = &pl061->gc.irq;
girq->chip = &pl061->irq_chip;
girq->parent_handler = pl061_irq_handler;
girq->num_parents = 1;
girq->parents = devm_kcalloc(dev, 1, sizeof(*girq->parents),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!girq->parents)
return -ENOMEM;
girq->parents[0] = irq;
girq->default_type = IRQ_TYPE_NONE;
girq->handler = handle_bad_irq;
//注册gpio资源
ret = devm_gpiochip_add_data(dev, &pl061->gc, pl061);
if (ret)
return ret;
amba_set_drvdata(adev, pl061);
dev_info(dev, "PL061 GPIO chip registered\n");
return 0;
}几个gpio_chip函数的实现 - pl061_get_direction
static int pl061_get_direction(struct gpio_chip *gc, unsigned offset)
{
//per-instance data assigned by the driver, return gc->gpiodev->data
struct pl061 *pl061 = gpiochip_get_data(gc);
//读取GPIODIR寄存器判断是输入或者输出并返回结果
if (readb(pl061->base + GPIODIR) & BIT(offset))
return GPIO_LINE_DIRECTION_OUT;
return GPIO_LINE_DIRECTION_IN;
}几个gpio_chip函数的实现 -pl061_set_value
static void pl061_set_value(struct gpio_chip *gc, unsigned offset, int value)
{
struct pl061 *pl061 = gpiochip_get_data(gc);
//设置GPIODATA寄存器
writeb(!!value << offset, pl061->base + (BIT(offset + 2)));
}3.2 gpiochip_add_data_with_key
1)
int gpiochip_add_data_with_key(struct gpio_chip *gc, void *data,
struct lock_class_key *lock_key,
struct lock_class_key *request_key)
{
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode = gc->parent ? dev_fwnode(gc->parent) : NULL;
unsigned long flags;
int ret = 0;
unsigned i;
int base = gc->base;
struct gpio_device *gdev;
bool block_gpio_read = false;
/*
* First: allocate and populate the internal stat container, and
* set up the struct device.
*/
gdev = kzalloc(sizeof(*gdev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!gdev)
return -ENOMEM;
gdev->dev.bus = &gpio_bus_type;
gdev->chip = gc;
gc->gpiodev = gdev;
if (gc->parent) {
gdev->dev.parent = gc->parent;
gdev->dev.of_node = gc->parent->of_node;
}
of_gpio_dev_init(gc, gdev);
/*
* Assign fwnode depending on the result of the previous calls,
* if none of them succeed, assign it to the parent's one.
*/
gdev->dev.fwnode = dev_fwnode(&gdev->dev) ?: fwnode;
//给chip分配唯一的ID
gdev->id = ida_alloc(&gpio_ida, GFP_KERNEL);
if (gdev->id < 0) {
ret = gdev->id;
goto err_free_gdev;
}
ret = dev_set_name(&gdev->dev, GPIOCHIP_NAME "%d", gdev->id);
if (ret)
goto err_free_ida;
device_initialize(&gdev->dev);
if (gc->parent && gc->parent->driver)
gdev->owner = gc->parent->driver->owner;
else if (gc->owner)
/* TODO: remove chip->owner */
gdev->owner = gc->owner;
else
gdev->owner = THIS_MODULE;因为传入的结构是 gpio_chip,他代表了是一个 Bank,但是并没有 gpio_device 的结构,所以,在这个函数中,首先分配一个 gpio_device 的结构,并将其结构体成员的 chip ,等等进行赋值,建立起相关的结构联系。
2)
gdev->descs = kcalloc(gc->ngpio, sizeof(gdev->descs[0]), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!gdev->descs) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_dev_name;
}
if (gc->ngpio == 0) {
chip_err(gc, "tried to insert a GPIO chip with zero lines\n");
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err_free_descs;
}
if (gc->ngpio > FASTPATH_NGPIO)
chip_warn(gc, "line cnt %u is greater than fast path cnt %u\n",
gc->ngpio, FASTPATH_NGPIO);
gdev->label = kstrdup_const(gc->label ?: "unknown", GFP_KERNEL);
if (!gdev->label) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err_free_descs;
}
gdev->ngpio = gc->ngpio;
gdev->data = data;由于 1 个 Bank不仅仅只有一个 GPIO,所以 gpio_chip->ngpio 的结构表示了这个 Bank 一共的 GPIO 个数,每一个 GPIO 使用一个 gpio_desc 表示,所以,这里分配了 ngpio 个 descs;
3)
spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags);
/*
* TODO: this allocates a Linux GPIO number base in the global
* GPIO numberspace for this chip. In the long run we want to
* get *rid* of this numberspace and use only descriptors, but
* it may be a pipe dream. It will not happen before we get rid
* of the sysfs interface anyways.
*/
if (base < 0) {
base = gpiochip_find_base(gc->ngpio);
if (base < 0) {
ret = base;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);
goto err_free_label;
}
/*
* TODO: it should not be necessary to reflect the assigned
* base outside of the GPIO subsystem. Go over drivers and
* see if anyone makes use of this, else drop this and assign
* a poison instead.
*/
gc->base = base;
}
gdev->base = base;
ret = gpiodev_add_to_list(gdev);
if (ret) {
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);
goto err_free_label;
}
for (i = 0; i < gc->ngpio; i++)
gdev->descs[i].gdev = gdev;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);
BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&gdev->notifier);
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRL
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&gdev->pin_ranges);
#endif
if (gc->names)
ret = gpiochip_set_desc_names(gc);
else
ret = devprop_gpiochip_set_names(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_from_list;
ret = gpiochip_alloc_valid_mask(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_from_list;
ret = of_gpiochip_add(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_free_gpiochip_mask;
ret = gpiochip_init_valid_mask(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_of_chip;
trace_android_vh_gpio_block_read(gdev, &block_gpio_read);
if (!block_gpio_read) {
for (i = 0; i < gc->ngpio; i++) {
struct gpio_desc *desc = &gdev->descs[i];
if (gc->get_direction && gpiochip_line_is_valid(gc, i)) {
assign_bit(FLAG_IS_OUT,
&desc->flags, !gc->get_direction(gc, i));
} else {
assign_bit(FLAG_IS_OUT,
&desc->flags, !gc->direction_input);
}
}
}
ret = gpiochip_add_pin_ranges(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_of_chip;
acpi_gpiochip_add(gc);
machine_gpiochip_add(gc);
ret = gpiochip_irqchip_init_valid_mask(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_acpi_chip;
ret = gpiochip_irqchip_init_hw(gc);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_acpi_chip;
ret = gpiochip_add_irqchip(gc, lock_key, request_key);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_irqchip_mask;
/*
* By first adding the chardev, and then adding the device,
* we get a device node entry in sysfs under
* /sys/bus/gpio/devices/gpiochipN/dev that can be used for
* coldplug of device nodes and other udev business.
* We can do this only if gpiolib has been initialized.
* Otherwise, defer until later.
*/
if (gpiolib_initialized) {
ret = gpiochip_setup_dev(gdev);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_irqchip;
}
return 0;
err_remove_irqchip:
gpiochip_irqchip_remove(gc);
err_remove_irqchip_mask:
gpiochip_irqchip_free_valid_mask(gc);
err_remove_acpi_chip:
acpi_gpiochip_remove(gc);
err_remove_of_chip:
gpiochip_free_hogs(gc);
of_gpiochip_remove(gc);
err_free_gpiochip_mask:
gpiochip_remove_pin_ranges(gc);
gpiochip_free_valid_mask(gc);
err_remove_from_list:
spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags);
list_del(&gdev->list);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);
err_free_label:
kfree_const(gdev->label);
err_free_descs:
kfree(gdev->descs);
err_free_dev_name:
kfree(dev_name(&gdev->dev));
err_free_ida:
ida_free(&gpio_ida, gdev->id);
err_free_gdev:
/* failures here can mean systems won't boot... */
pr_err("%s: GPIOs %d..%d (%s) failed to register, %d\n", __func__,
gdev->base, gdev->base + gdev->ngpio - 1,
gc->label ? : "generic", ret);
kfree(gdev);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(gpiochip_add_data_with_key);base 代表了每个 Bank 的编号,将其赋值;然后通过 gpiodev_add_to_list(gdev) 将这个 gdev 挂到全局的 gpio_devices :
/*
* Add a new chip to the global chips list, keeping the list of chips sorted
* by range(means [base, base + ngpio - 1]) order.
*
* Return -EBUSY if the new chip overlaps with some other chip's integer
* space.
*/
static int gpiodev_add_to_list(struct gpio_device *gdev)
{
struct gpio_device *prev, *next;
if (list_empty(&gpio_devices)) {
/* initial entry in list */
list_add_tail(&gdev->list, &gpio_devices);
return 0;
}
next = list_entry(gpio_devices.next, struct gpio_device, list);
if (gdev->base + gdev->ngpio <= next->base) {
/* add before first entry */
list_add(&gdev->list, &gpio_devices);
return 0;
}
prev = list_entry(gpio_devices.prev, struct gpio_device, list);
if (prev->base + prev->ngpio <= gdev->base) {
/* add behind last entry */
list_add_tail(&gdev->list, &gpio_devices);
return 0;
}
list_for_each_entry_safe(prev, next, &gpio_devices, list) {
/* at the end of the list */
if (&next->list == &gpio_devices)
break;
/* add between prev and next */
if (prev->base + prev->ngpio <= gdev->base
&& gdev->base + gdev->ngpio <= next->base) {
list_add(&gdev->list, &prev->list);
return 0;
}
}
dev_err(&gdev->dev, "GPIO integer space overlap, cannot add chip\n");
return -EBUSY;
}接着就是设置一些 name 字段,配置中断之类的,初始化每个 desc[] 结构的 flags,最后调用:
if (gpiolib_initialized) {
ret = gpiochip_setup_dev(gdev);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_irqchip;
}然后,不出意外的话,返回 0;
这里说一下 gpiochip_setup_dev 调用,这个是在 Gpiolib init 的时候调用 gpiochip_setup_devs:
static int __init gpiolib_dev_init(void)
{
int ret;
/* Register GPIO sysfs bus */
ret = bus_register(&gpio_bus_type);
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("gpiolib: could not register GPIO bus type\n");
return ret;
}
ret = driver_register(&gpio_stub_drv);
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("gpiolib: could not register GPIO stub driver\n");
bus_unregister(&gpio_bus_type);
return ret;
}
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&gpio_devt, 0, GPIO_DEV_MAX, GPIOCHIP_NAME);
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("gpiolib: failed to allocate char dev region\n");
driver_unregister(&gpio_stub_drv);
bus_unregister(&gpio_bus_type);
return ret;
}
gpiolib_initialized = true;
gpiochip_setup_devs();
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC) && IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_GPIO)
WARN_ON(of_reconfig_notifier_register(&gpio_of_notifier));
#endif /* CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC && CONFIG_OF_GPIO */
return ret;
}
core_initcall(gpiolib_dev_init);而这个 gpiochip_setup_devs 对每一个 gpio_devicecs 节点调用:gpiochip_setup_dev:
static void gpiochip_setup_devs(void)
{
struct gpio_device *gdev;
int ret;
list_for_each_entry(gdev, &gpio_devices, list) {
ret = gpiochip_setup_dev(gdev);
if (ret)
dev_err(&gdev->dev,
"Failed to initialize gpio device (%d)\n", ret);
}
}最后到:
static int gpiochip_setup_dev(struct gpio_device *gdev)
{
int ret;
ret = gcdev_register(gdev, gpio_devt);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = gpiochip_sysfs_register(gdev);
if (ret)
goto err_remove_device;
/* From this point, the .release() function cleans up gpio_device */
gdev->dev.release = gpiodevice_release;
dev_dbg(&gdev->dev, "registered GPIOs %d to %d on %s\n", gdev->base,
gdev->base + gdev->ngpio - 1, gdev->chip->label ? : "generic");
return 0;
err_remove_device:
gcdev_unregister(gdev);
return ret;
}
其实就是注册了字符设备,并且添加到了 sysfs;
debug logs:
char dev节点:/sys/bus/gpio/devices
ls -l /sys/bus/gpio/devices
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:52 gpiochip0 -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/f000000.pinctrl/gpiochip0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:52 gpiochip1 -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-00/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pmk8350@0:pinctrl@b000/gpiochip1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:52 gpiochip2 -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-02/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350c@2:pinctrl@8800/gpiochip2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:52 gpiochip3 -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-01/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm7325@1:pinctrl@8800/gpiochip3
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:52 gpiochip4 -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-03/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350b@3:pinctrl@8800/gpiochip4
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:52 gpiochip5 -> ../../../devices/platform/soc/soc:spf_core_platform/soc:spf_core_platform:lpi_pinctrl@3440000/gpiochip5
sysfs节点 /sys/class/gpio
ls -l /sys/class/gpio/
total 0
--w------- 1 root root 4096 2023-09-21 06:53 export
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:53 gpiochip287 -> ../../devices/platform/soc/soc:spf_core_platform/soc:spf_core_platform:lpi_pinctrl@3440000/gpio/gpiochip287
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:53 gpiochip310 -> ../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-03/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350b@3:pinctrl@8800/gpio/gpiochip310
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:53 gpiochip318 -> ../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-01/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm7325@1:pinctrl@8800/gpio/gpiochip318
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:53 gpiochip328 -> ../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-02/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350c@2:pinctrl@8800/gpio/gpiochip328
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:53 gpiochip337 -> ../../devices/platform/soc/c42d000.qcom,spmi/spmi-0/0-00/c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pmk8350@0:pinctrl@b000/gpio/gpiochip337
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 2023-09-21 06:53 gpiochip341 -> ../../devices/platform/soc/f000000.pinctrl/gpio/gpiochip341
--w------- 1 root root 4096 2023-09-21 06:53 unexportdev_dbg(&gdev->dev, "registered GPIOs %d to %d on %s\n", gdev->base, gdev->base + gdev->ngpio - 1, gdev->chip->label ? : "generic");
05-23 16:18:33.460 1 1 E gpiochip0: (f000000.pinctrl): william_gpio added GPIO chardev (254:0)
05-23 16:18:33.460 1 1 E gpiochip0: william_gpio registered GPIOs 341 to 511 on f000000.pinctrl
05-23 16:18:35.347 357 357 E gpiochip1: (c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pmk8350@0:pinctrl@b000): william_gpio added GPIO chardev (254:1)
05-23 16:18:35.347 357 357 E gpiochip1: william_gpio registered GPIOs 337 to 340 on c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pmk8350@0:pinctrl@b000
05-23 16:18:35.351 357 357 E gpiochip2: (c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350c@2:pinctrl@8800): william_gpio added GPIO chardev (254:2)
05-23 16:18:35.351 357 357 E gpiochip2: william_gpio registered GPIOs 328 to 336 on c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350c@2:pinctrl@8800
05-23 16:18:35.361 357 357 E gpiochip3: (c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm7325@1:pinctrl@8800): william_gpio added GPIO chardev (254:3)
05-23 16:18:35.361 357 357 E gpiochip3: william_gpio registered GPIOs 318 to 327 on c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm7325@1:pinctrl@8800
05-23 16:18:35.362 357 357 E gpiochip4: (c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350b@3:pinctrl@8800): william_gpio added GPIO chardev (254:4)
05-23 16:18:35.362 357 357 E gpiochip4: william_gpio registered GPIOs 310 to 317 on c42d000.qcom,spmi:qcom,pm8350b@3:pinctrl@8800
09-21 01:52:25.519 758 758 E gpiochip5: (soc:spf_core_platform:lpi_pinctrl@3440000): william_gpio added GPIO chardev (254:5)
09-21 01:52:25.519 758 758 E gpiochip5: william_gpio registered GPIOs 287 to 309 on soc:spf_core_platform:lpi_pinctrl@3440000
chip base ngpio gdev->chip->label
gpiochip0 341 170 f000000.pinctrl
gpiochip1 337 3 pmk8350@0:pinctrl@b000
gpiochip2 328 8 pm8350c@2:pinctrl@8800
gpiochip3 318 9 pm7325@1:pinctrl@8800
gpiochip4 310 7 pm8350b@3:pinctrl@8800
gpiochip5 287 22 lpi_pinctrl@3440000个人理解,因为不知道这个 init 和我们的对接底层的驱动的 init 谁先执行到,所以用了一个变量 gpiolib_initialized 来表示当前的 Gpiolib 是不是已经完成了相关的字符设备的注册,如果是 Gpiolib 先去 init 的话,那么 gpiolib_initialized ture,芯片对接底层的部分错过 gpio_chip setup 的机会,所以需要重新调用这个 gpiochip_setup_dev 接口,反之 OK;
到这里,对接底层驱动的部分基本上 OK 了,小伙伴们需要按照自己芯片的 Specific 去做自己的 gpio_chip 结构并最终通过 gpiochip_add_data 添加到 Gpiolib 子系统中;
还有一点需要注意到的是,小伙伴们需要自行定义一些结构,来获得并表示自己 Bank 的虚拟地址等等,这样才能操作到实际的硬件寄存器;
4,gpiolib 向上提供的操作接口
两种不同的gpio框架:
* descriptor-based interface: 基于描述符的接口, 新框架, 官方推荐;
* legacy integer-based interface: 基于整数的接口;
4.1 基于描述符的gpio在dts中使用
参考:
Documentation/gpio/board.txt
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
foo_device {
compatible = "acme,foo";
...
led-gpios = <&gpio 15 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>, /* red */
<&gpio 16 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>, /* green */
<&gpio 17 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; /* blue */
power-gpio = <&gpio 18 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
};
struct gpio_desc *red, *green, *blue, *power;
red = gpiod_get_index(dev, "led", 0);
green = gpiod_get_index(dev, "led", 1);
blue = gpiod_get_index(dev, "led", 2);
power = gpiod_get(dev, "power");
gpiod_direction_output(red, 1);
gpiod_direction_output(green, 1);
gpiod_direction_output(blue, 1);
gpiod_direction_output(power, 1);
gpiod_put(red); //释放gpio口;dts中gpio label的写法: name-gpios, 其中name是gpiod_get*()函数里的第二个参数;
The led GPIOs will be active-high, while the power GPIO will be active-low;
gpiod_is_active_low(power); 为true;
4.2 基于整数的gpio在dts中使用
device_node {
...
gpio_name = <&tlmm 99 0>;
...
}
int gpio_99 = of_get_named_gpio_flags(dev->of_node, "gpio_name", 0, NULL);
gpio_request(gpio_99, "gpio_name"); //通过gpio号申请gpio
gpio_direction_output(gpio_99, 1); //设置gpio_99输出,初始值为1
gpio_set_value(gpio_99, 0); //设置gpio_99值为0
gpio_free(gpio_99);
gpio_get_value(gpio_99, 0); //获取gpio_99的值这种方法目前最常用;
gpio_request()流程:
gpio_request()
*desc = gpio_to_desc(gpio);
gpiod_request(desc, label);
gpiod_request_commit(desc, label);
offset = gpio_chip_hwgpio(desc);
gc->request(gc, offset);
pl061->gc.request = gpiochip_generic_request;
pinctrl_gpio_request(gc->gpiodev->base + offset); //drivers/pinctrl/core.c
pin = gpio_to_pin(range, gpio);
pinmux_request_gpio(pctldev, range, pin, gpio);
pin_request(pctldev, pin, owner, range);
ops->gpio_request_enable(pctldev, gpio_range, pin);可以看到GPIO子系统是通过pinctrl子系统来实现的。
gpio_direction_output()流程:
gpio_direction_output()
gpiod_direction_output_raw(gpio_to_desc(gpio), value);
gpiod_direction_output_raw_commit(desc, value);
*gc = desc->gdev->chip;
gc->direction_output(gc, gpio_chip_hwgpio(desc), val);
pl061->gc.direction_output = pl061_direction_output;4.3 Device-managed variants函数
代码路径:drivers/gpio/gpiolib-devres.c
struct gpio_desc *devm_gpiod_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id,
enum gpiod_flags flags)
struct gpio_desc *devm_gpiod_get_index(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
unsigned int idx,
enum gpiod_flags flags)
struct gpio_desc *devm_gpiod_get_optional(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
enum gpiod_flags flags)
struct gpio_desc * devm_gpiod_get_index_optional(struct device *dev,
const char *con_id,
unsigned int index,
enum gpiod_flags flags)释放gpio:
void gpiod_put(struct gpio_desc *desc);
void devm_gpiod_put(struct device *dev, struct gpio_desc *desc); 4.4 新旧框架的相互转换
gpio与gpio_desc结构体的相互转换:
static struct gpio_desc gpio_desc[ARCH_NR_GPIOS]; //gpiolib.c
gpio_to_desc(unsigned gpio)
&gpio_desc[gpio] //这里的gpio_desc是同名结构体的数组;
int desc_to_gpio(const struct gpio_desc *desc) //gpiolib.c
return desc - &gpio_desc[0];参考链接:
Linux GPIO 驱动 (gpiolib)_devm_gpiochip_add_data-CSDN博客
linux gpio学习笔记(gpiolib)_devm_gpiod_get_verdicty的博客-CSDN博客