1、动态sql:
1、if标签:
mapper接口:
//if 标签 多条件查询
List<Car> selectByMultiConditional(@Param("brand") String brand,@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,@Param("carType") String carType);mapper映射文件:
<select id="selectByMultiConditional" resultType="Car">
select *
from t_car
where 1=1
<!-- if标签中的test的属性是必须的
if标签中的test的属性值是true或者是false
如果是ture 拼接if标签里面的sql语句
test属性中可以使用的数据:
如果使用啦Param的注解 那么只能只用Param的注解里面的参数
如果没有使用Param的注解的话,那么使用的是可以是Param1 param2... 或者arg0 arg1...
如果传递的不是某一个属性值而是对象,那么可以使用的数据只能是对象里面的字段
-->
<if test="brand !=null and brand!=''">
and brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</if>
<if test="guidePrice !=null and guidePrice!=''">
and guide_price > #{guidePrice}
</if>
<if test="carType !=null and carType!=''">
and car_type =#{carType}
</if>
</select>
测试类:
/**
* 使用if标签多条件查询
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> carList = mapper.selectByMultiConditional(null,null,null);//什么参数也没有
carList.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("--------------");
List<Car> carList1 = mapper.selectByMultiConditional("保时捷", 100.0, null);//两个参数
carList1.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("--------------");
List<Car> carList2 = mapper.selectByMultiConditional("比亚迪", 25.0, "混动");
carList2.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
2、where标签:
where标签的作用:让where子句更加动态智能。
- 所有条件都为空时,where标签保证不会生成where子句。
- 自动去除某些条件前面多余的and或or。
mapper接口:
//if 和 where标签一起使用
List<Car> selectByMultiConditionalWithWhere(@Param("brand") String brand,@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,@Param("carType") String carType);mapper映射文件:
<select id="selectByMultiConditionalWithWhere" resultType="Car">
select *
from t_car
<!--
where 标签的使用可以使where的语句更加灵活
如果所有的条件都不成立,那么就不会有where语句
真好 也不用拼1=1 啦
-->
<where>
<if test="brand !=null and brand!=''">
and brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</if>
<if test="guidePrice !=null and guidePrice!=''">
and guide_price > #{guidePrice}
</if>
<if test="carType !=null and carType!=''">
and car_type =#{carType}
</if>
</where>
</select>测试类:
/**
* 使用if 和 where 标签多条件查询
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> carList = mapper.selectByMultiConditionalWithWhere(null,null,null);//什么参数也没有
carList.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("--------------");
List<Car> carList1 = mapper.selectByMultiConditionalWithWhere("保时捷", 100.0, null);//两个参数
carList1.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("--------------");
List<Car> carList2 = mapper.selectByMultiConditionalWithWhere("比亚迪", 25.0, "混动");
carList2.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("--------------");
List<Car> carList3 = mapper.selectByMultiConditionalWithWhere(null, 100.0, null);
carList3.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
}
总结:
使用where的标签的话可以去where语句的前面的and或者or,但是不可去除条件语句的后面的and或者or
3、 trim标签:
trim标签的属性:
- prefix:在trim标签中的语句前添加内容
- suffix:在trim标签中的语句后添加内容
- prefixOverrides:前缀覆盖掉(去掉)
- suffixOverrides:后缀覆盖掉(去掉)
mapper接口:
<select id="selectByMultiConditionalWithTrim" resultType="Car">
select *
from t_car
<!--
prefix: 在trim标签的内容的前面加上 前缀
suffix: 在trim标签的内容的后面加上 后缀
prefixOverrides: 将删除trim标签 指定的前缀
suffixOverrides: 删除trim标签 指定的后缀
-->
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="or|and">
<if test="brand !=null and brand!=''">
brand like "%"#{brand}"%" and
</if>
<if test="guidePrice !=null and guidePrice!=''">
guide_price > #{guidePrice} and
</if>
<if test="carType !=null and carType!=''">
car_type =#{carType}
</if>
</trim>
</select>测试和接大差不差,就不复制粘贴啦,主要是看Trim标签怎么使用的!
4、set标签:
主要使用在update语句当中,用来生成set关键字,同时去掉最后多余的“,”
比如我们只更新提交的不为空的字段,如果提交的数据是空或者"",那么这个字段我们将不更新。
mapper接口:
//set 标签 通常用于更新操作
int updateCarWithSetById(Car car);
mapper映射文件:
<update id="updateCarWithSetById">
update t_car
<set>
<if test="carNum != null and carNum != ''">car_num = #{carNum},</if>
<if test="brand != null and brand != ''">brand = #{brand},</if>
<if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''">guide_price = #{guidePrice},</if>
<if test="produceTime != null and produceTime != ''">produce_time = #{produceTime},</if>
<if test="carType != null and carType != ''">car_type = #{carType},</if>
</set>
where
id =#{id}
</update>测试方法:
//测试 set标签
@Test
public void test5(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
int count = mapper.updateCarWithSetById(new Car(169L, "凯迪拉克", null, 12.5, null, "燃油"));
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}5、choose when otherwise:
语法格式:
<choose>
<when></when>
<when></when>
<when></when>
<otherwise></otherwise>
</choose>相当于java中的if-else 只有一个分支会被执行!!
需求:先根据品牌查询,如果没有提供品牌,再根据指导价格查询,如果没有提供指导价格,就根据生产日期查询。
mapper接口:
//choose when otherwise
/*需求:先根据品牌查询,如果没有提供品牌,再根据指导价格查询,如果没有提供指导价格,就根据生产日期查询。*/
List<Car> selectByChoose (@Param("brand") String brand,@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,@Param("produceTime") String produceTime);mapper映射文件:
<select id="selectByChoose" resultType="Car">
select *
from t_car
<where>
<choose>
<when test="brand != null and brand != ''">brand = #{brand}</when>
<when test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''">guide_price = #{guidePrice}</when>
<otherwise>produce_time = #{produceTime}</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>测试类:
//测试 choose when otherwise
@Test
public void test6(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> carList = mapper.selectByChoose("比亚迪汉", null, "2000-01-02");
carList.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("-------------------");
List<Car> carList1 = mapper.selectByChoose(null, 120.0, "2000-01-02");
carList1.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
System.out.println("-------------------");
List<Car> carList2 = mapper.selectByChoose(null, null, "2000-01-02");
carList2.forEach(car -> {
System.out.println(car);
});
}测试结果:
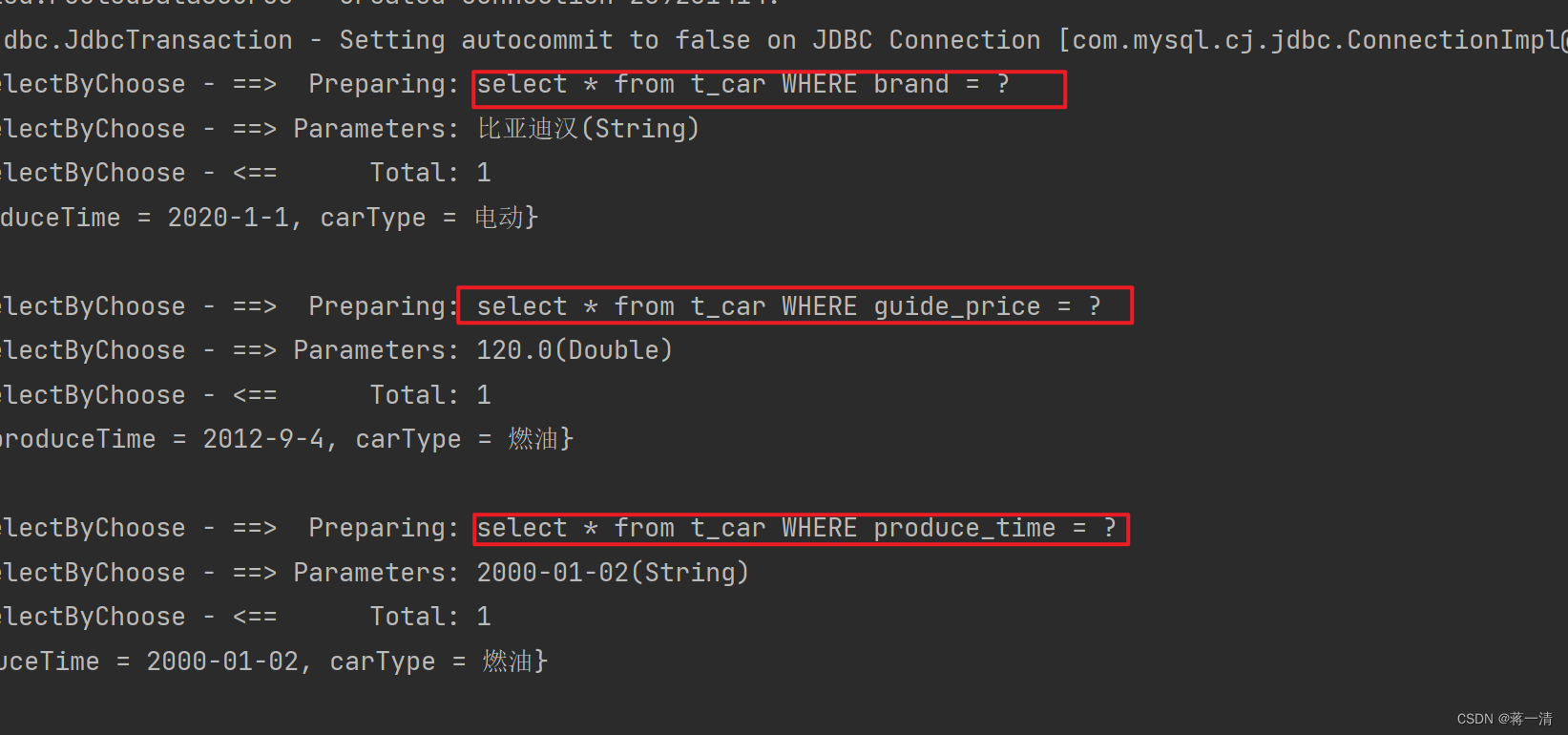
这里的sql语句可以很直观的看出来,这个choose的特点就是只有一个条件会被执行,即使其传递的参数也符合要求。
6、模糊查询的写法:
方法一:
brand like '%${brand}%'
方法二:
brand like concat('%',#{brand},'%')
方式三:
brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
经常使用方式三!
7、foreach标签:
(1)批量删除:
mapper接口:
//foreach 通过ids来批量删除
int deleteByIdsUseForeach(@Param("ids") Long[] ids);mapper映射文件:
<delete id="deleteByIdsUseForeach">
delete
from t_car
<!--
foreach 标签的属性 :
collection 用来指定是数组还是集合
item 代表数组或者集合中的元素
separtor 循环之间的分割符
-->
where id in (
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," >
#{id}
</foreach>
)
</delete>小括号也可以不写 就是 in(....)
<delete id="deleteByIdsUseForeach">
delete
from t_car
<!--
foreach 标签的属性 :
collection 用来指定是数组还是集合
item 代表数组或者集合中的元素
separtor 循环之间的分割符
open:foreach标签中所有内容的开始
close:foreach标签中所有内容的结束
-->
where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>测试类:
//测试批量删除
@Test
public void test7(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Long[] ids ={198L,199L,200L};
int count = mapper.deleteByIdsUseForeach(ids);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}