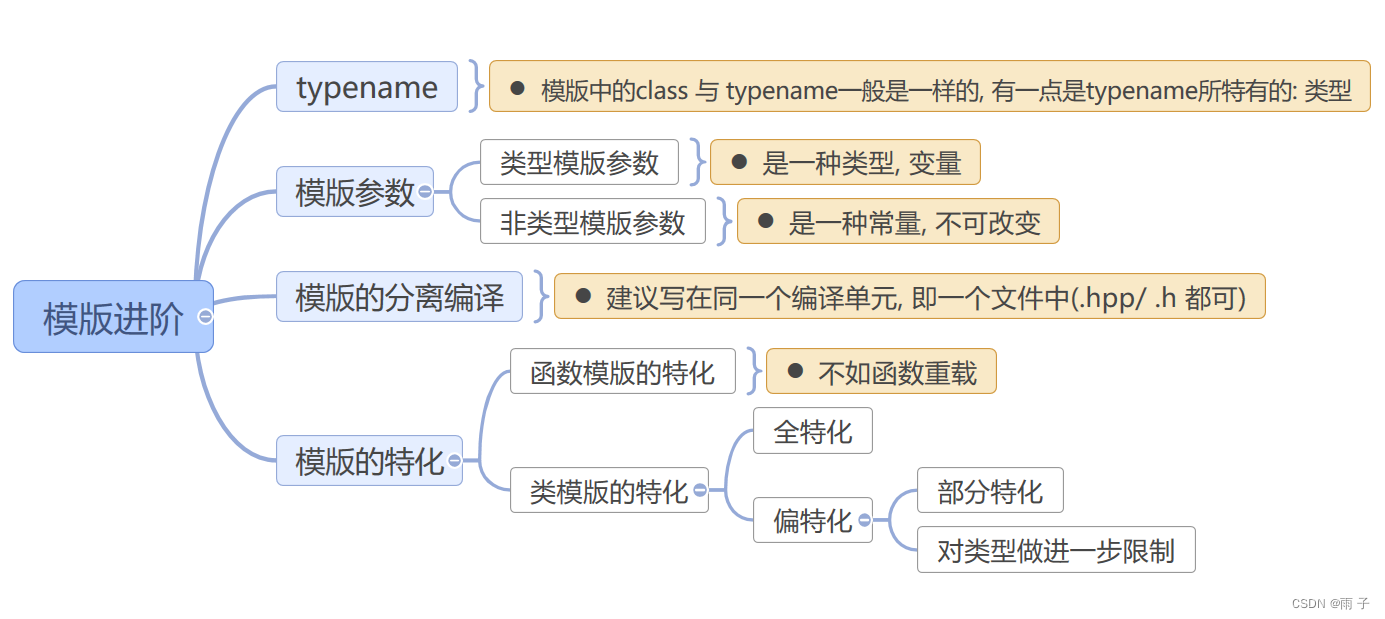
模版进阶
- 模版中 class 与 typename
- 非类型模版参数
- 模版的分离编译
- 模版的特化
- 函数模版的特化
- 类模板的特化
- 1. 全特化
- 2.偏特化

模版中 class 与 typename
一般情况下, 我们定义一个模版, 模版中的 class/ typename 的意义是一样的.
但是, 有一种情况除外👇👇👇
template<class Container>
void Print(const Container& v)
{
Continer::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
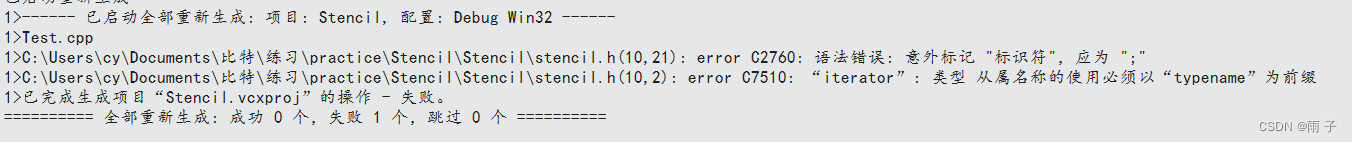
🗨️这是为什么呢?
- 首先,
iterator 迭代器是属于类的一种类型, 我们要指定类域 ⇒ 即Continer应该是一种类型才对
其次,编译器是从上到下编译的, 所以此时模版还没实例化⇒ 编译器不清楚Continer是一种类型还是一种对象?
编译器为什么会有这种疑惑呢?
因为用 :: 调用内部成员有两种方式: 1. 类型 2.静态成员对象
此时我们这里需要的是类型⇒ 所以, 我们需要在前面加上typename, 从而告诉编译器虽然这里还没有实例化, 但是这里是一种类型👇👇👇
template<class Container>
void Print(const Container& v)
{
typename Container::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
非类型模版参数
🗨️根据前面的学习, 我们知道了模版的参数可以是 类型, 容器适配器等, 它们都是一种变量, 是一种类型~~, 有没有一种模版参数是常量的, 不可改变的呢?
- 其实, 模板参数是分两类的:
- 类型模版参数 — — 在模版参数中跟在class/ typename的后面充当一种
类型 - 非类型模版参数 — — 用
常量来充当模版的一个参数, 在函数/ 类中就当做一个常量使用
- 类型模版参数 — — 在模版参数中跟在class/ typename的后面充当一种
构造一个静态数组来练练手:
namespace muyu
{
template<class T, size_t N = 10>
class Array
{
public:
Array()
{
}
T& operator[](size_t pos)
{
return _arr[pos];
}
const T& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
return _arr[pos];
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
private:
T _arr[N];
size_t _size = N;
};
}
void test_Array()
{
muyu::Array<int, 10> arr;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
arr[i] = i;
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_Array();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
总结:
- 非类型模版参数是常量,
不能修改 - 非类型模版参数必须是
整形家族
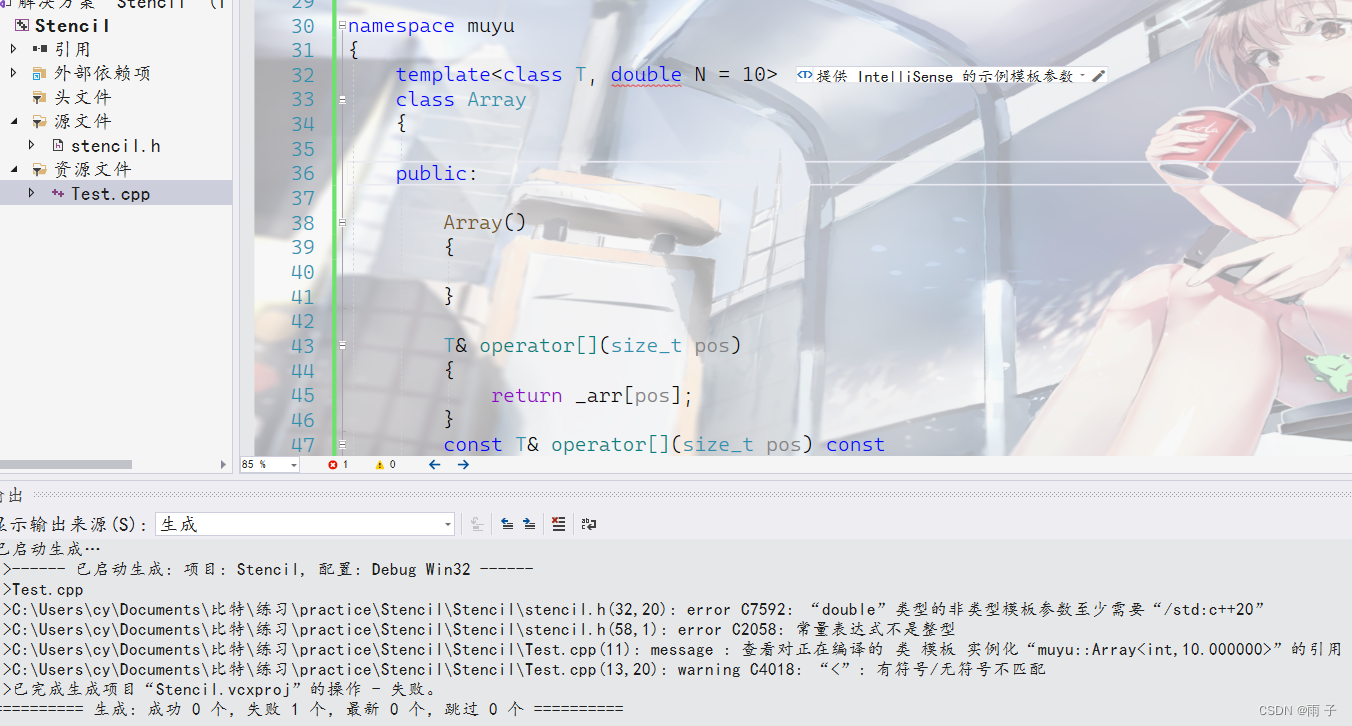
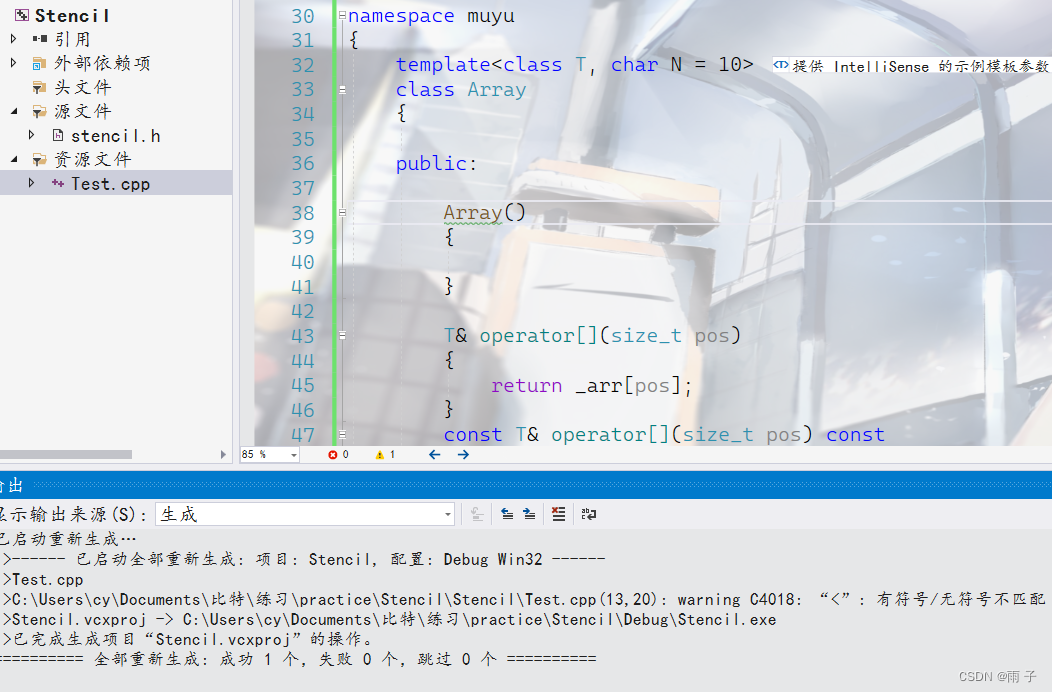
- 非类型模版参数的应用
array数组是非常的鸡肋, 跟普通的数组没有什么两样, 还是C++11更新的😥😥😥
模版的分离编译
🗨️什么是分离编译?
- 一个程序由多个源文件共同实现的, 每个源文件单独生成目标文件. 最后将所有的目标文件链接起来形成一个统一的可执行文件的过程.
接下来, 我们来看一下模版的分离编译的情况:
// stencil.h
template<class T>
// 声明
T& Add(const T& x, const T& y);
// implement.cpp
// 定义
template<class T>
T Add(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x + y;
}
// main.cpp
int main()
{
Add(1, 2);
return 0;
}

🗨️为什么模版的分离编译会出现 链接错误 ?
- 首先, 编译的四个阶段 :
预处理, 编译, 汇编, 链接
编译阶段 — — 对代码进行语法分析, 语义分析, 如果没有什么问题, 就生成汇编
链接阶段 — — 将多个.o文件链接形成一个目标文件, 同时检查地址问题
比如: 普通函数的声明与定义分离:
编译阶段 — — 如果语法检查, 语义检查没什么问题, 虽然定义没有, 但可以做一个承诺 -- 它的定义是有的, 先让它过去, 等链接阶段在深层次检查
链接阶段 — — 进一步检查是否有定义(地址)
🗨️普通函数是可以的, 为啥模版的分离编译有问题?- 先搞清楚, 普通函数的参数类型是已知的, 而模版参数是未知的 ⇐ 因为还没有模版实例化.
C++编译器在处理 函数模版 和 类模版的时候, 要进行实例化函数模版 和 类模版, 要求编译器在实例化模版时必须在上下文可以查看到其定义实体; 而反过来, 在看到实例化模版之前, 编译器对模版的定义是不做处理的. 原因很简单, 编译器怎么会预先知道typename实参是什么呢?
- 先搞清楚, 普通函数的参数类型是已知的, 而模版参数是未知的 ⇐ 因为还没有模版实例化.
🗨️那怎么样才能实现模版的分离编译呢?
- 1. 在定义的地方
显示实例化
不推荐这种, 因为不同类型就要显示实例化多次 ⇒ 那么就失去了模版的意义~~
// stencil.h
template<class T>
// 声明
T& Add(const T& x, const T& y);
// implement.cpp
// 定义
template<class T>
T Add(const T& x, const T& y)
{
// 显示实例化
template
class Add<int, int>
return x + y;
}
// main.cpp
int main()
{
Add(1, 2);
return 0;
}
- 将模版的声明与定义写在同一个文件中, 文件可以命名为
.hpp 或 .h都是可以的
模版的特化
先看下面的例子👇👇👇
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 函数模板 -- 参数匹配
template<class T>
bool Less(T left, T right)
{
return left < right;
}
int main()
{
cout << Less(1, 2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果错误
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1
1
0
由于我们传的是 地址, 属于 内置类型 && 我们不能改变 内置类型的比较规则 ⇒ 就需要对模板进行特化。即:在原模板类的基础上,针对特殊类型所进行特殊化的实现方式。
模板特化中分为函数模板特化与类模板特化。
函数模版的特化
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 函数模板 -- 参数匹配
template<class T>
bool Less(T left, T right)
{
return left < right;
}
// 函数模版的特化 -- Date*
template<>
bool Less<Date*>(Date* left, Date* right)
{
return *left < *right;
}
int main()
{
cout << Less(1, 2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl; // 这个时候改变了比较的类型
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1
1
1
- 函数模版的特化离不开原有模版
- 函数模版的特化的写法:
template<>函数名后面要跟上特化的类型, 然后改变里面进行比较的类型 - 函数模版的特化, 还不如写一个特殊类型的同名函数和原函数模版构成
函数重载
-
函数模版的特化, 还不如写一个函数重载👇👇👇
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 函数模板 -- 参数匹配
template<class T>
bool Less(T left, T right)
{
return left < right;
}
// 函数的重载
bool Less(Date* d1, Date* d2)
{
return *d1 < *d2;
}
int main()
{
cout << Less(1, 2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl; // 这个时候改变了比较的类型
return 0;
}
类模板的特化
函数模版的特化 可以用 函数重载 代替, 难道类模版的特化 也可以用 类的重载 来代替?
打你一耳光哦, 你听过类的重载吗~~
当然不行的啦
类模板的特化分为两种, 全特化 和 偏特化
1. 全特化
全特化, 顾名思义, 是 对类模板中的所有参数都 确定化
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<class T1, class T2> " << endl;
}
};
// 类模板的全特化
template<>
class Date<int, double>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<int, doule>" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Date<int, int> d1;
Date<int, double> d2;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Date<class T1, class T2>
Date<int, doule>
妙用:👇👇👇
// 优先级队列, 默认是大堆
namespace muyu
{
template <class T, class Continer = std::vector<T>, class Compare = Less<T> >
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if( com(_con[parent], _con[child]) )
{
std::swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
// 在内部更新child 和 parent
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
// 找到孩子中大的那一个
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]) )
{
child++;
}
if ( com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
priority_queue()
{
}
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
// 一股脑地倒进来
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
// 建堆
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AjustDown(i);
}
}
void push(const T& val = T())
{
_con.push_back(val);
AjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
std::swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AjustDown(0);
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.size() == 0;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Continer _con;
};
}
// 日期类
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 日期类重载留插入
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
// 仿函数
template <class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
// 全特化
template <>
class Less<Date*>
{
public:
bool operator()(const Date* x, const Date* y)
{
return *x < *y;
}
};
void test()
{
muyu::priority_queue<Date*> pq;
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 27));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 28));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 29));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 1));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2023-9-29 2023-9-28 2023-9-27 2023-9-1
这样的好处:
- 传参类型如果是
T, 那么就按照T来进行比较; 如果传参类型是Date*, 那么就按照Date来进行比较 - 其实没有 模版的特化, 我们无法同时写出
T 和 Date*的一个仿函数.
2.偏特化
偏特化又有两种形式: 部分特化 和 对参数做进一步限制
- 部分特化
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<class T1, class T2> " << endl;
}
};
// 类模板的偏特化
template<class T1>
class Date<T1, double>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<T1, double>" << endl;
}
};
// 类模板的偏特化
template<class T1>
class Date<T1, int&>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<T1, int&>" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Date<int, int> d1;
Date<int, double> d2;
Date<int, int&> d3;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Date<class T1, class T2>
Date<T1, double>
Date<T1, int&>
- 对参数做进一步限制
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<class T1, class T2> " << endl;
}
};
// 类模板的偏特化
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date<T1*, T2*>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<T1*, T2*>" << endl;
}
};
// 类模板的偏特化
template<class T1, class T2>
class Date<T1&, T2&>
{
public:
Date()
{
cout << "Date<T1&, T2&>" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Date<int, int> d1;
Date<int*, double*> d2;
Date<int& , int&> d3;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Date<class T1, class T2>
Date<T1*, T2*>
Date<T1&, T2&>
那么, 我们可以把所有 有关迭代器的比较 特化成 迭代器指向内容的比较, 从而达到我们比较的目的
// 优先级队列, 默认是大堆
namespace muyu
{
template <class T, class Continer = std::vector<T>, class Compare = Less<T> >
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if( com(_con[parent], _con[child]) )
{
std::swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
// 在内部更新child 和 parent
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
// 找到孩子中大的那一个
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]) )
{
child++;
}
if ( com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
priority_queue()
{
}
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
// 一股脑地倒进来
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
// 建堆
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AjustDown(i);
}
}
void push(const T& val = T())
{
_con.push_back(val);
AjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
std::swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AjustDown(0);
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.size() == 0;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Continer _con;
};
}
// 日期类
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 日期类重载留插入
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
// 仿函数
template <class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
// 偏特化
template <class T>
class Less<T*>
{
public:
bool operator()(const T* x, const T* y)
{
return *x < *y;
}
};
void test()
{
muyu::priority_queue<Date*> pq;
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 27));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 28));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 29));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 9, 1));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
模版的特化总结:
- 模版的特化离不开原模版, 不能独立存在
- 特化是做特殊化处理, 具体情况具体使用
弟子曰:一友常易动气责人。
阳明曰:学须反己。若徒责人,只见得人不是,不见自己非;若能反己,方见自己有许多未尽处,奚暇责人?
译文:
弟子说:有个朋友常常生气责怪别人。
先生说:如果只是责备别人,看不到自己的不足,那自己将无法进步,意识到这一点,怎么有空去指责别人呢?
心理学上有个说法叫:偏颇的思维定式。
如果事情成功了,人们倾向于这是自己的功劳。
如果事情做得很差,人们则认为这是别人的问题。
把问题归咎于别人,是人的本性。
所以,在某种意义上,反省自己并非一种美德,而是一种对自身偏颇思维的校正。
通过反省,我们才能公正地看待别人和自己。
认清自己,发现自己的问题和缺漏。
以缺为正,补偏救弊,这样才能不断改正,不断成长。