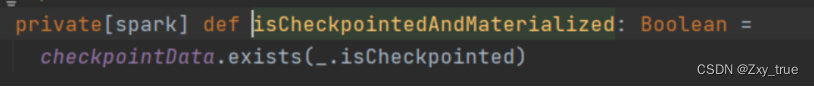
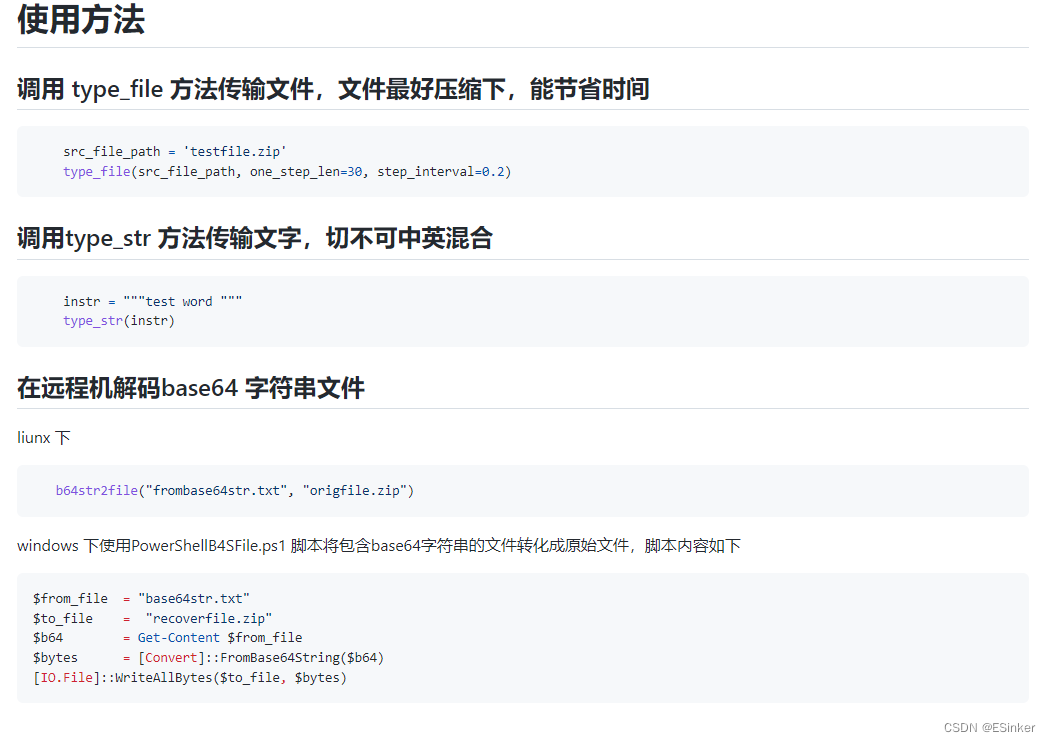
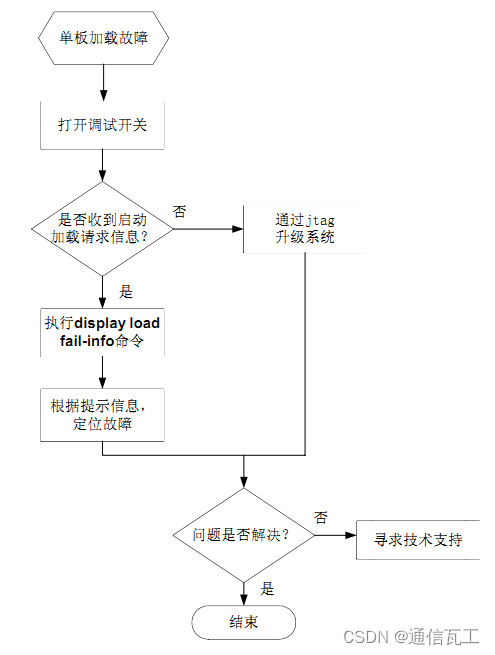
区别一:句子结构
- 口语中结构更为简单,较少使用从句
- 只有少量高频连词(and / but / or / so / because / if / when)
- 正式: While the region was remarkable for its natural beauty, the family experienced seriously disappointing weather, which continued throughout their stay.
- 口语: The place was lovely, but the weather was terrible the whole time.
区别二:被动语态
- 书面语中更常见被动语态
区别三:信息聚集程度
-
在书面语中,需要表达的信息经常会大量汇聚在一起从而写出比较复杂的结构;在口语中信息往往是一块儿一块儿出现的,便于听者理解
-
正式: a carefully constructed progressive three-level course incorporating built-in oral and written revision tests.
-
口语: a course with three-level, it’s carefully put together, it’s progressive, and it has got some oral and written tests.
-
区别四:口语中的前置
- 宾语前置: You can’t get those shirts any more.
- 书面语:倒装的条件(as / if / 否定词 / 副词 / so that)
- 口语:
- always gets it wrong, that woman.
- hasn’t a chance, Fred.
口语语法中的三种特殊疑问句
Declarative questions
- 功能:主要用于表达需要核实自己所讲的内容是否正确的时候
- 在口语中并不总需要疑问句的语序进行疑问表达,声调也可以将陈述句转化为疑问句的功能
- You’re working tomorrow?
- This is your car? = I suppose this is your car, isn’t it?
- When are you going?
You’re going? 不能是 When you’re going?
Echo questions 反问
- 要质疑别人已经说过的内容,可以简单重复对方说的话,注意,升调是比较常见的处理方法
- I’m getting married.
- You’re getting married?
- 【补充】只要质疑别人所说的话中某部分信息时,可以重复其他的部分,需要质疑的部分用疑问词替代即可
- Take a look at that bird.
Take a look at what? - She’s invited 133 people to dinner.
She’s invited how many?
- Take a look at that bird.
- 【补充】如果需要质疑的是对方所说的话中的动词
- 用 what / do what
- She set fire to the garage.
- She what / did what ?
Rhetorical questions 反问
- 不一定在询问未知信息,可能答案很明显或没有答案的问句会出现,功能在于向别人介绍某些信息
- Do you know what time it is?
- Who’s a lovely baby?
- What’s this?
- 【补充】why should … ? How should / would I know?(极具攻击性)
- Didn’t I tell you
口语语法习题
1. formal or informal
1.I 2.× 3.I 4.I 5.I 6.× 7.I 8.I 9.× 10.I 11.× 12.I 13.I 14.×


1. 判断正误(Echo questions)
1.T 2.T 3.F, you’ve bought what 4.F, I’m doing? 5.T

6.T 7.F, she’s going to marry who? 8.T 9.T 10.F, to whom




![[附源码]java毕业设计基于的网上点餐系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/92f7edecd9cf4f93857158c0c9503f0d.png)