🎃欢迎大家前去观看我的算法设计与分析专栏: 算法设计与分析_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客 希望对大家有所帮助!
🎃个人专栏:
🐬 算法设计与分析:算法设计与分析_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐳Java基础:Java基础_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐋c语言:c语言_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐟MySQL:数据结构_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐠数据结构:数据结构_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
💎C++:C++_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🥽C51单片机:C51单片机(STC89C516)_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
💻基于HTML5的网页设计及应用:基于HTML5的网页设计及应用_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🥏python:python_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
欢迎收看,希望对大家有用!
目录
🎯目的:
🎯内容:
🎯代码(Java):
🎯运行结果:
🎯 算法分析:
🎯其他程序语言的实现:
🎐C语言程序:
🎐python程序:
🎐C++程序:
🎯目的:
1)了解贪心算法思想及基本原理;
2)掌握使用贪心算法求解问题的一般特征;
3)能够针对实际问题,能够正确选择贪心策略;
4)能够针对选择的贪心策略,证明算法的正确性;
5)能够根据贪心策略,正确编写代码;
6)能够正确分析算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
🎯内容:
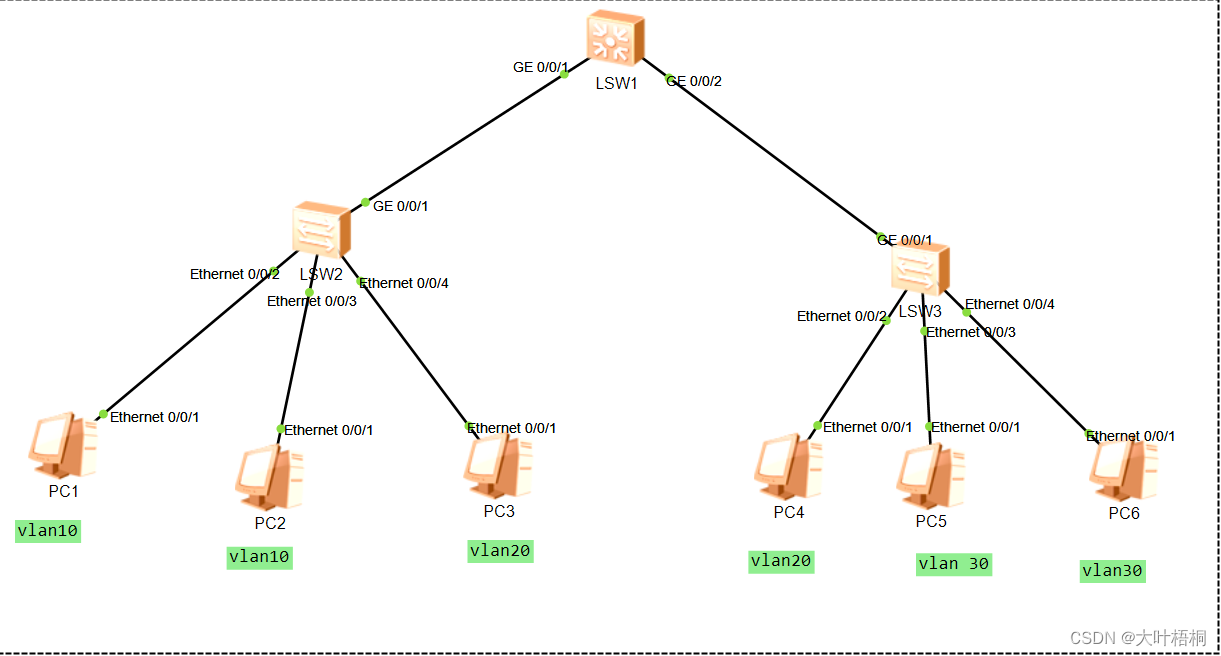
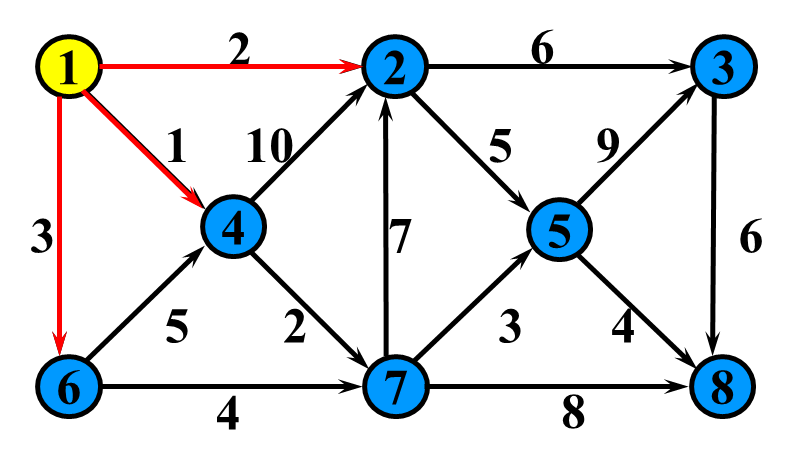
单源最短路径的贪心算法。
测试数据可选用下图,1为源点:
🎯代码(Java):
package one;
public class Three {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int x1[][] = { { 0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6 },
{ 0, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0 }, { 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 4, 0 },
{ 0, 7, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 8 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
int s = 1;// 表示原点
int[] dist = new int[x1.length];// 表示原点到各点的最短距离
boolean[] visited = new boolean[x1.length];
int [] pre=new int[x1.length];//记录最短路径的前驱结点
for (int i = 0; i < x1.length; i++) {// 初始化
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// 初始化为无穷大
visited[i] = false;// 初始化为没有被访问过
pre[i]=-1;//前去初始化为-1
}
dist[s - 1] = 0;// 自身到自身为0
// 找原点到各个顶点的距离
for (int i = 0; i < x1.length; i++) {
int mindist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;// 最短路径
int mindistindex = -1;// 最短路径的索引
// 寻找路径中最短的
for (int j = 0; j < x1.length; j++) {
if (!(visited[j]) && dist[j] < mindist) {
// 更新数据
mindist = dist[j];
mindistindex = j;
}
}
visited[mindistindex] = true;// 将顶点添加到已访问数组中
// 更新最短距离
for (int j = 0; j < x1.length; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && x1[mindistindex][j] != 0 && dist[mindistindex] != Integer.MAX_VALUE
&& dist[mindistindex] + x1[mindistindex][j] < dist[j]) {
dist[j] = dist[mindistindex] + x1[mindistindex][j];// 更新最短距离
pre[j]=mindistindex+1;//记录前驱结点
}
}
}
System.out.printf("顶点: ");
for (int i = 0; i < x1.length; i++) {
System.out.printf((i+1)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("距离: ");
for (int i = 1; i < x1.length; i++) {
System.out.printf(dist[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("前驱: ");
for (int i = 1; i < x1.length; i++) {
System.out.printf(pre[i]+" ");
}
}
🎯运行结果:
🎯 算法分析:
时间复杂度:
- 初始化阶段:需要遍历所有的顶点,时间复杂度为O(n)。
- 最短路径查找阶段:需进行n次迭代,每次迭代需要遍历所有顶点,时间复杂度为O(n^2),因此,总体时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
空间复杂度:
- 使用了四个数组,其中x1占用了O(n^2)的空间,dist,visited,pre占用各自O(n)的空间。因此,空间复杂度为O(n^2)。
需要注意的是,时间复杂度和空间复杂度的分析是基于给定图的规模为n的情况下。在实际应用中,如果图的规模非常大,可以考虑采用优化算法或数据结构来减小时间和空间的开销。
🎯其他程序语言的实现:
注:以下代码均有ai生成,读者如发现bug可以发在评论区,咱们一起解决❤️!
🎐C语言程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define SIZE 8 // 矩阵大小
void dijkstra(int graph[SIZE][SIZE], int source) {
int dist[SIZE]; // 原点到各点的最短距离
bool visited[SIZE]; // 记录节点是否被访问
int pre[SIZE]; // 记录最短路径的前驱结点
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
dist[i] = INT_MAX; // 初始化为无穷大
visited[i] = false; // 初始化为没有被访问过
pre[i] = -1; // 前驱初始化为-1
}
dist[source - 1] = 0; // 自身到自身为0
// 找原点到各个顶点的距离
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
int minDist = INT_MAX; // 最短路径
int minDistIndex = -1; // 最短路径的索引
// 寻找路径中最短的
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && dist[j] < minDist) {
minDist = dist[j];
minDistIndex = j;
}
}
visited[minDistIndex] = true; // 将顶点添加到已访问数组中
// 更新最短距离
for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) {
if (!visited[j] && graph[minDistIndex][j] != 0 && dist[minDistIndex] != INT_MAX &&
dist[minDistIndex] + graph[minDistIndex][j] < dist[j]) {
dist[j] = dist[minDistIndex] + graph[minDistIndex][j]; // 更新最短距离
pre[j] = minDistIndex + 1; // 记录前驱结点
}
}
}
printf("顶点: ");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
printf("%d ", i + 1);
}
printf("\n");
printf("距离: ");
for (int i = 1; i < SIZE; i++) {
printf("%d ", dist[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("前驱: ");
for (int i = 1; i < SIZE; i++) {
printf("%d ", pre[i]);
}
}
int main() {
int graph[SIZE][SIZE] = {
{0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6},
{0, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 4, 0},
{0, 7, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 8},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int source = 1; // 表示原点
dijkstra(graph, source);
return 0;
}
🎐python程序:
import sys
def dijkstra(x1, s):
dist = [sys.maxsize] * len(x1) # 表示原点到各点的最短距离
visited = [False] * len(x1)
pre = [-1] * len(x1) # 记录最短路径的前驱结点
dist[s - 1] = 0 # 自身到自身为0
for _ in range(len(x1)):
mindist = sys.maxsize # 最短路径
mindistindex = -1 # 最短路径的索引
# 寻找路径中最短的
for j in range(len(x1)):
if not visited[j] and dist[j] < mindist:
# 更新数据
mindist = dist[j]
mindistindex = j
visited[mindistindex] = True # 将顶点添加到已访问数组中
# 更新最短距离
for j in range(len(x1)):
if not visited[j] and x1[mindistindex][j] != 0 and dist[mindistindex] != sys.maxsize and dist[mindistindex] + x1[mindistindex][j] < dist[j]:
dist[j] = dist[mindistindex] + x1[mindistindex][j] # 更新最短距离
pre[j] = mindistindex + 1 # 记录前驱结点
print("顶点:", end=" ")
for i in range(len(x1)):
print(i + 1, end=" ")
print()
print("距离:", end=" ")
for i in range(1, len(x1)):
print(dist[i], end=" ")
print()
print("前驱:", end=" ")
for i in range(1, len(x1)):
print(pre[i], end=" ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
x1 = [[0, 2, 0, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6],
[0, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 4, 0],
[0, 7, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 8],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
s = 1 # 表示原点
dijkstra(x1, s)
请注意,Python中没有类似Java中的整型溢出问题,因此使用了
sys.maxsize作为无穷大。另外,Python的索引是从0开始的,所以在输出时顶点和索引都需要加1。希望对你有所帮助!如有其他问题,请随时问我。
🎐C++程序:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int x1[8][8]={{0,2,0,1,0,3,0,0},
{0,0,6,0,5,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,6},
{0,10,0,0,0,0,2,0},
{0,0,9,0,0,0,0,4},
{0,0,0,5,0,0,4,0},
{0,7,0,0,3,0,0,8},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}};
int s=1;
const int n=8;
int dist[n],pre[n];
bool visited[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
dist[i]=INT_MAX;
visited[i]=false;
pre[i]=-1;
}
dist[s-1]=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int mindist=INT_MAX,mindistindex=-1;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(!visited[j]&&dist[j]<mindist){
mindist=dist[j];
mindistindex=j;
}
}
visited[mindistindex]=true;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(!visited[j]&&x1[mindistindex][j]!=0&&dist[mindistindex]!=INT_MAX&&dist[mindistindex]+x1[mindistindex][j]<dist[j]){
dist[j]=dist[mindistindex]+x1[mindistindex][j];
pre[j]=mindistindex+1;
}
}
}
cout<<"顶点: ";
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<i+1<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"距离: ";
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
cout<<dist[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"前驱: ";
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
cout<<pre[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}





![[每周一更]-(第66期):Docker 守护进程说明](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/00aed5725b004cf49fd954a48851ba8a.png#pic_center)