八十七、匿名对象
- 概念:没有名字对象
- 格式 :类名();
- 作用
- 用匿名对象给有名对象初始化的
- 用匿名对象给对象数组初始化的
- 匿名对象作为函数实参使用
示例 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Dog
{
private:
string name;
string color;
int *age;
public:
//无参构造函数
Dog()
{
cout << "Dog::无参构造函数" << endl;
}
//有参构造函数
Dog(string name, string c, int age):name(name),color(c),age(new int(age))
{
cout << "Dog::有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Dog(const Dog &other):name(other.name),color(other.color),age(new int(*other.age))
{
cout << "Dog::拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Dog &operator=(const Dog &other)
{
if(this != &other) //避免自己给自己赋值
{
name = other.name;
color = other.color;
age = new int(*other.age); //深拷贝赋值函数
}
cout << "Dog::拷贝赋值函数" << endl;
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~Dog()
{
cout << "Dog::析构函数" << endl;
}
};
void fun(Dog g)//Dog g = Dog("大黄","lll",6)
{
//函数代码。。。
}
int main()
{
Dog d1 = Dog("大黄","lll",6); //匿名对象给有名对象初始化
Dog d[3] = {Dog("大","lll",6),Dog("黄","lll",6),Dog("大黄","lll",6)};
fun(Dog("大黄","lll",6)); //匿名对象作为函数实参使用
return 0;
}
八十八、友元
88.1 作用
- 可以让其他一些函数或者类访问 另一个类的私有数据成员
- 友元关键字 : friend
88.2 种类
- 全局函数做友元
- 类友元
- 成员函数做友元
88.3 全局函数做友元
- 让全局函数访问一个类私有数据成员。
示例 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Room {
friend void room_friend(Room &r);
private:
string keting;
public:
string zoulang;
Room();
};
Room::Room(){
this->keting = "客厅";
this->zoulang = "走廊";
}
void room_friend(Room &r){
cout << "全局友元函数在访问->" << r.zoulang <<endl;
cout << "全局友元函数在访问->" << r.keting <<endl;
}
int main()
{
Room r1;
room_friend(r1);
return 0;
}
88.4 类做友元
- 一个类去访问另一个类的私有属性。
88.5 成员函数做友元
- 一个类里的成员函数去访问另一个类的私有属性。
88.6 示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Room;
class Friend_Room{
private:
Room *r;
public:
Friend_Room();
void access_room();
};
class Room {
// friend class Friend_Room;
friend void Friend_Room::access_room();
private:
string keting;
public:
string zoulang;
Room();
};
Room::Room(){
this->keting = "客厅";
this->zoulang = "走廊";
}
Friend_Room::Friend_Room(){
this->r = new Room;
cout << "Friend_Room 的 构造函数" << endl;
}
void Friend_Room::access_room(){
cout << "Friend_Room 正在访问 " << this->r->zoulang << endl;
cout << "Friend_Room 正在访问 " << this->r->keting << endl;
}
int main()
{
Friend_Room f_r;
f_r.access_room();
return 0;
}
88.7 注意
- 不要过度使用友元,会降低或者破坏封装性
- 友元不具有交互性,传递性,继承性。
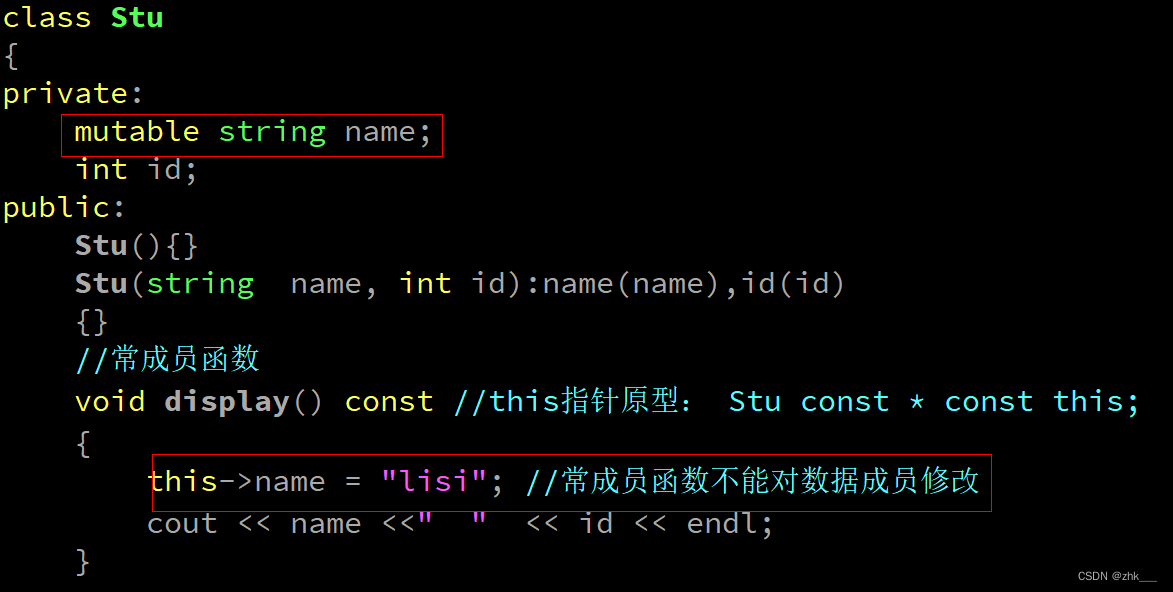
八十九、const修饰的成员函数和对象(常成员函数、常对象)
- 类中所有的成员函数都可以对类中数据成员进行修改操作,
- 如果想设计一个成员函数不能对数据成员修改操作,则需要用const修饰的成员函数实现。
89.1 常成员函数
- 常成员函数 :表示该成员函数不能修改数据成员的值。
- 格式 :
返回值类型 函数名(形参列表) const { 函数体内容; } - 同名的常成员函数和非常成员函数构成重载关系,
- 原因:this指针类型不同
89.2 常对象
- 常对象表示这个对象的数据成员不能被修改。
- 格式: const 类名 对象名;
- 非常对象可以调用常成员函数,也可以调用非常成员函数,优先调用非常成员函数
- 常对象只能调用常成员函数,如果没有常成员函数,则报错
示例 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stu
{
private:
string name;
int id;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(string name, int id):name(name),id(id)
{}
//常成员函数
void display() const //this指针原型: Stu const * const this;
{
//this->name = "lisi"; 常成员函数不能对数据成员修改
cout << name <<" " << id << endl;
}
//非常成员函数
void display() //this指针原型: Stu * const this;
{
this->name = "lisi";
cout << name <<" " << id << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
const Stu s1("zhangsan", 1001); //常对象
s1.display(); //常对象只能调用常成员函数
return 0;
}
89.3 mutable关键字
- mutable修饰成员变量,表示该成员变量可以在常成员函数中被修改 (取消常属性)
九十、运算符重载
- 概念:
运算符重载就是对运算符重新定义,赋予另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型。 - 每种运算符重载都有两种实现方式:
- 成员函数实现运算符重载
- 全局函数实现运算符重载
90.1 算术运算符重载
种类: + - * / %
表达式: L ? R (L 左操作数 ?运算符 R右操作数)
左操作数:可以是左值,可以右值,运算过程中不可以被改变
右操作数:可以是左值,可以右值,运算过程中不可以被改变
结果:右值 (不可以被改变)
- 算术运算符重载实现方式:
-
成员函数实现运算符重载
const 类名 operator#(const 类名 &R) const { 具体实现 }第一个const 表示结果是右值 不能被改变
第二个const 表示右操作数运算过程中不能被改变
第三个const 表示左操作数运算过程中不能被改变 -
全局函数实现运算符重载
const 类名 operator#(const 类名 &L, const 类名 &R) { 具体实现 }
-
示例 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
friend const Person operator+(const Person &L, const Person &R);
private:
int a;
int b;
public:
Person(){}
Person(int a, int b):a(a),b(b){}
//成员函数实现+号运算符重载
// const Person operator+(const Person &p) const
// {
// Person temp;
// temp.a = a + p.a;
// temp.b = b + p.b;
// return temp;
// }
void show()
{
cout << " a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
}
};
//全局函数实现+运算符重载
const Person operator+(const Person &L, const Person &R)
{
Person temp;
temp.a = L.a + R.a;
temp.b = L.b + R.b;
return temp;
}
int main()
{
Person p1(10,10);
Person p2(10,10);
//成员函数
//简化版本
//Person p3 = p1 + p2; //本质上 Person p3 = p1.operator+(p2)
Person p3 = p1 + p2; //本质上 Person p3 = operator+(p1, p2)
p3.show();
return 0;
}
90.2 关系运算符重载
种类: > 、 >= 、 <、 <=、 ==、 !=
表达式: L ? R (L 左操作数 ?运算符 R右操作数)
左操作数:可以是左值,可以右值,运算过程中不可以被改变
右操作数:可以是左值,可以右值,运算过程中不可以被改变
结果: bool类型
- 关系运算符重载实现方式:
- 成员函数实现运算符重载
bool operator#(const 类名 &R) const { 具体实现 } - 全局函数实现运算符重载
bool operator#(const 类名 &L, const 类名 &R) { 具体实现 }
- 成员函数实现运算符重载
示例 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//
class Person
{
friend bool operator>(const Person &L, const Person &R);
private:
int a;
int b;
public:
Person(){}
Person(int a, int b):a(a),b(b){}
//成员函数实现>号运算符重载
// bool operator>(const Person &R) const
// {
// if(a>R.a && b>R.b)
// {
// return true;
// }
// else
// {
// return false;
// }
// }
void show()
{
cout << " a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
}
};
//全局函数实现>号运算符重
bool operator>(const Person &L, const Person &R)
{
if(L.a>R.a && L.b>R.b)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
int main()
{
Person p1(10,10);
Person p2(10,10);
if(p3 > p2) //本质上 p3.operator>(p2)
//本质上 operator(p3,p2)
{
cout <<"p3>p2" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
90.3 赋值运算符重载
种类: = 、+= 、 -= 、*= 、/= 、%=
表达式: L ? R (L 左操作数 ?运算符 R右操作数)
左操作数:是左值,运算过程中要被改变
右操作数:可以是左值,可以右值,运算过程中不可以被改变
结果:自身的引用
- 赋值运算符重载实现方式:
- 成员函数实现运算符重载
类名 &operator#(const 类名 &R) { 具体实现 } - 全局函数实现运算符重载
类名 &operator#(类名 &L, const 类名 &R) { 具体实现 }
- 成员函数实现运算符重载
示例 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
friend Person &operator+=(Person &L,const Person &R);
private:
int a;
int b;
public:
Person(){}
Person(int a, int b):a(a),b(b){}
//成员函数实现+=号运算符重载
// Person &operator+=(const Person &R)
// {
// a += R.a; // a = a + R.a
// b += R.b;
// return *this;
// }
void show()
{
cout << " a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
}
};
//全局函数实现+=号运算符重载
Person &operator+=(Person &L,const Person &R)
{
L.a += R.a; // a = a + R.a
L.b += R.b;
return L;
}
int main()
{
Person p1(10,10);
Person p2(10,10);
p3+=p2; // p3 = p3 + p2 本质上 p3.operator+=(p2)
p3.show();
return 0;
}
小作业
- 整理代码
- 算术运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 赋值运算符
我写的
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stu {
//逻辑运算符重载的全局友元函数
friend bool operator>(const Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend bool operator>=(const Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend bool operator<(const Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend bool operator<=(const Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend bool operator==(const Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend bool operator!=(const Stu &l, const Stu &r);
//赋值运算符重载
friend Stu &operator+=(Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend Stu &operator-=(Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend Stu &operator*=(Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend Stu &operator/=(Stu &l, const Stu &r);
friend Stu &operator%=(Stu &l, const Stu &r);
private:
double high;
double weight;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(double h, double w):high(h),weight(w){}
void show(){
cout << "high = " << this->high << endl;
cout << "weight = " << this->weight << endl;
puts("");
}
//类内实现运算符重载
//算术运算符重载
const Stu operator+(const Stu &s)const{
Stu t;
t.high = this->high + s.high;
t.weight = this->weight + s.weight;
return t;
}
const Stu operator-(const Stu &s)const{
Stu t;
t.high = this->high + s.high;
t.weight = this->weight + s.weight;
return t;
}
const Stu operator*(const Stu &s)const{
Stu t;
t.high = this->high + s.high;
t.weight = this->weight + s.weight;
return t;
}
const Stu operator/(const Stu &s)const{
Stu t;
t.high = this->high + s.high;
t.weight = this->weight + s.weight;
return t;
}
const Stu operator%(const Stu &s)const{
Stu t;
t.high = (int)this->high % (int)s.high;
t.weight = (int)this->weight % (int)s.weight;
return t;
}
//重载赋值运算符
const Stu &operator=(const Stu &s){
this->high = s.high;
this->weight = s.weight;
return *this;
}
};
/*
* 全局函数实现运算符重载
* 访问类的私有属性需要添加为类的友元函数
*/
//逻辑运算符重载
bool operator>(const Stu &l, const Stu &r){
if(l.high > r.high && l.weight > r.weight)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator>=(const Stu &l, const Stu &r){
if(l.high >= r.high && l.weight >= r.weight)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator<(const Stu &l, const Stu &r){
if(l.high < r.high && l.weight < r.weight)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator<=(const Stu &l, const Stu &r){
if(l.high <= r.high && l.weight <= r.weight)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator==(const Stu &l, const Stu &r){
if(l.high == r.high && l.weight == r.weight)
return true;
return false;
}
bool operator!=(const Stu &l, const Stu &r){
if(l.high != r.high && l.weight != r.weight)
return true;
return false;
}
//赋值运算符重载
Stu &operator+=(Stu &l, const Stu &r){
l.high += r.high;
l.weight += r.weight;
return l;
}
Stu &operator-=(Stu &l, const Stu &r){
l.high -= r.high;
l.weight -= r.weight;
return l;
}
Stu &operator*=(Stu &l, const Stu &r){
l.high *= r.high;
l.weight *= r.weight;
return l;
}
Stu &operator/=(Stu &l, const Stu &r){
l.high /= r.high;
l.weight /= r.weight;
return l;
}
Stu &operator%=(Stu &l, const Stu &r){
l.high = (int)l.high % (int)r.high;
l.weight = (int)l.weight % (int)r.weight;
return l;
}
int main()
{
Stu s1(175, 60);
Stu s2(170, 55);
Stu s3 = s1 + s2;
Stu s4 = s1 - s2;
Stu s5 = s1 * s2;
Stu s6 = s1 / s2;
Stu s7 = s1 % s2;
s1.show();
s2.show();
s3.show();
s4.show();
s5.show();
s6.show();
s7.show();
return 0;
}





![Python库学习(九):Numpy[续篇三]:数组运算](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/ca61747b8ddf2c308913aba23ab10a02.png)