文章目录
- 首先回顾一下gin框架的路由如何使用的
- 从源码分析一下gin框架
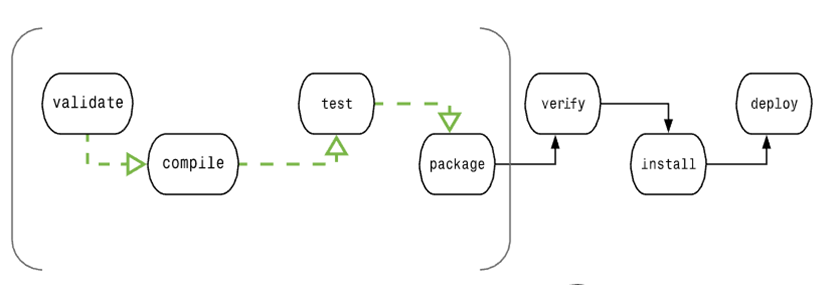
- gin的路由实现
- 前缀树
- 前缀树的实现
- 压缩前缀树--Radix Trie
- Trie VS Map
首先回顾一下gin框架的路由如何使用的
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
//创建一个gin Engine ,Engine实现了net/http包下Handler接口,本质上是一个http Handler
r := gin.Default()
//注册中间件
r.Use(middleware1)
r.Use(middleware2)
//注册一个path为/hello的处理函数,将/hello域名下的get请求路由到后面的handler函数来处理
r.GET("/hello", handler)
r.Run()
}
func middleware1(c *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println("Executing middleware1")
c.Next() //将控制权传递给下一个中间件或者处理函数
//c.Abort() //在请求处理过程中发现错误或异常情况时,立即终止处理并返回错误信息,后续的处理程序或者中间件不在执行
//Executing middleware1
//middle1 end
fmt.Println("middle1 end")
}
func middleware2(c *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println("Executing middleware2")
c.Next()
fmt.Println("middle2 end")
}
func handler(c *gin.Context) {
fmt.Println("Executing handler")
fmt.Println("handler end")
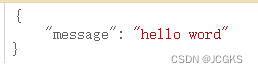
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"message": "hello word"})
}
/*
Executing middleware1
Executing middleware2
Executing handler
handler end
middle2 end
middle1 end
*/
运行程序
在浏览器输入“http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello”可以看到
http的请求有9种,GET\HEAD\POST\PUT\PATCH\DELETE\CONNECT\OPTIONS\TRACE
从源码分析一下gin框架
首先通过“gin.Default()”创建一个Engine实例并附带有“Logger\Recovery”中间件
// Default returns an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
func Default() *Engine {
debugPrintWARNINGDefault()
engine := New()
engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery())
return engine
}
Default()实际上是调用了New(),并使用use注册“Logger\Recovery”两个中间件
func New() *Engine {
debugPrintWARNINGNew()
engine := &Engine{
RouterGroup: RouterGroup{
Handlers: nil,
basePath: "/",
root: true,
},
FuncMap: template.FuncMap{},
RedirectTrailingSlash: true,
RedirectFixedPath: false,
HandleMethodNotAllowed: false,
ForwardedByClientIP: true,
RemoteIPHeaders: []string{"X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"},
TrustedPlatform: defaultPlatform,
UseRawPath: false,
RemoveExtraSlash: false,
UnescapePathValues: true,
MaxMultipartMemory: defaultMultipartMemory,
trees: make(methodTrees, 0, 9),
delims: render.Delims{Left: "{{", Right: "}}"},
secureJSONPrefix: "while(1);",
trustedProxies: []string{"0.0.0.0/0", "::/0"},
trustedCIDRs: defaultTrustedCIDRs,
}
engine.RouterGroup.engine = engine
engine.pool.New = func() any {
return engine.allocateContext(engine.maxParams)
}
return engine
}
New()函数初始化Engine实例并返回,接下来看一下Engine struct都有些什么
type Engine struct {
RouterGroup
// RedirectTrailingSlash enables automatic redirection if the current route can't be matched but a
// handler for the path with (without) the trailing slash exists.
// For example if /foo/ is requested but a route only exists for /foo, the
// client is redirected to /foo with http status code 301 for GET requests
// and 307 for all other request methods.
RedirectTrailingSlash bool
// RedirectFixedPath if enabled, the router tries to fix the current request path, if no
// handle is registered for it.
// First superfluous path elements like ../ or // are removed.
// Afterwards the router does a case-insensitive lookup of the cleaned path.
// If a handle can be found for this route, the router makes a redirection
// to the corrected path with status code 301 for GET requests and 307 for
// all other request methods.
// For example /FOO and /..//Foo could be redirected to /foo.
// RedirectTrailingSlash is independent of this option.
RedirectFixedPath bool
// HandleMethodNotAllowed if enabled, the router checks if another method is allowed for the
// current route, if the current request can not be routed.
// If this is the case, the request is answered with 'Method Not Allowed'
// and HTTP status code 405.
// If no other Method is allowed, the request is delegated to the NotFound
// handler.
HandleMethodNotAllowed bool
// ForwardedByClientIP if enabled, client IP will be parsed from the request's headers that
// match those stored at `(*gin.Engine).RemoteIPHeaders`. If no IP was
// fetched, it falls back to the IP obtained from
// `(*gin.Context).Request.RemoteAddr`.
ForwardedByClientIP bool
// AppEngine was deprecated.
// Deprecated: USE `TrustedPlatform` WITH VALUE `gin.PlatformGoogleAppEngine` INSTEAD
// #726 #755 If enabled, it will trust some headers starting with
// 'X-AppEngine...' for better integration with that PaaS.
AppEngine bool
// UseRawPath if enabled, the url.RawPath will be used to find parameters.
UseRawPath bool
// UnescapePathValues if true, the path value will be unescaped.
// If UseRawPath is false (by default), the UnescapePathValues effectively is true,
// as url.Path gonna be used, which is already unescaped.
UnescapePathValues bool
// RemoveExtraSlash a parameter can be parsed from the URL even with extra slashes.
// See the PR #1817 and issue #1644
RemoveExtraSlash bool
// RemoteIPHeaders list of headers used to obtain the client IP when
// `(*gin.Engine).ForwardedByClientIP` is `true` and
// `(*gin.Context).Request.RemoteAddr` is matched by at least one of the
// network origins of list defined by `(*gin.Engine).SetTrustedProxies()`.
RemoteIPHeaders []string
// TrustedPlatform if set to a constant of value gin.Platform*, trusts the headers set by
// that platform, for example to determine the client IP
TrustedPlatform string
// MaxMultipartMemory value of 'maxMemory' param that is given to http.Request's ParseMultipartForm
// method call.
MaxMultipartMemory int64
// UseH2C enable h2c support.
UseH2C bool
// ContextWithFallback enable fallback Context.Deadline(), Context.Done(), Context.Err() and Context.Value() when Context.Request.Context() is not nil.
ContextWithFallback bool
delims render.Delims
secureJSONPrefix string
HTMLRender render.HTMLRender
FuncMap template.FuncMap
allNoRoute HandlersChain
allNoMethod HandlersChain
noRoute HandlersChain
noMethod HandlersChain
pool sync.Pool
trees methodTrees
maxParams uint16
maxSections uint16
trustedProxies []string
trustedCIDRs []*net.IPNet
}
从结构体中发现,Engine有一个“sync.Pool”类型的pool变量:
sync.Pool是sync包下的一个内存池组件用来实现对象的复用,避免重复创建相同的对象,造成频繁的内存分配和gc,以达到提升程序性能的目的,虽然池子中的对象可以被复用,
但是sync.Pool并不会永久保存这个对象,池子中的对象会在一定时间后被gc回收,这个时间是随机的。所以用sync.Pool持久化存储对象不可取
sync.Pool本身是线程安全的,支持多个goroutine并发的往sync.Pool存取数据
sync.Pool的使用例子
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int
}
func main() {
pool := sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return &Student{
Name: "zhangsan",
Age: 23,
}
},
}
st := pool.Get().(*Student)
fmt.Println(st.Age, st.Name)
fmt.Printf("%p\n", &st)
pool.Put(st)
st = pool.Get().(*Student)
fmt.Println(st.Age, st.Name)
fmt.Printf("%p\n", &st)
}
//23 zhangsan
//0xc00000a028
//23 zhangsan
//0xc00000a028
Engine结构RouterGroup结构体,接下来看一下“RouterGroup”结构体
type RouterGroup struct {
//HandlersChain defines a HandlerFunc slice
//HandlerFunc defines the handler used by gin middleware as return value
Handlers HandlersChain
basePath string
engine *Engine
root bool
}
Engine中还有一个“methodTrees”类型的变量trees
trees methodTrees
type methodTrees []methodTree
type methodTree struct{
method string
root *node
}
type node struct {
path string
indices string
wildChild bool
nType nodeType
priority uint32
children []*node // child nodes, at most 1 :param style node at the end of the array
handlers HandlersChain
fullPath string
}
node 中最重要的两个结构就是
type node struct{
wildChild bool
children []*node
}
//其实这个就是前缀树实现的比较重要的两个数据变量
gin的路由实现
gin的每种请求,都是一个域名对应着一个路由处理函数,就是一种映射关系;直观上可以使用map存储这种映射关系,key存储域名,value存储域名对应的处理函数;
但实际上,gin路由底层实现这个映射使用的是压缩前缀树,首先介绍一下前缀树
前缀树
前缀树就是trie树,是一种树形结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串集合。基本思想就是将字符串中的每个字符作为树的一个节点,从根节点开始,每个节点代表代表字符串中的一个前缀。在Trie树,每个节点都包含一个指向子节点的指针数组,数组的大小等于字符集的大小。如果某个节点代表的字符串是一个单词的结尾,可以在该节点上做一个标记。
以下是前缀树的一些特性:
- 前缀匹配。前缀树可以高效地实现前缀匹配。给定一个前缀,可以在O(k)的时间复杂度内找到所有以该前缀开头的字符串,k是前缀的长度
- 高效存储和检索。前缀树可以高效地存储和检索字符串集合。在插入和查找字符串时,时间复杂度为O(k),k是字符串的长度。相比于哈希表和二叉搜索树,前缀树在字符串存储和检索方面具有更好的性能
- 消耗较大的空间。空间复杂度较高,每个节点都需要存储指向子节点的指针数组,节点的数量可能会非常多。空间复杂度为O(n*m)其中n为字符串集合中字符串的平均长度,m为字符串数量
- 支持删除操作。删除操作相对比较复杂,删除一个字符串需要同时删除相应的节点,需要处理节点合并的情况。
- 应用场景。单词查询,自动补全,模糊匹配
前缀树的实现
前缀树的实现可以参考力扣上的一道代码题
题目链接
大致的思路就是
go 语言实现
type Trie struct {
trie [26]*Trie
flag bool
}
func Constructor() Trie {
return Trie{}
}
func (this *Trie) Insert(word string) {
tr:= this
for i:=0;i<len(word);i++{
if tr.trie[word[i]-'a']==nil{
tr.trie[word[i]-'a'] = &Trie{}
}
tr=tr.trie[word[i]-'a']
}
tr.flag=true
}
func (this *Trie) Search(word string) bool {
tr:=this.startpre(word)
return tr!=nil && tr.flag
}
func (this *Trie) StartsWith(prefix string) bool {
return this.startpre(prefix)!=nil
}
func (this *Trie)startpre(pre string)*Trie{
tr:=this
for i:=0;i<len(pre);i++{
if tr.trie[pre[i]-'a']==nil{
return nil
}
tr=tr.trie[pre[i]-'a']
}
return tr
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor();
* obj.Insert(word);
* param_2 := obj.Search(word);
* param_3 := obj.StartsWith(prefix);
*/
C++实现版本,由于C++没有回收内存的机制所以需要手动释放内存
class Trie {
public:
~Trie(){
//析构函数释放内存
del(this);
}
Trie():trie(26),flag(false){
}
void insert(string word) {
Trie *tr = this;
for(const char&c:word){
if(!tr->trie[c-'a']) tr->trie[c-'a'] = new Trie();
tr=tr->trie[c-'a'];
}
tr->flag=true;
}
bool search(string word) {
Trie *tr = this;
for(const char&c:word){
if(!tr->trie[c-'a']) return false;
tr=tr->trie[c-'a'];
}
return tr->flag;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
Trie *tr = this;
for(const char&c:prefix){
if(!tr->trie[c-'a']) return false;
tr=tr->trie[c-'a'];
}
return true;
}
private:
vector<Trie*> trie;
bool flag;
private:
void del(Trie *tr){
for(int i=0;i<26;++i){
delete(tr->trie[i]);
tr->trie[i]=nullptr;
}
}
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/
解释一下其中的关键代码,del
void del(Trie *tr){
//由于每个Trie节点都有一个长度为26的指向子节点的指针数组,所以写了一个长度为26的for循环
for(int i=0;i<26;++i){
//由于tr->trie[i]是一个Trie的数据类型变量,所以在delete tr->trie[i]的时候会触发tr-trie[i]的析构函数,往下递归的进行内存释放
delete(tr->trie[i]);
//释放完之后为了防止野指针,将tr->trie[i]设置为nullptr
tr->trie[i]=nullptr;
}
}
压缩前缀树–Radix Trie
从上述的分析和代码实现可以看出,前缀树占用的空间特别大。那么为了优化空间的利用率,gin的路由采用了“压缩前缀树”。
使用如下方法进行压缩:
- 合并相邻的只有一个子节点的节点:遍历前缀树,当发现一个节点只有一个子节点时,将该节点与其子节点合并。合并时,将子节点的字符添加到父节点的字符中,形成新的字符
- 递归地压缩子树,在合并节点后,可能会出现新的节点也只有一个子节点的情况,可以递归的对子树进行压缩,直到无法压缩为止
- 使用特殊字符表示合并,为了在压缩前缀树中表示节点的合并,可以使用一些特殊的字符进行标记。例如可以使用$表示节点的合并
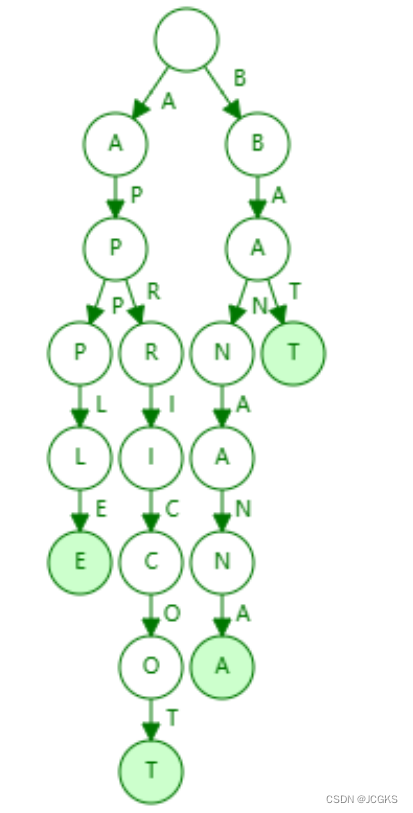
接下来,利用数据结构可视化工具查看两个结构的不同
依次插入[“apple”,“apricot”,“banana”,“bat”]
前缀树的结构如下
压缩前缀树的结构如下
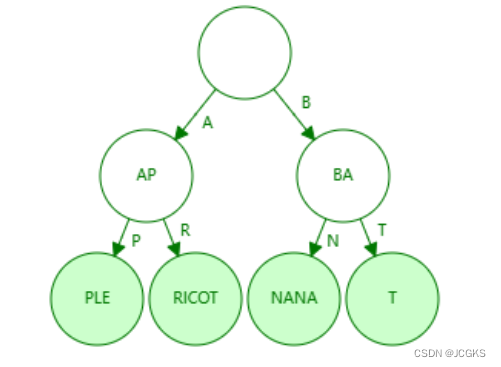
从两图可以看出,Radix Trie对Trie进行了压缩:遍历Trie发现某个节点只有一个子节点,就与子节点进行合并,减少指针数组的占用,优化空间
Trie VS Map
接下来说一下为什么不用map实现路径和路由函数之间的映射。
- map并不支持模糊匹配和参数提取;前缀树可以根据前缀进行参数提取,而使用map进行参数提取需要额外的步骤
- 前缀树可以根据前缀进行分组管理,而map不行