本篇文章纯属作为自己的笔记,因为每次写程序都忘记下面的内容,找起来又很浪费时间,所有就索性一次性都整理下来,后续又不新的不会的内弄也会及时更新到文章当中,方便以后查阅。
DeepLearn关于数组和数的操作
- Python
- 标准数据类型
- 数据类型之间的转换
- 字符串(String)
- 访问字符串中的值
- 转义字符
- 字符串运算符
- 字符串格式化
- 列表(List)
- 列表脚本操作符
- 列表函数&方法
- Python包含以下`函数`
- Python包含以下`方法`:
- 元组(Tuple)
- 元组运算符
- 元组内置函数
- 字典(Dictionary)
- 字典内置函数&方法
- Python字典包含了以下内置`函数`:
- Python字典包含了以下内置`方法`:
- 集合(Set)
- 集合内置方法完整列表
- python 四舍五入
- Numpy
- ndarray 对象
- ndarray 概念
- ndarray 内部关系
- ndarray 内存结构
- ndarray vs list
- ndarray 特点
- list 特点
- NumPy 数组属性
- NumPy 创建数组
- numpy.random
- numpy.random.seed
- numpy.random.rand
- numpy.random.uniform
- numpy.random.normal
- numpy.random.randn
- numpy.random.randint
- numpy.random.random_sample
- numpy.empty
- numpy.zeros
- numpy.ones
- numpy.eye
- 数组操作
- 修改数组形状
- 翻转数组
- 修改数组维度
- 连接数组
- 分割数组
- 数组元素的添加与删除
- 舍入函数
- numpy.around()
- numpy.floor()
- numpy.ceil()
- Pytorch
- Tensors
- Creation Ops
- Indexing, Slicing, Joining, Mutating Ops
- Random sampling
- 参考资料
Python
https://docs.python.org/3.7/c-api/index.html

标准数据类型
| 不可变数据 | 可变数据 |
|---|---|
| Number(数字) | List(列表) |
| String(字符串) | Dictionary(字典) |
| Tuple(元组) | Set(集合) |
数据类型之间的转换
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int(x [,base]) | 将x转换为一个整数 |
| float(x) | 将x转换到一个浮点数 |
| complex(real [,imag]) | 创建一个复数 |
| str(x) | 将对象 x 转换为字符串 |
| repr(x) | 将对象 x 转换为表达式字符串 |
| eval(str) | 用来计算在字符串中的有效Python表达式,并返回一个对象 |
| tuple(s) | 将序列 s 转换为一个元组 |
| list(s) | 将序列 s 转换为一个列表 |
| set(s) | 转换为可变集合 |
| dict(d) | 创建一个字典。d 必须是一个 (key, value)元组序列。 |
| frozenset(s) | 转换为不可变集合 |
| chr(x) | 将一个整数转换为一个字符 |
| ord(x) | 将一个字符转换为它的整数值 |
| hex(x) | 将一个整数转换为一个十六进制字符串 |
| oct(x) | 将一个整数转换为一个八进制字符串 |
字符串(String)
字符串是 Python 中最常用的数据类型。我们可以使用引号( ’ 或 " )来创建字符串。
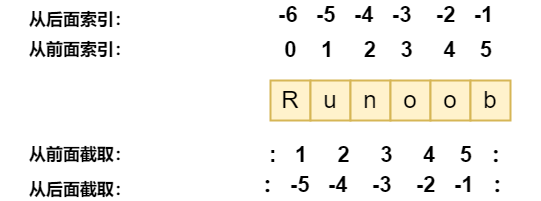
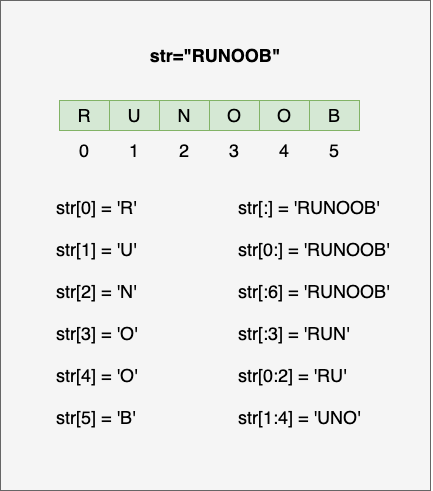
访问字符串中的值
Python 访问子字符串,可以使用方括号 [] 来截取字符串:
转义字符
| 转义字符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| (在行尾时) | 续行符 | 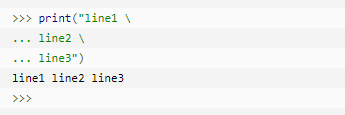 |
| \ | 反斜杠符号 |  |
| ’ | 单引号 |  |
| " | 双引号 |  |
| \a | 响铃 | 执行后电脑有响声。 |
| \b | 退格(Backspace) | 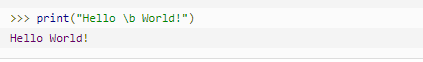 |
| \000 | 空 |  |
| \n | 换行 |  |
| \v | 纵向制表符 | 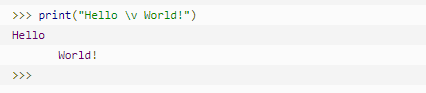 |
| \t | 横向制表符 | 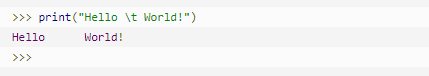 |
| \r | 回车,将 \r 后面的内容移到字符串开头,并逐一替换开头部分的字符,直至将 \r 后面的内容完全替换完成。 | 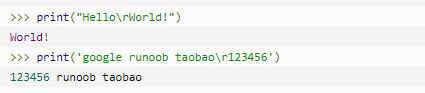 |
| \f | 换页 | 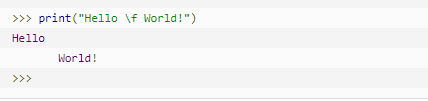 |
| \yyy | 八进制数,y 代表 0~7 的字符,例如:\012 代表换行。 | 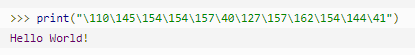 |
| \xyy | 十六进制数,以 \x 开头,y 代表的字符,例如:\x0a 代表换行 | 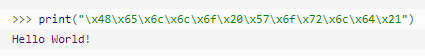 |
| \other | 其它的字符以普通格式输出 |
字符串运算符
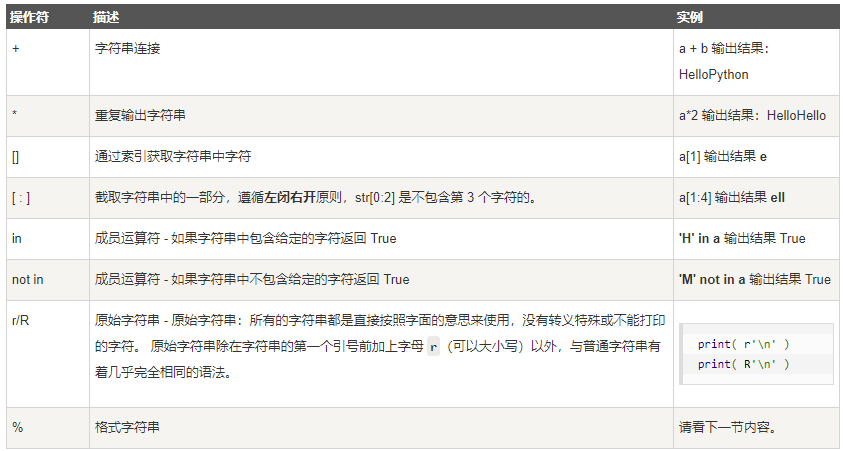
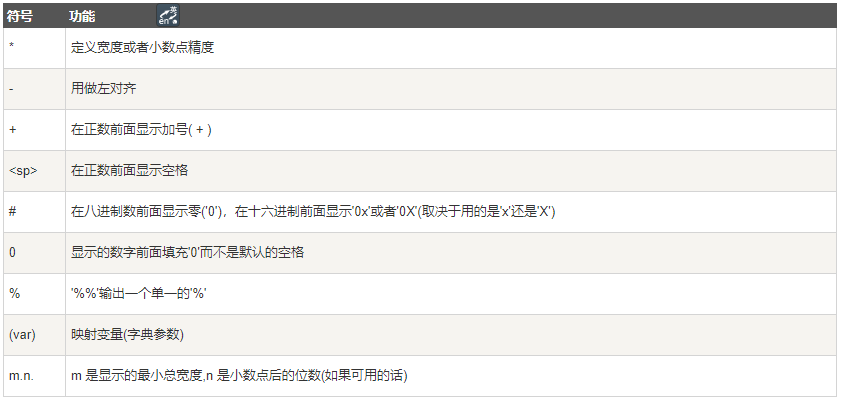
字符串格式化

格式化操作符辅助指令:
列表(List)
列表脚本操作符

列表函数&方法
Python包含以下函数
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| len(list) | 列表元素个数 |
| max(list) | 返回列表元素最大值 |
| min(list) | 返回列表元素最小值 |
| list(seq) | 将元组转换为列表 |
Python包含以下方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| list.append(obj) | 在列表末尾添加新的对象 |
| list.count(obj) | 统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 |
| list.extend(seq) | 在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表) |
| list.index(obj) | 从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置 |
| list.insert(index, obj) | 将对象插入列表 |
| list.pop([index=-1]) | 移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值 |
| list.remove(obj) | 移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项 |
| list.reverse() | 反向列表中元素 |
| list.sort( key=None, reverse=False) | 对原列表进行排序 |
| list.clear() | 清空列表 |
| list.copy() | 复制列表 |
元组(Tuple)
-
Python 的元组与列表类似,不同之处在于元组的元素不能修改。
-
元组使用小括号 ( ),列表使用方括号 [ ]。
-
元组创建很简单,只需要在括号中添加元素,并使用逗号隔开即可。

元组与字符串类似,下标索引从 0 开始,可以进行截取,组合等。

元组运算符
与字符串一样,元组之间可以使用 + 号和 * 号进行运算。这就意味着他们可以组合和复制,运算后会生成一个新的元组。
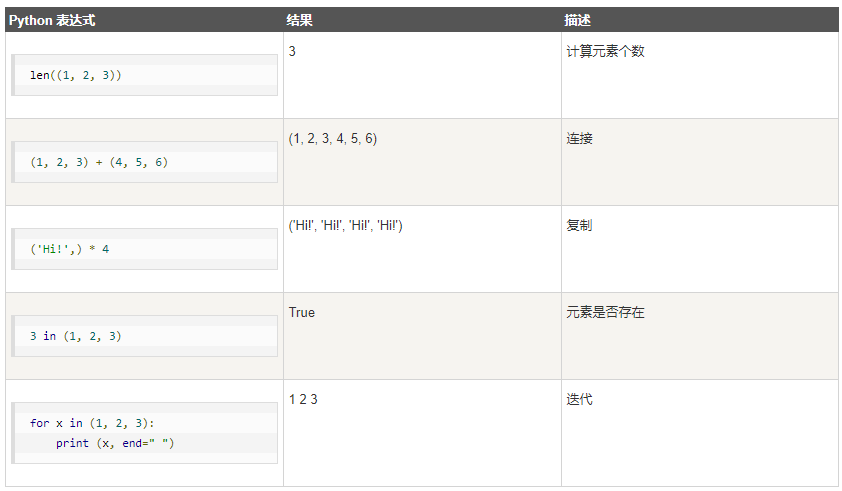
元组内置函数
Python元组包含了以下内置函数
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| len(tuple) | 计算元组元素个数。 |
| max(tuple) | 返回元组中元素最大值。 |
| min(tuple) | 返回元组中元素最小值。 |
| tuple(iterable) | 将可迭代系列转换为元组。 |
字典(Dictionary)
字典是另一种可变容器模型,且可存储任意类型对象。
字典的每个键值 key=>value 对用冒号 : 分割,每个对之间用逗号(,)分割,整个字典包括在花括号 {} 中 ,格式如下所示:
d = {key1 : value1, key2 : value2, key3 : value3 }
注意:dict 作为 Python 的关键字和内置函数,变量名不建议命名为 dict。
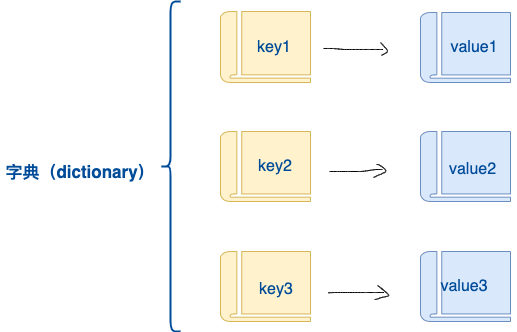
键必须是唯一的,但值则不必。
值可以取任何数据类型,但键必须是不可变的,如字符串,数字。
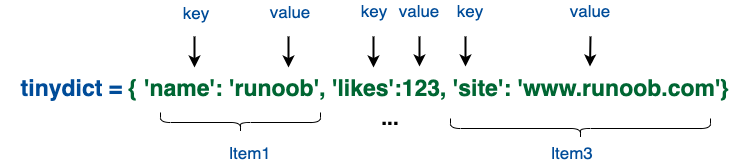
一个简单的字典实例:
tinydict = {'name': 'runoob', 'likes': 123, 'url': 'www.runoob.com'}
字典内置函数&方法
Python字典包含了以下内置函数:
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| len(dict) | 计算字典元素个数,即键的总数 |
| str(dict) | 输出字典,可以打印的字符串表示 |
| type(variable) | 返回输入的变量类型,如果变量是字典就返回字典类型 |
Python字典包含了以下内置方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| dict.clear() | |
| 删除字典内所有元素 | |
| dict.copy() | 返回一个字典的浅复制 |
| dict.fromkeys() | 创建一个新字典,以序列seq中元素做字典的键,val为字典所有键对应的初始值 |
| dict.get(key, default=None) | 返回指定键的值,如果键不在字典中返回 default 设置的默认值 |
| key in dict | 如果键在字典dict里返回true,否则返回false |
| dict.items() | 以列表返回一个视图对象 |
| dict.keys() | 返回一个视图对象 |
| dict.setdefault(key, default=None) | 和get()类似, 但如果键不存在于字典中,将会添加键并将值设为default |
| dict.update(dict2) | 把字典dict2的键/值对更新到dict里 |
| dict.values() | 返回一个视图对象 |
| pop(key[,default]) | 删除字典 key(键)所对应的值,返回被删除的值。 |
| popitem() | 返回并删除字典中的最后一对键和值。 |
集合(Set)
集合(set)是一个无序的不重复元素序列。
可以使用大括号 { } 或者 set() 函数创建集合,注意:创建一个空集合必须用 set() 而不是 { },因为 { } 是用来创建一个空字典。
创建格式:
parame = {value01,value02,...}
或者
set(value)
集合内置方法完整列表
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| add() | 为集合添加元素 |
| clear() | 移除集合中的所有元素 |
| copy() | 拷贝一个集合 |
| difference() | 返回多个集合的差集 |
| difference_update() | 移除集合中的元素,该元素在指定的集合也存在。 |
| discard() | 删除集合中指定的元素 |
| intersection() | 返回集合的交集 |
| intersection_update() | 返回集合的交集。 |
| isdisjoint() | 判断两个集合是否包含相同的元素,如果没有返回 True,否则返回 False。 |
| issubset() | 判断指定集合是否为该方法参数集合的子集。 |
| issuperset() | 判断该方法的参数集合是否为指定集合的子集 |
| pop() | 随机移除元素 |
| remove() | 移除指定元素 |
| symmetric_difference() | 返回两个集合中不重复的元素集合。 |
| symmetric_difference_update() | 移除当前集合中在另外一个指定集合相同的元素,并将另外一个指定集合中不同的元素插入到当前集合中。 |
| union() | 返回两个集合的并集 |
| update() | 给集合添加元素 |
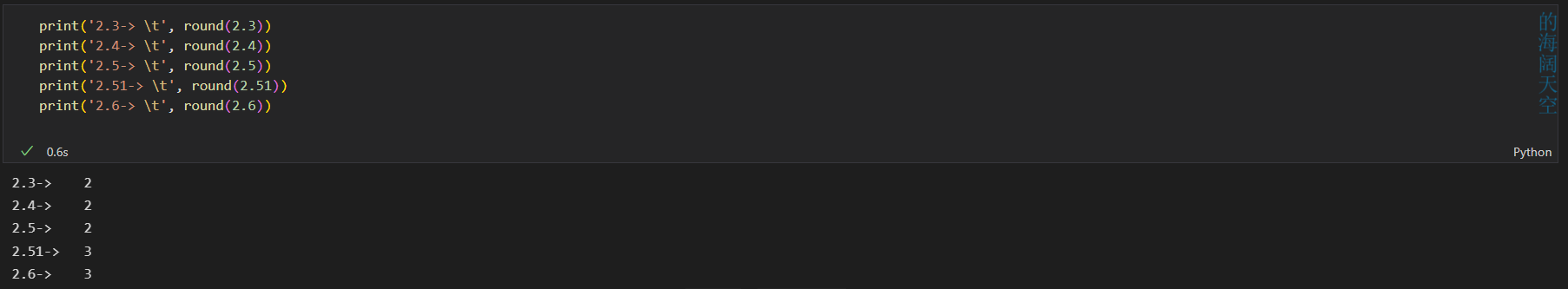
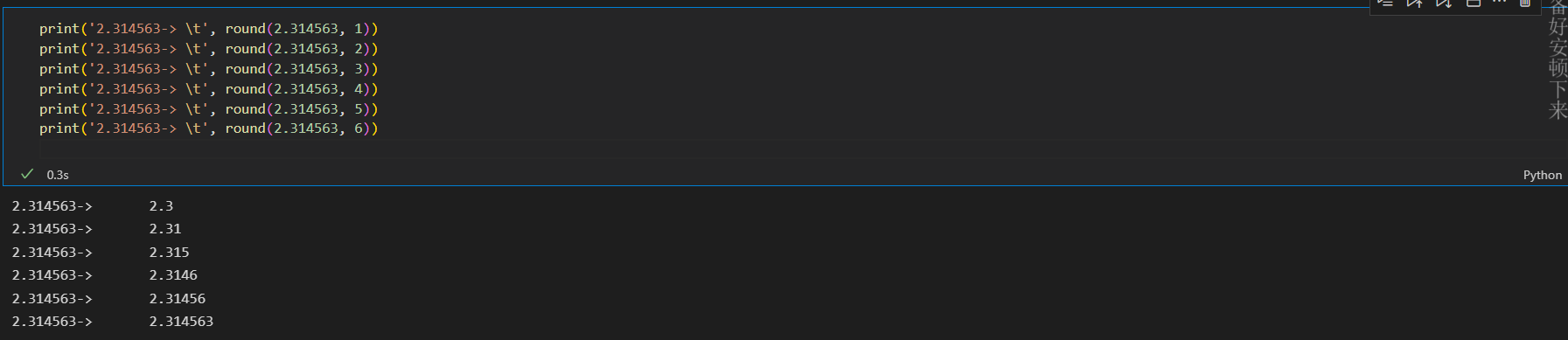
python 四舍五入
round(number[, ndigits])

print('2.3-> \t', round(2.3))
print('2.4-> \t', round(2.4))
print('2.5-> \t', round(2.5))
print('2.51-> \t', round(2.51))
print('2.6-> \t', round(2.6))
print('2.314563-> \t', round(2.314563, 1))
print('2.314563-> \t', round(2.314563, 2))
print('2.314563-> \t', round(2.314563, 3))
print('2.314563-> \t', round(2.314563, 4))
print('2.314563-> \t', round(2.314563, 5))
print('2.314563-> \t', round(2.314563, 6))
Numpy
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/index.html

NumPy(Numerical Python) 是 Python 语言的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库。
NumPy 是一个运行速度非常快的数学库,主要用于数组计算,包含:
- 一个强大的N维数组对象 ndarray
- 广播功能函数
- 整合 C/C++/Fortran 代码的工具
- 线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成等功能
ndarray 对象
ndarray 概念
NumPy 最重要的一个特点是其 N 维数组对象 ndarray,它是一系列同类型数据的集合,以 0 下标为开始进行集合中元素的索引。
ndarray 对象是用于存放同类型元素的多维数组。
ndarray 中的每个元素在内存中都有相同存储大小的区域。
ndarray 内部关系
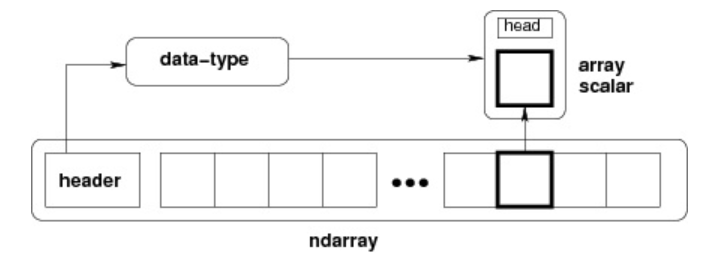
通过以上ndarray 内部结构,我们可以看到 ndarray 主要由 dtype、shape、stride组成
- 指向内存映射地址的指针-
data对象 - 元素解释形象-
dtype对象 - 每个维度的元素之间的间隔-
strides对象(tuple) - 对每个维度的数量和大小的描述-
shape对象(tuple)
跨度可以是负数,这样会使数组在内存中后向移动,切片中 obj[::-1] 或 obj[:,::-1] 就是如此。
创建一个 ndarray 只需调用 NumPy 的 array 函数即可:
numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
ndarray 内存结构
我们通过numpy.array 方法创建一个2维数组
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2],[4,5],[7,8]])
print("dim:",a.ndim)
print("strides:",a.strides)
print("dtype:",a.dtype)
print("data:",a.data)
print("shape:",a.shape)
print(a)
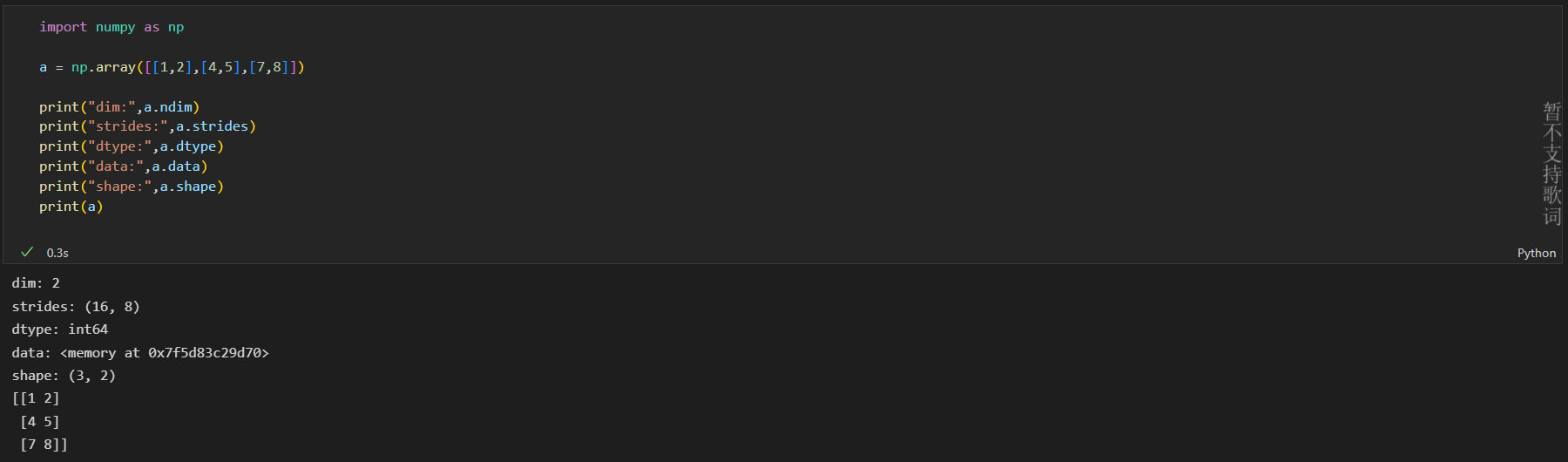
通过array对象调用ndarray 标量对象,可以获知ndarray 维度大小、元素类型、间隔等信息

通过上述图,我们可以知道 ndarray 内存主要划分为两部分:
-
raw data: 计算机一段连续的block,存储在C或者Fortran中的数组 -
metdata:有关原始数组数据的信息
ndarray vs list
ndarray 特点
- ndarray 要求所有数据都是同种类型的
- 每个数据占用空间一样
- 数组中存储的数据是一段连续的空间
list 特点
- 可以容纳不同数据类型
- list 中只存放对象的引用,再通过引用找到具体的对象
- 对象的物理地址并不是连续的
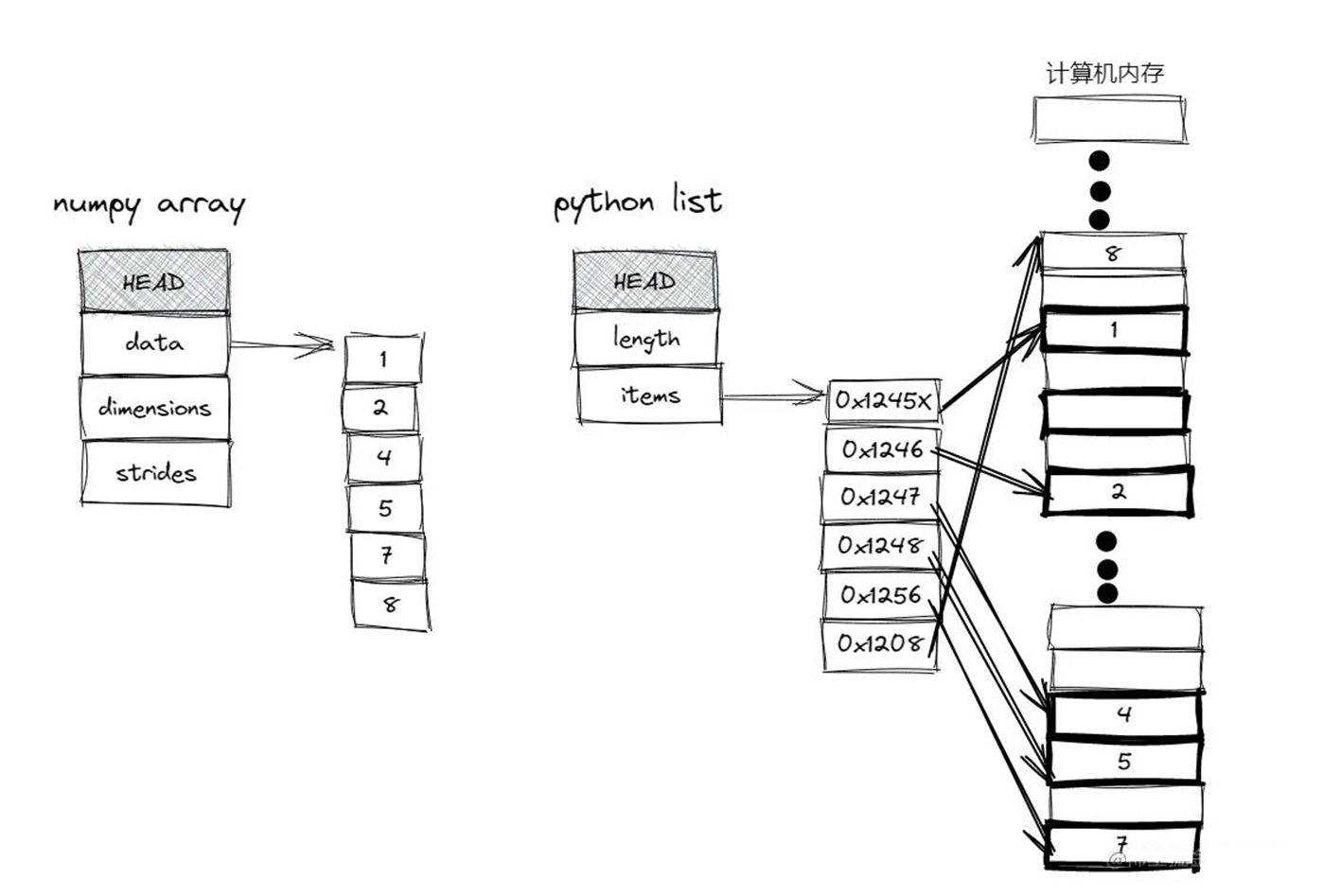
所以,综上所述,ndarray 查找数据运行效率比list快,同时ndarray 存储的数据是连续的一段空间,对比list 对象物理地址分散的,ndarray 比 list 更省空间。
NumPy 数组属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ndarray.ndim | 秩,即轴的数量或维度的数量 |
| ndarray.shape | 数组的维度,对于矩阵,n 行 m 列 |
| ndarray.size | 数组元素的总个数,相当于 .shape 中 n*m 的值 |
| ndarray.dtype | ndarray 对象的元素类型 |
| ndarray.itemsize | ndarray 对象中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位 |
| ndarray.flags | ndarray 对象的内存信息 |
| ndarray.real | ndarray元素的实部 |
| ndarray.imag | ndarray 元素的虚部 |
| ndarray.data | 包含实际数组元素的缓冲区,由于一般通过数组的索引获取元素,所以通常不需要使用这个属性。 |
NumPy 创建数组
numpy.random
numpy.random.seed
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.seed.html
random.seed(self, seed=None)
# 多次运行,程序输出结果一致
# 如果不设置随机数种子,多次运行输出结果不一致
numpy.random.rand
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.rand.html#numpy-random-rand
random.rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)
Create an array of the given shape and populate it with random samples from a uniform distribution over [0, 1).

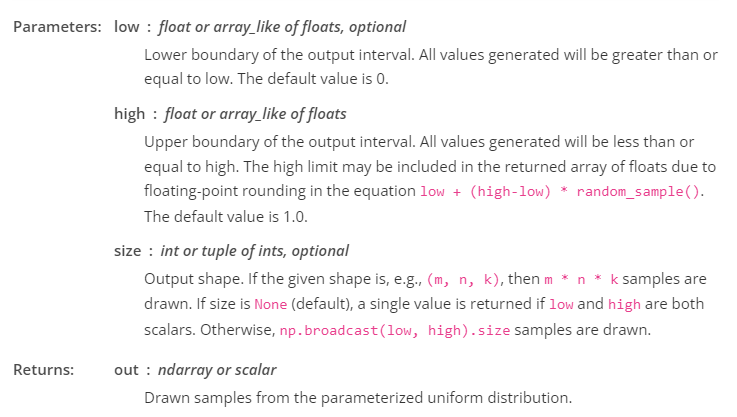
numpy.random.uniform
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.uniform.html
random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None)
Samples are uniformly distributed over the half-open interval [low, high) (includes low, but excludes high). In other words, any value within the given interval is equally likely to be drawn by uniform.
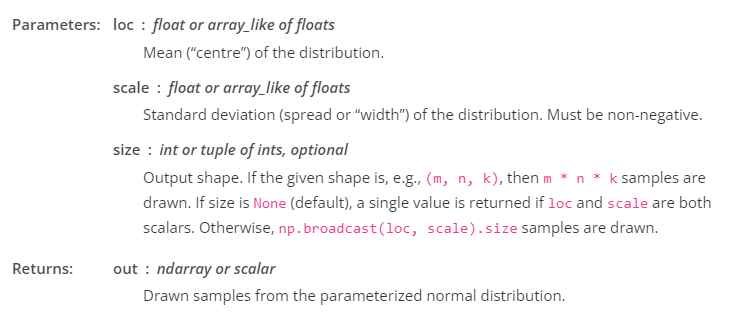
numpy.random.normal
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.normal.html
random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)
Draw random samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution.
numpy.random.randn
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.randn.html
random.randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)
Return a sample (or samples) from the “standard normal” distribution.

numpy.random.randint
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.randint.html
random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype=int)
Return random integers from the “discrete uniform” distribution of the specified dtype in the “half-open” interval [low, high). If high is None (the default), then results are from [0, low).

numpy.random.random_sample
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.random_sample.html#numpy.random.random_sample
random.random_sample(size=None)
Results are from the “continuous uniform” distribution over the stated interval. To sample U n i d [ a , b ) , b > a Unid[a, b), b>a Unid[a,b),b>a multiply the output of random_sample by (b-a) and add a:

numpy.empty
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.empty.html?highlight=empty#numpy.empty
numpy.empty(shape, dtype=float, order='C', *, like=None)
Return a new array of given shape and type, without initializing entries.

>>> np.empty([2, 2])
array([[ -9.74499359e+001, 6.69583040e-309],
[ 2.13182611e-314, 3.06959433e-309]]) #uninitialized
>>> np.empty([2, 2], dtype=int)
array([[-1073741821, -1067949133],
[ 496041986, 19249760]]) #uninitialized
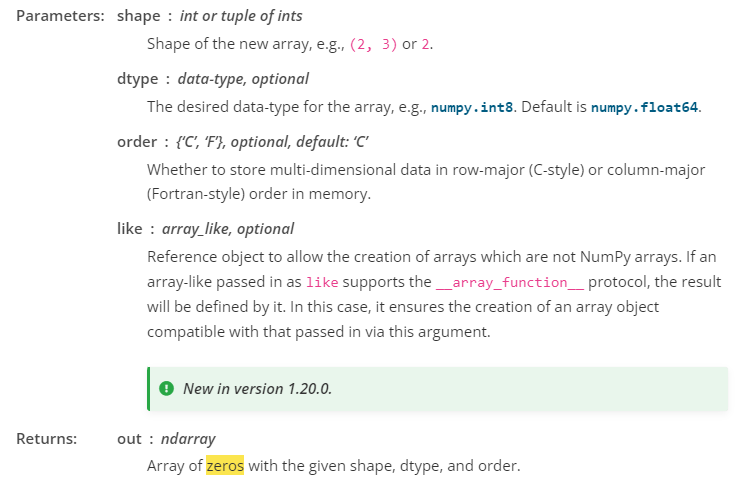
numpy.zeros
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.zeros.html?highlight=zeros#numpy.zeros
numpy.zeros(shape, dtype=float, order='C', *, like=None)
Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with zeros.
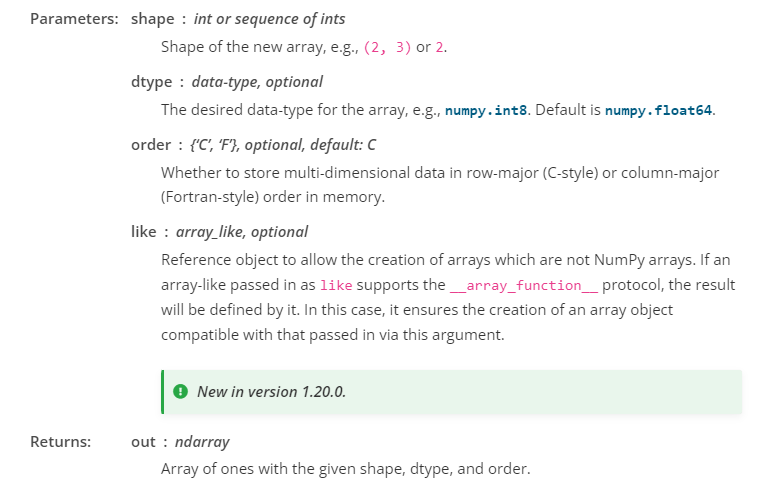
numpy.ones
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html
numpy.ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C', *, like=None)
Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones.
numpy.eye
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.eye.html
numpy.eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=<class 'float'>, order='C', *, like=None)
Return a 2-D array with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere.

数组操作
修改数组形状
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| reshape | 不改变数据的条件下修改形状 |
| flat | 数组元素迭代器 |
| flatten | 返回一份数组拷贝,对拷贝所做的修改不会影响原始数组 |
| ravel | 返回展开数组 |
翻转数组
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| transpose | 对换数组的维度 |
| ndarray.T | 和 self.transpose() 相同 |
| rollaxis | 向后滚动指定的轴 |
| swapaxes | 对换数组的两个轴 |
修改数组维度
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| expand_dims | 扩展数组的形状 |
| squeeze | 从数组的形状中删除一维条目 |
连接数组
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| concatenate | 连接沿现有轴的数组序列 |
| stack | 沿着新的轴加入一系列数组。 |
| hstack | 水平堆叠序列中的数组(列方向) |
| vstack | 竖直堆叠序列中的数组(行方向) |
分割数组
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| split | 将一个数组分割为多个子数组 |
| hsplit | 将一个数组水平分割为多个子数组(按列) |
| vsplit | 将一个数组垂直分割为多个子数组(按行) |
数组元素的添加与删除
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| resize | 返回指定形状的新数组 |
| append | 将值添加到数组末尾 |
| insert | 沿指定轴将值插入到指定下标之前 |
| delete | 删掉某个轴的子数组,并返回删除后的新数组 |
| unique | 查找数组内的唯一元素 |
舍入函数
numpy.around()
numpy.around(a,decimals)
函数返回指定数字的四舍五入值。
参数说明:
- a: 数组
- decimals: 舍入的小数位数。 默认值为0。 如果为负,整数将四舍五入到小数点左侧的位置
numpy.floor()
返回小于或者等于指定表达式的最大整数,即向下取整。
a = np.array([-1.7, 1.5, -0.2, 0.6, 10])
np.floor(a)

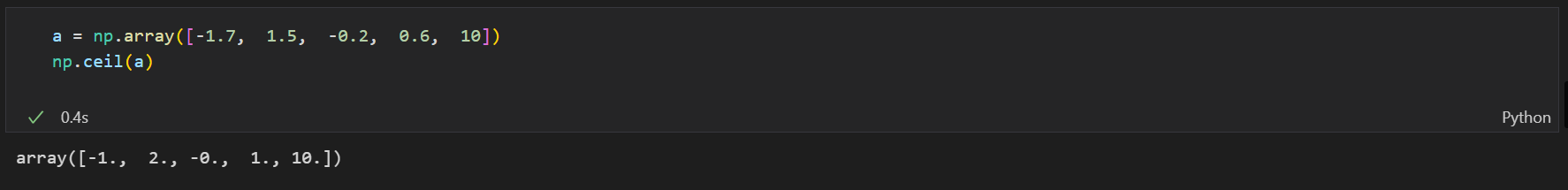
numpy.ceil()
返回大于或者等于指定表达式的最小整数,即向上取整。
a = np.array([-1.7, 1.5, -0.2, 0.6, 10])
np.ceil(a)
Pytorch
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/index.html

Tensors
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| is_tensor | Returns True if obj is a PyTorch tensor. |
Creation Ops
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tensor | Constructs a tensor with no autograd history (also known as a “leaf tensor”, see Autograd mechanics) by copying data. |
| as_tensor | Converts data into a tensor, sharing data and preserving autograd history if possible. |
| from_numpy | Creates a Tensor from a numpy.ndarray. |
| zeros | Returns a tensor filled with the scalar value 0, with the shape defined by the variable argument size. |
| zeros_like | Returns a tensor filled with the scalar value 0, with the same size as input. |
| ones | Returns a tensor filled with the scalar value 1, with the shape defined by the variable argument size. |
| ones_like | Returns a tensor filled with the scalar value 1, with the same size as input. |
| arange | Returns a 1-D tensor of size
⌈
end
−
start
step
⌉
\left\lceil \frac{\text{end} - \text{start}}{\text{step}} \right\rceil
⌈stepend−start⌉with values from the interval [start, end) taken with common difference step beginning from start. |
| range | Returns a 1-D tensor of size
⌊
end
−
start
step
⌋
+
1
\left\lfloor \frac{\text{end} - \text{start}}{\text{step}} \right\rfloor + 1
⌊stepend−start⌋+1with values from start to end with step step. |
| eye | Returns a 2-D tensor with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere. |
| empty | Returns a tensor filled with uninitialized data. |
Indexing, Slicing, Joining, Mutating Ops
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| cat | Concatenates the given sequence of seq tensors in the given dimension. |
| reshape | Returns a tensor with the same data and number of elements as input, but with the specified shape. |
| split | Splits the tensor into chunks. |
| squeeze | Returns a tensor with all the dimensions of input of size 1 removed. |
| unsqueeze | Returns a new tensor with a dimension of size one inserted at the specified position. |
| transpose | Returns a tensor that is a transposed version of input. |
Random sampling
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| seed | Sets the seed for generating random numbers to a non-deterministic random number. |
| normal | Returns a tensor of random numbers drawn from separate normal distributions whose mean and standard deviation are given. |
| rand | Returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a uniform distribution on the interval [0, 1)[0,1) |
| randint | Returns a tensor filled with random integers generated uniformly between low (inclusive) and high (exclusive). |
| randn | Returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1 (also called the standard normal distribution). |
| randperm | Returns a random permutation of integers from 0 to n - 1. |
参考资料
Python numpy ndarray
NumPy Ndarray 对象
Python3 基本数据类型
Python3 数据类型转换
Python3 字符串
Python3 列表
Python3 元组
Python3 字典
Numpy 数组操作
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#pointwise-ops

![[附源码]java毕业设计基于技术的新电商助农平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e7d114728606440bb9eb62e201e2a140.png)