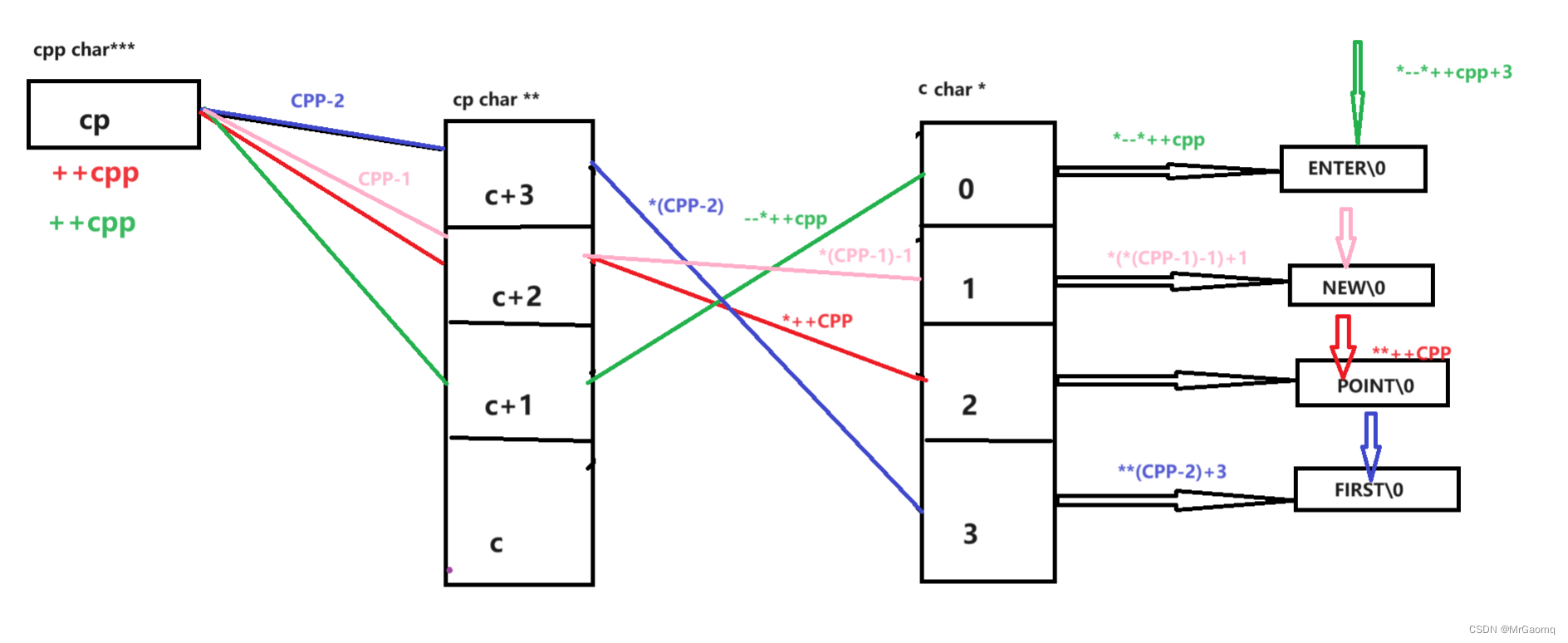
这篇文章我们来讲一下红黑树。
目录
1.概述
1.1红黑树的性质
2.红黑树的实现
3.总结
1.概述
首先,我们来大致了解一下什么是红黑树
红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树,是一种高效的查找树。红黑树具有良好的效率,它可在 O(logN) 时间内完成查找、增加、删除等操作。因此,红黑树在业界应用很广泛,比如 Java 中的 TreeMap,JDK 1.8 中的 HashMap。
1.1红黑树的性质
看过前面二叉查找树(即二叉搜索树)的同学都知道,普通的二叉查找树在极端情况下可退化成链表,此时的增删查效率都会比较低下。
为了避免这种情况,就出现了一些自平衡的查找树,比如 AVL,红黑树等。这些自平衡的查找树通过定义一些性质,将任意节点的左右子树高度差控制在规定范围内,以达到平衡状态。前面讲的AVL树实现自平衡的机制是设置一个平衡因子。
以红黑树为例,红黑树通过如下的性质定义实现自平衡:
- 所有节点都有两种颜色:红色或黑色。
- 根节点是黑色。
- 所有null视为黑色。
- 每个红色节点必须有两个黑色的子节点,即红色节点不能相邻(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点。)
- 从根节点到任意一个叶子节点,路径中的黑色节点数目一样(黑色完美平衡,简称黑高)。
有了上面的几个性质作为限制,即可避免二叉查找树退化成单链表的情况。
但是,仅仅避免这种情况还不够,这里还要考虑某个节点到其每个叶子节点路径长度的问题。
如果某些路径长度过长,那么,在对这些路径上的节点进行增删查操作时,效率也会大大降低。
这个时候性质4和性质5用途就凸显了,有了这两个性质作为约束,即可保证任意节点到其每个叶子节点路径最长不会超过最短路径的2倍。原因如下:
当某条路径最短时,这条路径必然都是由黑色节点构成。当某条路径长度最长时,这条路径必然是由红色和黑色节点相间构成(性质4限定了不能出现两个连续的红色节点)。而性质5又限定了从任一节点到其每个叶子节点的所有路径必须包含相同数量的黑色节点。此时,在路径最长的情况下,路径上红色节点数量 = 黑色节点数量。该路径长度为两倍黑色节点数量,也就是最短路径长度的2倍。
下面看几个红黑树:
2.红黑树的实现
下面来看一下红黑树的实现
package Tree;
/**红黑树的相关操作*/
public class L4_RBTree {
enum Color{RED,BLACK}
private Node root;
private static class Node {
int key;
Object value;
Node left;
Node right;
Node parent;//父节点
Color color = Color.RED;//颜色
public Node(int key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
//是否是左孩子
boolean isLeftChild(){
return parent != null && parent.left == this;
}
//找叔叔结点
Node isUncle(){
if (parent == null || parent.parent == null){
return null;
}
if (parent.isLeftChild()){
return parent.parent.right;
}else {
return parent.parent.left;
}
}
//找兄弟
Node sibling(){
if (parent == null){return null;}
if (this.isLeftChild()){
return parent.right;
}else {
return parent.left;
}
}
}
//判断是不是红色
boolean isRed(Node node){
return node != null && node.color == Color.RED;
}
//判断是不是黑色
boolean isBlack(Node node){
return !isRed(node);
}
/**
* 右旋
* 要对parent进行处理
* 选转后新根的父子关系
* */
private void rightRotate(Node node){
Node nodeParent = node.parent;
Node nodeLeft = node.left;
Node nodeLeftRight = nodeLeft.right;
if (nodeLeftRight != null){
nodeLeftRight.parent = node;
}
nodeLeft.right = node;
nodeLeft.parent = nodeParent;
node.left = nodeLeftRight;
node.parent = nodeLeft;
if (nodeParent == null){
root = nodeLeft;
}else if (nodeParent.left == node){
nodeParent.left = nodeLeft;
}else {
nodeParent.right = nodeLeft;
}
}
//左旋
private void leftRotate(Node node){
Node nodeParent = node.parent;
Node nodeRight = node.right;
Node nodeRightLeft = nodeRight.left;
if (nodeRightLeft != null){
nodeRightLeft.parent = node;
}
nodeRight.left = node;
nodeRight.parent = nodeParent;
node.right = nodeRightLeft;
node.parent = nodeRight;
if (nodeParent == null){
root = nodeRight;
}else if (nodeParent.left == node){
nodeParent.left = nodeRight;
}else {
nodeParent.right = nodeRight;
}
}
/**新增或更新*/
public void put(int key,Object value){
Node p = root;
Node parent = null;
while (p != null){
if (key < p.key){
p = p.left;
} else if(p.key < key){
p = p.right;
} else {
p.value = value;
return;
}
}
Node inserted = new Node(key,value);
if (parent == null){
root = inserted;
}else if (key < parent.key){
parent.left = inserted;
inserted.parent = parent;
}else {
parent.right = inserted;
inserted.parent = parent;
}
fixRedRed(inserted);
}
/**节点调整*/
private void fixRedRed(Node x){
//插入节点是跟节点
if (x == root){
x.color = Color.BLACK;
return;
}
//插入节点的父亲是黑色
if (isBlack(x.parent)){
return;
}
//红红相邻且叔叔为红
Node parent = x.parent;
Node uncle = x.isUncle();
Node grandparent = parent.parent;
if (isRed(uncle)){
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
uncle.color = Color.BLACK;
grandparent.color = Color.RED;
fixRedRed(grandparent);
return;
}
//红红相邻且叔叔为黑
if(parent.isLeftChild() && x.isLeftChild()){//LL
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
grandparent.color = Color.RED;
rightRotate(grandparent);
}else if (parent.isLeftChild() && !x.isLeftChild()){//LR
leftRotate(parent);
x.color = Color.BLACK;
grandparent.color = Color.RED;
rightRotate(grandparent);
} else if (!parent.isLeftChild() && !x.isLeftChild()){//RR
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
grandparent.color = Color.RED;
leftRotate(grandparent);
}else {//RL
rightRotate(parent);
x.color = Color.BLACK;
grandparent.color = Color.RED;
leftRotate(grandparent);
}
}
/**删除*/
public void remove(int key){
Node deleted = find(key);
if (deleted == null){return;}
doRemove(deleted);
}
private void doRemove(Node deleted){
Node replaced = findReplaced(deleted);
Node parent = deleted.parent;
if (replaced == null){//没有孩子
//删除的是根节点
if (deleted == root){
root = null;
}else {
if(isBlack(deleted)){
//复杂调整
fixDoubleBlack(deleted);
}else {
// 无需处理
}
if (deleted.isLeftChild()){
parent.left = null;
}else {
parent.right = null;
}
deleted.parent = null;
}
return;
}
//有一个孩子
if (deleted.left == null || deleted.right == null){
//删除的是根节点
if (deleted == null){
root.key = replaced.key;
root.value = replaced.value;
root.left = root.right = null;
}else {
if (deleted.isLeftChild()){
parent.left = replaced;
}else {
parent.right = replaced;
}
replaced.parent = parent;
deleted.left = deleted.right = deleted.parent = null;//有助于垃圾回收
if (isBlack(deleted) && isBlack(replaced)){
//复杂处理
fixDoubleBlack(replaced);
}else {
replaced.color = Color.BLACK;
}
}
return;
}
//有两个孩子(是一种转换的操作)
int t = deleted.key;
deleted.key = replaced.key;
replaced.key = t;
Object v = deleted.value;
deleted.value = replaced.value;
replaced.value = v;
doRemove(replaced);
}
/**遇到双黑的不平衡的复杂处理
* x表示待调整的结点
* */
private void fixDoubleBlack(Node x){
if (x == root){
return;
}
Node parent = x.parent;
Node sibling = x.sibling();
//被调整节点的兄弟节点为红色
if (isRed(sibling)){
if (x.isLeftChild()){
leftRotate(parent);
}else {
rightRotate(parent);
}
parent.color = Color.RED;
sibling.color = Color.BLACK;
fixDoubleBlack(x);
return;
}
//兄弟是黑色且两个侄子都是黑色
if (sibling != null){
if (isBlack(sibling.left) && isBlack(sibling.right)){
sibling.color = Color.RED;
if (isRed(parent)){
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
}else {
fixDoubleBlack(parent);
}
}
//兄弟是黑色但是侄子有红色
else {
//LL
if(sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.left)){
rightRotate(parent);
sibling.left.color = Color.BLACK;
sibling.color = parent.color;
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
}
//LR
else if (sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.right)){
sibling.right.color = parent.color;
leftRotate(sibling);
rightRotate(parent);
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
}
//RL
else if (!sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.left)){
sibling.left.color = parent.color;
rightRotate(sibling);
leftRotate(parent);
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
}
//RR
else {
leftRotate(parent);
sibling.right.color = Color.BLACK;
sibling.color = parent.color;
parent.color = Color.BLACK;
}
}
}else {
fixDoubleBlack(parent);
}
}
/**找到要删除的结点*/
private Node find(int key){
Node p = root;
while (p != null){
if (key < p.key){
p = p.left;
}else if (key > p.key){
p = p.right;
}else {
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
/**查找剩余结点*/
private Node findReplaced(Node deleted){
if (deleted.left == null && deleted.right == null){
return null;
}else if (deleted.left == null){
return deleted.right;
}else if(deleted.right == null){
return deleted.left;
}
Node s = deleted.right;
while (s.left != null){
s = s.left;
}
return s;
}
}
3.总结
有一说一,这红黑树确实比前面的几种树要难一点,主要是它的属性太多,限制太多。说实话,这篇文章中仅仅只是简单的介绍了一下红黑树,实现了一下红黑树的相关操作,但是红黑树的增加和删除中的一些操作没有细讲,这个有时间了我后面会单独再出一篇红黑树的补充文章然后细讲,这篇就这样了吧。
最后说一点,对于这种类似于链式的结构(实际是树形结构),我们要掌握它的定义,条件,然后画图,然后对照图来进行相关的操作,然后再用代码去实现,这样好一点,而不是凭空想象着去写,那样是写不出来的。