文章目录
- 前言
- 一、下载u8g2源文件
- 二、复制和更改文件
- 2.1 复制文件
- 2.2 修改文件
- u8g2_d_setup文件
- u8g2_d_memory
- 三、编写oled.c和oled.h文件
- 3.1 CubeMX配置I2C
- 3.2 编写文件
- oled.h
- oled.c
- 四、测试代码
- main函数测试代码
- 总结
前言
在本文中,我们将介绍如何在STM32上成功地移植u8g2图形库,以便能够轻松地控制OLED或LCD显示屏。u8g2库提供了一个灵活、功能强大的框架,可以简化图形界面的开发过程。通过合理地配置STM32 CubeMX以及适当的硬件连接,我们可以使得u8g2与STM32微控制器完美结合。
我们将逐步引导您完成整个移植过程,从STM32 CubeMX的项目创建,到u8g2库的集成和配置,最终实现一个简单的示例程序,以确保整个过程的顺利进行。让我们一起开始吧!
一、下载u8g2源文件
u8g2下载地址
如果进不去可以私信我。找我要源代码。
下载好之后解压出来
二、复制和更改文件
2.1 复制文件
1、首先,在工程下面创建一个u8g2文件夹
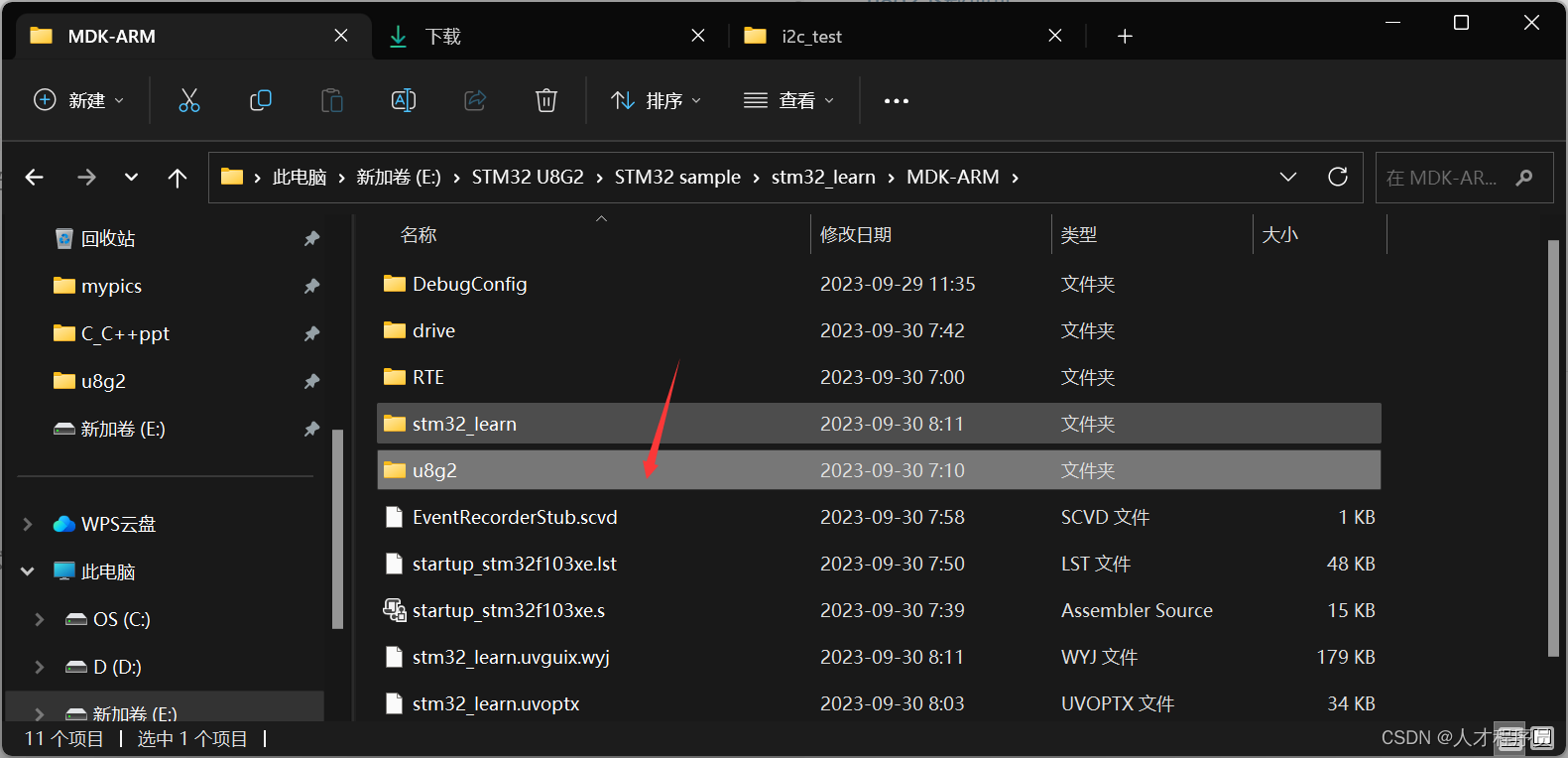
2、把我们下载好的u8g2文件夹里面的csrc下图中的这些文件复制进去

3、在工程中创建一个drive文件夹,里面放oled文件夹,oled文件夹放oled.c和oled.h,之后有用

4、打开keil,把前面的这些文件放进去

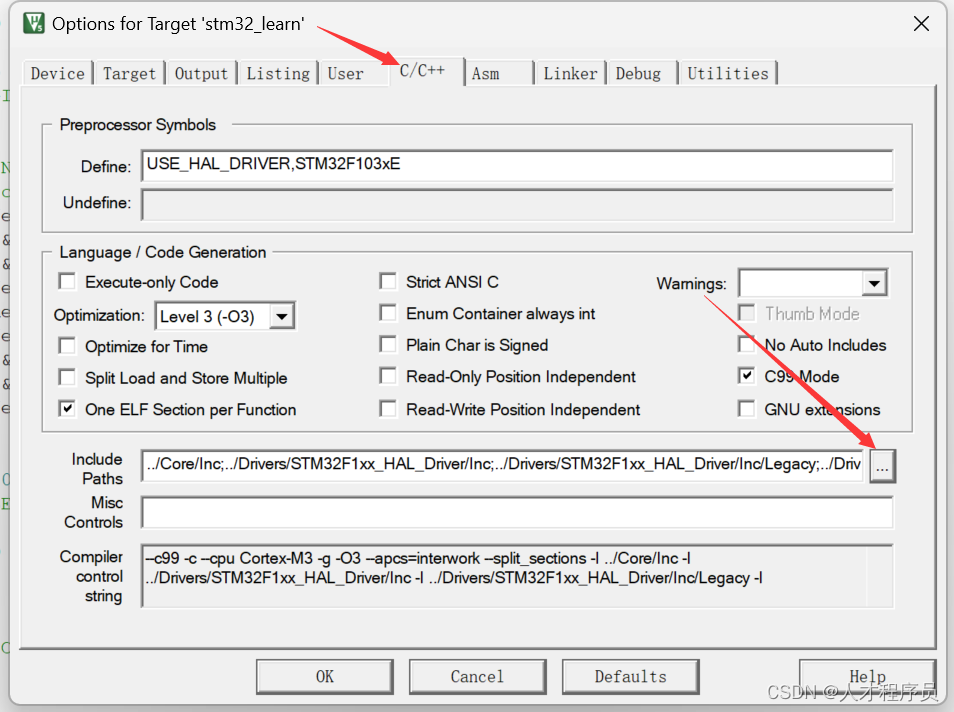
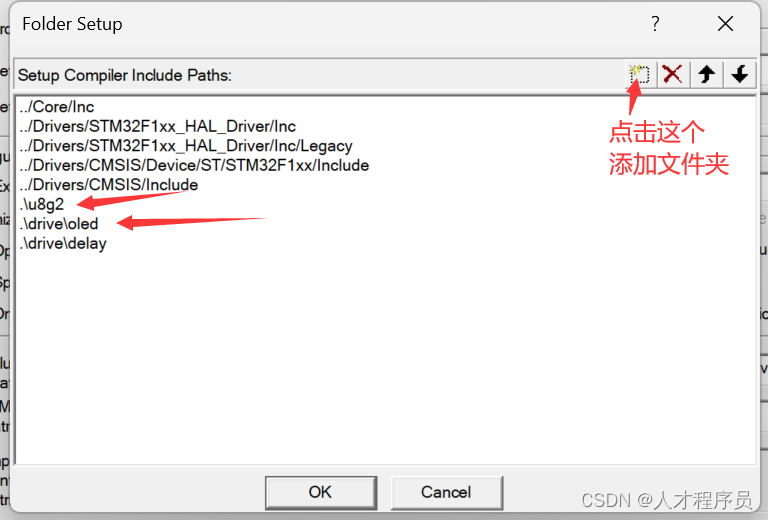

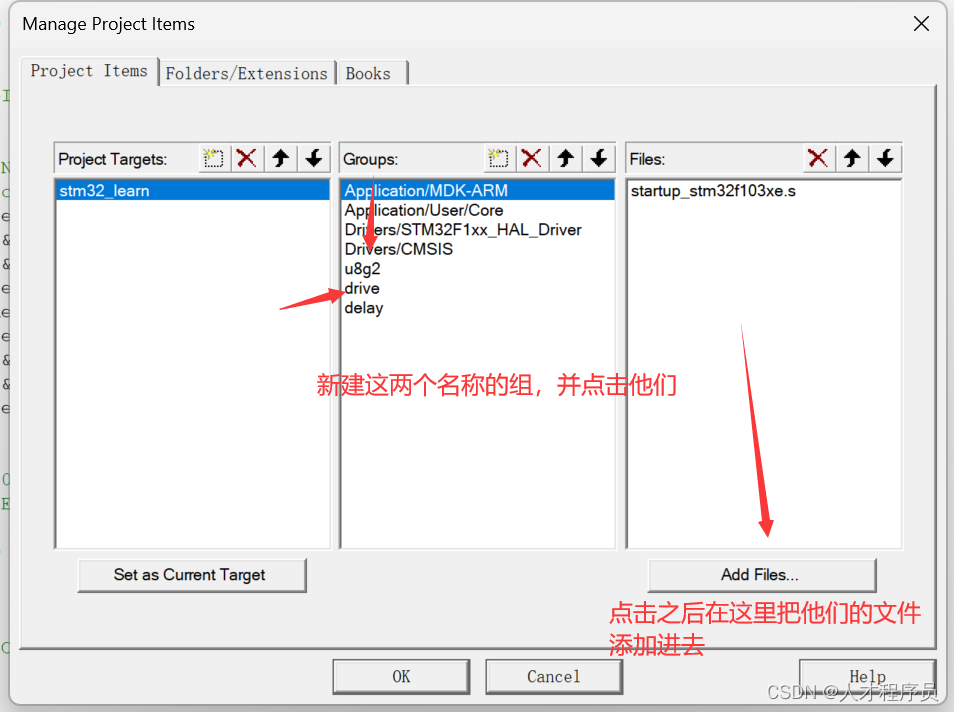
2.2 修改文件
u8g2_d_setup文件
我们需要找到下面这个函数:
void u8g2_Setup_ssd1306_i2c_128x64_noname_f(u8g2_t *u8g2, const u8g2_cb_t *rotation, u8x8_msg_cb byte_cb, u8x8_msg_cb gpio_and_delay_cb)
{
uint8_t tile_buf_height;
uint8_t *buf;
u8g2_SetupDisplay(u8g2, u8x8_d_ssd1306_128x64_noname, u8x8_cad_ssd13xx_fast_i2c, byte_cb, gpio_and_delay_cb);
buf = u8g2_m_16_8_f(&tile_buf_height);
u8g2_SetupBuffer(u8g2, buf, tile_buf_height, u8g2_ll_hvline_vertical_top_lsb, rotation);
}
然后把其他函数给删除或者注释掉。
u8g2_d_memory
我们需要找到下面这个函数
uint8_t *u8g2_m_16_8_f(uint8_t *page_cnt)
{
#ifdef U8G2_USE_DYNAMIC_ALLOC
*page_cnt = 8;
return 0;
#else
static uint8_t buf[1024];
*page_cnt = 8;
return buf;
#endif
}
把其他函数删除或注释掉.
三、编写oled.c和oled.h文件
3.1 CubeMX配置I2C
首先我们在CubeMX配置好我们的I2C,这个在之前的文章已经讲过了,这里不多赘述。
3.2 编写文件
oled.h
我们在oled.h文件里面,把下面的代码复制进去就可以了
#ifndef __oled_H
#define __oled_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
#include "u8g2.h"
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* USER CODE BEGIN Private defines */
/* USER CODE END Private defines */
#define u8 unsigned char // ?unsigned char ????
#define MAX_LEN 128 //
#define OLED_ADDRESS 0x78 // oled??????
#define OLED_CMD 0x00 // ???
#define OLED_DATA 0x40 // ???
/* USER CODE BEGIN Prototypes */
uint8_t u8x8_byte_hw_i2c(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr);
uint8_t u8x8_gpio_and_delay(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr);
void u8g2Init(u8g2_t *u8g2);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /*__ i2c_H */
/* USER CODE END Prototypes */
oled.c
我们需要把MX_I2C1_Init,这个函数复制进去,这个函数是CubeMX生成的不需要我们自己写,如果你的函数名和我的不同,那就把u8x8_byte_hw_i2c里面的MX_I2C1_Init替换成你的函数
#include "stm32f1xx_hal.h"
#include "u8g2.h"
#include "oled.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "main.h"
#include "oled.h"
I2C_HandleTypeDef hi2c1;
static void MX_I2C1_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN I2C1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END I2C1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN I2C1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END I2C1_Init 1 */
hi2c1.Instance = I2C1;
hi2c1.Init.ClockSpeed = 400000;
hi2c1.Init.DutyCycle = I2C_DUTYCYCLE_2;
hi2c1.Init.OwnAddress1 = 0;
hi2c1.Init.AddressingMode = I2C_ADDRESSINGMODE_7BIT;
hi2c1.Init.DualAddressMode = I2C_DUALADDRESS_DISABLE;
hi2c1.Init.OwnAddress2 = 0;
hi2c1.Init.GeneralCallMode = I2C_GENERALCALL_DISABLE;
hi2c1.Init.NoStretchMode = I2C_NOSTRETCH_DISABLE;
if (HAL_I2C_Init(&hi2c1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN I2C1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END I2C1_Init 2 */
}
uint8_t u8x8_byte_hw_i2c(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr)
{
/* u8g2/u8x8 will never send more than 32 bytes between START_TRANSFER and END_TRANSFER */
static uint8_t buffer[128];
static uint8_t buf_idx;
uint8_t *data;
switch (msg)
{
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_INIT:
{
/* add your custom code to init i2c subsystem */
MX_I2C1_Init(); //I2C???
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_START_TRANSFER:
{
buf_idx = 0;
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_SEND:
{
data = (uint8_t *)arg_ptr;
while (arg_int > 0)
{
buffer[buf_idx++] = *data;
data++;
arg_int--;
}
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_END_TRANSFER:
{
if (HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(&hi2c1, (OLED_ADDRESS), buffer, buf_idx, 1000) != HAL_OK)
return 0;
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_BYTE_SET_DC:
break;
default:
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void delay_us(uint32_t time)
{
uint32_t i = 8 * time;
while (i--)
;
}
uint8_t u8x8_gpio_and_delay(u8x8_t *u8x8, uint8_t msg, uint8_t arg_int, void *arg_ptr)
{
switch (msg)
{
case U8X8_MSG_DELAY_100NANO: // delay arg_int * 100 nano seconds
__NOP();
break;
case U8X8_MSG_DELAY_10MICRO: // delay arg_int * 10 micro seconds
for (uint16_t n = 0; n < 320; n++)
{
__NOP();
}
break;
case U8X8_MSG_DELAY_MILLI: // delay arg_int * 1 milli second
HAL_Delay(1);
break;
case U8X8_MSG_DELAY_I2C: // arg_int is the I2C speed in 100KHz, e.g. 4 = 400 KHz
delay_us(5);
break; // arg_int=1: delay by 5us, arg_int = 4: delay by 1.25us
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_I2C_CLOCK: // arg_int=0: Output low at I2C clock pin
break; // arg_int=1: Input dir with pullup high for I2C clock pin
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_I2C_DATA: // arg_int=0: Output low at I2C data pin
break; // arg_int=1: Input dir with pullup high for I2C data pin
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_MENU_SELECT:
u8x8_SetGPIOResult(u8x8, /* get menu select pin state */ 0);
break;
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_MENU_NEXT:
u8x8_SetGPIOResult(u8x8, /* get menu next pin state */ 0);
break;
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_MENU_PREV:
u8x8_SetGPIOResult(u8x8, /* get menu prev pin state */ 0);
break;
case U8X8_MSG_GPIO_MENU_HOME:
u8x8_SetGPIOResult(u8x8, /* get menu home pin state */ 0);
break;
default:
u8x8_SetGPIOResult(u8x8, 1); // default return value
break;
}
return 1;
}
void u8g2Init(u8g2_t *u8g2)
{
u8g2_Setup_ssd1306_i2c_128x64_noname_f(u8g2, U8G2_R0, u8x8_byte_hw_i2c, u8x8_gpio_and_delay); // ??? u8g2 ???
u8g2_InitDisplay(u8g2); // ??????????????,??????,?????????
u8g2_SetPowerSave(u8g2, 0); // ?????
u8g2_ClearBuffer(u8g2);
}
四、测试代码
到这里已经大功告成了,最后我们需要设置一下为C99标准:
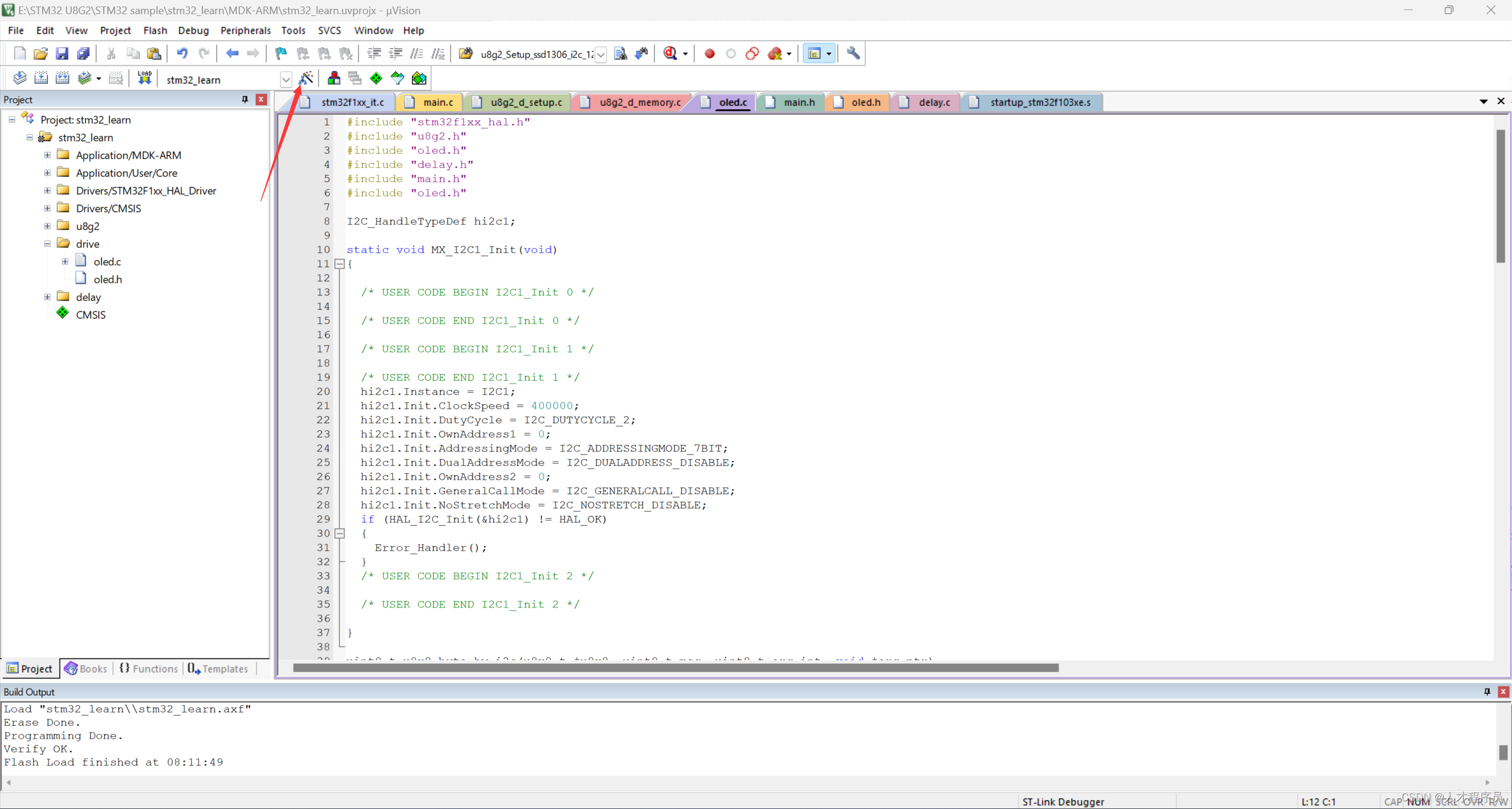

main函数测试代码
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2023 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "u8g2.h"
#include "oled.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_I2C1_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
u8g2_t u8g2; // a structure which will contain all the data for one display
u8g2Init(&u8g2);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
//u8g2_DrawCircle(&u8g2, 64, 32, 30, U8G2_DRAW_ALL);
u8g2_SendBuffer(&u8g2);
u8g2_DrawBox(&u8g2,0,0,20,20);
u8g2_DrawBox(&u8g2,20,20,20,20);
u8g2_SendBuffer(&u8g2);
u8g2_DrawFrame(&u8g2,10,40,20,20);
u8g2_SendBuffer(&u8g2);
u8g2_SetFont(&u8g2,u8g2_font_DigitalDiscoThin_tf);
u8g2_DrawStr(&u8g2,30,10,"Hello World");
u8g2_SendBuffer(&u8g2);
HAL_Delay(1000);
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEState = RCC_HSE_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEPredivValue = RCC_HSE_PREDIV_DIV1;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLMUL = RCC_PLL_MUL9;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief I2C1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
我们编译,烧写,即可看到oled已经显示了!
总结
通过本文的介绍与实践,我们成功地将u8g2图形库移植到了STM32微控制器上,并实现了一个简单的示例程序。以下是我们在整个过程中所取得的关键成果:
STM32 CubeMX项目创建:我们从零开始使用了STM32 CubeMX创建了一个新的项目,确保了正确的初始化和配置。
硬件连接:通过正确地连接OLED或LCD显示屏到STM32微控制器,我们保证了u8g2能够与硬件正确通信。
u8g2库的集成与配置:我们成功地将u8g2库添加到了STM32 CubeMX项目中,并配置了相关的参数,以确保适应我们的硬件需求。
示例程序的编写:我们编写了一个简单的示例程序,以验证u8g2库的正确移植与配置。
通过这个实例,我们展示了如何在STM32上成功地移植u8g2库,为您在嵌入式图形界面开发中提供了一个强大的工具。希望本文对您在此方面的工作和项目中能够提供有价值的参考。祝您的项目取得圆满成功!
![2023年中国新能源圆柱电池市场发展前景分析:新能源圆柱行业发展前景乐观向好[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/636c74587c35598ab2b6bea8b7024063.png)